Proton Adsorption Selectivity of Zeolites in Aqueous Media: Effect of Si/Al Ratio of Zeolites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
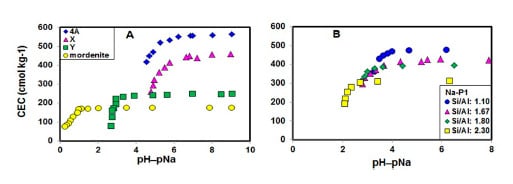
2.1. Stability of Zeolites with CEC Measurement
| Zeolite | Si/Al | pH 1 | [Na+] 2 | pH−pNa 3 | CEC 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4A | 1.00 | 11.36 | 0.26 | 9.05 | 565 |
| 10.85 | 0.47 | 8.04 | 560 | ||
| 10.16 | 0.68 | 6.99 | 558 | ||
| 10.05 | 0.69 | 6.88 | 556 | ||
| 9.26 | 0.92 | 6.23 | 553 | ||
| 8.49 | 1.94 | 5.78 | 532 | ||
| 7.87 | 2.55 | 5.28 | 520 | ||
| 7.23 | 4.98 | 4.90 | 471 | ||
| 6.91 | 6.04 | 4.68 | 450 | ||
| 6.64 | 7.65 | 4.55 | 418 | ||
| X | 1.24 | 11.29 | 0.96 | 8.99 | 461 |
| 10.65 | 1.17 | 7.99 | 457 | ||
| 9.84 | 0.63 | 7.22 | 440 | ||
| 9.64 | 1.53 | 6.81 | 449 | ||
| 9.40 | 1.79 | 6.63 | 444 | ||
| 8.28 | 3.19 | 5.75 | 416 | ||
| 7.89 | 4.47 | 5.51 | 391 | ||
| 7.49 | 5.86 | 5.22 | 363 | ||
| 7.10 | 7.86 | 4.95 | 323 | ||
| 6.97 | 9.30 | 4.89 | 294 | ||
| 6.79 | 10.92 | 4.78 | 262 | ||
| Y | 2.66 | 11.37 | 0.02 | 9.03 | 250 |
| 11.09 | 0.13 | 8.45 | 247 | ||
| 10.37 | 0.40 | 6.96 | 250 | ||
| 9.18 | 0.03 | 5.64 | 245 | ||
| 8.38 | 0.04 | 4.87 | 243 | ||
| 7.41 | 0.05 | 3.89 | 240 | ||
| 7.01 | 0.19 | 3.29 | 236 | ||
| 6.03 | 0.79 | 2.91 | 224 | ||
| 5.61 | 2.21 | 2.93 | 196 | ||
| 5.34 | 3.20 | 2.82 | 176 | ||
| 5.15 | 3.93 | 2.71 | 162 | ||
| 5.01 | 5.57 | 2.72 | 129 | ||
| 4.81 | 7.94 | 2.67 | 81 | ||
| Na-P1 | 1.10 | 10.21 | 0.28 | 6.40 | 478 |
| 8.54 | 0.48 | 4.90 | 476 | ||
| 7.61 | 1.15 | 4.24 | 470 | ||
| 6.88 | 3.18 | 4.13 | 459 | ||
| 6.60 | 4.18 | 3.84 | 449 | ||
| 6.19 | 4.54 | 3.63 | 409 | ||
| 6.03 | 6.67 | 3.54 | 367 | ||
| Na-P1 | 1.67 | 11.36 | 0.35 | 9.01 | 424 |
| 10.75 | 0.28 | 7.88 | 424 | ||
| 10.08 | 0.15 | 5.95 | 429 | ||
| 9.11 | 0.21 | 5.42 | 426 | ||
| 8.34 | 0.71 | 5.17 | 416 | ||
| 7.48 | 0.72 | 4.32 | 416 | ||
| 6.46 | 1.78 | 3.67 | 394 | ||
| 5.93 | 2.92 | 3.36 | 372 | ||
| 5.54 | 3.79 | 3.09 | 354 | ||
| 5.22 | 5.01 | 2.89 | 330 | ||
| 4.98 | 6.60 | 2.76 | 298 | ||
| Na-P1 | 1.80 | 10.36 | 0.14 | 6.51 | 397 |
| 7.98 | 0.28 | 4.41 | 394 | ||
| 6.86 | 0.61 | 3.63 | 387 | ||
| 6.26 | 1.11 | 3.29 | 377 | ||
| 5.76 | 1.84 | 3.00 | 363 | ||
| 5.43 | 3.12 | 2.90 | 337 | ||
| 5.17 | 4.24 | 2.77 | 315 | ||
| Na-P1 | 2.30 | 9.96 | 0.23 | 6.30 | 314 |
| 6.81 | 0.40 | 3.40 | 310 | ||
| 5.66 | 0.56 | 2.69 | 307 | ||
| 5.08 | 1.93 | 2.34 | 279 | ||
| 4.72 | 3.12 | 2.19 | 256 | ||
| 4.44 | 4.92 | 2.10 | 220 | ||
| 4.33 | 6.25 | 2.09 | 193 | ||
| morde-nite | 4.88 | 11.31 | 0.35 | 9.00 | 179 |
| 10.72 | 0.31 | 7.86 | 179 | ||
| 7.97 | 0.78 | 4.85 | 176 | ||
| 5.84 | 0.15 | 2.01 | 176 | ||
| 4.86 | 0.39 | 1.44 | 173 | ||
| 4.38 | 0.54 | 1.10 | 171 | ||
| 4.11 | 0.72 | 0.96 | 168 | ||
| 3.75 | 1.42 | 0.89 | 153 | ||
| 3.28 | 2.51 | 0.66 | 131 | ||
| 3.01 | 3.55 | 0.53 | 110 | ||
| 2.83 | 4.37 | 0.43 | 94 | ||
| 2.67 | 4.76 | 0.31 | 86 | ||
| 2.56 | 5.09 | 0.23 | 79 |


2.2. Effect of pH−pNa on Na+ Retention by Zeolites


2.3. Factors Affecting H+ Adsorption Selectivity
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Preparation of Na+-Saturated Zeolites
3.2. CEC Determination of Zeolites at Different pH
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Misaelides, P.; Misaelides, P. Application of natural zeolites in environmental remediation: A short review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 144, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuronen, M.; Harjula, R.; Jernstrom, J.; Vestenius, M.; Lehto, J. Effect of the framework charge density on zeolite ion exchange selectivities. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 2655–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabwadza-Corner, P.; Munthali, M.W.; Johan, E.; Matsue, N. Comparative study of copper adsorptivity and selectivity toward zeolites. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 5, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, G. Acid Catalysts in Industrial Hydrocarbon Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5366–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, M.B. Surface chemistry of soil minerals. In Minerals in Soil Environments; Dixon, J.B., Weed, S.B., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madson, WI, USA, 1989; pp. 35–88. [Google Scholar]
