Fluorination Effects on NOS Inhibitory Activity of Pyrazoles Related to Curcumin
Abstract
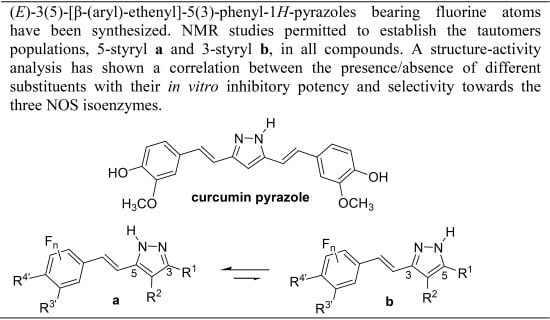
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization by NMR Spectroscopy

| Compound | Solvent (Temp) | F2′ | F3′ | F4′ | F5′ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | DMSO-d6 | −116.1 (67%) | |||
| 295 K | −116.8 (33%) | ||||
| MAS 300 K | −107.7 | ||||
| 13 | −136.0 (60%) | ||||
| DMSO-d6 | 3J = 4J = 10.8 | ||||
| 295 K | −136.2 (40%) | ||||
| 3J = 4J = 10.2 | |||||
| DMSO-d6 | −136.0 | ||||
| 360 K | |||||
| HMPA-d18 | −137.3 (67%) | ||||
| 295 K | −137.6 (33%) | ||||
| MAS 300 K | −129.2 | ||||
| 14 | DMSO-d6 | −136.4 (54%) | −132.1 (54%) | ||
| 295 K | −137.0 (46%) | −132.8 (46%) | |||
| MAS 300 K | −130.7 | −126.8 | |||
| 15 | DMSO-d6 | −121.3 (60%) | −140.6 | ||
| 295 K | −122.1 (40%) | ||||
| MAS 300 K | −114.2 | −134.8 | |||
| 16 | DMSO-d6 | −135.4 (57%) | |||
| 295 K | −136.3 (43%) | ||||
| HMPA-d18 | −136.9 (65%) | ||||
| 295 K | −137.8 (35%) | ||||
| CDCl3 295 K | −135.5 | ||||
| MAS 300 K | −132.6 |
| Compound | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % a | 42 [a] | 57 [b] | 64 | 60 | 85 [c] | 67 | 60 | 54 | 60 | 57 |

2.2. Crystal and Molecular Structures


| Comp | D-H···A [a] | Symmetry Operations | d(D-H) | d(H···A) | d(D···A) | <(DHA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | N1-H1···O1#1 | #1 –x + 1/2, y + 1/2, −z + 3/2 | 0.98 | 1.98 | 2.899(2) | 154.1 |
| N2···H1A-O1#2 | #2 x + 1/2, −y + 1/2, z − 1/2 | 1.01 | 1.72 | 2.711(2) | 164.3 | |
| 13 | N1-H1···O1#1 | #1 – x + 3/2, y + 1/2, −z + 1/2 | 1.02 | 1.86 | 2.871(3) | 171.1 |
| N2···H1A-O1#2 | #2 x − 1/2, −y + 3/2, z + 1/2 | 1.08 | 1.69 | 2.736(3) | 161.8 | |
| 16 | N1-H1···N2#1 | #1 − x, −y + 2, −z + 1 | 1.02 | 1.92 | 2. 852(2) | 150.2 |

2.3. NOS Inhibitory Activity

| Compound | R 1 | R 2 | R 4′ | nNOS | iNOS | eNOS | Predominant | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | H | OH | 51.2 ± 1.2 | 65.3 ± 2.1 | 77.4 ± 0.1 | eNOS | |
| 7 | CH3 | H | OH | 61.7 ± 1.6 | 45.6 ± 1.8 | 84.1 ± 0.7 | eNOS | |
| 8 | CH3 | CH3 | OH | 29.9 ± 0.7 | 46.4 ± 3.2 | 19.2 ± 1.8 | iNOS | |
| 9 | C6H5 | H | OH | 84.9 ± 0.1 | 63.5 ± 1.9 | 60.3 ± 1.5 | nNOS | |
| 10 | C6H5 | H | OCH3 | 20.0 ± 0.2 | 48.0 ± 0.9 | 23.4 ± 2.9 | iNOS | |
| 11 | C6H5 | CH3 | OCH3 | 19.0 ± 0.6 | 62.1 ± 1.2 | 40.6 ± 2.2 | iNOS | |
| Compound | R 2′ | R 3′ | R 4′ | R 5′ | nNOS | iNOS | eNOS | Predominant |
| 12 | F | H | OH | H | 65.9 ± 6.2 | 65.8 ± 1.2 | 37.6 ± 1.8 | n/iNOS |
| 13 | H | F | OH | H | 36.8 ± 1.5 | 83.7 ± 6.3 | 37.4 ± 2.3 | iNOS |
| 14 | F | OH | F | H | 24.1 ± 2.3 | 33.6 ± 4.7 | 40.3 ± 1.6 | eNOS |
| 15 | F | H | OH | F | 38.9 ± 1.4 | 36.3 ± 1.2 | 44.2 ± 0.0 | eNOS |
| 16 | H | OCH3 | F | H | 21.7 ± 0.3 | 46.0 ± 5.4 | 39.3 ± 3.5 | iNOS |
| 1H-indazoles [a] | ||||||||
| 7-nitro [3] | ---- | 88.0 | 84.0 | ---- | n/iNOS | |||
| 4,5,6,7-tetrafluoro [3] | ---- | 98.7 | 43.3 | 67.5 | nNOS | |||
| Compound | nNOS | iNOS | eNOS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.560 | 3.265 | 3.870 |
| 7 | 3.085 | 2.280 | 4.205 |
| 8 | 1.495 | 2.320 | 0.960 |
| 9 | 4.245 | 3.175 | 3.015 |
| 10 | 1.000 | 2.400 | 1.170 |
| 11 | 0.950 | 3.105 | 2.030 |
| 12 | 65.9 | 65.8 | 37.6 |
| 13 | 36.8 | 83.7 | 37.4 |
| 14 | 24.1 | 33.6 | 40.3 |
| 15 | 38.9 | 36.3 | 44.2 |
| 16 | 21.7 | 46.0 | 39.3 |
| F2′ | 66 | 66 | 38 |
| F3′ | 37 | 84 | 37 |
| F4′ | 22 | 46 | 39 |
| F5′ | −27 | −30 | 7 |
| OH-3′ | −64 | −78 | −37 |
| n | 11 | 11 | 11 |
| R2 | 0.995 | 0.997 | 0.994 |

3. Experimental Section
3.1. General

3.2. NMR Parameters
3.3. General Procedure for the Preparation of Pyrazole Derivatives (12–16)
3.4. In Vitro nNOS, iNOS and eNOS Activities Determination
3.5. Single-Crystal X-ray Analysis
| Crystal Data | 12 | 13 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCDC | 1040404 | 1040405 | 1040406 |
| Empirical formula | C17H13FN2O | C17H13FN2O | C18H15FN2O |
| Formula wt | 280.29 | 280.29 | 294.32 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | Monoclinic | Monoclinic |
| Space group | P21/n | P21/n | P21/c |
