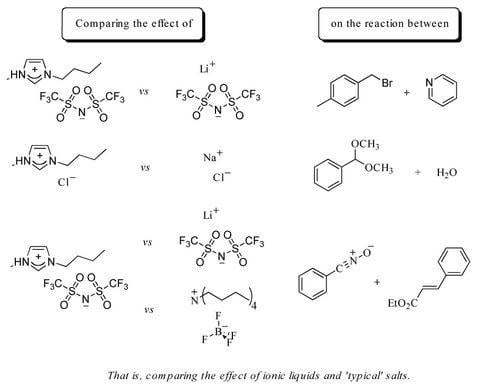
Ionic Liquids: Just Molten Salts After All?
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Bimolecular substitution of a benzyl bromide

| Solvent | ΔH‡ (kJ mol-1) | ΔS‡ (J K-1 mol-1) |
|---|---|---|
| Acetonitrile | 43.2 ± 1.1 | -219 ± 4 |
| Acetonitrile containing Li[N(CF3SO2)2] | 57.1 ± 0.5 | -191 ± 2 |
| [Bmim][N(CF3SO2)2] | 48.8 ± 0.9 | -193 ± 3 |
2.2. Hydrolysis of benzaldehyde dimethyl acetal (5)

| Solvent | ΔH‡ (kJ mol-1) | ΔS‡ (J K-1 mol-1) |
|---|---|---|
| Acetonitrile/water (10:1) | 136 ± 5 | 139 ± 17 |
| Acetonitrile/water containing NaCl | 110 ± 3 | 44 ± 10 |
| Acetonitrile/water containing [Bmim]Cl | 71 ± 4 | -84 ± 13 |
2.3. A nitrile oxide cycloaddition

| Solvent | 9a : 9b (% conversion) |
|---|---|
| Acetonitrile | (6.5 ± 0.4) : 1 (44%)[36] |
| Acetonitrile containing Li[N(CF3SO2)2] | (4.6 ± 0.3) : 1 (15%) |
| Acetonitrile containing [NBu4]BF4 | (7.5 ± 0.4) : 1 (30%) |
| [Bmim][N(CF3SO2)2] | (15.2 ± 0.8) : 1 (84%)[36] |
2.4. Results present in the literature
2.5. Comparison with molecular dynamics simulations
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
3.2. Bimolecular substitution of benzyl bromide
3.3. Hydrolysis of benzaldehyde dimethyl acetal (5)
3.4. A nitrile oxide cycloaddition
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Rogers, R.D.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic Liquids - Solvents of the Future? Science 2003, 302, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Abedin, S.Z.; Endres, F. Ionic Liquids: The Link to High-Temperature Molten Salts? Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussey, C.L. Room temperature haloaluminate ionic liquids. Novel solvents for transition metal solution chemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 1988, 60, 1763–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, R.H.; Zaworotko, M.J.; White, P.S. Complex hydrogen-bonded cations. X-ray crystal structure of [(C6H5CH2)NH3)4Cl][AlCl4]3 and its relevance to the structure of basic chloroaluminate room-temperature melts. Inorg. Chem. 1989, 28, 2019–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, J.S.; Zaworotko, M.J. Air and water stable 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium based ionic liquids. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1992, 965–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonhôte, P.; Das, A.; Papageorgiou, N.; Kalanasundram, K.; Grätzel, M. Hydrophobic, Highly Conductive Ambient-Temperature Molten Salts. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddleston, J.G.; Willauer, H.D.; Swatloski, R.P.; Visser, A.E.; Rogers, R.D. Room temperature ionic liquids as novel media for `clean' liquid-liquid extraction. Chem. Commun. 1998, 1765–1766. [Google Scholar]
- Seddon, K.R. Room-temperature ionic liquids: neoteric solvents for clean catalysis? Kinet. Catal. Engl. Transl. 1996, 37, 693–697. [Google Scholar]
- Stegemann, H.; Rhode, A.; Reiche, A.; Schnittke, A.; Füllbier, H. Room temperature molten polyiodides. Electrochim. Acta 1992, 37, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaiwi, A.; Hitchcock, P.B.; Seddon, K.R.; Srinivasan, N.; Tan, Y.M.; Welton, T. Hydrogen bonding in imidazolium salts and its implications for ambient-temperature halogenoaluminate(III) ionic liquids. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 1995, 3467–3472. [Google Scholar]
- Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids for clean technology? J. Chem. Tech. Biotech. 1997, 68, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freemantle, M. Designer solvents. Chem. Eng. News 1998, 76, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, C.M.; Holbrey, J.D.; Kennedy, A.R.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquid crystals: hexafluorophosphate salts. J. Mater. Chem. 1998, 8, 2627–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, D. Clean and green...but are they mean? Nature 2000, 407, 938–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.H., Jr.; Fox, P.A. From curiousities to commodities: ionic liquids begin the transition. Chem. Commun. 2003, 1209–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids. A taste of the future. Nature: Mat. 2003, 2, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, J.B.; Kobrak, M.N. Understanding organic processes in ionic liquids: Achievements so far and challenges remaining. Mini Rev. Org. Chem. 2006, 3, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, M.J.; Katdare, S.P.; Seddon, K.R. Paradigm Confirmed: The First Use of Ionic Liquids to Dramatically Influence the Outcome of Chemical Reactions. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.B.; March, J. March's Advanced Organic Chemistry, 5th ed.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, A.; Lancaster, N.L.; Sethi, A.R.; Welton, T. The role of hydrogen bonding in controlling the selectivity of Diels-Alder reactions in room-temperature ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2002, 4, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobuoka, K.; Kitaoka, S.; Kunimitsu, K.; Iio, M.; Harran, T.; Wakisaka, A.; Ishikawa, Y. Camphor Ionic Liquid: Correlation between Stereoselectivity and Cation-Anion Interaction. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 10106–10108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidis, A.; Ohlin, C.A.; Laurenczy, G.; Kuesters, E.; Sedelmeier, G.; Dyson, P.J. Rationalisation of solvent effects in the Diels-Alder reaction between cyclopentadiene and methyl acrylate in room temperature ionic liquids. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2005, 347, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harifi-Mood, A.R.; Habibi-Yangjeh, A.; Gholami, M.R. Kinetics study of a Diels-Alder reaction in mixtures of an ionic liquid with molecular solvents. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2008, 21, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, R.C.; Chiappe, C.; Mestre, V.L.; Pomellic, C.S.; Welton, T. A rationalization of the solvent effect on the Diels–Alder reaction in ionic liquids using multiparameter linear solvation energy relationships. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008, 6, 2522–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanke, C.G.; Johansson, A.; Harper, J.B.; Lynden-Bell, R.M. Why are aromatic compounds more soluble that aliphatic compounds in dimethylimidazolium ionic liquids? A simulation study. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2003, 374, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, J.B.; Lynden-Bell, R.M. Macroscopic and microscopic properties of solutions of aromatic compounds in an ionic liquid. Mol. Phys. 2004, 102, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobrak, M.N. The Chemical Environment of Ionic Liquids: Links Between Liquid Structure, Dynamics, and Solvation. Adv. Chem. Phys. 2008, 139, 85–138. [Google Scholar]
- Kobrak, M.N. Electrostatic Interactions of a Neutral Dipolar Solute with a Fused Salt: A New Model for Solvation in Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4755–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobrak, M.N.; Sandalow, N. An Electrostatic Interpretation of Structure-Property Relationships in Ionic Liquids. In Molten Salts {XIV}; Mantz, R.A., Ed.; The Electrochemical Society: Pennington, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Znamenskiy, B.; Kobrak, M.N. Molecular Dynamics Study of Polarity in Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 104, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, B.Y.W.; Hook, J.M.; Harper, J.B. Substitution reactions in ionic liquids. A kinetic study. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 7641–7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, H.M.; Barnes, S.A.; Hook, J.M.; Youngs, T.G.A.; Croft, A.K.; Harper, J.B. The importance of solvent reorganisation in the effect of an ionic liquid on a unimolecular substitution process. Chem. Commun. 2008, 3576–3578. [Google Scholar]
- Haberfield, P.; Nudelman, A.; Bloom, A.; Romm, R.; Ginsberg, H. Enthalpies of transfer of transition states in the Menshutkin reaction from a polar protic to a dipolar aprotic solvent. J. Org. Chem. 1971, 36, 1792–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, H. Activated complex in chemical reactions. J. Chem. Phys. 1935, 3, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, H.M.; Howe, A.G.; Hook, J.M.; Croft, A.K.; Harper, J.B. Solvent reorganisation as the driving force for rate changes of Menschutkin reactions in an ionic liquid. Org. Biomol. Chem 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosella, C.E.; Harper, J.B. The effect of ionic liquids on the outcome of nitrile oxide cycloadditions. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 992–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, C.J.; Hughes, C.M.M.; Savage, G.P.; Simpson, G.W. Cycloaddition reactions of nitrile oxides with alkenes. Adv. Het. Chem. 1994, 60, 261–327. [Google Scholar]
