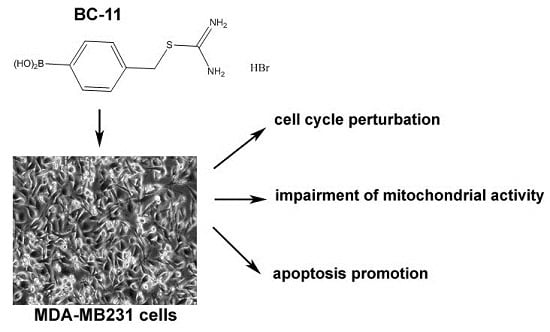
Cytotoxicity of the Urokinase-Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor Carbamimidothioic Acid (4-Boronophenyl) Methyl Ester Hydrobromide (BC-11) on Triple-Negative MDA-MB231 Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion




3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cell Culture and Drugs
3.2. MTT Assay
3.3. Flow Cytometry
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- André, F.; Zielinski, C.C. Optimal strategies for the treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer with currently approved agents. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, vi46–vi51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, B.S.; Sharma, S.C.; Chanana, P.; Jhamb, S. Systemic treatment strategies for triple-negative breast cancer. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niepel, M.; Hafner, M.; Pace, E.A.; Chung, M.; Chai, D.H.; Zhou, L.; Muhlich, J.L.; Schoeberl, B.; Sorger, P.K. Analysis of growth factor signaling in genetically diverse breast cancer lines. BMC Biol. 2014, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBeau, A.M.; Duriseti, S.; Murphy, S.T.; Pepin, F.; Hann, B.; Gray, J.W.; VanBrocklin, H.F.; Craik, C.S. Targeting uPAR with antagonistic recombinant human antibodies in aggressive breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2070–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deadman, J.J.; Spencer, J.; Greenidge, P.A.; Goodwin, C.A.; Kaakar, V.J.; Scully, M.F. Serine Protease Inhibitors Comprising a Hydrogen-Bond Acceptor. PCT Patent WO057273, 25 July 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, E.; Spencer, J.; Ali, M.; Abdinejad, M.; Kankanala, J.; Fishwick, C.; Philippou, H. Elucidating novel urokinase-type plasminogen activator inhibitors. In Proceedings of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis, Kyoto, Japan, 23–28 July 2011.
- Greenidge, P.A.; Mérette, S.A.; Beck, R.; Dodson, G.; Goodwin, C.A.; Scully, M.F.; Spencer, J.; Weiser, J.; Deadman, J.J. Generation of ligand conformations in continuum solvent consistent with protein active site topology: Application to thrombin. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 1293–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, J.; Burd, A.P.; Adatia, T.; Goodwin, C.A.; Mérette, S.A.M.; Scully, M.F.; Deadman, J.J. Synthesis, Structural Studies and Biological Evaluation of 2-Mercaptomethyl- and 2-Piperazinomethyl-Phenylboronic Acid Derivatives. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congreve, M.; Carr, R.; Murray, C.; Jhoti, H. A “rule of three” for fragment-based lead discovery? Drug Discov. Today 2003, 8, 876–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanova, V.V.; Tkachuck, V.A. Urokinase as a multidomain protein and polyfunctional cell regulator. Biochemistry 2002, 67, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Aguirre Ghiso, J.; Estrada, Y.; Ossowski, L. EGFR is a transducer of the urokinase receptor initiated signal that is required for in vivo growth of a human carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2012, 1, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, A.; Xue, M.; Jackson, C.; Smith, R.C. Suppression of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor inhibits proliferation and migration of pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells via regulation of ERK/p38 signaling. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowicki, T.S.; Zhao, H.; Darzynkiewicz, Z.; Moscatello, A.; Shin, E.; Schantz, S.; Tiwari, R.K.; Geliebter, J. Downregulation of uPAR inhibits migration, invasion, proliferation, FAK/PI3K/Akt signaling and induces senescence in papillary thyroid carcinoma cells. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Webb, D.J.; Jo, M.; Gonias, S.L. Endogenously produced urokinase-type plasminogen activator is a major determinant of the basal level of activated ERK/MAP kinase and prevents apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 3387–3396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alfano, D.; Franco, P.; Vocca, I.; Gambi, N.; Pisa, V.; Mancini, A.; Caputi, M.; Carriero, M.V.; Iaccarino, I.; Stoppelli, M.P. The urokinase plasminogen activator and its receptor: Role in cell growth and apoptosis. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 93, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholl, S.M.; Roztocil, E.; Davies, M.G. Urokinase-induced smooth muscle cell responses require distinct signaling pathways: A role for the epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Vasc. Surg. 2005, 41, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livasy, C.A.; Karaca, G.; Nanda, R.; Tretiakova, M.S.; Olopade, O.I.; Moore, D.T.; Perou, C.M. Phenotypic evaluation of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2006, 19, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlin, J.; Rosenkvist, J.; Andersson, T. TNK2 preserves epidermal growth factor receptor expression on the cell surface and enhances migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2008, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, M.; Mendelsohn, J.; Kim, Y.M.; Albanell, J.; Fry, D.W.; Baselga, J. PD153035, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, prevents epidermal growth factor receptor activation and inhibits growth of cancer cells in a receptor number-dependent manner. Clin. Cancer Res. 1997, 3, 2099–2106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lichtner, R.B.; Menrad, A.; Sommer, A.; Klar, U.; Schneider, M.R. Signaling-inactive epidermal growth factor receptor/ligand complexes in intact carcinoma cells by quinazoline tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 5790–5795. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Mahabeleshwar, G.H.; Kundu, G.C. Osteopontin induces AP-1-mediated secretion of urokinase-type plasminogen activator through c-Src-dependent epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation in breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 11051–11064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moiseeva, E.P.; Almeida, G.M.; Jones, G.D.; Manson, M.M. Extended treatment with physiologic concentrations of dietary phytochemicals results in altered gene expression, reduced growth, and apoptosis of cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 3071–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreyev, A.Y.; Kushnareva, Y.E.; Starkov, A.A. Mitochondrial metabolism of reactive oxygen species. Biochemistry 2005, 70, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchen, M.R. Roles of mitochondria in health and disease. Diabetes 2004, 53, S96–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Circu, M.L.; Aw, T.Y. Reactive oxygen species, cellular redox systems, and apoptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TOCRIS. Available online: http://www.tocris.com/dispprod.php?ItemId=321684#.U62r8a1OVLM (accessed on 1 April 2015).
