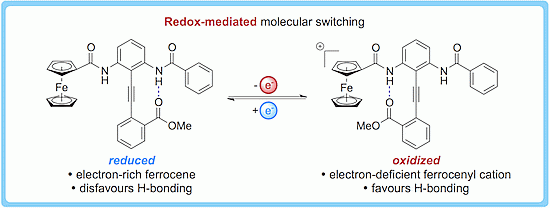
Redox-Dependent Conformational Switching of Diphenylacetylenes
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis

2.2. Solid-State Analysis of Conformation

2.3. Determining the Solution Phase Conformational Bias



2.4. Characterizing the Redox Properties of Switch 3 with Cyclic Voltammetry

2.5. Characterizing the Redox Properties of Switch 3 by Chemical Oxidation

2.6. Paramagnetic NMR Characterization of the Solution Phase Conformation

3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Methods
3.2. Synthetic Procedures
3.3. Chemical Oxidation Procedure
3.4. Single Crystal X-ray Diffraction
3.4.1. Data Collection
3.4.2. Data Reduction
3.4.3. Structure Solution and Refinement
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, M.-Y.; Ji, S.-R.; Bai, C.-J.; Kebir, D.E.; Li, H.-Y.; Shi, J.-M.; Zhu, W.; Costantino, S.; Zhou, H.-H.; Potempa, L.A.; et al. A redox switch in C-reactive protein modulates activation of endothelial cells. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 3186–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahara, N. Intermolecular disulfide bond to modulate protein function as a redox-sensing switch. Amino Acids 2011, 41, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, A.-L.; Berka, V.; Martin, F.; Ma, X.; van den Akker, F.; Fabian, M.; Olson, J.S. Is Nostoc H-NOX a NO Sensor or Redox Switch? Biochemistry 2010, 49, 6587–6599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Biase, P.M.; Paggi, D.A.; Doctorovich, F.; Hildebrandt, P.; Estrin, D.A.; Murgida, D.H.; Marti, M.A. Molecular Basis for the Electric Field Modulation of Cytochrome c Structure and Function. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16248–16256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Wang, C.; Fahrenbach, A.C.; Trabolsi, A.; Botros, Y.Y.; Stoddart, J.F. Dual Stimulus Switching of a [2]Catenane in Water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1805–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Amelia, M.; Klivansky, L.M.; Koshkakaryan, G.; Khan, S.I.; Semeraro, M.; Silvi, S.; Venturi, M.; Credi, A.; Liu, Y. Probing Donor–Acceptor Interactions and Co-Conformational Changes in Redox Active Desymmetrized [2]Catenanes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spruell, J.M.; Paxton, W.F.; Olsen, J.-C.; Benítez, D.; Tkatchouk, E.; Stern, C.L.; Trabolsi, A.; Friedman, D.C.; Goddard, W.A.; Stoddart, J.F. A Push-Button Molecular Switch. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11571–11580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, S.T.; Cooke, G.; Fitzpatrick, B.; Long, D.-L.; Rabani, G.; Rotello, V.M. A flavin-based [2]catenane. Chem. Commun. 2008, 5912–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niess, F.; Duplan, V.; Sauvage, J.-P. Interconversion between a Vertically Oriented Transition Metal-Complexed Figure-of-Eight and a Horizontally Disposed One. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5876–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabehie, S.; Xue, M.; Stieg, A.Z.; Liong, M.; Wang, K.L.; Zink, J.I. Heteroleptic Copper Switches. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15987–15996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Share, A.I.; Parimal, K.; Flood, A.H. Bilability is Defined when One Electron is Used to Switch between Concerted and Stepwise Pathways in Cu(I)-Based Bistable [2/3]Pseudorotaxanes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1665–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parimal, K.; Witlicki, E.H.; Flood, A.H. Interconverting Two Classes of Architectures by Reduction of a Self-Sorting Mixture. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4628–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canary, J.W.; Mortezaei, S.; Liang, J. Redox-reconfigurable tripodal coordination complexes: stereodynamic molecular switches. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 5850–5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNitt, K.A.; Parimal, K.; Share, A.I.; Fahrenbach, A.C.; Witlicki, E.H.; Pink, M.; Bediako, D.K.; Plaisier, C.L.; Le, N.; Heeringa, L.P.; et al. Reduction of a Redox-Active Ligand Drives Switching in a Cu(I) Pseudorotaxane by a Bimolecular Mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Das, D.; Dai, Z.; Holmes, A.; Canary, J.W. Exploring the scope of redox-triggered chiroptical switches: Syntheses, X-ray structures, and circular dichroism of cobalt and nickel complexes of N,N-Bis(arylmethyl)methionine derivatives. Chirality 2008, 20, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; DeIonno, E.; Dichtel, W.R.; Fang, L.; Trabolsi, A.; Olsen, J.-C.; Benítez, D.; Heath, J.R.; Stoddart, J.F. A solid-state switch containing an electrochemically switchable bistable poly[n]rotaxane. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, A.; Aucagne, V.; Carrillo, R.; Clarkson, G.J.; D’Souza, D.M.; Dunnett, J.A.; Leigh, D.A.; Mullen, K.M. Sulfur-containing amide-based [2]rotaxanes and molecular shuttles. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 1922–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berná, J.; Alajarín, M.; Orenes, R.-A. Azodicarboxamides as Template Binding Motifs for the Building of Hydrogen-Bonded Molecular Shuttles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10741–10747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Goddard, W.A.; Jang, S.S.; Dichtel, W.R.; Heath, J.R.; Stoddart, J.F. Free Energy Barrier for Molecular Motions in Bistable [2]Rotaxane Molecular Electronic Devices†. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 2136–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, M.; Ma, X.; Tian, H. Switchable V-Type [2]Pseudorotaxanes. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 3234–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fioravanti, G.; Haraszkiewicz, N.; Kay, E.R.; Mendoza, S.M.; Bruno, C.; Marcaccio, M.; Wiering, P.G.; Paolucci, F.; Rudolf, P.; Brouwer, A.M.; Leigh, D.A. Three State Redox-Active Molecular Shuttle That Switches in Solution and on a Surface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 2593–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikitin, K.; Lestini, E.; Stolarczyk, J.K.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Fitzmaurice, D. Quantitative Conformational Study of Redox-Active [2]Rotaxanes. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-H.; Prabhakar, C.; Huang, S.-L.; Lin, Y.-C.; Tan, W.S.; Misra, N.C.; Sun, W.-T.; Yang, J.-S. A Redox-Gated Slow-Fast-Stop Molecular Rotor. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 5632–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skibiński, M.; Gómez, R.; Lork, E.; Azov, V.A. Redox responsive molecular tweezers with tetrathiafulvalene units: synthesis, electrochemistry, and binding properties. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 10348–10354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azov, V.A.; Gómez, R.; Stelten, J. Synthesis of electrochemically responsive TTF-based molecular tweezers: evidence of tight intramolecular TTF pairing in solution. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, I.; Yamasaki, R.; Sawamura, M.; Kato, T.; Nagayama, N.; Takeya, T.; Tamura, O.; Masu, H.; Azumaya, I.; Yamaguchi, K.; et al. Redox-Induced Conformational Alteration of N,N-Diarylamides. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 5545–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, M.; Mori, T.; Inoue, Y.; Rathore, R. A New Class of Chiroptical Molecular Switches Based on the Redox-Induced Conformational Changes. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 3977–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frei, M.; Diederich, F.; Tremont, R.; Rodriguez, T.; Echegoyen, L. Tetrathiafulvalene (TTF)-Bridged Resorcin[4]arene Cavitands: Towards New Electrochemical Molecular Switches. Helv. Chim. Acta 2006, 89, 2040–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashenko, O.; Logtenberg, H.; Areephong, J.; Coleman, A.C.; Wesenhagen, P.V.; Geertsema, E.M.; Heureux, N.; Feringa, B.L.; Rudolf, P.; Browne, W.R. Remarkable Stability of High Energy Conformers in Self-Assembled Monolayers of a Bistable Electro- and Photoswitchable Overcrowded Alkene. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 22965–22975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, A.; Gatti, F.G.; Kay, E.R.; Leigh, D.A.; Martel, D.; Paolucci, F.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Wong, J.K.Y. Electrochemically Switchable Hydrogen-Bonded Molecular Shuttles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 8644–8654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, I.M.; Hamilton, A.D. Designed Molecular Switches: Controlling the Conformation of Benzamido-diphenylacetylenes. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 3651–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, I.M.; Lingard, H.; Hamilton, A.D. pH‐Dependent Conformational Switching in 2,6‐Benzamidodiphenylacetylenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 12569–12571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, P.; Tárraga, A.; Caballero, A. Ferrocene-Based Small Molecules for Multichannel Molecular Recognition of Cations and Anions. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 2008, 3401–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, P.D.; Gale, P.A. Anion Recognition and Sensing: The State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 486–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, P.A. Anion receptor chemistry: highlights from 1999. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2001, 213, 79–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebler, D.; Linseis, M.; Gasi, T.; Carrella, L.M.; Winter, R.F.; Förster, C.; Heinze, K. Oligonuclear Ferrocene Amides: Mixed-Valent Peptides and Potential Redox-Switchable Foldamers. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 4540–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansch, C.; Leo, A.; Taft, R.W. A survey of Hammett substituent constants and resonance and field parameters. Chem. Rev. 1991, 91, 165–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitterwolf, T.E.; Ling, A.C. Metallocene basicity. IV. Conformational and electronic behaviour of some protonated ferrocenes. J. Organomet. Chem. 1977, 141, 355–370. [Google Scholar]
