Various Extraction Methods for Obtaining Stilbenes from Grape Cane of Vitis vinifera L.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Absolute Concentration
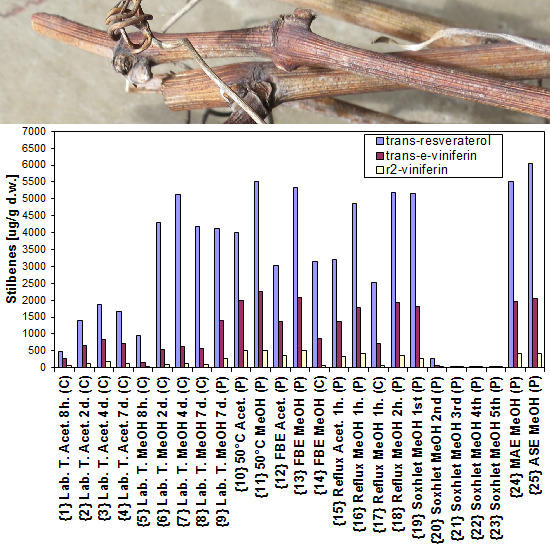
| No. | Short Terms (Legends) | Descriptions of Extraction Methods [Type and Temp./Time or Step Extraction/Material/Solvent] |
|---|---|---|
| {1} | Lab. T. Acet. 8 h (C) | Laboratory temperature, 8 h, cut, acetone |
| {2} | Lab. T. Acet. 2 d (C) | Laboratory temperature, 2 days, cut, acetone |
| {3} | Lab. T. Acet. 4 d (C) | Laboratory temperature, 4 days, cut, acetone |
| {4} | Lab. T. Acet. 7 d (C) | Laboratory temperature, 7 days, cut, acetone |
| {5} | Lab. T. MeOH 8 h (C) | Laboratory temperature, 8 h, cut, methanol |
| {6} | Lab. T. MeOH 2 d (C) | Laboratory temperature, 2 days, cut, methanol |
| {7} | Lab. T. MeOH 4 d (C) | Laboratory temperature, 4 days, cut, methanol |
| {8} | Lab. T. MeOH 7 d (C) | Laboratory temperature, 7 days, cut, methanol |
| {9} | Lab. T. MeOH 7 d (P) | Laboratory temperature, 7 days, powdered, methanol |
| {10} | 50 °C Acet. (P) | Increased temperature 50 °C, 2.75 h, powdered, acetone |
| {11} | 50 °C MeOH (P) | Increased temperature 50 °C, 2.75 h, powdered, methanol |
| {12} | FBE Acet. (P) | FBE (boiling temperature), 100 min, powdered, acetone |
| {13} | FBE MeOH (P) | FBE (boiling temperature), 100 min, powdered, methanol |
| {14} | FBE MeOH (C) | FBE (boiling temperature), 100 min, cut, methanol |
| {15} | Reflux Acet. 1 h (P) | Reflux (boiling temperature), 1 h, powdered, acetone |
| {16} | Reflux MeOH 1 h (P) | Reflux (boiling temperature), 1 h, powdered, methanol |
| {17} | Reflux MeOH 1 h (C) | Reflux (boiling temperature), 1 h, cut, methanol |
| {18} | Reflux MeOH 2 h (P) | Reflux (boiling temperature), 2 h, powdered, methanol |
| {19} | Soxhlet MeOH 1st (P) | Soxhlet (boiling temperature), 1st step, powdered, methanol |
| {20} | Soxhlet MeOH 2nd (P) | Soxhlet (boiling temperature), 2nd step, powdered, methanol |
| {21} | Soxhlet MeOH 3rd (P) | Soxhlet (boiling temperature), 3rd step, powdered, methanol |
| {22} | Soxhlet MeOH 4th (P) | Soxhlet (boiling temperature), 4th step, powdered, methanol |
| {23} | Soxhlet MeOH 5th (P) | Soxhlet (boiling temperature), 5th step, powdered, methanol |
| {24} | MAE MeOH (P) | MAE (boiling temperature), 30 min, powdered, methanol |
| {25} | ASE MeOH (P) | ASE (100 °C), 15 min, powdered, methanol |

2.2. The Highest Yields

2.3. The Effect of Conditions on Extraction of Stilbenes
2.3.1. Solvents
| Extraction | {1} | {2} | {3} | {4} | {15} | {10} | {12} | {5} | {6} | {7} | {8} | {16} | {11} | {13} |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resveratrol | 486.9 | 1401.9 | 1884.9 | 1663.3 | 3210.8 | 4016.5 | 3041.1 | 951.4 | 4314.1 | 5115.4 | 4189.0 | 4868.5 | 5521.6 | 5324.1 |
| Viniferin | 275.2 | 643.7 | 838.2 | 709.5 | 1366.3 | 1994.4 | 1359.1 | 157.9 | 536.0 | 632.1 | 563.1 | 1776.7 | 2260.3 | 2074.1 |
| r2-Viniferin | 67.0 | 139.8 | 170.1 | 133.5 | 344.7 | 504.5 | 373.3 | 27.2 | 98.3 | 115.1 | 108.7 | 422.7 | 496.9 | 507.5 |
| {1} | ||||||||||||||
| Lab. T. Acet. | ||||||||||||||
| 8 h (C) | ||||||||||||||
| {2} | ** | |||||||||||||
| Lab. T. Acet. | ** | |||||||||||||
| 2 d (C) | n.s. | |||||||||||||
| {3} | ** | n.s. | ||||||||||||
| Lab. T. Acet. | ** | n.s. | ||||||||||||
| 4 d (C) | * | n.s. | ||||||||||||
| {4} | ** | n.s. | n.s. | |||||||||||
| Lab. T. Acet. | ** | n.s. | n.s. | |||||||||||
| 7 d (C) | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |||||||||||
