Silica Bonded S-Sulfonic Acid: A Recyclable Catalyst for the Synthesis of Quinoxalines at Room Temperature
Abstract
:1. Introduction


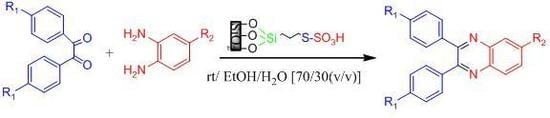
2. Results and Discussion
| Entry | Solvent | The amount of catalyst (g) | Time (min) | Yield (%)a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H2O | 0.1 | 240 | 40 |
| 2 | EtOH | 0.1 | 12 | 97 |
| 3 | CHCl3 | 0.1 | 60 | 63 |
| 4 | CH2Cl2 | 0.1 | 60 | 59 |
| 5 | EtOH/ H2O [30/ 70 (v/v)] | 0.1 | 40 | 88 |
| 6 | EtOH/ H2O [50/ 50 (v/v)] | 0.1 | 30 | 90 |
| 7 | EtOH/ H2O [70/ 30 (v/v)] | 0.1 | 5 | 96 |
| 8 | EtOH/ H2O [70/ 30 (v/v)] | 0.03 | 25 | 75 |
| 9 | EtOH/ H2O [70/ 30 (v/v)] | 0.05 | 20 | 90 |
| 10 | EtOH/ H2O [70/ 30 (v/v)] | 0.15 | 5 | 96 |
| Entry | Dicarbonyl compound | Diamine | Product | Time(min) | Yields(%)a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5a |  |  |  | 5 | 96 |
| 5b |  |  |  | 8 | 95 |
| 5c |  |  |  | 10 | 90 |
| 5d |  |  |  | 200 | 90 |
| 5e |  |  |  | 15 | 91 |
| 5f |  |  |  | 20 | 90 |
| 5g |  |  |  | 220 | 93 |
| 5h |  |  |  | 30 | 85 |
| 5i |  |  |  | 35 | 85 |
| 5j |  |  |  | 5 | 94 |
| 5k |  |  |  | 7 | 92 |
| 5l |  |  |  | 6 | 95 |
| 5m |  |  |  | 8 | 92 |
| 5n |  |  |  | 15 | 91 |
| 5o |  |  |  | 20 | 93 |
| 5p |  |  |  | 15 | 91 |


3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
3.2. Catalyst Preparation
3.3. General procedure for the synthesis of quinoxalines
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
References and Notes
- Choudhary, D.; Paul, S.; Gupta, R.; Clark, J.H. Catalytic properties of several palladium complexes covalently anchored onto silica for the aerobic oxidation of alcohols Green Chem. 2006, 8, 479–482. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, P.; Phillips, E.; Rippon, D.; Tsang, S.C. Catalytic oxidation of alcohols using molecular oxygen mediated by poly(ethylene glycol)-supported nitroxyl radicals. Appl. Catal. B Environmen. 2005, 61, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, B.; Khalkhali, M. Solid silica-based sulfonic acid as an efficient and recoverableinterphase catalyst for selective tetrahydropyranylation ofalcohols and phenols. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2005, 232, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, B.; Zareyee, D. Design of a Highly Efficient andWater-Tolerant Sulfonic AcidNanoreactor Based on Tunable Ordered Porous Silica for the von PechmannReaction. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 3989–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, P.; Zolfigol, M.A.; Shirini, F.; Baghbanzadeh, M. Silica Sulfuric Acid and Silica Chloride as Efficient Reagents for Organic Reactions. Curr. Org. Chem. 2006, 10, 2171–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknam, K.; Zolfigol, M.A. 1,3-Dihalo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin/NaNO2as an Efficient Heterogeneous System for theN-Nitrosation of N,N-Dialkylamines under Mild Conditions. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2006, 3, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknam, K.; Karami, B.; Zolfigol, M.A. Silica sulfuric acid promoted aromatization of 1,2-dihydroquinolinesby using NaNO2 as oxidizing agent under mild andheterogeneous conditions. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 1427–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikłam, K.; Zolfigol, M.A.; Chehardoli, G.; Dehghanian, M. Tribromoisocyanuric Acid and DABCO-Br as EfficientCatalysts for the Silylation of Hydroxyl Groups withHexamethyldisilazane. Chin. J. Catal. 2008, 29, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Garcia, H. Lewis Acids as Catalysts in Oxidation Reactions: From Homogeneous toHeterogeneous Systems. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 3837–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.; Lee, A.F.; Macquarrie, D.J.; Clark, J.H. Structure and reactivity of sol–gel sulphonic acid silicas. Appl. Catal. A 2002, 228, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melero, J.A.; Grieken, R.V.; Morales, G. Advances in the Synthesis and Catalytic Applications of Organosulfonic-Functionalized Mesostructured Materials. