Dammarane-type Triterpene Saponins from the Flowers of Panax notoginseng
Abstract
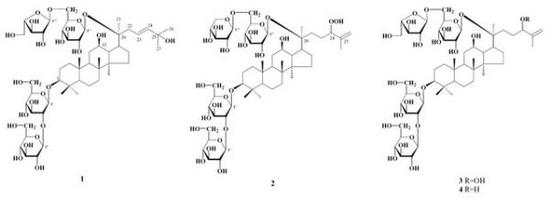
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion

| 1a) | 2c) | 3 c) | 4 c) | 5a) | 8a) | 9 c) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-1 | 39.9 | 39.2 | 39.2 | 39.2 | 40.2 | 40.2 | 39.2 |
| C-2 | 27.0 | 26.8 | 26.7 | 26.7 | 27.0 | 27.0 | 26.7 |
| C-3 | 91.3 | 89.0 | 89.0 | 89.0 | 91.3 | 91.3 | 89.0 |
| C-4 | 39.8 | 40.0 | 39.7 | 39.7 | 40.5 | 40.6 | 40.0 |
| C-5 | 57.6 | 56.4 | 56.3 | 56.3 | 57.5 | 57.5 | 56.4 |
| C-6 | 19.2 | 18.4 | 18.4 | 18.4 | 19.2 | 19.2 | 18.6 |
| C-7 | 35.8 | 35.1 | 35.1 | 35.0 | 35.8 | 35.8 | 35.1 |
| C-8 | 40.2 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 41.0 | 40.6 | 40.0 |
| C-9 | 50.0 | 50.2 | 50.2 | 50.1 | 51.0 | 52.5 | 50.2 |
| C-10 | 37.9 | 36.9 | 36.9 | 36.9 | 37.9 | 37.9 | 36.9 |
| C-11 | 30.9 | 30.9 | 30.9 | 30.9 | 30.9 | 30.9 | 30.9 |
| C-12 | 71.3 | 71.1 | 70.3 | 70.4 | 71.5 | 72.0 | 71.1 |
| C-13 | 50.0 | 49.5 | 49.4 | 49.3 | 49.8 | 52.5 | 49.4 |
| C-14 | 51.0 | 51.4 | 51.4 | 51.4 | 52.4 | 51.0 | 51.4 |
| C-15 | 30.1 | 30.7 | 30.7 | 30.8 | 31.3 | 31.3 | 30.8 |
| C-16 | 27.2 | 26.6 | 26.6 | 26.7 | 27.2 | 27.2 | 26.7 |
| C-17 | 52.5 | 51.5 | 51.5 | 52.0 | 53.1 | 53.1 | 51.8 |
| C-18 | 16.4 | 16.0 | 16.0 | 15.8 | 16.7 | 16.4 | 16.0 |
| C-19 | 16.7 | 16.3 | 16.3 | 16.3 | 16.7 | 16.7 | 16.3 |
| C-20 | 84.6 | 83.4 | 83.4 | 83.5 | 84.6 | 84.6 | 83.4 |
| C-21 | 23.4 | 22.4 | 22.4 | 22.5 | 23.3 | 23.4 | 22.6 |
| C-22 | 39.9 | 32.7 | 32.7 | 32.7 | 40.0 | 41.0 | 32.7 |
| C-23 | 123.8 | 26.3 | 26.5 | 30.4 | 123.8 | 127.5 | 30.7 |
| C-24 | 141.9 | 90.1 | 90.1 | 76.4 | 141.9 | 138.1 | 76.7 |
| C-25 | 71.5 | 146.2 | 146.1 | 149.5 | 71.5 | 82.6 | 149.4 |
| C-26 | 31.4 | 113.3 | 113.4 | 110.5 | 30.1 | 24.8 | 110.0 |
| C-27 | 31.4 | 17.4 | 17.7 | 18.0 | 29.8 | 25.2 | 18.4 |
| C-28 | 28.4 | 28.1 | 28.1 | 28.1 | 28.4 | 28.4 | 28.1 |
| C-29 | 16.7 | 16.6 | 16.6 | 16.6 | 16.7 | 16.7 | 16.6 |
| C-30 | 17.3 | 17.4 | 17.3 | 17.2 | 17.3 | 17.3 | 17.3 |
| Glc-1' | 105.4 | 105.1 | 105.1 | 105.1 | 105.3 | 105.4 | 105.1 |
| 2' | 81.1 | 83.4 | 83.3 | 83.3 | 81.0 | 83.2 | 83.7 |
| 3' | 78.5 | 78.3 | 78.3 | 78.2 | 78.4 | 78.3 | 78.2 |
| 4' | 71.9 | 71.6 | 71.6 | 71.6 | 71.8 | 71.5 | 71.6 |
| 5' | 78.1 | 78.1 | 78.3 | 78.2 | 78.0 | 78.1 | 78.1 |
| 6' | 62.8 | 62.9 | 62.9 | 62.8 | 63.0 | 62.8 | 62.8 |
| Glc-1'' | 104.5 | 106.0 | 106.0 | 106.0 | 104.4 | 105.4 | 106.0 |
| 2'' | 77.7 | 77.1 | 77.9 | 77.9 | 77.6 | 77.6 | 77.1 |
| 3'' | 77.9 | 78.1 | 78.1 | 78.9 | 77.8 | 77.8 | 78.1 |
| 4'' | 71.9 | 71.6 | 72.0 | 72.0 | 71.6 | 71.9 | 71.7 |
| 5'' | 78.3 | 78.3 | 78.8 | 78.9 | 78.2 | 78.1 | 78.2 |
| 6'' | 63.1 | 62.7 | 62.7 | 62.7 | 62.8 | 63.0 | 62.6 |
| Glc (Xyl)-1''' | 98.1 | 98.0 | 98.0 | 98.0 | 98.0 | 98.0 | 98.0 |
| 2''' | 75.3 | 75.0 | 74.9 | 75.0 | 75.3 | 75.3 | 75.9 |
| 3''' | 78.5 | 79.3 | 79.2 | 79.0 | 78.4 | 78.9 | 79.2 |
| 4''' | 71.5 | 71.6 | 71.6 | 71.6 | 71.1 | 71.5 | 71.6 |
| 5''' | 77.7 | 77.1 | 77.1 | 77.1 | 77.5 | 77.6 | 77.1 |
| 6''' | 68.5 | 70.0 | 68.3 | 68.3 | 70.1 | 63.0 | 69.8 |
| Ara (Xyl, Glc)-1'''' | 110.0 | 105.6 | 110.0 | 110.0 | 104.4 | 110.0 | 105.6 |
| 2'''' | 83.3 | 74.8 | 83.4 | 83.5 | 74.8 | 83.2 | 74.8 |
| 3'''' | 78.5 | 78.3 | 78.8 | 78.9 | 78.4 | 78.5 | 78.2 |
| 4'''' | 85.7 | 71.1 | 85.9 | 85.9 | 71.1 | 85.6 | 71.1 |
| 5'''' | 62.8 | 66.9 | 62.7 | 62.7 | 66.8 | 62.8 | 67.0 |
Experimental
General
Extraction and Isolation
Conclusions
References
