Assessing the Exergy Costs of a 332-MW Pulverized Coal-Fired Boiler
Abstract
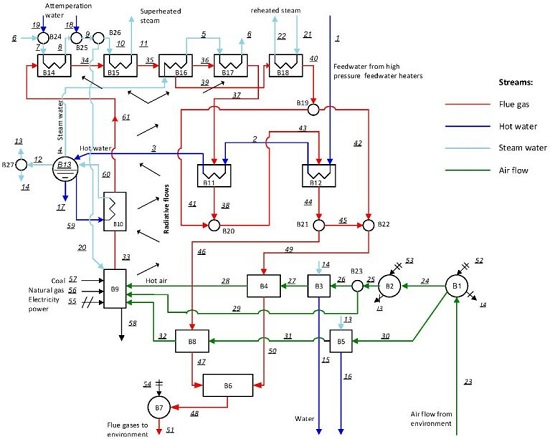
:1. Introduction
2. Case Study: General Considerations
2.1. Radiative Heat Exchangers
Modeling of Exergy Radiation
3. Thermoeconomics
3.1. Fuel-Product Concept
3.2. Modeling the Productive Structure
3.3. The Cost Formation Process
3.4. Exergy Costs of Components
3.5. Exergy Costs for Radiative Heat Exchangers
4. Thermoeconomic Model
4.1. Fuel-Product Model Definition
Boiler Section
4.2. Construction of the Productive Structure
4.3. Formulation of the Exergy Cost Equations
5. Results of the Exergy Costs
5.1. Exergy Costs for Exergy-Carrying Streams
5.2. Exergy Costs for Boiler Components
5.3. Effect of Changes in Operating Variables on the Unit Exergy Costs
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix: Definition of the Productive Structure Streams
| ID | Boiler |
|---|---|
References
- International Energy Statistics. Available online: http://www.eia.gov/cfapps/ipdbproject/IEDIndex3.cfm (accessed on 21 April 2016).
- Idehai, O.O.; Waheed, M.A.; Jekayinfa, S.O. Methodology for the physical and chemical exergetic analysis of steam boilers. Energy 2013, 53, 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Stultz, S.C.; Kitto, J.B. (Eds.) Steam: Its Generation and Use, 40th ed.; Babcock & Wilcox: Charlotte, NC, USA, 1992.
- Rosen, M.A. Energy and exergy-based comparison of coal-fired and nuclear steam power plants. Exergy Int. J. 2001, 3, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, M.A.; Zubair, S.M. 2nd Law-based thermodynamic analysis of regenerative re-heat rankine-cycle power plants. Energy 1992, 17, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Datta, A.; Duttagupta, S. Exergy analysis of a coal-based 210 MW thermal power plant. Int. J. Energy Res. 2007, 31, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Pouria, A.; Armita, H. Energy, exergy and exergoeconomic analysis of a steam power plant: A case study. Int. J. Energy Res. 2008, 33, 499–512. [Google Scholar]
- Goran, D.V.; Mirko, M.S.; Mica, V.V. First and second level of exergy destruction splitting in advanced exergy analysis for an existing boiler. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 104, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Tsatsaronis, G.; Park, M.H. On avoidable and unavoidable exergy destructions and investment costs in thermal systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 2002, 43, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulagadda, P.; Dincer, I.; Naterer, G.F. Exergy analysis of a thermal power plant with measured boiler and turbine losses. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2010, 30, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidur, R.; Ahamed, J.U.; Masjuki, H.H. Energy, exergy and economic analysis of industrial boilers. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 2188–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Hernandez, V.H. Thermoeconomic Diagnosis of Large Industrial Boilers: Microscopic Representation of the Exergy Cost Theory. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tsataronis, G. Thermoeconomic analysis and optimization of energy systems. Prog. Energ. Combust. 1993, 19, 227–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, A; Lozano, M.A.; Bartolomé, J.L. On-line monitoring of power plant performance, using exergetic cost techniques. Appl. Therm. Eng. 1996, 16, 933–948. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, C.; Veje, C.T.; Willatzen, M.; Andersen, P. Exergy costing for energy saving in combined heating and cooling applications. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 86, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacentino, A. Application of advanced thermodynamics, thermoeconomics and energy costing to a multiple effect-distillation plant: On-depth analysis of cost formation process. Desalination 2015, 371, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Orrego, D.; Julio, A.M.; Velásquez, H.; de Oliveira, S. Renewable and non-renewable energy costs on CO2 emissions in the production of fuels for brazilian transportation sector. Energy 2015, 88, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, L.; Uson, S.; Uche, J. Local exergy cost analysis of microwave heating systems. Energy 2015, 80, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, A.; Dominguez, A.; Valero, A. Exergy cost allocation of by-products in the mining and metallurgical. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 102, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasquer, B.; Uche, J.; Martinez-Gracia, A. Exergy costs analysis of groundwater use and water transfers. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 110, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, M.A.; Valero, A. Theory of the exergetic cost. Energy 1993, 18, 939–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szargut, J. Exergy Method: Technical and Ecological Applications, 1st ed.; WIT Press: Ashurst, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Diez, L.I.; Cortes, C.; Campo, A. Modeling of pulverized coal boilers: Review and validation of on-line simulation techniques. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2005, 25, 1516–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez, P.L. Real-Time Monitoring and Simulation of Pulverized-Coal Utility Boilers. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Valero, A.; Tomas, A.; Abadia, J.; Arnal, N.; Torres, C. A system for slagging control in a coal-fired utility boiler. In Analysis and Design of Energy Systems: Computer-Aided Engineering; ASME: New York City, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Petela, R. Exergy of heat radiation. J. Heat Transf. 1964, 86, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petela, R. Exergy of undiluted thermal radiation. Sol. Energy 2003, 74, 469–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeter, S.J. Maximum conversion efficiency for the utilization of direct solar radiation. Sol. Energy 1981, 26, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badescu, V. Letter to the editor. Sol. Energy 2004, 76, 509–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejan, A. Advanced Engineering Thermodynamics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, C. Symbolic thermoeconomic analysis of energy systems. In Exergy, Energy System Analysis and Optimization-Volume II: Thermoeconomic Analysis Modeling, Simulation and Optimization in Energy Systems; Eolss Publishers: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 61–104. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, C.; Valero, A.; Rangel, V.H.; Zaleta, A. On the cost formation process of the residues. Energy 2008, 33, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotas, T.J. The Exergy Method of Thermal Plant Analysis; Butterworths: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Serra, L.; Erlach, B.; Valero, A. Structural theory as standard for thermoeconomics. Energy Convers. Manag. 1999, 40, 1627–1649. [Google Scholar]
- Valero, A. The thermodynamic process of cost formation. In Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems; Eolss Publishers: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]