| a/Å | 12.5535(10) | 12.3701(12) | 16.245(5) |
| b/Å | 7.4573(4) | 7.4538(7) | 12.187(4) |
| c/Å | 15.0727(11) | 15.2521(15) | 7.559(2) |
| a α/° | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| b β/° | 106.759(8) | 105.101(2) | 94.205(6) |
| γ/° | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| V/Å3 | 1351.1(2) | 1357.7(2) | 3280.0(3) |
| Z | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Dc/g/cm3 | 1.378 | 1.371 | 1.310 |
| μ(Mo-Ka)/mm−1 | 0.097 | 0.096 | 0.091 |
| F(000) | 584 | 584 | 616 |
| θ range/° | 3.39 to 25.01 | 1.90 to 27.00 | 1.26 to 27.00 |
| Index ranges | −14,−8,−14 to 14, 8, 17 | −15,−9,−19 to 15, 8, 17 | −20,−15,−9 to 20, 15, 5 |
| Reflections collected | 5657 | 10842 | 13044 |
| Unique reflections | 2370 | 2972 | 3259 |
| [Rint] | [0.0278] | [0.0564] | [0.0593] |
| Completeness to θ | 99.7% | 99.7% | 99.9% |
| Data/restraints/params | 2370/0/190 | 2972/0/192 | 3259/0/199 |
| Goodness-of-fit on F2 | 0.997 | 0.997 | 0.995 |
| R1 | 0.0437 | 0.0507 | 0.0379 |
| (reflns obsd) [I > 2 s(I)] [a] | (1664) | (1415) | (1548) |
| wR2 (all data) [b] | 0.1218 | 0.1631 | 0.0867 |
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Acknowledgments
Authors Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Claramunt, R.M.; López, C.; Pérez-Medina, C.; Pérez-Torralba, M.; Elguero, J.; Escames, G.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Fluorinated indazoles as novel selective inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase (NOS): Synthesis and biological evaluation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6180–6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elguero, J.; Alkorta, I.; Claramunt, R.M.; López, C.; Sanz, D.; Santa María, D. Theoretical calculations of a model of NOS indazole inhibitors: Interaction of aromatic compounds with Zn-porphyrins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 8027–8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claramunt, R.M.; López, C.; López, A.; Pérez-Medina, C.; Pérez-Torralba, M.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J.; Escames, G.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Synthesis and biological evaluation of indazole derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornago, P.; Claramunt, R.M.; Bouissane, L.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. A study of the tautomerism of β-dicarbonyl compounds with special emphasis on curcuminoids. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 8089–8094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornago, P.; Cabildo, P.; Claramunt, R.M.; Pinilla, E.; Torres, M.R.; Elguero, J. The annular tautomerism of the curcuminoid NH-pyrazoles. New J. Chem. 2009, 33, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claramunt, R.M.; Bouissane, L.; Cabildo, P.; Cornago, P.; Elguero, J.; Radziwon, A.; Medina, C. Synthesis and biological evaluation of curcuminoid pyrazoles as new therapeutic agents in inflammatory bowel disease: Effect on matrix metalloproteinases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 1290–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornago, P.; Cabildo, P.; Sanz, D.; Claramunt, R.M.; Torralba, M.C.; Torres, M.R.; Elguero, J. Structures of hemi-curcuminoids in the solid-state and in solution. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 6043–6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredt, D.S.; Snyder, S.H. Nitric oxide: A physiologic messenger molecule. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1994, 63, 175–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escames, G.; León, J.; Macías, M.; Khaldy, H.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Melatonin counteracts lipopolysaccharide-induced expression and activity of mitochondrial nitric oxide synthase in rats. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 932–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacza, Z.; Pankotai, E.; Csordás, A.; Kiss, L.; Horváth, E.M.; Kollai, M.; Busija, D.W.; Szabó, C. Mitochondrial NO and reactive nitrogen species production: Does mtNOS exist? Nitric Oxide 2006, 14, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskin, J.D.; Laskin, D.L. Cellular and Molecular Biology of Nitric Oxide; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Suaifan, G.A.; Goodyer, C.L.M.; Threadgill, M.D. Synthesis of N-(methoxycarbonylthienylmethyl) thioureas and evaluation of their interaction with inducible and neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Molecules 2010, 15, 3121–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handy, R.L.C.; Wallace, P.; Gaffen, Z.A.; Whitehead, K.J.; Moore, P.K. The antinociceptive effect of 1-(2-trifluoromethylphenyl) imidazole (TRIM), a potent inhibitor of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in vitro, in the mouse. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 116, 2349–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doucet, M.V.; Levine, H.; Dev, K.K.; Harkin, A. Small-molecule inhibitors at the PSD-95/nNOS interface have antidepressant-like properties in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankaran, K.; Donnelly, K.L.; Shah, S.K.; Humes, J.L.; Pacholok, S.G.; Grant, S.K.; Green, B.G.; MacCoss, M. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase by benzoxazolones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1997, 7, 2887–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, C.S.; Martásek, H.; Li, P.; Babu, B.R.; Griffith, O.W.; Masters, B.S.; Poulos, T.L. Implications for isoform-selective inhibitor design derived from the binding mode of bulky isothioureas to the heme domain of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 26486–26491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, P.K.; Wallace, P.; Gaffen, Z.; Hart, S.L. Characterization of the novel nitric oxide synthase inhibitor 7-nitro indazole and related indazoles: Antinociceptive and cardiovascular effects. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 110, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babbedge, R.C.; Bland-Ward, P.A.; Hart, S.L.; Moore, P.K. Inhibition of rat cerebellar nitric oxide synthase by 7-nitro indazole and related substituted indazoles. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 110, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottyn, B.; Acher, F.; Ramassamy, B.; Alvey, L.; Lepoivre, M.; Frapart, Y.; Stuehr, D.; Mansuy, D.; Boucher, J.L.; Vichard, D. Inhibitory effects of a series of 7-substituted-indazoles toward nitric oxide synthases: Particular potency of 1H-indazole-7-carbonitrile. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 5962–5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrión, M.D.; Chayah, M.; Entrena, A.; López, A.; Gallo, M.A.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Camacho, M.E. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole derivatives as potential nNOS/iNOS selective inhibitors. Part 2: Influence of diverse substituents in both the phenyl moiety and the acyl group. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 4132–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Stanton, B.Z.; Igarashi, J.; Li, H.; Martásek, P.; Roman, L.J.; Poulos, T.L.; Silverman, R.B. Minimal pharmacophoric elements and fragment hoping, an approach directed at molecular diversity and isozyme selectivity. Design of selective neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 3900–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Delker, S.L.; Li, H.; Martásek, P.; Roman, L.J.; Poulos, T.L.; Silverman, R.B. Exploration of the active site of neuronal nitric oxide synthase by the design and synthesis of pyrrolidinomethyl 2-aminopyridine derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 7804–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinelli, M.A.; Li, H.; Chreifi, G.; Martásek, P.; Roman, L.J.; Poulos, T.L.; Silverman, R.B. Simplified 2-aminoquinoline-based scaffold for potent and selective neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibition. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 1513–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Tang, W.; Li, H.; Chreifi, G.; Martásek, P.; Roman, L.J.; Poulos, T.L.; Silverman, R.B. Nitric oxide synthase inhibitors that interact with both heme propionate and tetrahydrobiopterin show high isoform selectivity. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4382–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Jamal, J.; Delker, S.; Plaza, C.; Ji, H.; Jing, Q.; Huang, H.; Kang, S.; Silverman, R.B.; Poulos, T.L. The mobility of a conserved tyrosine residue controls isoform-dependent enzyme-inhibitor interactions in nitric oxide synthases. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 5272–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, P.; Li, H.; Sevrioukova, I.F.; Chreifi, G.; Martásek, P.; Roman, L.J.; Poulos, T.L.; Silverman, R.B. Novel 2,4-disubstituted pyrimidines as potent, selective, and cell-permeable inhibitors of neuronal nitric oxide synthase. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 1067–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Kumar, A.; Aggarwal, M.S.; Shihodia, S. Curcumin Derived from Turmeric (Curcuma longa): A Spice for All Seasons. In Phytopharmaceuticals in Cancer Chemoprevention; Bagchi, D., Preuss, H.G., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari, R.K.; Singh, A.K.; Gaddipati, J.; Srimal, R.C. Multiple biological activities of curcumin: A short review. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Beevers, C.S.; Huang, S. The targets of curcumin. Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esatbeyoglu, T.; Huebbe, P.; Ernst, I.M.A.; Chin, D.; Wagner, A.E.; Rimbach, G. Curcumin—From molecule to biological function. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5308–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, L.K. Turmeric-derived compound curcumin may treat Alzheimer’s. Chem. Eng. News 2012, 90, 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Tyagi, A.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin, a compound of golden spice: From bedside to bench and back. Adv. Biotech 2014, 32, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tizabi, Y.; Hurley, L.L.; Qualls, Z.; Akinfiresoye, L. Relevance of the anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin in neurodegenerative diseases and depression. Molecules 2014, 19, 20864–20879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, D.; Chojnacki, J.; Du, Y.; Fu, H.; Grant, S.; Zhang, S. Design and biological characterization of hybrid compounds of curcumin and thalidomide for multiple myeloma. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 4757–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chojnacki, J.E.; Liu, K.; Yan, X.; Toldo, S.; Selden, T.; Estrada, M.; Rodríguez-Franco, M.I.; Halquist, M.S.; Ye, D.; Zhang, S. Discovery of 5-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-oxo-pentanoic acid [2-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)-ethyl]-amide as a neuroprotectant for Alzheimer’s disease by hybridization of curcumin and melatonin. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2014, 5, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Wang, Z.; Ou, C.; Chen, M.; Wang, L.; Yang, Z. A supramolecular hydrogelator of curcumin. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 9413–9415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mareeswaran, P.M.; Babu, E.; Sathish, V.; Kim, B.; Woo, S.I.; Rajagopal, S. p-Sulfonatocalix[4]arene as a carrier for curcumin. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.K.; Sanphui, P.; Ramamurty, U.; Desiraju, G.R. Solubility-hardness correlation in molecular crystals: curcumin and sulfathiazole polymorphs. Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 3054–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirásek, P.; Amslinger, S.; Heilmann, J. Synthesis of natural and non-natural curcuminoids and their neuroprotective activity against glutamate-induced oxidative stress in HT-22 Cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2206–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, D.L.; Belliotti, T.R.; Boctor, A.M.; Connor, D.T.; Kostlan, C.R.; Nies, D.E.; Ortwine, D.F.; Schrier, D.J.; Sircar, J.C. Styrylpyrazoles, styrylisoxazoles, and styrylisothiazoles. Novel 5-lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 1991, 34, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, J.S.; Kim, D.H.