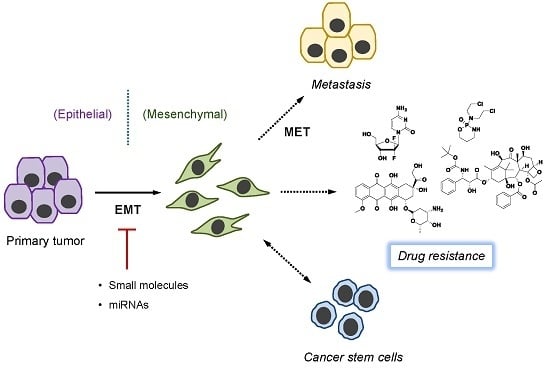
Targeting Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) to Overcome Drug Resistance in Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. EMT-Related Signaling Pathways
3. EMT and Cancer Drug Resistance
4. Mechanism of EMT-Induced Drug Resistance
5. Overcoming Drug Resistance by Targeting EMT
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Juchum, M.; Gunther, M.; Laufer, S.A. Fighting cancer drug resistance: Opportunities and challenges for mutation-specific EGFR inhibitors. Drug Resist. Update 2015, 20, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottesman, M.M. Mechanisms of cancer drug resistance. Ann. Rev. Med. 2002, 53, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartalou, M.; Essigmann, J.M. Mechanisms of resistance to cisplatin. Mutat. Res. 2001, 478, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, E.D. An overview of epithelio-mesenchymal transformation. Acta Anat. 1995, 154, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiery, J.P. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and pathologies. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2003, 15, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, D.M.; Medici, D. Signaling mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci. Signal 2014, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaimori, A.; Potter, J.; Kaimori, J.Y.; Wang, C.; Mezey, E.; Koteish, A. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 induces an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition state in mouse hepatocytes in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 22089–22101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yook, J.I.; Li, X.Y.; Ota, I.; Fearon, E.R.; Weiss, S.J. Wnt-dependent regulation of the E-cadherin repressor snail. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 11740–11748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmerman, L.A.; Grego-Bessa, J.; Raya, A.; Bertran, E.; Perez-Pomares, J.M.; Diez, J.; Aranda, S.; Palomo, S.; McCormick, F.; Izpisua-Belmonte, J.C.; et al. Notch promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition during cardiac development and oncogenic transformation. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, Y.A.; Kang, M.H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, B.H.; Park, J.K.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, J.S.; Oh, S.C. Sonic hedgehog pathway promotes metastasis and lymphangiogenesis via activation of Akt, EMT, and MMP-9 pathway in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7061–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokavec, M.; Oner, M.G.; Li, H.; Jackstadt, R.; Jiang, L.; Lodygin, D.; Kaller, M.; Horst, D.; Ziegler, P.K.; Schwitalla, S.; et al. IL-6R/STAT3/miR-34a feedback loop promotes EMT-mediated colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1853–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustakas, A.; Heldin, C.H. Non-Smad TGF-beta signals. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 3573–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamouille, S.; Connolly, E.; Smyth, J.W.; Akhurst, R.J.; Derynck, R. TGF-beta-induced activation of mTOR complex 2 drives epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell invasion. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 1259–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grotegut, S.; von Schweinitz, D.; Christofori, G.; Lehembre, F. Hepatocyte growth factor induces cell scattering through MAPK/Egr-1-mediated upregulation of Snail. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3534–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Litzenburger, B.C.; Cui, X.J.; Delgado, D.A.; Grabiner, B.C.; Lin, X.; Lewis, M.T.; Gottardis, M.M.; Wong, T.W.; Attar, R.M.; et al. Constitutively active type I insulin-like growth factor receptor causes transformation and xenograft growth of immortalized mammary epithelial cells and is accompanied by an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition mediated by NF-kappa B and snail. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 3165–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batlle, E.; Sancho, E.; Franci, C.; Dominguez, D.; Monfar, M.; Baulida, J.; de Herreros, A.G. The transcription factor Snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comijn, J.; Berx, G.; Vermassen, P.; Verschueren, K.; van Grunsven, L.; Bruyneel, E.; Mareel, M.; Huylebroeck, D.; van Roy, F. The two-handed E box binding zinc finger protein SIP1 downregulates E-cadherin and induces invasion. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Moreno, M.A.; Locascio, A.; Rodrigo, I.; Dhondt, G.; Portillo, F.; Nieto, M.A.; Cano, A. A new role for E12/E47 in the repression of E-cadherin expression and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 27424–27431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.Y.J.; Guilford, P.; Thiery, J.P. Early events in cell adhesion and polarity during epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 4417–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheelock, M.J.; Shintani, Y.; Maeda, M.; Fukumoto, Y.; Johnson, K.R. Cadherin switching. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.; Christofori, G. EMT, the cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009, 28, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommers, C.L.; Heckford, S.E.; Skerker, J.M.; Worland, P.; Torri, J.A.; Thompson, E.W.; Byers, S.W.; Gelmann, E.P. Loss of epithelial markers and acquisition of vimentin expression in adriamycin-resistant and vinblastine-resistant human breast-cancer cell-lines. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 5190–5197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, T.; Ramachandran, V.; Fournier, K.F.; Wang, H.M.; Marquis, L.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Gallick, G.E.; Logsdon, C.D.; McConkey, D.J.; Choi, W. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition contributes to drug resistance in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5820–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConkey, D.J.; Choi, W.; Marquis, L.; Martin, F.; Williams, M.B.; Shah, J.; Svatek, R.; Das, A.; Adam, L.; Kamat, A.; et al. Role of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in drug sensitivity and metastasis in bladder cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009, 28, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Li, H.Z.; Ren, G.S. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and drug resistance in breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.R.; Durrans, A.; Lee, S.; Sheng, J.T.; Li, F.H.; Wong, S.T.C.; Choi, H.J.; El Rayes, T.; Ryu, S.H.; Troeger, J.; et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is not required for lung metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance. Nature 2015, 527, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.F.; Carstens, J.L.; Kim, J.; Scheible, M.; Kaye, J.; Sugimoto, H.; Wu, C.C.; LeBleu, V.S.; Kalluri, R. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is dispensable for metastasis but induces chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 527, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teicher, B.A.; Holden, S.A.; Ara, G.; Chen, G. Transforming growth factor-beta in in vivo resistance. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1996, 37, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, D. Animal models and the tumor microenvironment: Studies of tumor-host symbiosis. Semin. Oncol. 2014, 41, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.P.; Liu, H.; Yu, J.P.; Yu, H.G. Chemoresistance to doxorubicin induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition via upregulation of transforming growth factor signaling in HCT116 colon cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Ginther, C.; Kim, J.; Mosher, N.; Chung, S.Y.; Slamon, D.; Vadgama, J.V. Expression of Wnt3 activates Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and promotes EMT-like phenotype in trastuzumab-resistant HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Corte, C.M.; Bellevicine, C.; Vicidomini, G.; Vitagliano, D.; Malapelle, U.; Accardo, M.; Fabozzi, A.; Fiorelli, A.; Fasano, M.; Papaccio, F.; et al. SMO gene amplification and activation of the Hedgehog pathway as novel mechanisms of resistance to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor drugs in human lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4686–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.J.; Zhang, W.; Xu, X.M.; Zhang, F.; Tao, W.P.; Ye, J.J.; Ge, W. Twist mediates an aggressive phenotype in human colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.J.; Zhang, L.; Xie, B.W.; Wang, X.P.; Yang, X.H.; Ding, N.H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.Q.; Tan, G.L.; Feng, D.Y.; et al. FOXC2 promotes chemoresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinomas via induction of epithelial mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. 2015, 363, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, W.T.; Huang, Y.F.; Tsai, H.Y.; Chen, C.C.; Chang, C.H.; Huang, S.C.; Hsu, K.F.; Chou, C.Y. FOXM1 confers to epithelial-mesenchymal transition, stemness and chemoresistance in epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 2349–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Tian, A.X.; Wang, Q.S.; Kong, P.Z.; Du, X.; Li, X.Q.; Feng, Y.M. FOXF2 suppresses the FOXC2-mediated epithelial mesenchymal transition and multidrug resistance of basal-like breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015, 367, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haslehurst, A.M.; Koti, M.; Dharsee, M.; Nuin, P.; Evans, K.; Geraci, J.; Childs, T.; Chen, J.; Li, J.R.; Weberpals, J.; Davey, S.; et al. EMT transcription factors snail and slug directly contribute to cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebzehnrubl, F.A.; Silver, D.J.; Tugertimur, B.; Deleyrolle, L.P.; Siebzehnrubl, D.; Sarkisian, M.R.; Devers, K.G.; Yachnis, A.T.; Kupper, M.D.; Neal, D.; et al. The ZEB1 pathway links glioblastoma initiation, invasion and chemoresistance. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 1196–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Hawkins, C.; Clarke, I.D.; Squire, J.A.; Bayani, J.; Hide, T.; Henkelman, R.M.; Cusimano, M.D.; Dirks, P.B. Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature 2004, 432, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, M.A.; Kraut, N.; Beug, H. Molecular requirements for epithelial-mesenchymal transition during tumor progression. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 2005, 17, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, S.A.; Guo, W.; Liao, M.J.; Eaton, E.N.; Ayyanan, A.; Zhou, A.Y.; Brooks, M.; Reinhard, F.; Zhang, C.C.; Shipitsin, M.; et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 2008, 133, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Settleman, J. EMT, cancer stem cells and drug resistance: An emerging axis of evil in the war on cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4741–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biddle, A.; Liang, X.; Gammon, L.; Fazil, B.; Harper, L.J.; Emich, H.; Costea, D.E.; Mackenzie, I.C. Cancer stem cells in squamous cell carcinoma switch between two distinct phenotypes that are preferentially migratory or proliferative. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5317–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.L.; Cong, Y.; Wang, D.; Sun, Y.; Deng, L.; Liu, Y.J.; Martin-Trevino, R.; Shang, L.; McDermott, S.P.; Landis, M.D.; et al. Breast cancer stem cells transition between epithelial and mesenchymal states reflective of their normal counterparts. Stem Cell Rep. 2014, 2, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocana, O.H.; Corcoles, R.; Fabra, A.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Acloque, H.; Vega, S.; Barrallo-Gimeno, A.; Cano, A.; Nieto, M.A. Metastatic colonization requires the repression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition inducer Prrx1. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 709–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottesman, M.M.; Fojo, T.; Bates, S.E. Multidrug resistance in cancer: Role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aller, S.G.; Yu, J.; Ward, A.; Weng, Y.; Chittaboina, S.; Zhuo, R.P.; Harrell, P.M.; Trinh, Y.T.; Zhang, Q.H.; Urbatsch, I.L.; et al. Structure of P-plycoprotein reveals a molecular basis for poly-specific drug binding. Science 2009, 323, 1718–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, M.; Henderson, M.; Haber, M.; Norris, M. Role of the MRP1/ABCC1 multidrug transporter protein in cancer. IUBMB Life 2007, 59, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, K.; Xie, Y.; Baer, M.R.; Ross, D.D. Role of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) in cancer drug resistance. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 1084–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, M.; Stephens, M.A.; Pathak, H.; Rangarajan, A. Transcription factors that mediate epithelial-mesenchymal transition lead to multidrug resistance by upregulating ABC transporters. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uramoto, H.; Iwata, T.; Onitsuka, T.; Shimokawa, H.; Hanagiri, T.; Oyama, T. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in EGFR-TKI acquired resistant lung adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 2513–2517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, X.; Jin, H. EGFR-TKI resistance in NSCLC patients: Mechanisms and strategies. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2014, 4, 411–435. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Witta, S.E.; Gemmill, R.M.; Hirsch, F.R.; Coldren, C.D.; Hedman, K.; Ravdel, L.; Helfrich, B.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Chan, D.C.; Sugita, M.; et al. Restoring E-cadherin expression increases sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.H.; Tsai, M.F.; Su, K.Y.; Wu, S.G.; Huang, C.P.; Yu, S.L.; Yu, Y.L.; Lan, C.C.; Yang, C.H.; Lin, S.B.; et al. Slug confers resistance to the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care 2011, 183, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; He, C.S.; Wei, S.H.; Zhang, L. Notch-1 contributes to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor acquired resistance in non-small cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 3559–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soucheray, M.; Capelletti, M.; Pulido, I.; Kuang, Y.; Paweletz, C.P.; Becker, J.H.; Kikuchi, E.; Xu, C.; Patel, T.B.; Al-Shahrour, F.; et al. Intratumoral heterogeneity in EGFR-mutant NSCLC results in divergent resistance mechanisms in response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibition. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4372–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Song, L.; Bai, Y.; Kinose, F.; Li, J.; Ohaegbulam, K.C.; Munoz-Antonia, T.; Qu, X.; Eschrich, S.; Uramoto, H.; et al. ZEB1 Mediates Acquired Resistance to the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremnes, R.M.; Donnem, T.; Al-Saad, S.; Al-Shibli, K.; Andersen, S.; Sirera, R.; Camps, C.; Marinez, I.; Busund, L.T. The role of tumor stroma in cancer progression and prognosis: Emphasis on carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, J.; Zhang, H.; Wen, Z.; Gu, Y.M.