| {15} | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||||||||||
| Reflux Acet. | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||||||||||
| 1 h (P) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||||||||||
| {10} | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | |||||||||
| 50 °C Acet. | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||||||||
| (P) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||||||||
| {12} | ** | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | ** | ||||||||
| FBE Acet. | ** | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | ** | ||||||||
| (P) | ** | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | ** | ||||||||
| {5} | n.s. | n.s. | ** | n.s. | ** | ** | ** | |||||||
| Lab. T. | n.s. | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||||||
| MeOH 8 h (C) | n.s. | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||||||
| {6} | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | ** | ** | ||||||
| Lab. T. | * | n.s. | ** | n.s. | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||||||
| MeOH 2 d (C) | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | ||||||
| {7} | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | |||||
| Lab. T. | ** | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | ** | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | |||||
| MeOH 4 d (C) | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | ** | ** | ** | * | n.s. | |||||
| {8} | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | ** | ** | n.s. | ** | ||||
| Lab. T. | ** | n.s. | * | n.s. | ** | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | n.s. | ||||
| MeOH 7 d (C) | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | ||||
| {16} | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | ** | ** | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |||
| Reflux MeOH | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||
| 1 h (P) | ** | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | ** | ** | ** | ** | |||
| {11} | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | ** | n.s. | ||
| 50 °C MeOH | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| (P) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | ||
| {13} | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | ** | n.s. | n.s. | |
| FBE MeOH | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | |
| (P) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | n.s. |
2.3.2. Powdered Versus Cut Materials
| Extraction | {14} | {17} | {8} | {13} | {16} | {9} |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resveratrol | 3152.3 | 2511.1 | 4189.0 | 5324.1 | 4868.5 | 4109.0 |
| Viniferin | 869.8 | 727.3 | 563.1 | 2074.1 | 1776.7 | 1388.8 |
| r2-viniferin | 78.1 | 69.1 | 108.7 | 507.5 | 422.7 | 286.2 |
| {14} | ||||||
| FBE MeOH | ||||||
| (C) | ||||||
| {17} | n.s. | |||||
| Reflux MeOH | n.s. | |||||
| 1 h (C) | n.s. | |||||
| {8} | ** | ** | ||||
| Lab. T. MeOH | ** | n.s. | ||||
| 7 d (C) | n.s. | n.s. | ||||
| {13} | ** | ** | ** | |||
| FBE MeOH | ** | ** | ** | |||
| (P) | ** | ** | ** | |||
| {16} | ** | ** | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| Reflux MeOH | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| 1 h (P) | ** | ** | ** | * | ||
| {9} | ** | ** | n.s. | ** | * | |
| Lab. T. MeOH | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| 7 d (P) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
2.3.3. Temperature