- Kanemasa, S.; Nishiuchi, M.; Wada, E. Regiocontrol of Nitrile Oxide Cycloaddition to Allyl Alcohols. Synthesis of 4-Substituted and 4,4-Disubstituted 5-Hydroxymethyl-2-isoxazolines. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 1357–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryshtal, G.V.; Zhdankina, G.M.; Zlotin, S.G. Tetraalkylammonium and 1,3-dialkylimidazolium salts with fluorinated anions as recoverable phase-transfer catalysts in solid base-promoted cross-aldol condensations. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 2822–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diels, O.; Alder, K. Synthesen in der hydroaromatischen Reihe. Liebigs Ann Chem. 1928, 460, 98–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A. Salt Effects on Diels-Alder Reaction Kinetics. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieco, P.A.; Nunes, J.J.; Gaul, M.D. Dramatic Rate Acceleration of Diels-Alder Reactions in 5 M Lithium Perchlorate-Diethyl Ether: The Cantharidin Problem Reexamined. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 4595–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauben, W.G.; Kessel, C.R.; Takemura, K.H. Simple, efficient total synthesis of cantharidin via a high-pressure Diels-Alder reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 6893–6894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslow, R. Hydrophobic effects on simple organic reactions in water. Acc. Chem. Res. 1991, 24, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; le Noble, W.J. Activation and Reaction Volumes in Solution. Chem. Rev 1978, 78, 407–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eldik, R.; Asano, T.; le Noble, W.J. Activation and Reaction Volumes in Solution 2. Chem. Rev 1989, 89, 549–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drljaca, A.; Hubbard, C.D.; van Eldik, R.; Asano, T.; Basilevsky, M.V.; le Noble, W.J. Activation and Reaction Volumes in Solution. 3. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 2167–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, G.; Elam, C.; Edwards, A.; Bowe, C.; Boyles, D.; Bartmess, J.; Chandler, M.; West, K.; Williams, J.; Green, J.; Pagni, R.M.; Kabalka, G.W. Chemical and Spectroscopic Studies Related to the Lewis Acidity of Lithium Perchlorate in Diethyl Ether. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 2202–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faita, G.; Righetti, P.P. Inorganic Perchlorates and Pericyclic Reactions. IV. Rate Enhancement by Specific Cation-Substrate Interaction or by Increased Internal Pressure? Tetrahedron 1995, 51, 9091–9102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, M.J.; McCormac, P.B.; Seddon, K.R. Diels-Alder Reactions in Ionic Liquids. Green Chem. 1999, 1, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.E.; Shim, W.H.; Roh, E.J.; Lee, S.G.; Choi, J.H. Ionic liquids as powerful media in scandium triflate catalysed Diels–Alder reactions: significant rate acceleration, selectivity improvement and easy recycling of catalyst. Chem. Commun. 2001, 1122. [Google Scholar]
- Pégot, B.; Vo-Thanh, G. Ionic Liquid Promoted Aza-Diels-Alder Reaction of Danishefsky's Diene with Imines. Synlett 2005, 1409–1412. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Pawar, S.S. Converting exo-Selective Diels-Alder Reaction to endo-Selective in Chloroaluminate Ionic Liquids. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 1419–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludley, P.; Karodia, N. Phosphonium tosylates as solvents for the Diels-Alder reaction with 1,3-cyclopentadiene. ARKIVOC 2002, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiderski, K.; McLean, A.; Gordon, C.M. Estimates of internal energies of vaporisation of some room temperature ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2004, 2178–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynden-Bell, R.M.; Del Pópolo, M.G.; Youngs, T.G.A.; Kohanoff, J.; Hanke, C.G.; Harper, J.B.; Pinilla, C.C. Simulations of ionic liquids, solutions and surfaces. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- For some examples see the work of the members of the Atomistic Simulation Centre (Queen's University, Belfast, UK) and from the groups of Balaubramanian (Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Bangalore,, India), Canongia Lopes (Instituto Superior Técnico and Universidade Nova de Lisboa, Portugal), Kobrak (Brooklyn College, City University of New York, USA), Voth (University of Utah, USA) and Wipff (Institut de Chimie, Strasbourg, France), along with many others.