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, D.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, K.W.; Ahn, J.W.; Yoo, J.S.; Rho, J.R.; et al. Hydrazinocurcumin, a novel synthetic curcumin derivative, is a potent inhibitor of endothelial cell proliferation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2002, 10, 2439–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, J.; Ohtsu, H.; Tachibana, Y.; Nakanishi, Y.; Bastow, K.F.; Nagai, M.; Wang, H.K.; Itokawa, H.; Lee, K.H. Antitumor agents. Part 214: Synthesis and evaluation of curcumin analogues as cytotoxic agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2002, 10, 3481–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldarelli, A.; Penucchini, E.; Caprioglio, D.; Genazzani, A.A.; Minassi, A. Synthesis and tubulin-binding properties of non-symmetrical click C5-curcuminoids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 5510–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvam, C.; Jachak, S.M.; Thilagavathia, R.; Chakraborti, A.K. Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking of curcumin analogues as antioxidant, cyclooxygenase inhibitory and anti-inflammatory agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 1793–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Dargush, R.; Maher, P.; Schubert, D. A broadly neuroprotective derivative of curcumin. J. Neurochem. 2008, 105, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, P.; Akaishi, T.; Schubert, D.; Abe, K. A pyrazole derivative of curcumin enhances memory. Neurobiol. Aging 2010, 31, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapchak, P.A.; McKim, J.M. CeeTox™ analysis of CNB-001 a novel curcumin-based neurotrophic/neuroprotective lead compound to treat stroke: comparison with NXY-059 and Radicut. Transl. Stroke Res. 2011, 2, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Prior, M.; Dargush, R.; Roberts, A.; Riek, R.; Eichmann, C.; Chiruta, C.; Akaishi, T.; Abe, K.; Maher, P.; et al. A novel neurotrophic drug for cognitive enhancement and Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narlawar, R.; Pickhardt, M.; Leuchtenberger, S.; Baumann, K.; Krause, S.; Dyrks, T.; Weggen, S.; Mandelkow, E.; Schmidt, B. Curcumin-derived pyrazoles and isoxazoles: Swiss army knives or blunt tools for Alzheimer’s disease? ChemMedChem 2008, 3, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Park, J.H.; Yoon, S.S. Synthesis and biological evaluation of curcumin analogs as antiplatelet inhibitor. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2014, 35, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouet, I.; Ohshima, H. Curcumin, an anti-tumor promoter and anti-inflammatory agent, inhibits induction of nitric oxide synthase in activated macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 206, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.M.Y.; Huang, H.I.; Fenton, M.R.; Fong, D. In vivo inhibition of nitric oxide synthase gene expression by curcumin, a cancer preventive natural product with anti-inflammatory properties. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998, 55, 1955–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoda, M.; Inano, H. Effect of curcumin on the production of nitric oxide by cultured rat mammary gland. Nitric Oxide 2000, 4, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Shen, S.C.; Lee, W.R.; Hou, W.C.; Yang, L.L.; Lee, T.J.F. Inhibition of NOS inhibitors and lipopolysaccharide induced inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase 2 gene expressions by rutin, quercetin, and quercetin pentaacetate in RAW264.7 macrophages. J. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 82, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surh, Y.J.; Chun, K.S.; Cha, H.H.; Han, S.S.; Keum, Y.S.; Park, K.K.; Lee, S.S. Molecular mechanisms underlying chemopreventive activities of anti-inflammatory phytochemicals: Down-regulation of COX-2 and iNOS through suppression of NF-kappa B activation. Mutat. Res. 2001, 480, 243–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inano, H.; Onoda, M. Role of nitric oxide in radiation-induced initiation of mammary tumorigenesis in rats. Nitric Oxide 2003, 8, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tang, X.Q.; Zhi, J.L.; Cui, Y.; Yu, H.M.; Tang, E.H.; Sun, S.N.; Feng, J.Q.; Chen, P.X. Curcumin protects PC12 cells against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion-induced apoptosis by bcl-2-mitochondria-ROS-iNOS pathway. Apoptosis 2006, 11, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhad, A.; Pilkhwal, S.; Sharma, S.; Tirkey, N.; Chopra, K. Effect of curcumin on inflammation and oxidative stress in cisplatin-induced experimental nephrotoxicity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 10150–10155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, V.P.; Sudheer, A.R. The Molecular Targets and Therapeutic Uses of Curcumin in Health and Disease; Aggarwal, B.B., Surh, Y.J., Shishodia, S., Eds.; Springer Science & Business Media: Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ben, P.; Liu, J.; Lu, C.; Xu, Y.; Fu, J.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Luo, L.; Yin, Z. Curcumin promotes degradation of inducible nitric oxide synthase and suppresses its enzyme activity in RAW 264.7 cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.H.; Lin-Shiau, S.Y.; Lin, J.K. Comparative studies on the suppression of nitric oxide synthase by curcumin and its hydrogenated metabolites through down-regulation of IkappaB kinase and NFkappaB activation in macrophages. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 60, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motterlini, R.; Foresti, R.; Bassi, R.; Green, C.J. Curcumin, an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, induces heme oxygenase-1 and protects endothelial cells against oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braidy, N.; Grant, R.; Adams, S.; Guillemin, G. Neuroprotective effects of naturally occurring polyphenols on quinolinic acid-induced excitotoxicity in human neurons. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 368–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.Y.; Zhang, M.; Luo, J.; Zhang, L.; Shao, Y.; Li, G. Curcumin ameliorates memory deficits via neuronal nitric oxide synthase in aged mice. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 45, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, T.; Taguchi, T.; Ojima, I. Unique Properties of Fluorine and Their Relevance to Medicinal Chemistry and Chemical Biology. In Fluorine in Medicinal Chemistry and Biology; Ojima, I., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Elguero, J. Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry II; Katritzky, A.R., Rees, C.W., Scriven, E.F., Eds.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1996; Volume 3, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Stanovnik, B.; Svete, J. Science of Synthesis; Neier, R., Ed.; Thieme: Stuttgart, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fustero, S.; Simón-Fuentes, A.; Sanz-Cervera, J.F. Recent advances in the synthesis of pyrazoles. A review. Org. Prep. Proced. Int. 2009, 41, 253–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claramunt, R.M.; Cornago, P.; Torres, V.; Pinilla, E.; Torres, M.R.; Samat, A.; Lokshin, V.; Valés, M.; Elguero, J. The structure of pyrazoles in the solid state: A combined CPMAS, NMR, and crystallographic study. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 6881–6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oki, M. Applications of Dynamic NMR Spectroscopy to Organic Chemistry; VCH Verlagsgesellschaft: Weinheim, Germany, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Bredt, D.S.; Snyder, S.H. Nitric oxide mediates glutamate-linked enhancement of cGMP levels in the cerebellum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 9030–9033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansch, C.; Leo, A. Exploring QSAR; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; p. 208. [Google Scholar]