- Connelly, N.G.; Geiger, W.E. Chemical Redox Agents for Organometallic Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 877–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, J.D.; Lambert, L.; Hibbs, D.E.; Hursthouse, M.B.; Malik, K.M.A.; Tucker, J.H.R. Novel electrochemical sensors for neutral molecules. Chem. Commun. 1997, 1649–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.D.; Coles, S.J.; Hursthouse, M.B.; Light, M.E.; Tucker, J.H.R.; Westwood, J. Redox-Switched Control of Binding Strength in Hydrogen-Bonded Metallocene Complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 3296–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynes, O.; Maillard, F.; Moutet, J.-C.; Royal, G.; Saint-Aman, E.; Stanciu, G.; Dutasta, J.-P.; Gosse, I.; Mulatier, J.-C. Complexation and electrochemical sensing of anions by amide-substituted ferrocenyl ligands. J. Organomet. Chem. 2001, 637–639, 356–363. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, G.; Rotello, V.M. Methods of modulating hydrogen bonded interactions in synthetic host–guest systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2002, 31, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, G.; de Cremiers, H.A.; Duclairoir, F.M.A.; Leonardi, J.; Rosair, G.; Rotello, V.M. Ferrocene incorporating host–guest dyads with electrochemically controlled three-pole hydrogen bonding properties. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 3341–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, J.; Coles, S.J.; Collinson, S.R.; Gasser, G.; Green, S.J.; Hursthouse, M.B.; Light, M.E.; Tucker, J.H.R. Binding and Electrochemical Recognition of Barbiturate and Urea Derivatives by a Regioisomeric Series of Hydrogen-Bonding Ferrocene Receptors. Organometallics 2004, 23, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoli, A.; Marcuzzo, V.; Moretto, A.; Toniolo, C.; Cardena, R.; Bisello, A.; Santi, S. Charge Mapping in 310-Helical Peptide Chains by Oxidation of the Terminal Ferrocenyl Group. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 1282–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, I.M.; Hamilton, A.D. Anion-Dependent Switching: Dynamically Controlling the Conformation of Hydrogen-Bonded Diphenylacetylenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 4597–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sy, W.-W. Iodination of Aromatic Amines with Iodine and Silver Sulfate. Synth. Commun. 1992, 22, 3215–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebler, D.; Förster, C.; Gasi, T.; Heinze, K. Biferrocene Amino Acid, a Ferrocenylogoue of Ferrocene Amino Acid: Synthesis, Cross-Linking, and Redox Chemistry. Organometallics 2011, 30, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojánek, A.; Langmaier, J.; Šebera, J.; Záliš, S.; Barbe, J.-M.; Girault, H.H.; Samec, Z. Fine tuning of the catalytic effect of a metal-free porphyrin on the homogeneous oxygen reduction. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 5446–5448. [Google Scholar]
- Garden, S.J.; Wardell, J.L.; Skakle, J.M.S.; Low, J.N.; Glidewell, C. Hydrogen bonding in substituted nitroanilines: hydrogen-bonded sheets in 4-iodo-3-nitroaniline. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C-Cryst. Struct. Commun. 2004, 60, o328–o330. [Google Scholar]
- CCDC 871793the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge via http://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif (or from the CCDC, 12 Union Road, Cambridge CB2 1EZ, UK; Fax: +44 1223 336033; E-Mail: [email protected]).
- Altomare, A.; Cascarano, G.; Giacovazzo, C.; Guagliardi, A.; Burla, M.C.; Polidori, G.; Camalli, M. SIR 92—A program for automatic solution of crystal structures by direct methods. J. Appl. Cryst. 1994, 27, 435–435. [Google Scholar]
- Cromer, D.T.; Waber, J.T. Atomic Scattering Factors for X-rays. In International Tables for X-ray Crystallography; Ibers, J.A., Hamilton, W.C., Eds.; The Kynoch Press: Birmingham, UK, 1974; Volume IV, pp. 71–98. [Google Scholar]
- Ibers, J.; Hamilton, W. Dispersion Corrections and Crystal Structure Refinements. Acta Crystallogr. 1964, 17, 781–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creagh, D.C.; McAuley, W.J. X-ray Dispersion Corrections. In International Tables for Crystallography; Wilson, A.J.C., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1992; Volume C, pp. 219–222. [Google Scholar]
- Creagh, D.C.; Hubbell, J.H. X-ray Absorption (or attenuation) Coefficients. In International Tables for Crystallography; Wilson, A.J.C., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1992; Volume C, pp. 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- CrystalStructure 4.0: Crystal Structure Analysis Package; Rigaku and Rigaku Americas: The Woodlands, TX, USA; pp. 2000–2010.
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 2007, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Jones, I.M.; Knipe, P.C.; Michaelos, T.; Thompson, S.; Hamilton, A.D. Redox-Dependent Conformational Switching of Diphenylacetylenes. Molecules 2014, 19, 11316-11332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811316
Jones IM, Knipe PC, Michaelos T, Thompson S, Hamilton AD. Redox-Dependent Conformational Switching of Diphenylacetylenes. Molecules. 2014; 19(8):11316-11332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811316
Chicago/Turabian StyleJones, Ian M., Peter C. Knipe, Thoe Michaelos, Sam Thompson, and Andrew D. Hamilton. 2014. "Redox-Dependent Conformational Switching of Diphenylacetylenes" Molecules 19, no. 8: 11316-11332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811316
APA StyleJones, I. M., Knipe, P. C., Michaelos, T., Thompson, S., & Hamilton, A. D. (2014). Redox-Dependent Conformational Switching of Diphenylacetylenes. Molecules, 19(8), 11316-11332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811316