- Zhonghuabencao Editorial Board. Zhonghuabencao; Shanghai Science and Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Morikawa, T.; Kashima, Y.; Ninomiya, K.; Matsuda, H. Structures of new dammarane-type triterpene saponins from the flower buds of Panax notoginseng and hepatoprotective effects of principal ginseng saponins. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Murakami, T.; Ueno, T.; Hirokawa, K.Y.; Murakami, N.; Yamahara, J.; Matsuda, H.; Saijoh, R.; Tanaka, O. Bioactive saponins and glycosides. IX. Notoginseng (2): structures of five new dammaranes-type triterpene oligoglycosides, notoginsenosides-E, -G,-H, -I, and -J, and a novel acetylenic fatty acid glycoside, notoginsenic acid β-sophoroside, from the dried root of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F. H. Chen. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 45, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Wang, D.; Ma, X.X.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yang, C.R. Two new dammarane-type bisdemosides from the fruit pedicels of Panax notoginseng. Helv. Chim. Acta 2002, 91, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, G.Y.; Wei, J.X.; Du, Y.C; Cao, S.M; Chen, Y.G. Saponins from flower-buds of Sanchi (Panax notoginseng (Burk) F. H. Chen). Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 1991, 3, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Taniyasu, S.; Tanaka, O.; Yang, T.R.; Zhou, J. Dammarane saponins of flower buds of Panax notoginseng (Sanchi-Ginseng). Planta Med. 1982, 4, 124–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Hu, L.H.; Pan, R.X. Novel Dammarane-type glycosides from Gynostemma pentaphyllum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, F.; Hu, L.H.; Lou, F.C.; Pan, R.X. Dammarane-type glycosides from Gynostemma pentaphyllum. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Sugimoto, S.; Nakamura, S.; Sakumae, H.; Matsuda, H. Medicinal Flowers. XVI. New dammaranes-type tetraglycosides and gastroprotective principles from flower buds of Panax ginseng. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Takemoto, T.; Arihara, S. Studies on the constituents of Cucurbitaceae plants. XVL. On the saponin constituents of Gynostemma pentaphyllum Makino (II). Yakugaku Zasshi 1987, 107, 262–267. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.-H.; Fukuoka, R.; Aoki, F.; Tanaka, T.; Kouno, I. Dammarane-type triterpene glycosides from the leaves of Rhoiptelea chiliantha. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 47, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Murakami, T.; Ueno, T.; Yashiro, K.; Hirokawa, N.; Murakami, N.; Yamahara, J.; Matsuda, H.; Saijoh, R.; Tanaka, O. Bioactive saponins and glycosides. VIII. Notoginseng (1), New dammaranes-type triterpene oligoglycosides, notoginsenosides-A, -B,-C, and -D from the dried root of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F. H. Chen. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 45, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, N.M.; Kasai, R.; Ohtani, K.; Ito, A.; Nham, N.T.; Yamasaki, K.; Tanaka, O. Saponins from Vietnamese ginseng, Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grushv collected in central Vietnam II. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 42, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1-4 are available from the authors.
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.-R.; Yamasaki, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Kouno, I.; Jiang, Z.-H. Dammarane-type Triterpene Saponins from the Flowers of Panax notoginseng. Molecules 2009, 14, 2087-2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14062087
Wang J-R, Yamasaki Y, Tanaka T, Kouno I, Jiang Z-H. Dammarane-type Triterpene Saponins from the Flowers of Panax notoginseng. Molecules. 2009; 14(6):2087-2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14062087
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jing-Rong, Yuko Yamasaki, Takashi Tanaka, Isao Kouno, and Zhi-Hong Jiang. 2009. "Dammarane-type Triterpene Saponins from the Flowers of Panax notoginseng" Molecules 14, no. 6: 2087-2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14062087
APA StyleWang, J. -R., Yamasaki, Y., Tanaka, T., Kouno, I., & Jiang, Z. -H. (2009). Dammarane-type Triterpene Saponins from the Flowers of Panax notoginseng. Molecules, 14(6), 2087-2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14062087