Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Baicalin-Induced Drug Interaction and Its Pharmacokinetics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Pharmacokinetics of Baicalin and Baicalein
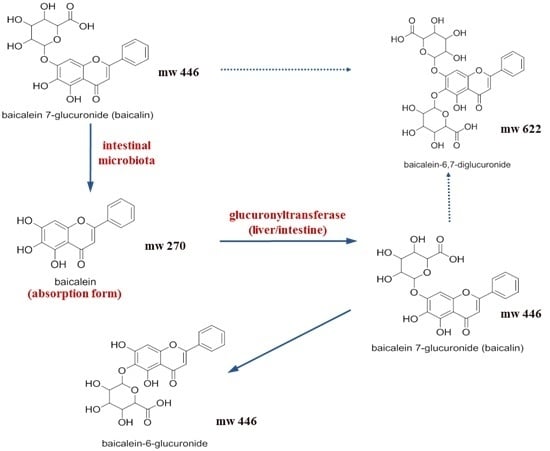
2.1. Pharmacokinetic Change of Baicalin and Baicalein by Intestinal Microbiota
2.2. Effects of Various Factors Affecting the Growth of Intestinal Microbiota on the Pharmacokinetics of Baicalin and Baicalein
3. Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Efficacy and Toxicity of Baicalin and Baicalein
3.1. Anti-Cancer Effects of Baicalin and Baicalein
3.2. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Baicalin and Baicalein
3.3. Anti-Pruritic Effect of Baicalin and Baicalein
3.4. Toxicity of Baicalin and Baicalein in HepG2 Cells
4. Baicalin and Baicalein Induced in Vivo Drug Interaction
4.1. Metabolic Enzymes and Plasma Protein Binding Displacement-Mediated Drug Interaction
4.2. Transporter-Mediated Drug Interaction
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gorbach, S.L. Microbiology of the gastrointestinal tract. In Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; Baron, S., Ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- O’Hara, A.M.; Shanahan, F. The gut flora as a forgotten organ. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekirov, I.; Russell, S.L.; Antunes, L.C.; Finlay, B.B. Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 859–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.N.; St Amand, A.L.; Feldman, R.A.; Boedeker, E.C.; Harpaz, N.; Pace, N.R. Molecular-phylogenetic characterization of microbial community imbalances in human inflammatory bowel diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13780–13785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinane, C.M.; Cotter, P.D. Role of the gut microbiota in health and chronic gastrointestinal disease: Understanding a hidden metabolic organ. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2013, 6, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.J.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, J.S.; Oh, D.G.; Um, Y.J.; Seo, C.S.; Han, J.W.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, G.H.; Jeong, T.C.; et al. The effect of gut microbiota on drug metabolism. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2013, 9, 1295–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikov, M. The metabolism of drugs by the gut flora. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 1994, 19, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.G.; Kang, M.J.; Kim, H.G.; Oh, D.G.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, S.K.; Jeong, T.C. Role of intestinal microflora in xenobiotic-induced toxicity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.J.; Ha, H.W.; Kim, G.H.; Lee, S.K.; Ahn, Y.T.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, H.G.; Jeong, T.C. Role of metabolism by intestinal bacteria in arbutin-induced suppression of lymphoproliferative response in vitro. Biomol. Ther. 2012, 20, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.J.; Ha, H.W.; Kim, H.G.; Lee, D.H.; Kong, M.J.; Ahn, Y.T.; Kim, D.H.; Shin, B.S.; Kang, W.; Jeong, H.G.; et al. Role of metabolism by intestinal bacteria in arbutin-induced toxicity in vitro. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.J.; Khanal, T.; Kim, H.G.; Lee, D.H.; Yeo, H.K.; Lee, Y.S.; Ahn, Y.T.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, H.G.; Jeong, T.C. Role of metabolism by human intestinal microflora in geniposide-induced toxicity in HepG2 cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.J.; Ko, G.S.; Oh, D.G.; Kim, J.S.; Noh, K.; Kang, W.; Yoon, W.K.; Kim, H.C.; Jeong, H.G.; Jeong, T.C. Role of metabolism by intestinal microbiota in pharmacokinetics of oral baicalin. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishimaru, K.; Nishikawa, K.; Omoto, T.; Asai, I.; Yoshihira, K.; Shimomura, K. Two flavone 2′-glucosides from Scutellaria baicalensis. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Shieh, D.E. The anti-inflammatory activity of Scutellaria rivularis extracts and its active components, baicalin, baicalein and wogonin. Am. J. Chin. Med. 1996, 24, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li-Weber, M. New therapeutic aspects of flavones: The anticancer properties of Scutellaria and its main active constituents wogonin, baicalein and baicalin. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2009, 35, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, H.T.; Joh, E.H.; Kwak, H.Y.; Baek, N.I.; Kim, D.H. Anti-pruritic effect of baicalin and its metabolites, baicalein and oroxylin A, in mice. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2010, 31, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Jang, I.S.; Lee, H.K.; Jung, E.A.; Lee, K.Y. Metabolism of glycyrrhizin and baicalin by human intestinal bacteria. Arch. Pharm. Res. 1996, 19, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Jung, E.A.; Sohng, I.S.; Han, J.A.; Kim, T.H.; Han, M.J. Intestinal bacterial metabolism of flavonoids and its relation to some biological activities. Arch. Pharm. Res. 1998, 21, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, J.J.; Cho, K.H.; Jung, W.S.; Moon, S.K.; Park, E.K.; Kim, D.H. Biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1, crocin, amygdalin, geniposide, puerarin, ginsenoside Re, hesperidin, poncirin, glycyrrhizin, and baicalin by human fecal microflora and its relation to cytotoxicity against tumor cells. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 18, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, G.; Chang, Q.; Zuo, Z. Role of intestinal first-pass metabolism of baicalein in its absorption process. Pharm. Res. 2005, 22, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, G.; Zuo, Z. Involvement of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases in the extensive liver and intestinal first-pass metabolism of flavonoid baicalein. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.J.; Kim, U.; Kim, I.S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, D.H.; Han, S.B.; Kwon, O.S.; Yoo, H.H. Effects of gut microflora on pharmacokinetics of hesperidin: A study on non-antibiotic and pseudo-germ-free rats. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2010, 73, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, J.; Chen, X.; Sun, Y.; Luan, Y.; Zhong, D. Interaction of baicalin and baicalein with antibiotics in the gastrointestinal tract. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2005, 57, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akao, T.; Kawabata, K.; Yanagisawa, E.; Ishihara, K.; Mizuhara, Y.; Wakui, Y.; Sakashita, Y.; Kobashi, K. Baicalin, the predominant flavone glucuronide of scutellariae radix, is absorbed from the rat gastrointestinal tract as the aglycone and restored to its original form. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2000, 52, 1563–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Delzenne, N.M. The role of the gut microbiota in energy metabolism and metabolic disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 1546–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, M.; Qian, D.; Shang, E.X.; Jiang, S.; Guo, J.; Duan, J.A.; Du, L. Comparative metabolism of Radix scutellariae extract by intestinal bacteria from normal and type 2 diabetic mice in vitro. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 153, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.X.; Shi, Q.Z.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X.J.; Liu, S.Z.; Qiu, X.M. Comparative pharmacokinetics of baicalin in normal and the type 2 diabetic rats after oral administration of the Radix scutellariae extract. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.S.; Hwang, C.J.; Jung, H.W.; Park, Y.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Kang, J.S.; Cho, C.W. Comparative pharmacokinetics of a marker compound, baicalin in KOB extract after oral administration to normal and allergic-induced rats. Drug Deliv. 2014, 21, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, J.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Moon, S.K.; Cho, K.H.; Bae, H.S.; Kim, J.J.; Park, E.K.; Kim, D.H. Metabolic activities of ginsenoside Rb1, baicalin, glycyrrhizin and geniposide to their bioactive compounds by human intestinal microflora. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 1580–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobashi, K.; Akao, T. Relation of intestinal bacteria to pharmacological effects of glycosides. Biosci. Microflora 1997, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human Microbiome Project Consortium. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Nam, Y.D.; Jung, M.J.; Roh, S.W.; Kim, M.S.; Bae, J.W. Comparative analysis of Korean human gut microbiota by barcoded pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Ruan, Q.; Bedner, E.; Deptala, A.; Wang, X.; Hsieh, T.C.; Traganos, F.; Darzynkiewicz, Z. Effects of the flavonoid baicalin and its metabolite baicalein on androgen receptor expression, cell cycle progression and apoptosis of prostate cancer cell lines. Cell Prolif. 2001, 34, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikemoto, S.; Sugimura, K.; Yoshida, N.; Yasumoto, R.; Wada, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Kishimoto, T. Antitumor effects of Scutellariae radix and its components baicalein, baicalin, and wogonin on bladder cancer cell lines. Urology 2000, 55, 951–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiming, L.; Xuehua, J. Investigation of the absorption mechanisms of baicalin and baicalein in rats. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.A.; Jang, S.E.; Hong, S.W.; Hana, M.J.; Kim, D.H. The role of intestinal microflora in anti-inflammatory effect of baicalin in mice. Biomol. Ther. 2012, 20, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanal, T.; Kim, H.G.; Choi, J.H.; Park, B.H.; Do, M.T.; Kang, M.J.; Yeo, H.K.; Kim, D.H.; Kang, W.; Jeong, T.C.; et al. Protective role of intestinal bacterial metabolism against baicalin-induced toxicity in HepG2 cell cultures. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 37, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Qi, B.; Liu, F.J.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Jia, L.J.; Qiao, H.L. Inhibition of baicalin on metabolism of phenacetin, a probe of CYP1A2, in human liver microsomes and in rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Fang, Y.; Qi, B.; Jia, L.J.; Jin, H.; Qiao, H.L. Pharmacokinetic changes of unbound theophylline are due to plasma protein binding displacement and CYP1A2 activity inhibition by baicalin in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 150, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, K.; Nepal, M.R.; Jeong, K.S.; Kim, S.A.; Um, Y.J.; Seo, C.S.; Kang, M.J.; Park, P.H.; Kang, W.; Jeong, H.G.; et al. Effects of baicalin on oral pharmacokinetics of caffeine in rats. Biomol. Ther. 2015, 23, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Cheng, Z.Y.; Jin, H.; Gao, J.; Qiao, H.L. Inhibitory effects of baicalin on the expression and activity of CYP3A induce the pharmacokinetic changes of midazolam in rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.Y.; Tian, X.; Gao, J.; Li, H.M.; Jia, L.J.; Qiao, H.L. Contribution of baicalin on the plasma protein binding displacement and CYP3A activity inhibition to the pharmacokinetic changes of nifedipine in rats in vivo and in vitro. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Zou, D.; Qiao, H.L. Concentration-dependent inhibitory effect of baicalin on the plasma protein binding and metabolism of chlorzoxazone, a CYP2E1 probe substrate, in rats in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalapos-Kovacs, B.; Magda, B.; Jani, M.; Fekete, Z.; Szabo, P.T.; Antal, I.; Krajcsi, P.; Klebovich, I. Multiple ABC transporters efflux baicalin. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 1987–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Zhang, W.; Guo, D.; Tan, Z.R.; Xu, P.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.Z.; Zhang, L.; He, T.Y.; Hu, D.L.; et al. The effect of herbal medicine baicalin on pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin, substrate of organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1B1. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, S.; Nabekura, T.; Takahashi, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Sakamoto, H.; Tano, H.; Hirai, M.; Tsukahara, G. Structure-activity relationships of the inhibitory effects of flavonoids on P-glycoprotein-mediated transport in KB-C2 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 2274–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.A.; Choi, J.S.; Burm, J.P. Effects of the antioxidant baicalein on the pharmacokinetics of nimodipine in rats: A possible role of P-glycoprotein and CYP3A4 inhibition by baicalein. Pharmacol. Rep. 2011, 63, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.Y.; Hsiu, S.L.; Hou, Y.C.; Tsai, S.Y.; Chao, P.D. Significant decrease of cyclosporine bioavailability in rats caused by a decoction of the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis. Planta Med. 2004, 70, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Kim, M.; Choi, H.; Choi, J. Effects of baicalein on the pharmacokinetics of tamoxifen and its main metabolite, 4-hydroxytamoxifen, in rats: Possible role of cytochrome P450 3A4 and P-glycoprotein inhibition by baicalein. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 1965–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Mial, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. In vitro potential modulation of baicalin and baicalein on P-glycoprotein activity and expression in Caco-2 cells and rat gut sacs. Pharm. Biol. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Gandra, S.; Ashok, A.; Caudron, Q.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global antibiotic consumption 2000 to 2010: An analysis of national pharmaceutical sales data. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.Y.; Zhang, L.; Moro, A.; Chen, M.C.; Harris, D.M.; Eibl, G.; Go, V.L. Detection of baicalin metabolites baicalein and oroxylin-a in mouse pancreas and pancreatic xenografts. Pancreas 2012, 41, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H. Gut-microbiota-mediated drug-antibiotic interactions. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2015, 43, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miocinovic, R.; McCabe, N.P.; Keck, R.W.; Jankun, J.; Hampton, J.A.; Selman, S.H. In vivo and in vitro effect of baicalein on human prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 26, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Test Substances (Route of Administration) | Substrate Drugs (Route of Administration) | Pharmacokinetic Change of Substrate Drugs | Mechanism of Drug Interaction | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baicalin (i.v.) | Phenacetin (i.v.) | Cmax ↓, C60min ↑, t1/2 ↑, Vd ↑, CL ↓, AUC∞ ↑ | Plasma protein binding displacement CYP1A2 inhibition | [38] |
| Baicalin (i.v.) | Theophylline (i.v.) | Cmax ↓, t1/2 ↑, Vd ↑, CL ↓, AUC∞ ↑ | Plasma protein binding displacement CYP1A2 inhibition | [39] |
| Baicalin (p.o.) | Caffeine (p.o.) | No significant changes in parameters | Plasma baicalin was not enough for CYP inhibition | [40] |
| Baicalin (i.v.) | Midazolam (i.v.) | CL ↓, AUC∞ ↑ | CYP3A inhibition | [41] |
| Baicalin (i.v.) | Nifedipine (i.v.) | Cmax ↓, Vd ↑, CL ↑, AUC∞ ↓ | Plasma protein binding displacement CYP3A inhibition | [42] |
| Baicalin (i.v.) | Chlorzoxazone (i.v.) | Cmax ↓, t1/2 ↑, Vd ↑ | Plasma protein binding displacement CYP2E1 inhibition | [43] |
| Baicalin (p.o.) | Rosuvastatin (p.o.) | t1/2 ↓, CL ↑, AUC∞ ↓ | OATP1B1 induction | [45] |
| Baicalein (p.o.) | Nimodipine (p.o.) | Cmax ↑, AUC ↑ | CYP3A inhibition P-gp inhibition | [47] |
| Baicalin (p.o.) | Cyclosporine (p.o.) | Cmax ↑, AUC ↑ | CYP3A inhibition P-gp inhibition | [48] |
| Baicalein (p.o.) | Cyclosporine (p.o.) | - | CYP3A inhibition P-gp inhibition | [48] |
| Baicalein (p.o.) | Tamoxifen (p.o.) | Cmax ↑, AUC ↑, CL ↓ | CYP3A inhibition P-gp inhibition | [49] |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noh, K.; Kang, Y.; Nepal, M.R.; Jeong, K.S.; Oh, D.G.; Kang, M.J.; Lee, S.; Kang, W.; Jeong, H.G.; Jeong, T.C. Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Baicalin-Induced Drug Interaction and Its Pharmacokinetics. Molecules 2016, 21, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030337
Noh K, Kang Y, Nepal MR, Jeong KS, Oh DG, Kang MJ, Lee S, Kang W, Jeong HG, Jeong TC. Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Baicalin-Induced Drug Interaction and Its Pharmacokinetics. Molecules. 2016; 21(3):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030337
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoh, Keumhan, Youra Kang, Mahesh Raj Nepal, Ki Sun Jeong, Do Gyeong Oh, Mi Jeong Kang, Sangkyu Lee, Wonku Kang, Hye Gwang Jeong, and Tae Cheon Jeong. 2016. "Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Baicalin-Induced Drug Interaction and Its Pharmacokinetics" Molecules 21, no. 3: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030337
APA StyleNoh, K., Kang, Y., Nepal, M. R., Jeong, K. S., Oh, D. G., Kang, M. J., Lee, S., Kang, W., Jeong, H. G., & Jeong, T. C. (2016). Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Baicalin-Induced Drug Interaction and Its Pharmacokinetics. Molecules, 21(3), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030337