Ruthenium Polypyridine Complexes Combined with Oligonucleotides for Bioanalysis: A Review
Abstract
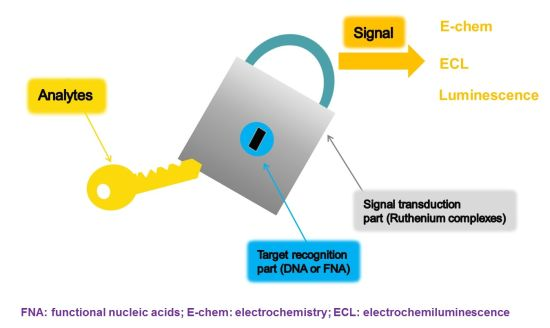
:1. Introduction

2. Electrochemical Methods




3. Electrochemiluminescent Methods
3.1. Mechanism of ECL
3.2. ECL Detection of DNA
| ECL Luminophore | LOD (mol/L) | Linear Range (mol/L) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ru(bpy)32+ | 1.0 × 10−13 | 2.0 × 10−13–2.0 × 10−9 | [72] |
| Ru(bpy)32+ | 3.9 × 10−1° | 3.9 × 10−9–1.9 × 10−7 | [75] |
| Ru(bpy)32+ | 1.0 × 10−15 | 2.0 × 10−15–2.0 × 10−11 | [100] |
| Ru(bpy)32+ | 2.0 × 10−13 | 1.0 × 10−12–1.0 × 10−6 | [156] |
| Ru(bpy)3-[B(C6F5)4]2 | — | 1.0 × 10−15–1.0 × 10−8 | [175] |
| Ru(bpy)32+ | 9.0 × 10−15 | 2.4 × 10−14–1.7 × 10−12 | [176] |
| Ru(bpy)2(dcbpy)-NHS | 9.0 × 10−11 | 2.7 × 10−10–4.0 × 10−9 | [177] |
| Ru(bpy)2(dcbpy)-NHS | 6.7 × 10−12 | 1.7 × 10−11–1.7 × 10−9 | [178] |
| Ru(bpy)32+-NHS | 1.2 × 10−15 | 5.0 × 10−15–1.0 × 10−13 | [180] |
| Ru(bpy)32+ | 1.0 × 10−15 | 1.0 × 10−14–1.0 × 10−11 | [181] |
| Ru(bpy)2(cbpy)-NHS | 5.0 × 10−13 | 1.0 × 10−12–1.0 × 10−7 | [182] |
| Ru(bpy)32+ | 1.0 × 10−15 | 1.0 × 10−14–1.0 × 10−11 | [183] |
| Ru(bpy)2(cbpy)-NHS | 1.0 × 10−13 | 1.0 × 10−13–1.0 × 10−9 | [184] |
| [Ru(bpy)2(mcbpy)]2+ | 4.0 × 10−11 | 1.0 × 10−10–1.0 × 10−7 | [185] |
| Ru(bpy)32+ | 9.1 × 10−14 | 1.0 × 10−13–1.0 × 10−9 | [186] |
| Ru(phen)32+ | 1.5 × 10−14 | 2.5 × 10−14–1.0 × 10−10 | [187] |
| [Ru(dmbpy)2(PIND)2]2+ | 4 × 10−13 | 7 × 10−13–4 × 10−10 | [56] |
3.2.1. DNA as the Co-reactant for Detection

3.2.2. Ru(bpy)32+-Conjugated Probes for DNA Detection







3.2.3. Label-free ECL DNA Detection

3.3. ECL Detection of Other Targets with Functional Nucleic Acids
3.3.1. Ru(bpy)32+-conjugated Functional Nucleic Acids as Probes for Detection






3.3.2. Label-Free Method



4. Photoluminescent Methods

4.1. Ruthenium Complexes as “Light Switch” Effect Probes
4.1.1. Mechanism of “Light Switch” Effect
4.1.2. Factors Affecting the “Light Switch” of Ruthenium Complexes

4.1.3. Probing DNA Conformational Changes by Light Switchable Ruthenium Complexes


4.1.4. Bioanalysis Based on the “Light Switch” Effect

4.2. Ruthenium Complexes Beyond “Light Switch” Probes
4.2.1. Ruthenium Complexes as Luminophores

4.2.2. Ruthenium Complexes as Quenchers

5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wenger, O.S. Vapochromism in organometallic and coordination complexes: Chemical sensors for volatile organic compounds. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 3686–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Chen, C.G.; Han, B.Y.; Wang, E.K. Enzyme colorimetric assay using unmodified silver nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 7051–7055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKay, B.A.; Fryzuk, M.D. Dinitrogen coordination chemistry: On the biomimetic borderlands. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, J.J.; Gagne, M.R. Exploiting the synergy between coordination chemistry and molecular imprinting in the quest for new catalysts. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswamy, N.; Tylus, U.; Jia, Q.Y.; Mukerjee, S. Activity descriptor identification for oxygen reduction on nonprecious electrocatalysts: Linking surface science to coordination chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15443–15449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, K.L.; Franz, K.J. Application of metal coordination chemistry to explore and manipulate cell biology. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4921–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Li, B.L.; Du, Y.; Dong, S.J.; Wang, E. Nucleobase-metal hybrid materials: Preparation of submicrometer-scale, spherical colloidal particles of adenine-gold(III) via a supramolecular hierarchical self-assembly approach. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 2987–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, E.K. Submicrometre scale single-crystalline gold plates of nanometre thickness: Synthesis through a nucleobase process and growth mechanism. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 295603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, E.K. Silver nanoparticles coated with adenine: Preparation, self-assembly and application in surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 175610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, Z.D.; Yang, L.M.; Tian, S.L.; Hou, C.J.; Lu, Y. Lysozyme-stabilized gold fluorescent cluster: Synthesis and application as Hg2+ sensor. Analyst 2010, 135, 1406–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Wang, Z.D.; Zhang, J.; House, S.; Gao, Y.G.; Yang, L.M.; Robinson, H.; Tan, L.H.; Xing, H.; Hou, C.J.; et al. Time-dependent, protein-directed growth of gold nanoparticles within a single crystal of lysozyme. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.C.; Zeng, H.C. Coordination chemistry and antisolvent strategy to rare-earth solid solution colloidal spheres. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 19084–19091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Lu, Y. Catalysis of gold nanoparticles within lysozyme single crystals. Chem. Asian J. 2012, 7, 680–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Wang, E.K. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): Next-generation artificial enzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6060–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; House, S.; Wu, J.J.X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.D.; He, Y.; Gao, E.J.; Gao, Y.G.; Robinson, H.; Li, W.; et al. Enhanced and tunable fluorescent quantum dots within a single crystal of protein. Nano. Res. 2013, 6, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.L.; Irudayaraj, J. Fluorescent Ag clusters via a protein-directed approach as a Hg(II) ion sensor. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 2883–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, F.G.; Sun, Y.J.; Guo, C.L.; Cui, K.; Shi, Y.; Wen, Z.W.; Li, Z. Seed-mediated synthesis of Au nanocages and their electrocatalytic activity towards glucose oxidation. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 9248–9256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.L.; Song, Y.H.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.J.; Guo, C.L.; Liu, Z.L.; Li, Z. DNA-templated gold nanoparticles formation. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 4415–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurisson, S.; Berning, D.; Jia, W.; Ma, D.S. Coordination-compounds in nuclear-medicine. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 1137–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, A.M. Radiometal complexes in molecular imaging and therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 3673–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, Z.P.; Tang, W.; Guo, C.L.; Chen, H.M.; Lin, X.; Liu, G.; Fei, B.W.; Chen, X.Y.; Xu, B.Q.; Xie, J. Ferritin nanocages to encapsulate and deliver photosensitizers for efficient photodynamic therapy against cancer. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6988–6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianneschi, N.C.; Masar, M.S.; Mirkin, C.A. Development of a coordination chemistry-based approach for functional supramolecular structures. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Hao, X.Q.; Wang, M.; Guo, C.L.; Xu, B.Q.; Tan, E.N.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Yu, Y.H.; Li, Z.Y.; Yang, H.B.; et al. Self-assembly of giant supramolecular cubes with terpyridine ligands as vertices and metals on edges. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.H.; Guo, C.L.; Sun, L.L.; Wei, G.; Peng, C.Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.J.; Li, Z. Effects of bridge ions, DNA species, and developing temperature on flat-lying DNA monolayers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.H.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.G.; Wei, G.; Wang, L.; Sun, L.L.; Guo, C.L.; Sun, Y.J.; Yang, T. A novel strategy to construct a flat-lying DNA monolayer on a mica surface. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 10792–10798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noffke, A.L.; Habtemariam, A.; Pizarro, A.M.; Sadler, P.J. Designing organometallic compounds for catalysis and therapy. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5219–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, S.P.; Clavier, H. Chemoselective olefin metathesis transformations mediated by ruthenium complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3305–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, J.G.; Kelly, J.M. Ruthenium polypyridyl chemistry; from basic research to applications and back again. Dalton Trans. 2006, 4869–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.Z.; Xu, G.B. Applications and trends in electrochemiluminescence. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3275–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, M.R.; Thomas, J.A. Ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes and DNA-from structural probes to cellular imaging and therapeutics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3179–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardo, S.; Meyer, G.J. Photodriven heterogeneous charge transfer with transition-metal compounds anchored to TiO2 semiconductor surfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 115–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.Y.; Gu, C.; Tang, S.; Fei, T.; Gu, X.; Wang, H.M.; Wang, Z.M.; Wang, F.F.; Lu, D.; Ma, Y.G. A new kind of peripheral carbazole substituted ruthenium(II) complexes for electrochemical deposition organic light-emitting diodes. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 3941–3949. [Google Scholar]
- Troian-Gautier, L.; Moucheron, C. Ruthenium(II) complexes bearing fused polycyclic ligands: from fundamental aspects to potential applications. Molecules 2014, 19, 5028–5087. [Google Scholar]