- Munthali, M.W.; Kabwadza-Corner, P.; Johan, E.; Matsue, N. Decrease in Cation Exchange Capacity of Zeolites at Neutral pH: Examples and Proposal of a Determination Method. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Katada, N.; Suzuki, K.; Noda, T.; Sastre, G.; Niwa, M. Correlation between Brønsted acid strength and local structure in zeolites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 19208–19217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre, G.; Katada, N.; Niwa, M. Computational study of Brønsted acidity of mordenite. Effect of the electric field on the infrared OH stretching frequencies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 15424–15431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katada, N.; Niwa, M. Analysis of acidic properties of zeolitic and non-zeolitic solid acid catalysts using temperature-programmed desorption of ammonia. Catal. Surv. Asia 2004, 8, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, T.; Suzuki, K.; Katada, N.; Niwa, M. Combined study of IRMS-TPD measurement and DFT calculation on Brønsted acidity and catalytic cracking activity of cation-exchanged Y zeolites. J. Catal. 2008, 259, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Kim, H.S.; Seo, S.M.; Ko, S.O.; Suh, J.M.; Kim, G.H.; Lim, W.T. Location of Na+ ions in fully dehydrated Na+-saturated zeolite Y (FAU, Si/Al = 1.56). Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2012, 33, 2785–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortier, W.J.; Bosmans, H.J.; Uytterhoeven, J.B. Location of univalent cations in synthetic zeolites of the Y and X type with varying silicon to aluminum ratio. II dehydrated potassium exchanged forms. J. Phys. Chem. 1972, 76, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, P.A. Acid zeolites: an attempt to develop unifying concepts. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 1982, 24, 415–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulthess, C.P.; Taylor, R.W.; Ferreir, D.R. The nanopore inner sphere enhancement effect on cation adsorption: Sodium and nickel. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 46–56. [Google Scholar]
- Weitkamp, J. Zeolites and catalysis. Sol. State Ion. 2000, 131, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regli, L.; Zecchina, A.; Vitillo, J.G.; Cocina, D; Spoto, G.; Lamberti, C.; Lillerud, K.P.; Olsbye, U.; Bordiga, S. Hydrogen storage in chabazite zeolite frameworks. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3197–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitillo, J.G.; Ricchiardi, G.; Spoto, G.; Zecchina, A. Theoretical maximal storage of hydrogen in zeolitic frameworks. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3948–3954. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkin, R.T.; Barnes, H.L. Solubility and stability of zeolites in aqueous solution: I. Analcime, Na-, and K-clinoptilolite. Am. Mineral. 1998, 83, 746–761. [Google Scholar]
- Hartman, R.L.; Fogler, H.S. Understanding the dissolution of zeolites. Langmuir 2007, 23, 5477–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, S.; Kawabata, K. Ion adsorption on variable charge materials and thermodynamics of ion exchange. Soil Sci. Plant. Nutr. 1991, 37, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.E; Lobo, R.F. Zeolite and molecular sieve synthesis. Chem. Mater. 1992, 4, 156–768. [Google Scholar]