- Bridges, A.J.; Zhou, H.; Cody, D.R.; Rewcastle, G.W.; McMichael, A.; Showalter, H.D.; Fry, D.W.; Kraker, A.J.; Denny, W.A. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors. 8. An unusually steep structure-activity relationship for analogues of 4-(3-bromoanilino)-6,7-dimethoxyquinazoline (PD 153035), a potent inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, D.W.; Kraker, A.J.; McMichael, A.; Ambroso, L.A.; Nelson, J.M.; Leopold, W.R.; Connors, R.W.; Bridges, A.J. A specific inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Science 1994, 265, 1093–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, J.; Chuckowree, I.; Tizzard, G.J.; Coles, S.J.; Wang, M.; Bingham, J.P.; Hartley, J.A.; Spencer, J. Targeting epidermal growth factor receptor with ferrocene-based kinase inhibitors. Organometallics 2013, 32, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librizzi, M.; Longo, A.; Chiarelli, R.; Amin, J.; Spencer, J.; Luparello, C. Cytotoxic effects of Jay Amin hydroxamic acid (JAHA), a ferrocene-based class I histone deacetylase inhibitor, on triple-negative MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 2608–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luparello, C.; Del Rosso, M. In vitro anti-proliferative and anti-invasive role of aminoterminal fragment of urokinase-type plasminogen activator on 8701-BC breast cancer cells. Eur. J. Cancer 1996, 32, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C.; Martin, N. CompuSyn Software for Drug Combinations and for General Dose-Effect Analysis, and User’s Guide; ComboSyn Inc.: Paramus, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, S.J.; Tomsho, J.W.; Benkovic, S.J. Boron-containing inhibitors of synthetases. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4279–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trippier, P.C.; McGuigan, C.; Balzarini, J. Phenylboronic-acid-based carbohydrate binders as antiviral therapeutics: Monophenylboronic acids. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2010, 20, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds BC-11, 3-B and 4-B are available from the authors.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Longo, A.; Librizzi, M.; Chuckowree, I.S.; Baltus, C.B.; Spencer, J.; Luparello, C. Cytotoxicity of the Urokinase-Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor Carbamimidothioic Acid (4-Boronophenyl) Methyl Ester Hydrobromide (BC-11) on Triple-Negative MDA-MB231 Breast Cancer Cells. Molecules 2015, 20, 9879-9889. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20069879
Longo A, Librizzi M, Chuckowree IS, Baltus CB, Spencer J, Luparello C. Cytotoxicity of the Urokinase-Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor Carbamimidothioic Acid (4-Boronophenyl) Methyl Ester Hydrobromide (BC-11) on Triple-Negative MDA-MB231 Breast Cancer Cells. Molecules. 2015; 20(6):9879-9889. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20069879
Chicago/Turabian StyleLongo, Alessandra, Mariangela Librizzi, Irina S. Chuckowree, Christine B. Baltus, John Spencer, and Claudio Luparello. 2015. "Cytotoxicity of the Urokinase-Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor Carbamimidothioic Acid (4-Boronophenyl) Methyl Ester Hydrobromide (BC-11) on Triple-Negative MDA-MB231 Breast Cancer Cells" Molecules 20, no. 6: 9879-9889. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20069879
APA StyleLongo, A., Librizzi, M., Chuckowree, I. S., Baltus, C. B., Spencer, J., & Luparello, C. (2015). Cytotoxicity of the Urokinase-Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor Carbamimidothioic Acid (4-Boronophenyl) Methyl Ester Hydrobromide (BC-11) on Triple-Negative MDA-MB231 Breast Cancer Cells. Molecules, 20(6), 9879-9889. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20069879