| Extraction | {11} | {25} | {9} | {13} | {16} | {19} | {24} |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resveratrol | 5521.6 | 6032.3 | 4189.0 | 5324.1 | 4868.5 | 5170.5 | 5505.7 |
| Viniferin | 2260.3 | 2059.8 | 563.1 | 2074.1 | 1776.7 | 1822.8 | 1962.5 |
| r2-viniferin | 496.9 | 414.0 | 108.7 | 507.5 | 422.7 | 282.9 | 418.4 |
| {11} | |||||||
| 50 °C MeOH | |||||||
| (P) | |||||||
| {25} | n.s. | ||||||
| ASE MeOH | n.s. | ||||||
| (P) | n.s. | ||||||
| {9} | * | ** | |||||
| Lab. T. MeOH | ** | ** | |||||
| 7 d (P) | ** | ** | |||||
| {13} | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | ||||
| FBE MeOH | n.s. | n.s. | ** | ||||
| (P) | n.s. | n.s. | ** | ||||
| {16} | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |||
| Reflux MeOH | n.s. | n.s. | ** | n.s. | |||
| 1 h (P) | n.s. | n.s. | ** | n.s. | |||
| {19} | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| Soxhlet MeOH | n.s. | n.s. | ** | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| 1st (P) | ** | n.s. | ** | ** | * | ||
| {24} | n.s. | n.s. | * | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| MAE MeOH | n.s. | n.s. | ** | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| (P) | n.s. | n.s. | ** | n.s. | n.s. | * |
2.3.4. Extraction Time

| Extraction | {5} | {1} | {6} | {2} | {7} | {3} | {8} | {4} |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resveratrol | 951.4 | 486.9 | 4314.1 | 1401.9 | 5115.4 | 1884.9 | 4189.0 | 1663.3 |
| Viniferin | 157.9 | 275.2 | 536.0 | 643.7 | 632.1 | 838.2 | 563.1 | 709.5 |
| r2-viniferin | 27.2 | 67.0 | 98.3 | 139.8 | 115.1 | 170.1 | 108.7 | 133.5 |
| {5} | ||||||||
| Lab. T. MeOH | ||||||||
| 8 h (C) | ||||||||
| {1} | n.s. | |||||||
| Lab. T. Acet. | n.s. | |||||||
| 8 h (C) | n.s. | |||||||
| {6} | ** | ** | ||||||
| Lab. T. MeOH | ** | * | ||||||
| 2 d (C) | * | n.s. | ||||||
| {2} | n.s. | ** | ** | |||||
| Lab. T. Acet. | ** | ** | n.s. | |||||
| 2 d (C) | ** | * | n.s. | |||||
| {7} | ** | ** | * | ** | ||||
| Lab. T. MeOH | ** | ** | n.s. | n.s. | ||||
| 4 d (C) | ** | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | ||||
| {3} | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | ** | |||
| Lab. T. Acet. | ** | ** | ** | n.s. | n.s. | |||
| 4 d (C) | ** | ** | * | n.s. | n.s. | |||
| {8} | ** | ** | n.s. | ** | ** | ** | ||
| Lab. T. MeOH 7 | ** | ** | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | ** | ||
| d (C) | ** | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | * | ||
| {4} | * | ** | ** | n.s. | ** | n.s. | ** | |
| Lab. T. Acet. | ** | ** | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| 7 d (C) | ** | * | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
2.3.5. Multiple Extractions

| Extraction | {19} | {20} | {21} | {22} | {23} |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resveratrol | 5170.5 | 282.2 | 29.9 | 8.2 | 7.7 |
| Viniferin | 1822.8 | 61.5 | 13.3 | 8.3 | 2.8 |
| r2-viniferin | 282.9 | 20.7 | 5.2 | 2.5 | 0.8 |
| {19} | |||||
| Soxhlet MeOH | |||||
| 1st (P) | |||||
| {20} | ** | ||||
| Soxhlet MeOH | ** | ||||
| 2nd (P) | ** | ||||
| {21} | ** | n.s. | |||
| Soxhlet MeOH | ** | n.s. | |||
| 3rd (P) | ** | n.s. | |||
| {22} | ** | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| Soxhlet MeOH | ** | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| 4th (P) | ** | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| {23} | ** | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| Soxhlet MeOH | ** | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| 5th (P) | ** | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
