Artificial and Natural Sialic Acid Precursors Influence the Angiogenic Capacity of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of Artificial Sialic Acid Precursors

2.2. Integration of Artificial Sialic Acids into Glycoconjugates in HUVECs



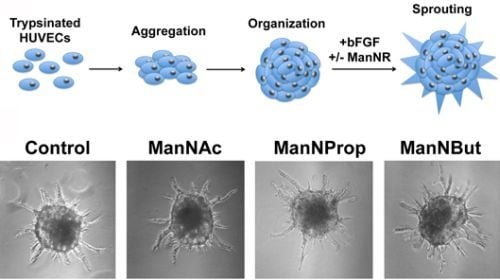
2.3. Artificial Sialic Acids Influence Capillary Sprouting of HUVECs

3. Experimental
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Synthesis of Ac4-ManN Derivatives
3.3. Cell Culture
3.4. Sample Preparation for the Analysis of Sialic Acids
3.5. DMB-Labeling of Sialic Acids
3.6. HPLC-Separation
3.7. GC (-MS) Analyses
3.8. nanoLC-ESI-MS(/MS)-Analysis
3.9. NMR-Analysis
3.10. Spheroid Assay
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Angata, T.; Varki, A. Chemical diversity in the sialic acids and related alpha-keto acids: An evolutionary perspective. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 439–469. [Google Scholar]
- Schauer, R. Achievements and challenges of sialic acid research. Glycoconj. J. 2000, 17, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, R. Sialic acids: Fascinating sugars in higher animals and man. Zoology (Jena) 2004, 107, 49–64. [Google Scholar]
- Schauer, R. Sialic acids as regulators of molecular and cellular interactions. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2009, 19, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEver, R.P.; Moore, K.L.; Cummings, R.D. Leukocyte trafficking mediated by selectin-carbohydrate interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 11025–11028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Meledeo, M.A.; Wang, Z.; Khanna, H.S.; Paruchuri, V.D.; Yarema, K.J. Metabolic glycoengineering: Sialic acid and beyond. Glycobiology 2009, 19, 1382–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppler, O.T.; Horstkorte, R.; Pawlita, M.; Schmidt, C.; Reutter, W. Biochemical engineering of the N-acyl side chain of sialic acid: Biological implications. Glycobiology 2001, 11, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppler, O.T.; Stehling, P.; Herrmann, M.; Kayser, H.; Grunow, D.; Reutter, W.; Pawlita, M. Biosynthetic modulation of sialic acid-dependent virus-receptor interactions of two primate polyoma viruses. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Strilic, B.; Eglinger, J.; Krieg, M.; Zeeb, M.; Axnick, J.; Babal, P.; Muller, D.J.; Lammert, E. Electrostatic cell-surface repulsion initiates lumen formation in developing blood vessels. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 2003–2009. [Google Scholar]
- Aich, U.; Campbell, C.T.; Elmouelhi, N.; Weier, C.A.; Sampathkumar, S.G.; Choi, S.S.; Yarema, K.J. Regioisomeric SCFA attachment to hexosamines separates metabolic flux from cytotoxicity and MUC1 suppression. ACS Chem. Biol. 2008, 3, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galuska, S.P.; Geyer, H.; Weinhold, B.; Kontou, M.; Rohrich, R.C.; Bernard, U.; Gerardy-Schahn, R.; Reutter, W.; Munster-Kuhnel, A.; Geyer, R. Quantification of nucleotide-activated sialic acids by a combination of reduction and fluorescent labeling. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4591–4598. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, A.; Diaz, S.; Ferreira, I.; Lamblin, G.; Roussel, P.; Manzi, A.E. New sialic acids from biological sources identified by a comprehensive and sensitive approach: Liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS) of SIA quinoxalinones. Glycobiology 1997, 7, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korff, T.; Augustin, H.G. Integration of endothelial cells in multicellular spheroids prevents apoptosis and induces differentiation. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesano, R.; Pepper, M.S.; Vassalli, J.D.; Orci, L. Phorbol ester induces cultured endothelial cells to invade a fibrin matrix in the presence of fibrinolytic inhibitors. J. Cell Physiol. 1987, 132, 509–516. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, Y.; Isaji, T.; Tajiri, M.; Yoshida-Yamamoto, S.; Yoshinaka, T.; Somehara, T.; Fukuda, T.; Wada, Y.; Gu, J. An N-glycosylation site on the beta-propeller domain of the integrin alpha5 subunit plays key roles in both its function and site-specific modification by beta1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase III. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 11873–11881. [Google Scholar]
- Isaji, T.; Sato, Y.; Fukuda, T.; Gu, J. N-Glycosylation of the I-like domain of beta1 integrin is essential for beta1 integrin expression and biological function: Identification of the minimal N-glycosylation requirement for alpha5beta1. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 12207–12216. [Google Scholar]
- Duchesne, L.; Tissot, B.; Rudd, T.R.; Dell, A.; Fernig, D.G. N-Glycosylation of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 regulates ligand and heparan sulfate co-receptor binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 27178–27189. [Google Scholar]