| ID | Description of Boiler Section | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gross power output | 332 | |
| 2 | Boiler Feeding water flow rate | 998,880 | |
| 3 | Make-up water flow rate | 10,592 | |
| 4 | Main steam flow rate | 1,019,620 | |
| 5 | Main steam pressure | 15.7 | |
| 6 | Main steam temperature | 538 | |
| 7 | Reheat steam flow rate | 905,378 | |
| 8 | Inlet reheat steam pressure | 3.8 | |
| 9 | Inlet reheat steam temperature | 353 | |
| 10 | Outlet reheat steam pressure | 3.5 | |
| 11 | Outlet reheat steam temperature | 538 | |
| 12 | 2nd superheater leaving steam temperature | 464 | |
| 13 | Steam drum pressure | 17.6 | |
| 14 | Dew point | 7 | |
| 15 | Atmospheric temperature | 19 | |
| 16 | Atmospheric pressure | 94.7 | |
| 17 | Fuel rate | 193,456 | |
| 18 | Forced-draft fan electrical power | 1235 | |
| 19 | Induced-draft fan electrical power | 2106 | |
| 20 | Primary-air fan electrical power | 981 | |
| 21 | Higher heating value of fuel | 4100 | |
| 22 | Boiler efficiency | 83.52 | % |
| 23 | Natural gas consumption | 5554 | |
| 24 | Air temperature entering air preheaters | 32 | |
| 25 | Flue gas temperature entering air preheaters | 418 | |
| 26 | Flue gas temperature leaving air preheaters | 179 | |
| 27 | Unit output to cycle | 768 |
| ID | Boiler Section |
|---|---|
| B1 | Forced-draft fan |
| B2 | Primary air-fan |
| B3 | First steam coil heater |
| B4 | Primary air pre-heater |
| B5 | Secondary steam coil heater |
| B6 | Precipitators |
| B7 | Induced draft-fan |
| B8 | Secondary air pre-heater |
| B9 | Furnace |
| B10 | Evaporator |
| B11 | Secondary economizer |
| B12 | Primary economizer |
| B13 | Steam drum |
| B14 | Secondary superheater |
| B15 | Final superheater |
| B16 | Plenum |
| B17 | Primary superheater |
| B18 | Reheater |
| ID of the Component | Exergy Cost Equations | Equation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | =0 | 1 | |
| =0 | 2 | ||
| =0 | 3 | ||
| B2 | =0 | 4 | |
| B3 | =0 | 5 | |
| =0 | 6 | ||
| B4 | =0 | 7 | |
| =0 | 8 | ||
| B5 | =0 | 9 | |
| =0 | 10 | ||
| B6 | =0 | 11 | |
| B7 | =0 | 12 | |
| B8 | =0 | 13 | |
| =0 | 14 | ||
| B9 | |||
| =0 | 15 | ||
| =0 | 16 | ||
| =0 | 17 | ||
| B10 | =0 | 18 | |
| =0 | 19 | ||
| B11 | =0 | 20 | |
| =0 | 21 | ||
| B12 | 22 | ||
| 23 | |||
| B13 | =0 | 23 | |
| =0 | 24 | ||
| =0 | 25 | ||
| =0 | 26 | ||
| B14 | =0 | 27 | |
| =0 | 28 | ||
| =0 | 29 | ||
| =0 | 30 | ||
| B15 | |||
| =0 | 31 | ||
| =0 | 32 | ||
| =0 | 33 | ||
| =0 | 34 | ||
| B16 | |||
| =0 | 35 | ||
| =0 | 36 | ||
| =0 | 37 | ||
| =0 | 38 | ||
| =0 | 39 | ||
| B17 | =0 | 40 | |
| =0 | 41 | ||
| B18 | =0 | 42 | |
| =0 | 43 |
| No. | Flow | ṁ (kg/s) | P (kg/cm2) | T (°C) | B (kW) | B* (kW) | k* (kW/kW) | (kW/kW) | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Water | 289.70 | 180 | 253 | 98,224 | 306,220 | 3.118 | 3.735 | −19.78 |
| 2 | Water | 289.70 | 179 | 294 | 128,272 | 356,306 | 2.778 | 3.389 | −21.99 |
| 3 | Water | 289.70 | 178 | 321 | 150,973 | 396,434 | 2.626 | 3.240 | −23.38 |
| 4 | Steam | 282.90 | 182 | 358 | 313,906 | 798,483 | 2.544 | 3.309 | −29.56 |
| 5 | Steam | 282.90 | 175 | 360 | 331,272 | 823,422 | 2.486 | 3.239 | −30.28 |
| 6 | Steam | 282.90 | 173 | 424 | 397,879 | 930,814 | 2.339 | 3.062 | −32.19 |
| 7 | Steam | 293.70 | 173 | 405 | 398,208 | 934,752 | 2.347 | 3.073 | −30.93 |
| 8 | Steam | 293.70 | 169 | 465 | 440,923 | 1,113,003 | 2.524 | 2.998 | −18.77 |
| 9 | Steam | 305.60 | 169 | 437 | 440,708 | 1,117,360 | 2.535 | 3.018 | −19.05 |
| 10 | Steam | 303.50 | 169 | 437 | 437,752 | 1,109,864 | 2.535 | 3.019 | −19.09 |
| 11 | Steam | 303.50 | 161 | 537 | 499,415 | 1,267,764 | 2.538 | 2.848 | −12.21 |