- Drummond, T.G.; Hill, M.G.; Barton, J.K. Electrochemical DNA sensors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassolas, A.; Leca-Bouvier, B.D.; Blum, L.J. DNA biosensors and microarrays. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 109–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolpashchikov, D.M. Binary probes for nucleic acid analysis. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4709–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gooding, J.J. Electrochemical DNA hyhridization biosensors. Electroanalysis 2002, 14, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickelsen, S.R. Electrochemical biosensors for DNA sequence detection. Electroanalysis 1996, 8, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palecek, E.; Jelen, F. Electrochemistry of nucleic acids and development of DNA sensors. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2002, 32, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Electrochemical nucleic acid biosensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 469, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palecek, E. Oscillographic polarography of highly polymerized deoxyribonucleic acid. Nature 1960, 188, 656–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palecek, E.; Bartosik, M. Electrochemistry of nucleic acids. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3427–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labuda, J.; Brett, A.M.O.; Evtugyn, G.; Fojta, M.; Mascini, M.; Ozsoz, M.; Palchetti, I.; Palecek, E.; Wang, J. Electrochemical nucleic acid-based biosensors: Concepts, terms, and methodology (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2010, 82, 1161–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, D.H.; Glasgow, K.C.; Thorp, H.H. Electrochemical measurement of the solvent accessibility of nucleobases using electron-transfer between dna and metal-complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 8933–8938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napier, M.E.; Loomis, C.R.; Sistare, M.F.; Kim, J.; Eckhardt, A.E.; Thorp, H.H. Probing biomolecule recognition with electron transfer: Electrochemical sensors for DNA hybridization. Bioconjugate Chem. 1997, 8, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ontko, A.C.; Armistead, P.M.; Kircus, S.R.; Thorp, H.H. Electrochemical detection of single-stranded DNA using polymer-modified electrodes. Inorg. Chem. 1999, 38, 1842–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sistare, M.F.; Holmberg, R.C.; Thorp, H.H. Electrochemical studies of polynucleotide binding and oxidation by metal complexes: Effects of scan rate, concentration, and sequence. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 10718–10728. [Google Scholar]
- Szalai, V.A.; Thorp, H.H. Electrocatalysis of guanine electron transfer: New insights from submillimeter carbon electrodes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 6851–6859. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, I.V.; Thorp, H.H. Modification of indium tin oxide electrodes with repeat polynucleotides: Electrochemical detection of trinucleotide repeat expansion. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 5316–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szalai, V.A.; Jayawickamarajah, J.; Thorp, H.H. Electrocatalysis of guanine oxidation in polyethylene glycol solutions: The interplay of adsorption and reaction rate. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 709–716. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, I.V.; Ropp, P.A.; Thorp, H.H. Toward electrochemical resolution of two genes on one electrode: Using 7-deaza analogues of guanine and adenine to prepare PCR products with differential redox activity. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armistead, P.M.; Thorp, H.H. Electrochemical detection of gene expression in tumor samples: Overexpression of Rak nuclear tyrosine kinase. Bioconjugate Chem. 2002, 13, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Rusling, J.F. Detection of chemically induced DNA damage in layered films by catalytic square wave voltammetry using Ru(bpy)32+. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 4780–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasalathanthri, D.P.; Mani, V.; Tang, C.K.; Rusling, J.F. Microfluidic electrochemical array for detection of reactive metabolites formed by cytochrome p450 enzymes. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9499–9506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugweru, A.; Rusling, J.F. Catalytic square-wave voltammetric detection of DNA with reversible metallopolymer-coated electrodes. Electrochem. Commun. 2001, 3, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Tansil, N.C.; Gao, Z.Q. A redox active and electrochemiluminescent threading bis-intercalator and its applications in DNA assays. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2006, 11, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar]
- García, T.; Revenga-Parra, M.; Abruña, H.D.; Pariente, F.; Lorenzo, E. Single-mismatch position-sensitive detection of dna based on a bifunctional ruthenium complex. Anal. Chem. 2007, 80, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Weizman, H.; Tor, Y. Redox-active metal-containing nucleotides: Synthesis, tunability, and enzymatic incorporation into DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 1568–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, D.J.; Tor, Y. Ru(II) and Os(II) nucleosides and oligonucleotides: Synthesis and properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 3749–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrabel, M.; Hocek, M.; Havran, L.; Fojta, M.; Votruba, I.; Klepetarova, B.; Pohl, R.; Rulisek, L.; Zendlova, L.; Hobza, P.; et al. Purines bearing phenanthroline or bipyridine ligands and their Ru-II complexes in position 8 as model compounds for electrochemical DNA labeling-synthesis, crystal structure, electrochemistry, quantum chemical calculations, cytostatic and antiviral activity. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 1752–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrabel, M.; Pohl, R.; Votruba, I.; Sajadi, M.; Kovalenko, S.A.; Ernsting, N.P.; Hocek, M. Synthesis and photophysical properties of 7-deaza-2'-deoxyadenosines bearing bipyridine ligands and their Ru(II)-complexes in position 7. Org. Biochem. Chem. 2008, 6, 2852–2860. [Google Scholar]
- Vrabel, M.; Pohl, R.; Klepetarova, B.; Votruba, I.; Hocek, M. Synthesis of 2'-deoxyadenosine nucleosides bearing bipyridine-type ligands and their Ru-complexes in position 8 through cross-coupling reactions. Org. Biochem. Chem. 2007, 5, 2849–2857. [Google Scholar]
- Vrabel, M.; Horakova, P.; Pivonkova, H.; Kalachova, L.; Cernocka, H.; Cahova, H.; Pohl, R.; Sebest, P.; Havran, L.; Hocek, M.; et al. Base-modified dna labeled by Ru(bpy)32+ and Os(bpy)32+ complexes: Construction by polymerase incorporation of modified nucleoside triphosphates, electrochemical and luminescent properties, and applications. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 1144–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jager, S.; Rasched, G.; Kornreich-Leshem, H.; Engeser, M.; Thum, O.; Famulok, M. A versatile toolbox for variable DNA functionalization at high density. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 15071–15082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leland, J.K.; Powell, M.J. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence-an oxidative-reduction type ecl reaction sequence using tripropyl amine. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1990, 137, 3127–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenten, J.H.; Gudibande, S.; Link, J.; Willey, J.J.; Curfman, B.; Major, E.O.; Massey, R.J. Improved electrochemiluminescent label for dna probe assays-rapid quantitative assays of hiv-1 polymerase chain-reaction products. Clin. Chem. 1992, 38, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deaver, D.R. A new nonisotopic detection system for immunoassays. Nature 1995, 377, 758–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, W.J.; Bard, A.J. Electrogenerated chemluminescence. 72. Determination of immobilized DNA and C-reactive protein on Au(111) electrodes using Tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) labels. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 5825–5834. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Wei, H.; Kang, J.Z.; Yan, J.L.; Yin, X.B.; Yang, X.R.; Wang, E.K. Microchip capillary electrophoresis with solid-state electrochemiluminescence detector. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 7993–7997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.H.; Gao, Y.; Wei, H.; Du, Y.; Wang, E.K. Field-amplified sample stacking capillary electrophoresis with electrochemiluminescence applied to the determination of illicit drugs on banknotes. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1115, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.P.; Wei, H.; Jin, W.R.; Yang, X.R.; Wang, E.K. Kinetic study of paracetamol on prolidase activity in erythrocytes by capillary electrophoresis with Ru(bpy)32+ electrochemiluminescence detection. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 4047–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Z.; Zhou, J.M.; Zhao, K.; Zhu, N.N.; He, P.G.; Fang, Y.Z. Ru(bpy)32+-doped silica nanoparticle DNA probe for the electrogenerated chemiluminescence detection of DNA hybridization. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 52, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.X.; Qi, H.L.; Zhang, M.N. Homogeneous electrogenerated chemiluminescence immunoassay for the determination of digoxin emploting Ru(bpy)2(dcbpy)NHS and carrier protein. Luminescence 2007, 22, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, W.; Bard, A.J. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence. 83. Immunoassay of human C-reactive protein by using Ru(bpy)32+-encapsulated liposomes as labels. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 459–463. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Du, Y.; Kang, J.Z.; Wang, E.K. Label free electrochemiluminescence protocol for sensitive DNA detection with a tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) modified electrode based on nucleic acid oxidation. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, E. Electrochemiluminescence-based DNA detection using guanine oxidation at electrostatic self-assembly of Ru(bpy)32+-doped silica nanoparticles on indium tin oxide electrode. Chem. Lett. 2007, 36, 210–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Du, Y.; Kang, J.Z.; Xu, G.B.; Wang, E.K. Tris(2,2'-bipyridyl) ruthenium(II) doped silica film modified indium tin oxide electrode and its electrochemiluminescent properties. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2007, 25, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, M.H.; Liu, X.Q.; Wei, H.; Xu, Y.H.; Xu, G.B.; Wang, E.K. Enhanced electrochemiluminescence sensor from tris(2,2'-bipyridyl) ruthenium(II) incorporated into MCM-41 and an ionic liquid-based carbon paste electrode. Analyst 2007, 132, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xu, Y.H.; Wei, H.; Huo, T.; Wang, E.K. Electrochemiluminescence sensor based on partial sulfonation of polystyrene with carbon nanotubes. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 5439–5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Wang, E. Solid-state electrochemiluminescence of tris(2,2'-bipyridyl) ruthenium. TrAC Trend. Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.Y.; Lv, Z.Z.; Wei, H.; Wang, E. A electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for detection of thrombin incorporating the capture aptamer labeled with gold nanoparticles immobilized onto the thio-silanized ITO electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 628, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Liu, J.; Zhou, L.; Li, J.; Jiang, X.; Kang, J.; Yang, X.; Dong, S.; Wang, E. [Ru(bpy)3]2+-doped silica nanoparticles within layer-by-layer biomolecular coatings and their application as a biocompatible electrochemiluminescent tag material. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 3687–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Yin, J.Y.; Wang, E. Bis(2,2'-bipyridine)(5,6-epoxy-5,6-dihydro-[1,10] phenanthroline)ruthenium: Synthesis and electrochemical and electrochemiluminescence characterization. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 5635–5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.G.; Wei, H.; Li, B.L.; Song, L.H.; Fang, L.Y.; Lv, Z.Z.; Zhou, W.H.; Wang, E.K. [Ru(bpy)2(dcbpy)NHS] labeling/aptamer-based biosensor for the detection of lysozyme by increasing sensitivity with gold nanoparticle amplification. Chem. Asian J. 2008, 3, 1935–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Zhou, L.L.; Li, J.; Liu, J.F.; Wang, E.K. Electrochemical and electrochemiluminescence study of Ru(bpy)32+-doped silica nanoparticles with covalently grafted biomacromolecules. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2008, 321, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.Y.; Lu, Z.Z.; Wei, H.; Wang, E.K. Quantitative electrochemiluminescence detection of proteins: Avidin-based sensor and tris(2,2'-bipyridine) ruthenium(II) label. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1645–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, L. An aptamer-based electrochemiluminescent biosensor for ATP detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3269–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.Z.; Bian, Z.; Li, H.J.; Han, S.; Yuan, Y.L.; Gao, L.X.; Xu, G.B. [Ru(bpy)2dppz]2+ electrochemiluminescence switch and its applications for DNA interaction study and label-free ATP aptasensor. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 9807–9811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoncello, P.; Forster, R.J. Nanostructured materials for electrochemiluminescence (ECL)-based detection methods: Recent advances and future perspectives. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3191–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.F.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, S.S. Electrochemical and electrochemiluminescence determination of cancer cells based on aptamers and magnetic beads. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 10707–10714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.B.; Liu, J.F.; Tang, Y.B.; Xing, D. A reusable DNA biosensor for the detection of genetically modified organism using magnetic bead-based electrochemiluminescence. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2010, 149, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.P.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Zou, G.Z.; Zhang, X.L.; Jin, W.R. Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence method for determination of DNA using Ru(bpy)32+-coated magnetic submicrobeads wrapped with carbon nanotubes. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 1499–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence detection of Mercury(II) ions based on DNA probe labeled with ruthenium complex. Anal. Sci. 2011, 27, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Wang, E. Electrochemiluminescence of tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium and its applications in bioanalysis: A review. Luminescence 2011, 26, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, H.; He, P.G.; Fang, Y.Z. Research on DNA electrochemiluminescence biosensing. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2012, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, R.; Arai, K.; Nakamoto, K.; Kato, D.; Niwa, O. Determination of DNA methylation using electrochemiluminescence with surface accumulable coreactant. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1799–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, E.K. Applications of tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) in electrochemiluminescence. Chem. Rec. 2012, 12, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Guo, S.J.; Wang, E.K. Recent advances in new luminescent nanomaterials for electrochemiluminescence sensors. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 3579–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Qi, H.L.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, C.X. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence biosensor incorporating ruthenium complex-labelled concanavalin a as a probe for the detection of Escherichia coli. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 35, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.X.; Zhang, X.L. Electrochemiluminescence DNA sensor based on Ru(bpy)32+-doped silica nanoparticle labeling and proximity-dependent surface hybridization assay. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2012, 16, 247–252. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.H.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhu, J.B.; Wang, E.K. Discovered triethylamine as impurity in synthetic DNAs for and by electrochemiluminescence techniques. Talanta 2013, 116, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.H.; Lv, Z.Z.; Xia, Y.; Han, Y.C.; Lou, B.H.; Wang, E.K. Highly porous magnetite/graphene nanocomposites for a solid-state electrochemiluminescence sensor on paper-based chips. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 3549–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.L.; Qiu, X.Y.; Wang, C.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, C.X. Digital electrogenerated chemiluminescence biosensor for the determination of multiple proteins based on Boolean logic gate. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 612–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.H.; Yang, F.; Zhang, L.H.; Zheng, X.W. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence energy transfer for the label-free detection of DNA. Sensor. Actuat. B Chem. 2013, 177, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Chen, C.G.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.B.; Wang, E.K. New insight into a microfluidic-based bipolar system for an electrochemiluminescence sensing platform. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 5335–5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.M.; Zhu, D.B.; Liao, Y.H.; Liu, W.P.; Liu, H.X.; Ma, Z.K.; Xing, D. Synthesis, labeling and bioanalytical applications of a tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II)-based electrochemiluminescence probe. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 1146–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, W.L.; Xu, Y.H.; Lou, B.H.; Lyu, Z.Z.; Wang, E.K. One-step process for fabricating paper-based solid-state electrochemiluminescence sensor based on functionalized graphene. Electrochem. Commun. 2014, 38, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, X.D.; Xiang, Q.; Wang, K.Q. Electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on PEDOT-PSS- graphene functionalized ITO electrode. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.L.; Gan, X.X.; Chai, Y.Q.; Yuan, R. A novel electrochemiluminescence aptasensor based on in situ generated proline and matrix polyamidoamine dendrimers as coreactants for signal amplication. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 55, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, C.C.; Zheng, J.B.; Qi, H.L.; Cao, W.; Wei, Y.M. Label-free electrogenerated chemiluminescence biosensing method for trace bleomycin detection based on a Ru(phen)32+-hairpin DNA composite film electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 44, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, C.C.; Zheng, J.B.; Qi, H.L. Ultrasensitive electrogenerated chemiluminescent DNA-based biosensing switch for the determination of bleomycin. Talanta 2013, 103, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.W.; Li, J.; Jia, X.F.; Li, D.Y.; Wang, E.K. Full-featured electrochemiluminescence sensing platform based on the multichannel closed bipolar system. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5595–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, N.; Xiong, M.; Zhang, J.D.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. Portable thermo-powered high-throughput visual electrochemiluminescence sensor. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11715–11719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, Y.; Liao, N.; Chai, Y.Q.; Gui, G.F.; Zhao, M.; Han, J.; Xiang, Y.; Yuan, R. Ultrasensitive apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 immunosensing based on self-enhanced electrochemiluminescence of a Ru(II) complex. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Wu, D.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Xu, G. Electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer based on Ru(phen)32+-doped silica nanoparticles and its application in “Turnon” detection of ozone. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3207–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.S.; He, L.J.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. RuSi@Ru(bpy)32+/Au@Ag2S nanoparticles electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer system for sensitive DNA detection. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 4559–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.L.; Li, M.; Dong, M.M.; Ruan, S.P.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, C.X. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence peptide-based biosensor for the determination of prostate-specific antigen based on target-induced cleavage of peptide. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.H.; Huang, R.; Ma, Z.K.; Wu, Y.X.; Zhou, X.M.; Xing, D. Target-triggered enzyme-free amplification strategy for sensitive detection of microrna in tumor cells and tissues. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 4596–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.J.; Xu, M.; Pang, L.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhang, W.; Majeed, S.; Xu, G.B. Electrochemiluminescence detection of TNT by resonance energy transfer through the formation of a TNT-amine complex. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 4829–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Han, S.; Hu, L.Z.; Yuan, Y.L.; Wang, J.G.; Xu, G.B. Cathodic electrochemiluminescence and reversible electrochemistry of Ru(bpy)32+/+ in aqueous solutions on tricresyl phosphate-based carbon paste electrode with extremely high hydrogen evolution potential. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 3427–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.H.; Liu, X.Q.; Li, H.J.; Xu, G.B. Electrochemiluminescent detection based on solid-phase extraction at tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II)-modified ceramic carbon electrode. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 7330–7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.B.; Pang, H.L.; Xu, B.; Dong, S.J.; Wong, K.Y. Enhancing the electrochemiluminescence of tris(2,2'-bipyridyl) ruthenium(II) by ionic surfactants. Analyst 2005, 130, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Y.; Xu, G.B.; Dong, S.J. Electrochemiluminescence sensor using tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) immobilized in Eastman-AQ55D-silica composite thin-films. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 480, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Xu, G.B.; Dong, S.J. Electrochemiluminescence of tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium (II) ion-exchanged in polyelectrolyte-silica composite thin-films. Electroanalysis 2002, 14, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, G.; Dong, S. Electrochemiluminescence of dichlorotris (1,10-phenanthroline) ruthenium (II) with peroxydisulfate in purely aqueous solution at carbon paste electrode. Microchem. J. 2002, 72, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Xu, G.B.; Dong, S.J. Electrochemiluminescence of tris(2,2'-bipyridine)ruthenium(II) immobilized in poly(p-styrenesulfonate)-silica-Triton X-100 composite thin-films. Analyst 2001, 126, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.B.; Dong, S.J. Electrochemiluminescent detection of chlorpromazine by selective preconcentration at a lauric acid-modified carbon paste electrode using tris(2,2'-bipyridine)ruthenium(II). Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 5308–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.B.; Dong, S.J. Electrochemiluminescence of the Ru(bpy)32+/S2O82− system in purely aqueous solution at carbon paste electrode. Electroanalysis 2000, 12, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.B.; Dong, S.J. Effect of metal ions on Ru(bpy)32+ electrochemiluminescence. Analyst 1999, 124, 1085–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Q.; Shi, L.H.; Li, H.J.; Niu, W.X.; Xu, G.B. Environmentally friendly and highly sensitive Ruthenium(II) tris(2,2'-bipyridyl) electrochemiluminescent system using 2-(dibutylamino) ethanol as co-reactant. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 421–424. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.Q.; Shi, L.H.; Li, H.J.; Niu, W.X.; Xu, G.B. Tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) electrochemiluminescent detection of coreactants containing aromatic diol group by the interaction between diol and borate anion. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 2666–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.B.; Cheng, L.; Dong, S.J. Effects of heteropoly acids and surfactant on electrochemiluminescence of tris(2,2'-bipyridine) ruthenium(II). Anal. Lett. 1999, 32, 2311–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Chen, J.A.; Han, S.; Niu, W.X.; Liu, X.Q.; Xu, G.B. Electrochemiluminescence from tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II)-graphene-Nafion modified electrode. Talanta 2009, 79, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.J.; Shi, L.H.; Liu, X.Q.; Niu, W.X.; Xu, G.B. Determination of isocyanates by capillary electrophoresis with tris(2,2'-bipyridine) ruthenium(II) electrochemiluminescence. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 3926–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Niu, W.X.; Li, H.J.; Hu, L.Z.; Yuan, Y.L.; Xu, G.B. Effect of hydroxyl and amino groups on electrochemiluminescence activity of tertiary amines at low tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) concentrations. Talanta 2010, 81, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.A.; Li, H.J.; Hu, L.Z.; Yuan, Y.L.; Xu, G.B. Electrochemiluminescence of tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II)/pyruvate system in the absence of cerium(III). Anal. Methods 2010, 2, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.L.; Li, H.J.; Han, S.A.; Hu, L.Z.; Xu, G.B. Application of cement as new electrode material and solid-phase microextraction material demonstrated by electrochemiluminescent detection of perphenazine. Talanta 2011, 84, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.Z.; Li, H.J.; Han, S.; Xu, G.B. Ru(bpy)32+ electrochemiluminescence in the presence of formaldehyde or formic acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 656, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.Z.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, G.B. Electrochemiluminescence of tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) in the presence of hydrazine and its derivatives. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 1786–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.L.; Li, H.J.; Han, S.; Hu, L.Z.; Parveen, S.; Xu, G.B. Vitamin C derivatives as new coreactants for tris(2,2'-bipyridine)ruthenium(II) electrochemiluminescence. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 701, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.L.; Li, H.J.; Han, S.; Hu, L.Z.; Parveen, S.; Cai, H.R.; Xu, G.B. Immobilization of tris(1,10-phenanthroline)ruthenium with graphene oxide for electrochemiluminescent analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 720, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parveen, S.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, Y.L.; Hu, L.Z.; Gilani, M.; Rehman, A.U.; Xu, G.B. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence of Ru(phen)32+/2-(dibutylamino)ethanol system. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2013, 688, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.J.; Gabr, M.T.; Liu, Z.Y.; Hu, L.Z.; Han, M.Y.; Zhu, S.Y.; Xu, G.B. Tris(2,2'-bipyridyl) ruthenium(II) electrochemiluminescence of glyoxal, glyoxylic acid, methylglyoxal, and acetaldehyde. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 89, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-S.; Yuan, D.-J.; Xu, J.-J.; Chen, H.-Y. Sensitive electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on Au-ITO hybrid bipolar electrode amplification system for cell surface protein detection. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11960–11965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.; Pan, S.; Tang, C.; Li, D.; Rusling, J.F. Voltammetric microwell array for oxidized guanosine in intact ds-DNA. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11061–11067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardesai, N.P.; Barron, J.C.; Rusling, J.F. Carbon nanotube microwell array for sensitive electrochemiluminescent detection of cancer biomarker proteins. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 6698–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.-S.; Shi, H.-W.; He, L.-J.; Xu, J.-J.; Chen, H.-Y. Microchip device with 64-Site Electrode array for multiplexed immunoassay of cell surface antigens based on electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 4207–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurita, R.; Niwa, O. DNA methylation analysis triggered by bulge specific immuno-recognition. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 7533–7538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, A.; Lu, F.; Chen, Y.; Gao, W. An electrochemiluminescence biosensor for sensitive and selective detection of Hg2+ based on π–π interaction between nucleotides and ferrocene–graphene nanosheets. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 3263–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zheng, L.; Gao, G.; Chi, Y.; Chen, G. Electrochemiluminescence imaging-based high-throughput screening platform for electrocatalysts used in fuel cells. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 7700–7707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, F.; Jiang, H.; Fang, D.; Jiang, D. Potential-resolved electrochemiluminescence for determination of two antigens at the cell surface. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 6896–6902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Bhirde, A.A.; Morgan, N.Y.; Eden, H.S.; Chen, X. Electrochemical Immunosensors for Detection of Cancer Protein Biomarkers. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6546–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, K.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; Shao, F.; Li, T.; Ye, S.; Chen, L.; Han, H. Stretch-stowage-growth strategy to fabricate tunable triply-amplified electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of pseudorabies virus antibody. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5749–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, G.-F.; Zhuo, Y.; Chai, Y.-Q.; Xiang, Y.; Yuan, R. In situ generation of self-enhanced luminophore by β-lactamase catalysis for highly sensitive electrochemiluminescent aptasensor. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5873–5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, J. Modification of indium tin oxide with dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles to provide enhanced stable electrochemiluminescence of Ru(bpy)32+/tripropylamine while preserving optical transparency of indium tin oxide for sensitive electrochemiluminescence-based analyses. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburn, G.F.; Shah, H.P.; Kenten, J.H.; Leland, J.; Kamin, R.A.; Link, J.; Peterman, J.; Powell, M.J.; Shah, A.; Talley, D.B.; et al. Electrochemiluminescence detection for development of immunoassays and DNA probe assays for clinical diagnostics. Clin. Chem. 1991, 37, 1534–1539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Richter, M.M. Electrochemiluminescence (ECL). Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 3003–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, W.J. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence and its biorelated applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2506–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, A.W.; Greenway, G.M. Occurrence, mechanisms and analytical applications of electrogenerated chemiluminescence-review. Analyst 1994, 119, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.Y. Tris (2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) electrogenerated chemiluminescence in analytical science. Microchim. Acta 1997, 127, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerardi, R.D.; Barnett, N.W.; Lewis, S.W. Analytical applications of tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(III) as a chemiluminescent reagent. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 378, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, A.W. A review of recent trends in analytical applications of electrogenerated chemiluminescence. TrAC Trend. Anal. Chem. 1999, 18, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukoba, A.V.; Bykh, A.I.; Svir, I.B. Analytical applications of electrochemiluminescence: An overview. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 2000, 368, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahnrich, K.A.; Pravda, M.; Guilbault, G.G. Recent applications of electrogenerated chemiluminescence in chemical analysis. Talanta 2001, 54, 531–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.B.; Dong, S.J.; Wang, E. Analytical applications of the electrochemiluminescence of tris (2.2'-bipyridyl) ruthenium and its derivatives. TrAC Trend. Anal. Chem. 2004, 23, 432–441. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.B.; Wang, E. Capillary electrophoresis coupling with electrochemilurninescence detection: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 533, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, B.A.; Francis, P.S.; Barnett, N.W. Tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) chemiluminescence. Analyst 2006, 131, 616–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyati, R.; Richter, M.M. ECL-Electrochemical luminescence. Annu. Rep. Prog. Chem. Sect. C Phys. Chem. 2007, 103, 12–78. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Wang, E.K. Capillary electrophoresis and microchip capillary electrophoresis with electrochemical and electrochemiluminescence detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 875–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.J.; Han, S.; Hu, L.Z.; Xu, G.B. Progress in Ru(bpy)32+ electrogenerated chemiluminescence. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2009, 37, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, R.J.; Bertoncello, P.; Keyes, T.E. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2009, 2, 359–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenten, J.H.; Casadei, J.; Link, J.; Lupold, S.; Willey, J.; Powell, M.; Rees, A.; Massey, R. Rapid electrochemiluminescence assays of polymerase chain-reaction products. Clin. Chem. 1991, 37, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.H.; Yang, H.C.; Mallouk, T.E.; Bard, A.J. Immobilization of DNA on an Aluminum(III) alkanebisphosphonate thin-film with electrogenerated chemiluminescent detection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 8386–8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.H.; Bard, A.J. Immobilization and hybridization of DNA on an Aluminum(III) alkanebisphosphonate thin-film with electrogenerated chemiluminescent detection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 2627–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.J.; Bard, A.J. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence. 77. DNA hybridization detection at high amplification with [Ru(bpy)3]2+-containing microspheres. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 5379–5386. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Qi, H.L.; Fang, F.; Zhang, C.X. Ultrasensitive electrogenerated chemiluminescence detection of DNA hybridization using carbon-nanotubes loaded with tris(2,2'-bipyridyl) ruthenium derivative tags. Talanta 2007, 72, 1704–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Qi, H.L.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, C.X. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence DNA biosensor based on hairpin DNA probe labeled with ruthenium complex. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2888–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Qi, H.L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, C.X. Detection of DNA immobilized on bare gold electrodes and gold nanoparticle-modified electrodes via electrogenerated chemiluminescence using a ruthenium complex as a tag. Microchim. Acta 2009, 164, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.F.; Wang, L.R.; Guo, L.H. Highly sensitive electrochemiluminescence displacement method for the study of DNA/small molecule binding interactions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 676, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.P.; Sun, Y.M.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Zou, G.Z.; Zhang, X.L.; Jin, W.R. Heterogeneous electrochemiluminescence spectrometry of Ru(bpy)32+ for determination of trace DNA and its application in measurement of gene expression level. Talanta 2012, 89, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.W.; Oh, J.W.; Shin, I.S.; Cho, M.S.; Kim, Y.R.; Kim, H.; Hong, J.I. Highly sensitive detection of DNA by electrogenerated chemiluminescence amplification using dendritic Ru(bpy)32+-doped silica nanoparticles. Analyst 2010, 135, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, L. Electrochemiluminescent sensor for the detection of DNA hybridization using stem-loop structure DNA as capture probes. Microchim. Acta 2009, 165, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, P.; Fang, Y. A solid-state electrochemiluminescence biosensing switch for detection of DNA hybridization based on ferrocene-labeled molecular beacon. J. Lumin. 2010, 130, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, L.; Zhang, N.; Pan, L.; Xing, N.N. An electrochemiluminescent DNA sensor based on nano-gold enhancement and ferrocene quenching. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Yu, Y.Q.; Li, Q.; Zhou, M.; Cui, H. A homogeneous signal-on strategy for the detection of rpob genes of mycobacterium tuberculosis based on electrochemiluminescent graphene oxide and ferrocene quenching. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1608–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.F.; Zhao, D.; He, J.C.; Li, F.W.; Peng, J.X.; Zhang, M.N. Quenching of the electrochemiluminescence of Tris(2,2'-bipyridine)ruthenium(II)/Tri-n-propylamine by pristine carbon nanotube and its application to quantitative detection of DNA. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 1711–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Su, J.; Xiang, Y.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y. In situ hybridization chain reaction amplification for universal and highly sensitive electrochemiluminescent detection of DNA. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 7750–7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennany, L.; Forster, R.J.; Rusling, J.F. Simultaneous direct electrochemiluminescence and catalytic voltammetry detection of DNA in ultrathin films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 5213–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.B.; Ma, W.G.; Xing, X.B. Application of electrochemiluminescence assay in nucleic acid detection. Prog. Chem. 2012, 24, 2367–2373. [Google Scholar]