- Manfredi, M.G.; Lim, S.; Claffey, K.P.; Seyfried, T.N. Gangliosides influence angiogenesis in an experimental mouse brain tumor. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5392–5397. [Google Scholar]
- Ziche, M.; Morbidelli, L.; Alessandri, G.; Gullino, P.M. Angiogenesis can be stimulated or repressed in vivo by a change in GM3:GD3 ganglioside ratio. Lab. Invest. 1992, 67, 711–715. [Google Scholar]
- Bork, K.; Gagiannis, D.; Orthmann, A.; Weidemann, W.; Kontou, M.; Reutter, W.; Horstkorte, R. Experimental approaches to interfere with the polysialylation of the neural cell adhesion molecule in vitro and in vivo. J Neurochem 2007, 103 (Suppl. 1), 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstkorte, R.; Muhlenhoff, M.; Reutter, W.; Nohring, S.; Zimmermann-Kordmann, M.; Gerardy-Schahn, R. Selective inhibition of polysialyltransferase ST8SiaII by unnatural sialic acids. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 298, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidemann, W.; Klukas, C.; Klein, A.; Simm, A.; Schreiber, F.; Horstkorte, R. Lessons from GNE-deficient embryonic stem cells: Sialic acid biosynthesis is involved in proliferation and gene expression. Glycobiology 2010, 20, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchansky, S.J.; Yarema, K.J.; Takahashi, S.; Bertozzi, C.R. GlcNAc 2-epimerase can serve a catabolic role in sialic acid metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 8035–8042. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, C.T.; Sampathkumar, S.G.; Yarema, K.J. Metabolic oligosaccharide engineering: Perspectives, applications, and future directions. Mol. BioSyst. 2007, 3, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, E.A.; Nachman, R.L.; Becker, C.G.; Minick, C.R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J. Clin. Invest. 1973, 52, 2745–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, S.; Takemori, Y.; Yamaguchi, M.; Nakamura, M.; Ohkura, Y. Fluorometric high-performance liquid chromatography of N-acetyl- and N-glycolylneuraminic acids and its application to their microdetermination in human and animal sera, glycoproteins, and glycolipids. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 164, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galuska, S.P.; Geyer, H.; Mink, W.; Kaese, P.; Kuhnhardt, S.; Schafer, B.; Muhlenhoff, M.; Freiberger, F.; Gerardy-Schahn, R.; Geyer, R. Glycomic strategy for efficient linkage analysis of di-, oligo- and polysialic acids. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 5266–5278. [Google Scholar]
- Keppler, O.T.; Herrmann, M.; von der Lieth, C.W.; Stehling, P.; Reutter, W.; Pawlita, M. Elongation of the N-acyl side chain of sialic acids in MDCK II cells inhibits influenza A virus infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 253, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.; Horstkorte, R.; Glanz, D.; Biskup, K.; Blanchard, V.; Berger, M.; Bork, K. Glycoengineering the N-acyl side chain of sialic acid of human erythropoietin affects its resistance to sialidase. Biol. Chem. 2012, 393, 777–783. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Artificial sialic acids are available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Bayer, N.B.; Schubert, U.; Sentürk, Z.; Rudloff, S.; Frank, S.; Hausmann, H.; Geyer, H.; Geyer, R.; Preissner, K.T.; Galuska, S.P. Artificial and Natural Sialic Acid Precursors Influence the Angiogenic Capacity of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Molecules 2013, 18, 2571-2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18032571
Bayer NB, Schubert U, Sentürk Z, Rudloff S, Frank S, Hausmann H, Geyer H, Geyer R, Preissner KT, Galuska SP. Artificial and Natural Sialic Acid Precursors Influence the Angiogenic Capacity of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Molecules. 2013; 18(3):2571-2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18032571
Chicago/Turabian StyleBayer, Nils B., Uwe Schubert, Zehra Sentürk, Silvia Rudloff, Sandra Frank, Heike Hausmann, Hildegard Geyer, Rudolf Geyer, Klaus T. Preissner, and Sebastian P. Galuska. 2013. "Artificial and Natural Sialic Acid Precursors Influence the Angiogenic Capacity of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells" Molecules 18, no. 3: 2571-2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18032571
APA StyleBayer, N. B., Schubert, U., Sentürk, Z., Rudloff, S., Frank, S., Hausmann, H., Geyer, H., Geyer, R., Preissner, K. T., & Galuska, S. P. (2013). Artificial and Natural Sialic Acid Precursors Influence the Angiogenic Capacity of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Molecules, 18(3), 2571-2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18032571