- Free, S.M.; Wilson, J.W. A mathematical contribution to structure-activity studies. J. Med. Chem. 1964, 7, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, T.; Ban, T. Structure–activity study of phenethylamines as substrates of biosynthetic enzymes of sympathetic transmitters. J. Med. Chem. 1971, 14, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkorta, I.; Rozas, I.; Elguero, J. Molecular complexes between silicon derivatives and electron-rich groups. J. Phys. Chem. 2001, 105, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Sánchez, J.C.; Santa María, D.; Claramunt, R.M.; Elguero, J. Molecular recognition studies on naphthyridine derivatives. Molecules 2010, 15, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berger, S.; Braun, S. 200 and More NMR Experiments: A Practical Course; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, P.D. Improvement in the cross-polarization NMR experiment for suppression of rigid protonated carbons. J. Magn. Reson. 1983, 52, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, P.D. Pulse sequences for the selective observations of nonprotonated and methyl carbon NMR resonances in solids. J. Magn. Reson. 1985, 62, 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Alemany, L.B.; Grant, D.M.; Alger, T.D.; Pugmire, R.J. Cross polarization and magic angle sample spinning NMR spectra of model organic compounds. 3. Effect of the 13C-1H dipolar interaction on cross polarization and carbon-proton dephasing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 6697–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, E.; Macías, M.; Pozo, D.; Escames, G.; Martin, M.; Vives, F.; Guerrero, J.M.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Melatonin inhibits expression of the inducible NO synthase II in liver and lung and prevents endotoxemia in lipopolysaccharide-induced multiple organ dysfunction in rats. FASEB J. 1999, 13, 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- León, J.; Macías, M.; Escames, G.; Camacho, E.; Khaldy, H.; Martín, M.; Espinosa, A.; Gallo, M.A.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Structure-related inhibition of calmodulin-dependent neuronal nitric-oxide synthase activity by melatonin and synthetic kynurenines. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 58, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- SHELX, 97, Program for Refinement of Crystal Structure; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1997.
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 7–16 are available from the authors.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nieto, C.I.; Cabildo, M.P.; Cornago, M.P.; Sanz, D.; Claramunt, R.M.; Torralba, M.C.; Torres, M.R.; Elguero, J.; García, J.A.; López, A.; et al. Fluorination Effects on NOS Inhibitory Activity of Pyrazoles Related to Curcumin. Molecules 2015, 20, 15643-15665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200915643
Nieto CI, Cabildo MP, Cornago MP, Sanz D, Claramunt RM, Torralba MC, Torres MR, Elguero J, García JA, López A, et al. Fluorination Effects on NOS Inhibitory Activity of Pyrazoles Related to Curcumin. Molecules. 2015; 20(9):15643-15665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200915643
Chicago/Turabian StyleNieto, Carla I., María Pilar Cabildo, María Pilar Cornago, Dionisia Sanz, Rosa M. Claramunt, María Carmen Torralba, María Rosario Torres, José Elguero, José A. García, Ana López, and et al. 2015. "Fluorination Effects on NOS Inhibitory Activity of Pyrazoles Related to Curcumin" Molecules 20, no. 9: 15643-15665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200915643
APA StyleNieto, C. I., Cabildo, M. P., Cornago, M. P., Sanz, D., Claramunt, R. M., Torralba, M. C., Torres, M. R., Elguero, J., García, J. A., López, A., & Acuña-Castroviejo, D. (2015). Fluorination Effects on NOS Inhibitory Activity of Pyrazoles Related to Curcumin. Molecules, 20(9), 15643-15665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200915643