| 12 | Steam | 2.04 | 182 | 358 | 2264 | 5758 | 2.544 | 3.309 | −29.95 |
| 13 | Steam | 0.01 | 182 | 358 | 11 | 28 | 2.544 | 3.309 | −29.95 |
| 14 | Steam | 20.30 | 182 | 358 | 2253 | 5730 | 2.554 | 3.309 | −29.95 |
| 15 | Steam | 20.30 | 12 | 188 | 392 | 998 | 2.554 | 3.309 | −29.95 |
| 16 | Steam | 0.01 | 12 | 188 | 2 | 5 | 2.554 | 3.309 | −29.95 |
| 17 | Steam | 4.82 | 182 | 358 | 3284 | 8355 | 2.554 | 3.309 | −29.95 |
| 18 | Water | 11.88 | 187 | 170 | 2121 | 6846 | 3.228 | 4.022 | −24.59 |
| 19 | Water | 10.82 | 187 | 170 | 1931 | 6235 | 3.228 | 4.022 | −24.59 |
| 20 | Steam | 2.05 | 169 | 437 | 2957 | 7496 | 2.535 | 3.019 | −19.09 |
| 21 | Steam | 271.00 | 41 | 350 | 351,641 | 892,640 | 2.538 | 2.849 | −12.25 |
| 22 | Steam | 271.00 | 38 | 538 | 422,984 | 1,010,030 | 2.338 | 2.746 | −17.45 |
| 23 | Air | 378.40 | 1 | 17 | 492 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 24 | Air | 135.50 | 1 | 22 | 224 | 1398 | 6.250 | 5.293 | 15.31 |
| 25 | Air | 135.50 | 1 | 27 | 281 | 4499 | 16.036 | 15.250 | 4.90 |
| 26 | Air | 113.00 | 1 | 27 | 234 | 3749 | 16.036 | 15.240 | 4.90 |
| 27 | Air | 113.00 | 1 | 57 | 697 | 8482 | 12.171 | 13.950 | −14.61 |
| 28 | Air | 113.00 | 1 | 392 | 17,617 | 30,064 | 1.707 | 2.241 | −31.28 |
| 29 | Air | 22.59 | 1 | 27 | 47 | 750 | 16.036 | 15.240 | 4.90 |
| 30 | Air | 242.80 | 1 | 22 | 401 | 2504 | 6.250 | 5.293 | 15.31 |
| 31 | Air | 242.80 | 1 | 22 | 401 | 2527 | 6.308 | 5.368 | 14.90 |
| 32 | Air | 242.80 | 1 | 356 | 32,494 | 51,222 | 1.576 | 2.135 | −35.47 |
| 33 | Gases | 434.80 | 1 | 2048 | 843,979 | 929,580 | 1.101 | 1.519 | −37.96 |
| 34 | Gases | 434.80 | 1 | 1253 | 436,208 | 480,451 | 1.101 | 1.519 | −37.96 |
| 35 | Gases | 434.80 | 1 | 1126 | 376,506 | 414,693 | 1.101 | 1.519 | −37.96 |
| 36 | Gases | 249.40 | 1 | 1083 | 204,770 | 225,539 | 1.101 | 1.519 | −37.96 |
| 37 | Gases | 249.40 | 1 | 728 | 118,042 | 130,015 | 1.101 | 1.519 | −37.96 |
| 38 | Gases | 249.40 | 1 | 579 | 85,955 | 94,672 | 1.101 | 1.519 | −37.96 |
| 39 | Gases | 185.40 | 1 | 1083 | 152,910 | 167,626 | 1.101 | 1.519 | −37.96 |
| 40 | Gases | 185.40 | 1 | 536 | 57,428 | 63,253 | 1.101 | 1.519 | −37.96 |
| 41 | Gases | 185.40 | 1 | 536 | 57,428 | 63,253 | 1.101 | 1.519 | −37.96 |
| 42 | Gases | 0.00 | 1 | 536 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 43 | Gases | 434.80 | 1 | 561 | 143,333 | 157,925 | 1.102 | 1.520 | −37.96 |
| 44 | Gases | 34.80 | 1 | 444 | 104,477 | 115,113 | 1.102 | 1.520 | −37.96 |
| 45 | Gases | 117.40 | 1 | 444 | 28,208 | 31,079 | 1.102 | 1.520 | −37.96 |
| 46 | Gases | 317.40 | 1 | 444 | 76,269 | 84,034 | 1.102 | 1.520 | −37.96 |
| 47 | Gases | 317.40 | 1 | 216 | 32,073 | 35,338 | 1.102 | 1.520 | −37.96 |
| 48 | Gases | 434.80 | 1 | 198 | 40,452 | 44,835 | 1.108 | 1.529 | −37.96 |
| 49 | Gases | 117.40 | 1 | 444 | 28,208 | 31,079 | 1.102 | 1.520 | −37.96 |
| 50 | Gases | 117.40 | 1 | 152 | 8620 | 9497 | 1.102 | 1.520 | −37.96 |
| 51 | Gases | 434.80 | 1 | 205 | 41,835 | 51,490 | 1.231 | 1.598 | −29.81 |
| 52 | Elect | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 1235 | 3901 | 3.160 | 3.154 | 0.18 |
| 53 | Elect | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 981 | 3102 | 3.160 | 3.154 | 0.18 |
| 54 | Elect | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 2106 | 6654 | 3.160 | 3.154 | 0.18 |
| 55 | Elect | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 2106 | 6654 | 3.160 | 3.154 | 0.18 |
| 56 | Elect | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 2525 | 7981 | 3.160 | 3.154 | 0.18 |
| 57 | N.G. | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 58 | Coal | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 1,089,023 | 1,089,023 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