- Senchenya, I.N.; Kazansky, V.B.; Beran, S. Quantum chemical study of the effect of the structural characteristics of zeolites on the properties of their bridging OH groups, 2. J. Phys. Chem. 1986, 90, 4857–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herron, N.; Corbin, D.R. Inclusion Chemistry with Zeolites: Nanoscale Materials by Design; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 1995; ISBN 978-0-7923-3606-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi, Y.; Masakazi, A. Photofunctional Zeolites: Synthesis, Characterization, Photocatalytic Reactions, Light Harvesting; Nova Science Publishers: Huntington, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Van Santen, R.A.; Neurock, M. Molecular Heterogeneous Catalysis: A Conceptual and Computational Approach; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; ISBN-13: 978-3-527-29662-0; ISBN-10: 3-527-29662-X. [Google Scholar]
- Beran, S.; Dubskÿ, J. Quantum chemical study of the electronic structure of Na-X and Na-Y zeolites. J. Phys. Chem. 1979, 83, 2538–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watling, T.C.; Rees, L.V.C. Ion exchange in zeolite EU-I: part 1. The effect of Si/Al ratio. Zeolites 1994, 14, 687–692. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S.; Choi, S.Y.; Lim, W.T. Complete Li+ exchange into zeolite X (FAU, Si/Al=1.09) from undried methanol solution. J. Porous Mater. 2013, 20, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansel, B. Significance of thermodynamic and physical characteristics on permeation of ions during membrane separation: Hydrated radius, hydration free energy and viscous effects. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 86, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querol, X.; Moreno, N.; Umana, J.C.; Alastuey, A.; Hernandez, E.; Lopez-Soler, A.; Plana, F. Synthesis of zeolites from coal fly ash: An overview. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2002, 50, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, R.C.; Roy, R.K.; Hirao, K. Local reactivity descriptors to predict the strength of Lewis acid sites in alkali cation-exchanged zeolites. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 389, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonenfant, D.; Kharoune, M.; Niquette, P.; Mimeault, M.; Hausler, R. Advances in principal factors influencing carbon dioxide adsorption on zeolites. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2008, 9, 013007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, Y. Volumes of aqueous hydrogen and hydroxide ions at 0 to 200 °C. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 154501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuznikov, A.; Vasilyev, V.; Goursot, A. Relationships between the structure of a zeolite and its adsorption properties. Surf. Sci. 1998, 397, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.L.; Beck, L.W.; Haw, J.F. Characterization of hydrogen bonding in zeolites by H+ solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 6182–6189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Munthali, M.W.; Elsheikh, M.A.; Johan, E.; Matsue, N. Proton Adsorption Selectivity of Zeolites in Aqueous Media: Effect of Si/Al Ratio of Zeolites. Molecules 2014, 19, 20468-20481. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191220468
Munthali MW, Elsheikh MA, Johan E, Matsue N. Proton Adsorption Selectivity of Zeolites in Aqueous Media: Effect of Si/Al Ratio of Zeolites. Molecules. 2014; 19(12):20468-20481. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191220468
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunthali, Moses Wazingwa, Mohammed Abdalla Elsheikh, Erni Johan, and Naoto Matsue. 2014. "Proton Adsorption Selectivity of Zeolites in Aqueous Media: Effect of Si/Al Ratio of Zeolites" Molecules 19, no. 12: 20468-20481. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191220468
APA StyleMunthali, M. W., Elsheikh, M. A., Johan, E., & Matsue, N. (2014). Proton Adsorption Selectivity of Zeolites in Aqueous Media: Effect of Si/Al Ratio of Zeolites. Molecules, 19(12), 20468-20481. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191220468