Qingxuan Jiangya Decoction Reverses Vascular Remodeling by Inducing Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Apoptosis in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. HPLC Fingerprint Analysis of QXJYD
2.2. QXJYD Decreased Elevation of Blood Pressure in SHRs
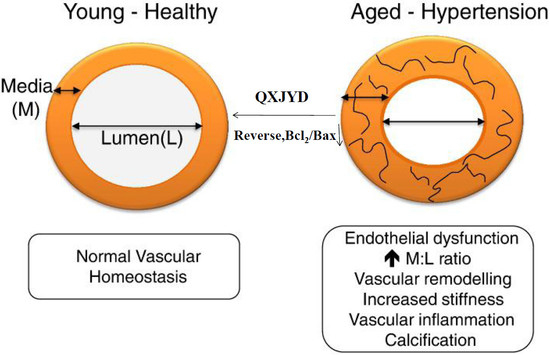
2.3. QXJYD Reversed Vascular Remodeling in SHRs
2.4. QXJYD Promoted VSMC Apoptosis in SHRs
2.5. QXJYD Inhibited Anti-Apoptotic Bcl-2/Bax Ratio in Thoracic Aorta of SHRs
2.6. QXJYD Reduced Plasma Ang II Production in SHRs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Preparation and HPLC Analysis of QXJYD
4.3. Animals
4.4. Drug Administration and Blood Pressure Measurement
4.5. Vessel Morphometry
4.6. In Situ Apoptosis Detection by TUNEL Staining
4.7. Immunohistochemistry Analysis
4.8. RNA Extraction and Quantitative PCR Analysis
4.9. Measurement of Ang II in Rat Plasma
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piper, M.A.; Evans, C.V.; Burda, B.U.; Margolis, K.L.; O’Connor, E.; Smith, N.; Webber, E.; Perdue, L.A.; Bigler, K.D.; Whitlock, E.P. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Evidence Syntheses, formerly Systematic Evidence Reviews. In Screening for High Blood Pressure in Adults: A Systematic Evidence Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.S.; Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Danaei, G.; Shibuya, K.; Adair-Rohani, H.; Amann, M.; Anderson, H.R.; Andrews, K.G.; Aryee, M.; et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2224–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulter, N.R.; Prabhakaran, D.; Caulfield, M. Hypertension. Lancet 2015, 386, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, G.R.; Selemidis, S.; Griendling, K.K.; Sobey, C.G. Combating oxidative stress in vascular disease: Nadph oxidases as therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birns, J.; Markus, H.; Kalra, L. Blood pressure reduction for vascular risk: Is there a price to be paid? Stroke J. Cereb. Circ. 2005, 36, 1308–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzoni, D.; Agabiti-Rosei, E. Structural abnormalities of small resistance arteries in essential hypertension. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2012, 7, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heistad, D.D.; Armstrong, M.L.; Baumbach, G.L.; Faraci, F.M. Sick vessel syndrome. Recovery of atherosclerotic and hypertensive vessels. Hypertension 1995, 26, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folkow, B. Hypertensive structural changes in systemic precapillary resistance vessels: How important are they for in vivo haemodynamics? J. Hypertens. 1995, 13, 1546–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutouyrie, P.; Bussy, C.; Lacolley, P.; Girerd, X.; Laloux, B.; Laurent, S. Association between local pulse pressure, mean blood pressure, and large-artery remodeling. Circulation 1999, 100, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchand, E.L.; Der Sarkissian, S.; Hamet, P.; deBlois, D. Caspase-dependent cell death mediates the early phase of aortic hypertrophy regression in losartan-treated spontaneously hypertensive rats. Circ. Res. 2003, 92, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A.B.; Ettenson, D.S.; Jonas, M.; Nugent, M.A.; Iozzo, R.V.; Edelman, E.R. Endothelial cells provide feedback control for vascular remodeling through a mechanosensitive autocrine TGF-beta signaling pathway. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurtry, M.S.; Bonnet, S.; Wu, X.; Dyck, J.R.; Haromy, A.; Hashimoto, K.; Michelakis, E.D. Dichloroacetate prevents and reverses pulmonary hypertension by inducing pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell apoptosis. Circ. Res. 2004, 95, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, J.F.; Wyllie, A.H.; Currie, A.R. Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br. J. Cancer 1972, 26, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, C.B. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 1995, 267, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, F.; Panizo, A.; Pardo-Mindan, J.; Diez, J. Susceptibility to apoptosis measured by MYC, BCL-2, and BAX expression in arterioles and capillaries of adult spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 1999, 12, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.R.; Evan, G.I.; Newby, A.C. Deregulated expression of the c-MYC oncogene abolishes inhibition of proliferation of rat vascular smooth muscle cells by serum reduction, interferon-gamma, heparin, and cyclic nucleotide analogues and induces apoptosis. Circ. Res. 1994, 74, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez, J.; Panizo, A.; Hernandez, M.; Pardo, J. Is the regulation of apoptosis altered in smooth muscle cells of adult spontaneously hypertensive rats? Hypertension 1997, 29, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, T.; Xu, J.; Bian, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y. Effect and mechanism of gastrodin in relaxing isolated thoracic aorta rings in rats. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2012, 37, 2135–2138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.Y.; Rhyu, M.R. Synergistic vasorelaxant and antihypertensive effects of Ligusticum wallichii and Angelica gigas. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 130, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Zhong, R.; Xia, Z.; Song, J.; Feng, L. Neuroprotective effects of rhynchophylline against ischemic brain injury via regulation of the AKT/mtor and tlrs signaling pathways. Molecules 2014, 19, 11196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, X.; Cui, Y.; Deng, W.; Xu, D.; Han, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, D. Isorhynchophylline protects against pulmonary arterial hypertension and suppresses pasmcs proliferation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 450, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, D.S.; Chang, Y.S.; Li, T.C.; Peng, W.H. Prescription pattern of Chinese herbal products for hypertension in Taiwan: A population-based study. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 1534–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, Y.; Chao, S.; Ju, Z.Y.; Wang, J.; Xue, X.; Qi, T.G.; Cheng, G.H.; Kong, F. Therapeutic effects of baicalin on monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension by inhibiting inflammatory response. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 26, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Yan, S.; Chen, M.; Chen, A.; Yao, D.; Xu, X.; Cai, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, X. Effects of baicalin on collagen iota and collagen iotaiotaiota expression in pulmonary arteries of rats with hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 35, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hillege, H.L.; Girbes, A.R.; de Kam, P.J.; Boomsma, F.; de Zeeuw, D.; Charlesworth, A.; Hampton, J.R.; van Veldhuisen, D.J. Renal function, neurohormonal activation, and survival in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 2000, 102, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, S.; Boutouyrie, P. The structural factor of hypertension: Large and small artery alterations. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1007–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoo, S.; Koyama, M.; Kato, M.; Hirata, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Yamasaki, H.; Wada, A.; Wada, K.; Nishibe, S.; Nakamura, K. The restorative effects of Eucommia ulmoides oliver leaf extract on vascular function in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Molecules 2015, 20, 21971–21981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bascands, J.L.; Girolami, J.P.; Troly, M.; Escargueil-Blanc, I.; Nazzal, D.; Salvayre, R.; Blaes, N. Angiotensin II induces phenotype-dependent apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertension 2001, 38, 1294–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Akishita, M.; Pollman, M.J.; Gibbons, G.H.; Dzau, V.J.; Horiuchi, M. Angiotensin II type 2 receptor mediates vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis and antagonizes angiotensin II type 1 receptor action: An in vitro gene transfer study. Life Sci. 1998, 63, PL289–PL295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Chen, W.; Gao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Luo, M. Molecular mechanisms associated with angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptide activity on vascular extracellular matrix remodeling. Cardiology 2014, 127, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovdahl, C.; Thyberg, J.; Hultgardh-Nilsson, A. The synthetic metalloproteinase inhibitor batimastat suppresses injury-induced phosphorylation of map kinase ERK1/ERK2 and phenotypic modification of arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro. J. Vasc. Res. 2000, 37, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashino, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Numazawa, S. NRF2/keap1 system regulates vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis for vascular homeostasis: Role in neointimal formation after vascular injury. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhu, J.; Gao, S.; Pang, J.; Zhu, D.; Sun, Z. Transforming growth factor-beta1 upregulation triggers pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation and apoptosis imbalance in rats with hypoxic pulmonary hypertension via the PTEN/AKT pathways. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 77, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nour-Eldine, W.; Ghantous, C.M.; Zibara, K.; Dib, L.; Issaa, H.; Itani, H.A.; El-Zein, N.; Zeidan, A. Adiponectin attenuates angiotensin II-induced vascular smooth muscle cell remodeling through nitric oxide and the rhoa/rock pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Not available.






| Gene Name | Sequence |
|---|---|
| β-actin | F: 5′-TGTCACCAACTGGGACGATA-3′ |
| R: 5′-GGGGTGTTGAAGGTCTCAAA-3′ | |
| Bax | F: 5′-TGCTACAGGGTTTCATCCAG-3′ |
| R: 5′-TGTTGTTGTCCAGTTCATCG-3′ | |
| Bcl-2 | F: 5′-GGTGGACAACATCGCTCTG-3′ |
| R: 5′-ACAGCCAGGAGAAATCAAACA-3′ |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, F.; He, F.; Chen, H.; Lin, S.; Shen, A.; Chen, Y.; Chu, J.; Peng, J. Qingxuan Jiangya Decoction Reverses Vascular Remodeling by Inducing Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Apoptosis in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Molecules 2016, 21, 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070956
Xiao F, He F, Chen H, Lin S, Shen A, Chen Y, Chu J, Peng J. Qingxuan Jiangya Decoction Reverses Vascular Remodeling by Inducing Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Apoptosis in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Molecules. 2016; 21(7):956. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070956
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Fei, Fei He, Hongwei Chen, Shan Lin, Aling Shen, Youqin Chen, Jianfeng Chu, and Jun Peng. 2016. "Qingxuan Jiangya Decoction Reverses Vascular Remodeling by Inducing Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Apoptosis in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats" Molecules 21, no. 7: 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070956
APA StyleXiao, F., He, F., Chen, H., Lin, S., Shen, A., Chen, Y., Chu, J., & Peng, J. (2016). Qingxuan Jiangya Decoction Reverses Vascular Remodeling by Inducing Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Apoptosis in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Molecules, 21(7), 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070956