- Rampazzo, E.; Bonacchi, S.; Genovese, D.; Juris, R.; Marcaccio, M.; Montalti, M.; Paolucci, F.; Sgarzi, M.; Valenti, G.; Zaccheroni, N.; et al. Nanoparticles in metal complexes-based electrogenerated chemiluminescence for highly sensitive applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 1664–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.D.; Ferrance, J.P.; Demas, J.; Landers, J.P. Quenching of the electrochemiluminescence of tris( 2,2'-bipyridine) ruthenium(II) by ferrocene and its potential application to quantitative DNA detection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7572–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Yun, W.; Dong, P.; Zhou, J.M.; He, P.G.; Fang, Y.Z. A controllable solid-state Ru(bpy)32+ electrochemiluminescence film based on conformation change of ferrocene-labeled DNA molecular beacon. Langmuir 2008, 24, 2200–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, M.T.; Bard, A.J. Electrochemical investigations of the interaction of metal chelates with DNA. 3. Electrogenerated chemiluminescent investigation of the interaction of tris (1,10-phenanthroline) ruthenium (II) with DNA. Bioconjugate Chem. 1990, 1, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Tombelli, S.; Minunni, A.; Mascini, A. Analytical applications of aptamers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 2424–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.W.; Cao, Z.H.; Lu, Y. Functional nucleic acid sensors. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 1948–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, H.; Li, B.; Ren, W.; Guo, S.; Dong, S.; Wang, E. SERS opens a new way in aptasensor for protein recognition with high sensitivity and selectivity. Chem. Commun. 2007, 5220–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Wei, H.; Dong, S.J. Amplified electrochemical aptasensor taking AuNPs based sandwich sensing platform as a model. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.L.; Du, Y.; Wei, H.; Dong, S.J. Reusable, label-free electrochemical aptasensor for sensitive detection of small molecules. Chem. Commun. 2007, 3780–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, B.L.; Wei, H.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, E.K. Multifunctional label-free electrochemical biosensor based on an integrated aptamer. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 5110–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Guo, C.L.; Zhang, M.M.; Park, B.; Xu, B.Q. High-resolution single-molecule recognition imaging of the molecular details of ricin-aptamer interaction. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 5316–5322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Guo, C.L.; Chen, G.J.; Park, B.; Xu, B.Q. Following aptamer-ricin specific binding by single molecule recognition and force spectroscopy measurements. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1644–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Li, B.L.; Li, J.; Wang, E.K.; Dong, S.J. Simple and sensitive aptamer-based colorimetric sensing of protein using unmodified gold nanoparticle probes. Chem. Commun. 2007, 3735–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.L.; Wei, H.; Dong, S.J. Sensitive detection of protein by an aptamer-based label-free fluorescing molecular switch. Chem. Commun. 2007, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Li, B.L.; Li, J.; Dong, S.J.; Wang, E.K. DNAzyme-based colorimetric sensing of lead (Pb2+) using unmodified gold nanoparticle probes. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 095501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.B.; Wei, H.; Li, J.; Li, T.; Li, D.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, E.K. A carbon nanotubes based ATP apta-sensing platform and its application in cellular assay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1897–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.Z.; Wei, H.; Li, B.L.; Wang, E.K. Colorimetric recognition of the coralyne-poly(dA) interaction using unmodified gold nanoparticle probes, and further detection of coralyne based upon this recognition system. Analyst 2009, 134, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Lin, Z.Y.; Chen, L.F.; Qiu, B.; Chen, G.A. A sensitive and specific electrochemiluminescent sensor for lead based on DNAzyme. Chem. Commun. 2009, 6050–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Sun, B.; Qi, H.L.; Zhang, H.G.; Gao, Q.A.; Zhang, C.X. A signal-on electrogenerated chemiluminescent biosensor for lead ion based on DNAzyme. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 683, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Qi, H.L.; Ma, F.; Gao, Q.A.; Zhang, C.X.; Miao, W.J. Double covalent coupling method for the fabrication of highly sensitive and reusable electrogenerated chemiluminescence sensors. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5046–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Qi, H.L.; Gao, Q.A.; Yang, J.; Zhang, C.X. Nanomaterial-amplified “signal off/on” electrogenerated chemiluminescence aptasensors for the detection of thrombin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.L.; Li, G.; Mao, C.M. An electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for tumor cells assay based on signal amplification of Ru(II) covalently doped silica nanoparticles. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 1244–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qi, H.L.; Peng, Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, C.X. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence aptamer-based method for the determination of thrombin incorporating quenching of tris(2,2'-bipyridine)ruthenium by ferrocene. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 1322–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.H.; Zhang, A.; Chen, Y.S.; Chen, Z.X.; Chen, Y.W.; Lu, F.S.; Chen, Z.G. A novel probe density controllable electrochemiluminescence biosensor for ultra-sensitive detection of Hg2+ based on DNA hybridization optimization with gold nanoparticles array patterned self-assembly platform. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 49, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Dong, P.; Yun, W.; Xu, Y.; He, P.G.; Fang, Y.Z. A solid-state electrochemiluminescence biosensing switch for detection of thrombin based on ferrocene-labeled molecular beacon aptamer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3288–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Dong, P.; He, P.G.; Fang, Y.Z. A solid-state electrochemiluminescence sensing platform for detection of adenosine based on ferrocene-labeled structure-switching signaling aptamer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 658, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S.J.; Li, H.X.; Cao, W. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence detection of adenosine based on triplex DNA biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2215–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.H.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.Q.; Mao, L.; Zhuo, Y.; Yuan, Y.L.; Bai, L.J.; Yuan, S.R. Electrochemiluminescence quenching via capture of ferrocene-labeled ligand-bound aptamer molecular beacon for ultrasensitive detection of thrombin. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2011, 158, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Qi, H.L.; Yang, H.Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, C.X. Simple and highly sensitive electrogenerated chemiluminescence adenosine aptasensor formed by adsorbing a ruthenium complex-tagged aptamer on single-walled carbon nanotubes. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.B.; Xin, Y.Y.; Zhao, Y. Label-Free Electrochemiluminescent Aptasensor with Attomolar Mass Detection Limits Based on a Ru(phen)32+-Double-Strand DNA Composite Film Electrode. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 9299–9305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.X.; Zhao, Y.; He, X.W.; Yin, X.B. A “turn-on” electrochemiluminescent biosensor for detecting Hg2+ at femtomole level based on the intercalation of Ru(phen)32+ into ds-DNA. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 9022–9024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; He, X.W.; Yin, X.B. Analyte-induced formation of partial duplexes for the preparation of a label-free electrochemiluminescent aptasensor. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6419–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.Y.; Xin, Y.Y.; He, X.W.; Yin, X.B. A sensitive, non-damaging electrochemiluminescent aptasensor via a low potential approach at DNA-modified gold electrodes. Analyst 2011, 136, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Qi, H.L.; Gao, Q.A.; Zhang, C.X. Label-free and sensitive electrogenerated chemiluminescence aptasensor for the determination of lysozyme. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2733–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.F.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, M.N. Sensitive and reusable electrochemiluminescent aptasensor achieved with diblock oligonucleotides immobilized solely through preferential adenine-Au interaction. Analyst 2013, 138, 5706–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, G.F.; Zhuo, Y.; Chai, Y.Q.; Liao, N.; Zhao, M.; Han, J.; Zhu, Q.; Yuan, R.; Xiang, Y. Supersandwich-type electrochemiluminescenct aptasensor based on Ru(phen)32+ functionalized hollow gold nanoparticles as signal-amplifying tags. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 47, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, A.E.; Chambron, J.C.; Sauvage, J.P.; Turro, N.J.; Barton, J.K. Molecular light switch for DNA-Ru(bpy)2(dppz)2+. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 4960–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Liu, Y.-J.; Li, Q.; Wang, K.-Z. pH- and DNA-induced dual molecular light switches based on a novel ruthenium(II) complex. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2009, 103, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moucheron, C.; Kirsch-De Mesmaeker, A. New DNA-binding ruthenium(II) complexes as photo-reagents for mononucleotides and DNA. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 1998, 11, 577–583. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, M.G.; Gonzalez, V.; Chekmeneva, E.; Thomas, J.A. Temperature-switched binding of a RuII(dppz)/DNA light-switch complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12107–12110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, N.A.; Stevens, N.; Samaroo, D.; Solomon, M.R.; Marti, A.A.; Dyer, J.; Vishwasrao, H.; Akins, D.L.; Kandel, E.R.; Turro, N.J. A covalently linked phenanthridine-ruthenium(II) complex as a RNA probe. Chem. Commun. 2009, 2640–2642. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Zhao, J.; Geng, X.T.; Yao, T.M.; Huang, H.L.; Liu, T.L.; Zheng, L.F.; Li, Z.H.; Yang, D.J.; Ji, L.N. Molecular “light switch” for G-quadruplexes and i-motif of human telomeric DNA: [Ru(phen)2(dppz)]2+. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 2490–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, D.; Huang, J.; Deng, M.G.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, X. High fluorescence selectivity and visual detection of G-quadruplex structures by a novel dinuclear ruthenium complex. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 743–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Geng, X.T.; Zhao, J.; Yao, T.M.; Wang, C.R.; Yang, D.J.; Zheng, L.F.; Ji, L.N. Interaction of [Ru(bpy)2(dppz)]2+ with human telomeric DNA: Preferential binding to G-quadruplexes over i-motif. Biochimie 2010, 92, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, G.L.; Chen, X.; Ji, L.N.; Chao, H. Visual specific luminescent probing of hybrid G-quadruplex DNA by a ruthenium polypyridyl complex. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10781–10783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Zhao, J.; Gao, X.; Lv, C.; Yang, L.; Hao, J.; Huang, H.; Yao, J.; Sun, W.; Yao, T.; et al. Molecular “light switch” for G-quadruplex DNA: Cycling the switch on and off. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 5789–5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.-L.; Gao, X.; Sun, W.; Shi, S.; Yao, T.-M. [Ru(bpy)2dppz-idzo]2+: A colorimetric molecular “light switch” and powerful stabilizer for G-quadruplex DNA. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 5661–5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajput, C.; Rutkaite, R.; Swanson, L.; Haq, I.; Thomas, J.A. Dinuclear monointercalating Ru-II complexes that display high affinity binding to duplex and quadruplex DNA. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 4611–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Wang, K.; Bai, G.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, L. The pH-induced emission switching and interesting DNA-binding properties of a novel dinuclear Ruthenium(II) complex. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.-G.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Duan, Z.-M.; Wang, K.-Z.; Wei, H.-B.; Bian, Z.-Q.; Huang, C.-H. Dual molecular light switches for pH and DNA BASED on a novel Ru(II) complex. A non-intercalating Ru(II) complex for DNA molecular light switch. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 6425–6436. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.-L.; Gao, X.; Sun, W.; Fan, X.-Z.; Shi, S.; Yao, T.-M. A naked-eye on-off-on molecular “light switch” based on a reversible “conformational switch” of G-quadruplex DNA. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 12591–12593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.B.; Teng, E.S.; Kirkland, S.L.; Murphy, C.J. Synthesis and DNA-binding properties of [Ru(NH3)4dppz]2+. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tysoe, S.A.; Kopelman, R.; Schelzig, D. Flipping the molecular light switch off: Formation of DNA-bound heterobimetallic complexes using Ru(bpy)2tpphz2+ and transition metal ions. Inorg. Chem. 1999, 38, 5196–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chouai, A.; Degtyareva, N.N.; Lutterman, D.A.; Dunbar, K.R.; Turro, C. Chemical control of the DNA light switch: Cycling the switch on and off. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 10796–10797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutterman, D.A.; Chouai, A.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Stewart, C.D.; Dunbar, K.R.; Turro, C. Intercalation is not required for DNA light-switch behavior. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, C.G.; McGarvey, J.J.; Callaghan, P.L.; Coletti, M.; Hamilton, J.G. Probing the interaction of [Ru(phen)2(dppz)]2+ with single-stranded DNA-What degree of protection is required for operation of the “light-switch effect”? J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 730–735. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, J.; Lincoln, P. Stereoselectivity for DNA threading intercalation of short binuclear ruthenium complexes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 14768–14775. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.S.; Yoon, M.; Baeg, J.O.; Kim, J. Label-free dual assay of DNA sequences and potassium ions using an aptamer probe and a molecular light switch complex. Chem. Commun. 2009, 7419–7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.R.; Li, Y.; Su, H.R.; Zhang, S.S. Highly sensitive and selective detection of Hg2+ using mismatched DNA and a molecular light switch complex in aqueous solution. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, B.N.; Park, S.; Ren, J.; Jang, Y.J.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, J. Label-free emission assay of mercuric ions using DNA duplexes of poly(dT). Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 6494–6499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.-L.; Liu, H.-Q.; Tzeng, B.-C.; You, Y.-S.; Peng, S.-M.; Yang, M.; Che, C.-M. Syntheses of Ruthenium(II) quinonediimine complexes of cyclam and characterization of their dna-binding activities and cytotoxicity. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 41, 3161–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, J.; Fornander, L.H.; Abrahamsson, M.; Tuite, E.; Nordell, P.; Lincoln, P. Lifetime heterogeneity of dna-bound dppz complexes originates from distinct intercalation geometries determined by complex-complex interactions. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 52, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebarz, M.; Marcelis, L.; Menand, M.; Cornut, D.; Moucheron, C.; Jabin, I.; Kirsch-De Mesmaeker, A. Revisited photophysics and photochemistry of a Ru-TAP complex using chloride ions and a calix 6 crypturea. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 2635–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Huang, S.; Ge, Y.S.; He, Z.K.; Liu, Y.; Liang, J.G. A novel fluorescent silver ion biosensor based on nucleic acid molecular “light switch”. J. Fluoresc. 2010, 20, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierroz, V.; Joshi, T.; Leonidova, A.; Mari, C.; Schur, J.; Ott, I.; Spiccia, L.; Ferrari, S.; Gasser, G. Molecular and cellular characterization of the biological effects of Ruthenium(II) complexes incorporating 2-pyridyl-2-pyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 20376–20387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, M.; Reichardt, C.; Pinto, M.; Wächtler, M.; Sainuddin, T.; Shi, G.; Yin, H.; Monro, S.; Sampson, E.; Dietzek, B.; et al. Ru(II) Dyads derived from 2-(1-Pyrenyl)-1H-imidazo[4,5-f][1,10]phenanthroline: Versatile photosensitizers for photodynamic applications. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-Z.; Yin, H.-J.; Wang, K.-Z. A β-d-allopyranoside-grafted Ru(II) complex: Synthesis and acid-base and DNA-binding properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 11039–11047. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Shi, S.; Yao, T. Graphene oxide-Ru complex for label-free assay of DNA sequence and potassium ions via fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 2472–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.L.; Yao, T.M.; Shi, S. A molecular light switch Ru complex and quantum dots for the label-free, aptamer-based detection of thrombin. Analyst 2012, 137, 1550–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.L.; Yao, J.L.; Yao, T.M.; Shi, S. Label-free fluorescent DNA sensor for the detection of silver ions based on molecular light switch Ru complex and unmodified quantum dots. Analyst 2013, 138, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yao, T.; Shi, S.; Cao, Y.; Sun, W. A label-free fluorescent probe for Hg(2+) and biothiols based on graphene oxide and Ru-complex. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Wang, X.; Sun, W.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Yao, T.M.; Ji, L.N. Label-free fluorescent DNA biosensors based on metallointercalators and nanomaterials. Methods 2013, 64, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, L.S.; He, Z.K.; Wu, F.W.; Luo, Q.Y.; Zeng, Y.E. Progress of the nucleic acid molecular “Light Switch”. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. Chin. 2000, 21, 527–531. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Yao, T.; Ji, L. DNA molecular light switch and biosensors based on ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes. Sci. Sin. Chim. 2014, 44, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.L.; Ma, V.P.Y.; Chan, D.S.H.; Leung, K.H.; He, H.Z.; Leung, C.H. Recent advances in luminescent heavy metal complexes for sensing. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 3087–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartshorn, R.M.; Barton, J.K. Novel dipyridophenazine complexes of Ruthenium(II)-exploring luminescent reporters of DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 5919–5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, Y.; Friedman, A.E.; Turro, N.J.; Barton, J.K. Characterization of dipyridophenazine complexes of Ruthenium(ii)-the light switch effect as a function of nucleic-acid sequence and conformation. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 10809–10816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennaman, M.K.; Alstrum-Acevedo, J.H.; Fleming, C.N.; Jang, P.; Meyer, T.J.; Papanikolas, J.M. Turning the [Ru(bpy)2dppz]2+ light-switch on and off with temperature. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 15094–15098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, E.J.C.; Hu, D.; Hormann, A.; Jonkman, A.M.; Arkin, M.R.; Stemp, E.D.A.; Barton, J.K.; Barbara, P.F. First observation of the key intermediate in the “light-switch” mechanism of [Ru(phen)2dppz]2+. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 11458–11467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hammitt, R.; Lutterman, D.A.; Thummel, R.P.; Turro, C. Marked differences in light-switch behavior of Ru(II) complexes possessing a tridentate DNA intercalating ligand. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 6011–6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Lutterman, D.A.; Turro, C. Role of electronic structure on DNA light-switch behavior of Ru(II) intercalators. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 6427–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinley, A.W.; Lincoln, P.; Tuite, E.M. Sensitivity of [Ru(phen)2dppz]2+ light switch emission to ionic strength, temperature, and DNA sequence and conformation. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 4081–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggaley, E.; Weinstein, J.A.; Williams, J.A.G. Lighting the way to see inside the live cell with luminescent transition metal complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 1762–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coogan, M.P.; Fernandez-Moreira, V. Progress with, and prospects for, metal complexes in cell imaging. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 384–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggaley, E.; Gill, M.R.; Green, N.H.; Turton, D.; Sazanovich, I.V.; Botchway, S.W.; Smythe, C.; Haycock, J.W.; Weinstein, J.A.; Thomas, J.A. Dinuclear Ruthenium(II) complexes as two- photon, time- resolved emission microscopy probes for cellular DNA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 3367–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niyazi, H.; Hall, J.P.; O’Sullivan, K.; Winter, G.; Sorensen, T.; Kelly, J.M.; Cardin, C.J. Crystal structures of Lambda-[Ru(phen)2dppz]2+ with oligonucleotides containing TA/TA and AT/AT steps show two intercalation modes. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Kaiser, J.T.; Barton, J.K. Crystal structure of Delta-[Ru(bpy)2dppz]2+ bound to mismatched DNA reveals side-by-side metalloinsertion and intercalation. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.L.; He, H.Z.; Leung, K.H.; Chan, D.S.H.; Leung, C.H. Bioactive luminescent transition-metal complexes for biomedical applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 7666–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.F.; Harry, E.J.; Bottomley, A.L.; Edstein, M.D.; Birrell, G.W.; Woodward, C.E.; Keene, F.R.; Collins, J.G. Dinuclear ruthenium(II) antimicrobial agents that selectively target polysomes in vivo. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennaman, M.K.; Meyer, T.J.; Papanikolas, J.M. [Ru(bpy)2dppz]2+ light-switch mechanism in protic solvents as studied through temperature-dependent lifetime measurements. J. Phys. Chem. A 2004, 108, 9938–9944. [Google Scholar]
- Hiort, C.; Lincoln, P.; Norden, B. DNA-binding of delta-[Ru(Phen)2dppz]2+ and lambda-[Ru(Phen)2dppz]2+. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 3448–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruba, E.; Hart, J.R.; Barton, J.K. [Ru(bpy)2(L)]Cl2: Luminescent metal complexes that bind DNA base mismatches. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 4570–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, J.K.; Danishefsky, A.T.; Goldberg, J.M. Tris(phenanthroline)ruthenium(II): Stereoselectivity in binding to DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 2172–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.P.; Cook, D.; Morte, S.R.; McIntyre, P.; Buchner, K.; Beer, H.; Cardin, D.J.; Brazier, J.A.; Winter, G.; Kelly, J.M.; et al. X-ray Crystal Structure of rac-[Ru(phen)2dppz]2+ with d(ATGCAT)2 Shows Enantiomer Orientations and Water Ordering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 12652–12659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinley, A.; Andersson, J.; Lincoln, P.; Tuite, E.M. DNA sequence and ancillary ligand modulate the biexponential emission decay of intercalated [Ru(L)2dppz]2+ enantiomers. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 15142–15150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foxon, S.P.; Metcalfe, C.; Adams, H.; Webb, M.; Thomas, J.A. Electrochemical and photophysical properties of DNA metallo-intercalators containing the ruthenium(II) tris(1-pyrazolyl)methane unit. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foxon, S.P.; Phillips, T.; Gill, M.R.; Towrie, M.; Parker, A.W.; Webb, M.; Thomas, J.A. A multifunctional light switch: DNA binding and cleavage properties of a heterobimetallic ruthenium-rhenium dipyridophenazine complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2007, 46, 3686–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metcalfe, C.; Adams, H.; Haq, I.; Thomas, J.A. A ruthenium dipyridophenazine complex that binds preferentially to GC sequences. Chem. Commun. 2003, 1152–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moucheron, C.; Kirsch-De Mesmaeker, A.; Choua, S. Photophysics of Ru(phen)2(PHEHAT)2+: A novel “Light Switch” for DNA and photo-oxidant for mononucleotides. Inorg. Chem. 1997, 36, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordell, P.; Westerlund, F.; Reymer, A.; El-Sagheer, A.H.; Brown, T.; Norden, B.; Lincoln, P. DNA Polymorphism as an origin of adenine-thymine tract length-dependent threading intercalation rate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14651–14658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelmsson, L.M.; Westerlund, F.; Lincoln, P.; Norden, B. DNA-binding of semirigid binuclear ruthenium complex Delta, Delta-mu-(11,11'-bidppz)(phen)(4)Ru-2 (4+): Extremely slow intercalation kinetics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 12092–12093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olofsson, J.; Onfelt, B.; Lincoln, P. Three-state light switch of [Ru(phen)2dppz]2+: Distinct excited-state species with two, one, or no hydrogen bonds from solvent. J. Phys. Chem. A 2004, 108, 4391–4398. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.J.; Turro, C. Highly solvent dependent luminescence from Ru(bpy)(n)(dppp2)(3-n)2+ (n=0–2). Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 5025–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmlin, R.E.; Stemp, E.D.A.; Barton, J.K. Ru(phen)2dppz2+ luminescence: Dependence on DNA sequences and groove-binding agents. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, M.H.; Song, H.; Olmon, E.D.; Dervan, E.E.; Barton, J.K. Sensitivity of Ru(bpy)2dppz2+ luminescence to DNA defects. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 5392–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, A.J.; Lim, M.H.; Olmon, E.D.; Song, H.; Dervan, E.E.; Barton, J.K. Luminescent properties of Ruthenium(II) complexes with sterically expansive ligands bound to DNA defects. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 12511–12520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.D.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, S.K.; Lincoln, P.; Tuite, E.; Norden, B. Binding mode of [ruthenium(II) (1,10-phenanthroline)2L]2+ with poly(dT*dA-dT) triplex. Ligand size effect on third-strand stabilization. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, F.W.; Feigon, J. Quadruplex structure of oxytricha telomeric DNA oligonucleotides. Nature 1992, 356, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankin, S.; Reszka, A.P.; Huppert, J.; Zloh, M.; Parkinson, G.N.; Todd, A.K.; Ladame, S.; Balasubramanian, S.; Neidle, S. Putative DNA quadruplex formation within the human c-kit oncogene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 10584–10589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.Y.; Guo, K.X.; Rusche, J.J.; Hurley, L.H. Facilitation of a structural transition in the polypurine/polypyrimidine tract within the proximal promoter region of the human VEGF gene by the presence of potassium and G-quadruplex-interactive agents. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 6070–6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dexheimer, T.S.; Sun, D.; Hurley, L.H. Deconvoluting the structural and drug-recognition complexity of the G-quadruplex-forming region upstream of the bcl-2 P1 promoter. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 5404–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petraccone, L.; Trent, J.O.; Chaires, J.B. The tail of the telomere. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 16530–16532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.C.; Kuo, I.C.; Ling, I.F.; Chen, C.T.; Chen, H.C.; Lou, P.J.; Lin, J.J.; Chang, T.C. Detection of quadruplex DNA structures in human telomeres by a fluorescent carbazole derivative. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 4490–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paeschke, K.; Simonsson, T.; Postberg, J.; Rhodes, D.; Lipps, H.J. Telomere end-binding proteins control the formation of G-quadruplex DNA structures in vivo. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paeschke, K.; Juranek, S.; Simonsson, T.; Hempel, A.; Rhodes, D.; Lipps, H.J. Telomerase recruitment by the telomere end binding protein-beta facilitates G-quadruplex DNA unfolding in ciliates. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2008, 15, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipps, H.J.; Rhodes, D. G-quadruplex structures: In vivo evidence and function. Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolensky, E.D.; Peterson, K.L.; Weitz, E.A.; Lewandowski, C.; Pierre, V.C. Magnetoluminescent light switches-dual modality in DNA detection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 8966–8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Ding, Y.; Wei, H. Ruthenium Polypyridine Complexes Combined with Oligonucleotides for Bioanalysis: A Review. Molecules 2014, 19, 11933-11987. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811933
Zhang S, Ding Y, Wei H. Ruthenium Polypyridine Complexes Combined with Oligonucleotides for Bioanalysis: A Review. Molecules. 2014; 19(8):11933-11987. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811933
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shuyu, Yubin Ding, and Hui Wei. 2014. "Ruthenium Polypyridine Complexes Combined with Oligonucleotides for Bioanalysis: A Review" Molecules 19, no. 8: 11933-11987. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811933
APA StyleZhang, S., Ding, Y., & Wei, H. (2014). Ruthenium Polypyridine Complexes Combined with Oligonucleotides for Bioanalysis: A Review. Molecules, 19(8), 11933-11987. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811933