2.3.6. Extraction Efficiency
2.4. Quantity and Quality of Stilbenes
2.4.1. Determination of Stilbenes

2.4.2. Identification of Viniferins
| trans-ε-Viniferin C28H22O6 | r2-Viniferin C56H42O12 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formula | Found [m/z] | Calculated [m/z] | Formula | Found [m/z] | Calculated [m/z] |
| C28H23O6+ [M+H]+ | 455.1482 | 455.1489 | C56H43O12+ [M+H]+ | 907.2745 | 907.2749 |
| C28H21O5+ [M−H2O)+ | 437.1373 | 437.1383 | [M+Na]+ | 929.2960 | 929.2968 |
| C22H17O5+ [M−C6H5O]+ | 361.0740 | 361.070 | [M+K]+ | 945.2305 | 945.2307 |
| C13H11O3+ | 215.0709 | 215.0702 | C35H27O7+ | 559.1709 | 559.1751 |
| C28H21O6+ | 453.1339 | 453.1332 | |||
| C22H17O5+ | 361.1038 | 361.1070 | |||
| C13H11O3+ | 215.0690 | 215.0702 | |||
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Standards and Solvents
3.2. Samples Analysis
3.2.1. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
3.2.2. Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)
3.2.3. Liquid Chromatography– Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LC-NMR)


3.2.4. High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HRMS)
3.3. Samples
3.4. Extraction Method
3.4.1. Extraction at Laboratory Temperature
3.4.2. Extraction at 50 °C
3.4.3. Extraction with Solvent Heated to Reflux
3.4.4. Fluidized-Bed Extraction
3.4.5. Soxhlet Extraction
3.4.6. Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE)
3.4.7. Accelerated Solvent Extraction (ASE)
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Langcake, P.; Pryce, R.J. The production of resveratrol by Vitis vinifera and other members of the Vitaceae as a response to infection or injury. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1976, 9, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotheeswaran, S.; Pasupathy, V. Distribution of resveratrol oligomers in plants. Phytochemistry 1993, 32, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaud, S.; de Lorgeril, M. Wine, alcohol, platelets, and the French paradox for coronary heart disease. Lancet 1992, 339, 1523–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalgol, B.; Batirel, S.; Taga, Y.; Ozer, N.K. Resveratrol: French paradox revisited. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaviksaar, A.; Haga, M.; Pussa, T.; Roasto, M.; Tsoupras, G. Purification of resveratrol from vine stems. Proc. Est. Acad. Sci.-Chem. 2003, 52, 155–164. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlus, A.D.; Sahli, R.; Bisson, J.; Rivière, C.; Delaunay, J.C.; Richard, T.; Gomès, E.; Bordenave, L.; Waffo-Téguo, P.; Mérillon, J.M. Stilbenoid profiles of canes from Vitis and Muscadinia species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Park, H.J.; Chung, H.J.; Shin, Y.; Min, H.Y.; Hong, J.Y.; Kang, Y.J.; Ahn, Y.H.; Pyee, J.H.; Lee, S.K. Antimetastatic activity of pinosylvin, a natural stilbenoid, is associated with the suppression of matrix metalloproteinases. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormack, D.; McFadden, D. A review of pterostilbene antioxidant activity and disease modification. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 575482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Cui, L.; Zhou, G.; Jing, H.; Guo, Y.; Sun, W. Pterostilbene, a natural small-molecular compound, promotes cytoprotective macroautophagy in vascular endothelial cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balík, J.; Kyseláková, M.; Vrchotová, N.; Tříska, J.; Kumšta, M.; Veverka, J.; Híc, P.; Totušek, J.; Lefnerová, D. Relations between polyphenols content and antioxidant activity in vine grapes and leaves. Czech J. Food Sci. 2008, 26, S25–S32. [Google Scholar]