- Bhargava, B.L.; Balasubramanian, S.; Klein, M.L. Modelling room temperature ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2008, 3339–3351. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, J.N.C.; Deschamps, J.; Pádua, A.H.H. Modelling Ionic Liquids Using a Systematic All-Atom Force Field. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 2038–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.N.C.; Pádua, A.H.H. Molecular Force Field for Ionic Liquids Composed of Triflate or Bistriflylimide Anions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 16893–16898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.N.C.; Pádua, A.H.H. Using Spectroscopic Data on Imidazolium Cation Conformations To Test a Molecular Force Field for Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7485–7489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.N.C.; Pádua, A.H.H. Molecular Force Field for Ionic Liquids III: Imidazolium, Pyridinium, and Phosphonium Cations; Chloride, Bromide and Dicyanamide Anions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 19586–19592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambasivarao, S.V.; Acevedo, O. Development of OPLS-AA Force Field Parameters for 68 Uniquie Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2009, 5, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pópolo, M.G.; Lynden-Bell, R.M.; Kohanoff, J. Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics Simulation of a Room Temperature Ionic Liquid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 5895–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhl, M.; Chaumont, A.; Schurhammer, R.; Wipff, G. Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics of Liquid 1,3-Dimethylimidazolium Chloride. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 18591–18599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, B.L.; Balasubramanian, S. Dynamics in a room-temperature ionic liquid: A computer simulation study of 1,3-dimethylimidazolium chloride. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 123, 144505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, B.L.; Balasubramanian, S. Intermolecular structure and dynamics in an ionic liquid: A Car-Parrinello molecular dynamics simulation study of 1,3-dimethylimidazolium chloride. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 417, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngs, T.G.A.; Del Pópolo, M.G.; Kohanoff, J. Development of Complex Classical Force Fields through Force Matching to ab Initio Data: Application to a Room-Temperature Ionic Liquid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 5697–5707. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, P.A.; Kirchner, B.; Welton, T. Characterising the Electronic Structure of Ionic Liquids: An Examination of the 1-Butyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride Ion Pair. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 6762–6775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzuki, S.; Tokuda, H.; Hayamizo, K.; Watanabe, M. Magnitude and Directionality of Interaction in Ion Pairs of Ionic Liquids: Relationship with Ionic Conductivity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 16474–16481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, Y.; Kim, H.J. Free Energy and Dynamics of Electron-Transfer Reactions in a Room Temperature Ionic Liquid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4510–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pópolo, M.G.; Kohanoff, J.; Lynden-Bell, R.M. Solvation Structure and Transport of Acidic Protons in Ionic Liquids: A First-principles Simulation Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 8798–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, C.J.; Hughes, C.M.M.; Lincoln, S.F.; Simpson, G.W.; Vuckovic, G.J. Effect of β-cyclodextrin on the extraction of isozaxolines from aqueous ethanol into chloroform. ARKIVOC 2001, xii, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Armarego, W.L.F.; Chai, C. Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, 5th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, MA, USA; p. 2003.
- Sample Availability: Samples of each of the substrates and the ionic liquids are available from the authors.
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yau, H.M.; Chan, S.J.; George, S.R.D.; Hook, J.M.; Croft, A.K.; Harper, J.B. Ionic Liquids: Just Molten Salts After All? Molecules 2009, 14, 2521-2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14072521
Yau HM, Chan SJ, George SRD, Hook JM, Croft AK, Harper JB. Ionic Liquids: Just Molten Salts After All? Molecules. 2009; 14(7):2521-2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14072521
Chicago/Turabian StyleYau, Hon Man, Si Jia Chan, Stephen R. D. George, James M. Hook, Anna K. Croft, and Jason B. Harper. 2009. "Ionic Liquids: Just Molten Salts After All?" Molecules 14, no. 7: 2521-2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14072521
APA StyleYau, H. M., Chan, S. J., George, S. R. D., Hook, J. M., Croft, A. K., & Harper, J. B. (2009). Ionic Liquids: Just Molten Salts After All? Molecules, 14(7), 2521-2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14072521