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 3790–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknam, K.; Zolfigol, M.A.; Khorramabadi-Zad, A.; Zare, R.; Shayegh, M. Silica sulfuric acid as an efficient and recyclable catalyst for themethoxymethylation of alcohols under solvent-free conditions. Catal. Commun. 2006, 7, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknam, K.; Zolfigol, M.A.; Sadabadi, T.; Nejati, A. Preparation of Indolylmethanes Catalyzed by Metal Hydrogen Sulfates. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2006, 3, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknam, K.; Zolfigol, M.A.; Sadabadi, T. Ca(HSO4)2 Mediated Conversion of Alcohols into N-Substituted Amides underHeterogeneous Conditions: A Modified Ritter Reaction. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2007, 4, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknam, K.; Zolfigol, M.A.; Hossieninejad, Z.; Daneshvar, N. Efficient Synthesis of 3,4-Dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-one UsingMetal Hydrogen Sulfates M(HSO4)n as Catalyst underSolvent-Free Conditions. Chin. J. Catal. 2007, 28, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknam, K.; Zolfigol, M.A.; Dehghani, A. Friedlander Quinoline Synthesis Catalyzedby M(HSO4)n (M=Al, Mg, Ca) under Solvent-Free Conditions. Heterocycles 2008, 75, 2513–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaji, V.M.; Sastry, M.N.V.; Wang, C.C.; Ching-Fa, Y. Molecular iodine: a powerful catalyst for the easy and efficient synthesis of quinoxalines. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 6345–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, X.; Desrivot, J.; Bories, C.; Loiseau, P.M.; Franck, X.; Hocquemiller, R.; Figadere, B. Synthesis and antiprotozoal activity of some new synthetic substituted quinoxalines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, G.; Makino, K.; Kurasama, Y. Recent Progress in the Quinoxaline Chemistry. Synthesis and Biological Activity. Heterocycles 1988, 27, 2481–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, L.E.; Suling, W.J.; Reynolds, R.C. Synthesis and Antimycobacterial Activity of Pyrazine and QuinoxalineDerivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 5604–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dailey, S.; Feast, J.W.; Peace, R.J.; Sage, I.C.; Till, S.; Wood, E.L. Synthesis and device characterisation of side-chain polymer electrontransport materials for organic semiconductor applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2001, 11, 2238–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, T.; Wei, W.H.; Eller, L.R.; Sessler, J.L. Phenanthroline Complexes Bearing Fused Dipyrrolylquinoxaline AnionRecognition Sites: Efficient Fluoride Anion Receptors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 1134–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossley, J.C.; Johnston, L.A. Laterally-extended porphyrin systems incorporating a switchable unit. Chem. Commun. 2002, 1122–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.J. Quinoxalines: supplement II. In The Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds; Taylor, E.C., Wipf, P., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Antoniotti, S.; Donach, E. Direct and catalytic synthesis of quinoxaline derivatives from epoxides and ene-1,2-diamines. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 3971–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.S.; Taylor, R.J.K. Quinoxaline Synthesis from a-Hydroxy Ketones via a Tandem Oxidation Process Using Catalysed Aerobic Oxidation. Synlett. 2005, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Raw, S.A.; Wilfred, C.D.; Taylor, R.J.K. Tandem oxidation processes for the preparation of nitrogen-containing heteroaromatic and heterocyclic compounds. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, C.; Singh, B.; Mahata, P.K.; Ha, H.; Junjappa, H. Heteroannulation of Nitroketene N,S-Arylaminoacetals with POCl3: A Novel Highly Regioselective Synthesisof Unsymmetrical 2,3-Substituted Quinoxalines. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 2169–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xekoukoulotakis, N.P.; Hadjiantonious, M.C.P.; Maroulis, A.J. Synthesis of quinoxalines by cyclization of a-arylimino oximes of a-dicarbonyl compounds. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 10299–10302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotharkar, S.A.; Shinde, D.B. Lead Oxide (PbO) Mediated Synthesis of Quinoxaline. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2006, 3, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heravi, M.M.; Tehrani, M.H.; Bakhtiari, K.; Oskooie, H.A. Zn[(L)proline]: A powerful catalyst for the very fast synthesis ofquinoxaline derivatives at room temperature. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 1341–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.S.; Oh, S.G. Copper-catalyzed oxidative cyclization of α-hydroxyketone with o-phenylenediamines leading to quinoxalines. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2007, 276, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.K.; Wang, R.; Shi, L.; Lu, X.X. Montmorillonite K-10: An efficient and reusable catalystfor the synthesis of quinoxaline derivatives in water. Catal. Commun. 2008, 9, 1143–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portewar, T.M.; Ingale, S.A.; Srinivasan, K.V. Efficient Synthesis of Quinoxalines in the IonicLiquid 1-n-Butylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborate([Hbim]BF4) at Ambient Temperature. Synth. Commun. 2008, 38, 3601–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknam, K.; Zolfigol, M.A.; Tavakoli, Z.; Heydari, Z. Metal Hydrogen Sulfates M(HSO4)n: As Efficient Catalysts for the Synthesis of Quinoxalines in EtOH at Room Temperature. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2008, 55, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Hasaninejad, A.; Zare, A.; Mohammadizadeh, M.R.; Shekouhy, M. Oxalic acid as an efficient, cheap, and reusable catalyst for the preparation of quinoxalines via condensation of 1,2-diamines with α-diketones at room temperature. ARKIVOC 2008, xiii, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsenzadeh, F.; Aghapoor, K.; Darabi, H.R. Benign Approaches for the Microwave-assisted Synthesis of Quinoxalines. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2007, 18, 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Markgraf, J.H.; Katt, R.J. Strained Heterocyclic Systems. VI. Basicities of Some Quinoxalines. J. Org. Chem. 1972, 37, 717–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Niknam, K.; Saberi, D.; Mohagheghnejad, M. Silica Bonded S-Sulfonic Acid: A Recyclable Catalyst for the Synthesis of Quinoxalines at Room Temperature. Molecules 2009, 14, 1915-1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14051915
Niknam K, Saberi D, Mohagheghnejad M. Silica Bonded S-Sulfonic Acid: A Recyclable Catalyst for the Synthesis of Quinoxalines at Room Temperature. Molecules. 2009; 14(5):1915-1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14051915
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiknam, Khodabakhsh, Dariush Saberi, and Maleki Mohagheghnejad. 2009. "Silica Bonded S-Sulfonic Acid: A Recyclable Catalyst for the Synthesis of Quinoxalines at Room Temperature" Molecules 14, no. 5: 1915-1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14051915
APA StyleNiknam, K., Saberi, D., & Mohagheghnejad, M. (2009). Silica Bonded S-Sulfonic Acid: A Recyclable Catalyst for the Synthesis of Quinoxalines at Room Temperature. Molecules, 14(5), 1915-1926. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14051915