- Rayne, S.; Karacabey, E.; Mazza, G. Grape cane waste as a source of trans-resveratrol and trans-viniferin: High-value phytochemicals with medicinal and anti-phytopathogenic applications. Ind. Crops Prod. 2008, 27, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, C.; von Baer, D.; Mardones, C.; Wilkens, A.; Wernekinck, K.; Damm, A.; Macke, S.; Gorena, T.; Winterhalter, P. Stilbene levels in grape cane of different cultivars in southern Chile: Determination by HPLC-DAD-MS/MS method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, D.T.; Chen, Q.C.; Hung, T.M.; Youn, U.J.; Ngoc, T.M.; Thuong, P.T.; Kim, H.J.; Seong, Y.H.; Min, B.S.; Bae, K. Stilbenes and oligostilbenes from leaf and stem of Vitis amurensis and their cytotoxic activity. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2009, 32, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korhammer, S.; Reniero, F.; Mattivi, F. An oligostilbene from Vitis roots. Phytochemistry 1995, 38, 1501–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, M.A.; Sirat, M.H.; Aminah, N.S. Stilbenoids from Vitis labrusca “Isabella” stems. Chem. Natur. Comp. 2013, 49, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestrelab Research S.L., Spain, NMR program MestReNova, Version 8.1.4-12489. Available online: http://www.mestrelab.com (accessed on 2 April 2015).
- Tříska, J.; Vrchotová, N.; Olejníčková, J.; Jílek, R.; Sotolář, R. Separation and identification of highly fluorescent compounds derived from trans-resveratrol in the leaves of Vitis vinifera infected by Plasmopara viticola. Molecules 2012, 17, 2773–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tříska, J.; Vrchotová, N.; Sýkora, J.; Moos, M. Separation and identification of 1,2,4-trihydroxynaphthalene-1-O-glucoside in Impatiens glandulifera Royle. Molecules 2013, 18, 8429–8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smallcombe, S.H.; Patt, S.L.; Keifer, P.A. WET solvent suppression and its applications to LC NMR and high-resolution NMR spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. A 1995, 117, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the extracts are available from the authors.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soural, I.; Vrchotová, N.; Tříska, J.; Balík, J.; Horník, Š.; Cuřínová, P.; Sýkora, J. Various Extraction Methods for Obtaining Stilbenes from Grape Cane of Vitis vinifera L. Molecules 2015, 20, 6093-6112. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20046093
Soural I, Vrchotová N, Tříska J, Balík J, Horník Š, Cuřínová P, Sýkora J. Various Extraction Methods for Obtaining Stilbenes from Grape Cane of Vitis vinifera L. Molecules. 2015; 20(4):6093-6112. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20046093
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoural, Ivo, Naděžda Vrchotová, Jan Tříska, Josef Balík, Štěpán Horník, Petra Cuřínová, and Jan Sýkora. 2015. "Various Extraction Methods for Obtaining Stilbenes from Grape Cane of Vitis vinifera L." Molecules 20, no. 4: 6093-6112. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20046093
APA StyleSoural, I., Vrchotová, N., Tříska, J., Balík, J., Horník, Š., Cuřínová, P., & Sýkora, J. (2015). Various Extraction Methods for Obtaining Stilbenes from Grape Cane of Vitis vinifera L. Molecules, 20(4), 6093-6112. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20046093