| 59 | Heat | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 106,523 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 60 | Water | 393.40 | 182 | 358 | 268,051 | 681,840 | 2.544 | 3.309 | −30.07 |
| 61 | Steam | 393.40 | 181 | 357 | 437,299 | 1,089,021 | 2.490 | 3.303 | −32.65 |
| 62 | Gases | 434.80 | 1 | 1375 | 495,193 | 545,418 | 1.101 | 1.519 | −37.96 |
| R9 | Rad | 280,044 | 338,313 | 1.208 | |||||
| R9-14 | Rad | 97,737 | 118,073 | 1.208 | |||||
| R9-15 | Rad | 76,213 | 92,071 | 1.208 | |||||
| R14-9 | Rad | 210 | 253 | 1.208 | |||||
| R15-9 | Rad | 210 | 253 | 1.208 | |||||
| R16-15 | Rad | 3016 | 3643 | 1.208 | |||||
| R16-17 | Rad | 1726 | 2086 | 1.208 | |||||
| R16-18 | Rad | 1524 | 1841 | 1.208 | |||||
| R14-15 | Rad | 584 | 705 | 1.208 | |||||
| R14-14 | Rad | 750 | 906 | 1.208 | |||||
| R15-16 | Rad | 730 | 882 | 1.208 | |||||
| R17-16 | Rad | 234 | 282 | 1.208 | |||||
| R18-16 | Rad | 286 | 345 | 1.208 |
| No. | Component | F (kW) | P (kW) | I (kW) | (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Induced-draft fan | 1234 | 132 | 1102 | 3.161 | 29.475 | 10.73 |
| 2 | Primary-air fan | 981 | 57 | 924 | 3.161 | 54.506 | 5.80 |
| 3 | primary coil heater | 1860 | 463 | 1397 | 2.710 | 10.890 | 24.89 |
| 4 | Primary air pre-heater | 19,588 | 16,920 | 2668 | 1.139 | 1.318 | 86.38 |
| 5 | Precipitator | 40,692 | 40,452 | 240 | 1.139 | 1.145 | 99.41 |
| 6 | Induced-draft fan | 2105 | 1383 | 722 | 3.161 | 4.814 | 65.67 |
| 7 | Secondary air pre-heater | 44,195 | 32,093 | 12,102 | 1.139 | 1.568 | 72.62 |
| 8 | Furnace | 1,180,000 | 1,140,000 | 36,900 | 1.001 | 1.068 | 92.02 |
| 9 | Evaporator | 348,786 | 169,247 | 179,539 | 1.138 | 3.109 | 36.61 |
| 10 | Secondary economizer | 32,088 | 22,703 | 9385 | 1.207 | 1.788 | 67.50 |
| 11 | Primary economizer | 38,856 | 30,048 | 8808 | 1.268 | 1.738 | 72.94 |
| 12 | Steam drum | 588,268 | 587,503 | 765 | 3.114 | 3.182 | 97.88 |
| 13 | Secondary heat exchanger | 155,928 | 42,714 | 113,214 | 1.132 | 4.212 | 26.86 |
| 14 | Final heat exchanger | 136,289 | 61,663 | 74,626 | 1.147 | 2.578 | 44.51 |
| 15 | Plenum | 19,545 | 17,365 | 2180 | 1.224 | 1.455 | 84.12 |
| 16 | Primary heat exchanger | 86,728 | 66,610 | 20,118 | 1.199 | 1.629 | 73.56 |
| 17 | Reheater | 94,762 | 71,343 | 23,419 | 1.199 | 1.663 | 72.10 |
| 18 | Lower attemperation | 399,813 | 398,208 | 1605 | 2.713 | 2.719 | 99.78 |
| 19 | Higher attemperation | 443,043 | 440,708 | 2335 | 2.713 | 2.723 | 99.65 |
| 20 | Boiler | 1,126,000 | 472,160 | 653,840 | 1.013 | 2.352 | 43.09 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rangel-Hernandez, V.H.; Damian-Ascencio, C.; Belman-Flores, J.M.; Zaleta-Aguilar, A. Assessing the Exergy Costs of a 332-MW Pulverized Coal-Fired Boiler. Entropy 2016, 18, 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/e18080300
Rangel-Hernandez VH, Damian-Ascencio C, Belman-Flores JM, Zaleta-Aguilar A. Assessing the Exergy Costs of a 332-MW Pulverized Coal-Fired Boiler. Entropy. 2016; 18(8):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/e18080300
Chicago/Turabian StyleRangel-Hernandez, Victor H., Cesar Damian-Ascencio, Juan M. Belman-Flores, and Alejandro Zaleta-Aguilar. 2016. "Assessing the Exergy Costs of a 332-MW Pulverized Coal-Fired Boiler" Entropy 18, no. 8: 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/e18080300
APA StyleRangel-Hernandez, V. H., Damian-Ascencio, C., Belman-Flores, J. M., & Zaleta-Aguilar, A. (2016). Assessing the Exergy Costs of a 332-MW Pulverized Coal-Fired Boiler. Entropy, 18(8), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/e18080300