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, T.T.; Jia, C.W.; Lu, Z.H.; Chen, J. Retinoic acid inhibits pancreatic cancer cell migration and EMT through the downregulation of IL-6 in cancer associated fibroblast cells. Cancer Lett. 2014, 345, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, H.; Zhu, L.; Deng, W.; Li, Q. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and drug resistance: Role, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic strategies. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2014, 37, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, M.; Nan, K.J. Activation of PI3 kinase/Akt/HIF-1 alpha pathway contributes to hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 40, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bellamy, W.T. P-glycoproteins and multidrug resistance. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. 1996, 36, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, W.S.; Crowley, J.J.; Salmon, S.S.; Grogan, T.M.; Laufman, L.R.; Weiss, G.R.; Bonnet, J.D. A Phase-III randomized study of oral verapamil as a chemosensitizer to reverse drug-resistance in patients with refractory myeloma—A Southwest Oncology Group study. Cancer 1995, 75, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnle, M.; Egger, M.; Muller, C.; Mahringer, A.; Bernhardt, G.; Fricker, G.; Konig, B.; Buschauer, A. Potent and selective inhibitors of breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2) derived from the P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) modulator tariquidar. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancet, J.E.; Baer, M.R.; Duran, G.E.; List, A.F.; Fielding, R.; Marcelletti, J.F.; Multani, P.S.; Sikic, B.I. A phase I trial of continuous infusion of the multidrug resistance inhibitor zosuquidar with daunorubicin and cytarabine in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2009, 33, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.B.; Onder, T.T.; Jiang, G.; Tao, K.; Kuperwasser, C.; Weinberg, R.A.; Lander, E.S. Identification of selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput screening. Cell 2009, 138, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liang, C.; Xue, F.; Chen, W.; Zhi, X.; Feng, X.; Bai, X.; Liang, T. Salinomycin decreases doxorubicin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting the beta-catenin/TCF complex association via FOXO3a activation. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 10350–10365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermawan, A.; Wagner, E.; Roidl, A. Consecutive salinomycin treatment reduces doxorubicin resistance of breast tumor cells by diminishing drug efflux pump expression and activity. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toden, S.; Okugawa, Y.; Jascur, T.; Wodarz, D.; Komarova, N.L.; Buhrmann, C.; Shakibaei, M.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Curcumin mediates chemosensitization to 5-fluorouracil through miRNA-induced suppression of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in chemoresistant colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meidhof, S.; Brabletz, S.; Lehmann, W.; Preca, B.T.; Mock, K.; Ruh, M.; Schuler, J.; Berthold, M.; Weber, A.; Burk, U.; et al. ZEB1-associated drug resistance in cancer cells is reversed by the class I HDAC inhibitor mocetinostat. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 831–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namba, T.; Kodama, R.; Moritomo, S.; Hoshino, T.; Mizushima, T. Zidovudine, an anti-viral drug, resensitizes gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine by inhibition of the Akt-GSK3 beta-Snail pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.M.; Donnelly, L.A.; Emslie-Smith, A.M.; Alessi, D.R.; Morris, A.D. Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in diabetic patients. BMJ 2005, 330, 1304–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomimoto, A.; Endo, H.; Sugiyama, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Hosono, K.; Takahashi, H.; Nakajima, N.; Nagashima, Y.; Wada, K.; Nakagama, H.; et al. Metformin suppresses intestinal polyp growth in ApcMin/+ mice. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 2136–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiralerspong, S.; Palla, S.L.; Giordano, S.H.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Liedtke, C.; Barnett, C.M.; Hsu, L.; Hung, M.C.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M. Metformin and pathologic complete responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in diabetic patients with breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3297–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, H.A.; Iliopoulos, D.; Tsichlis, P.N.; Struhl, K. Metformin selectively targets cancer stem cells, and acts together with chemotherapy to block tumor growth and prolong remission. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7507–7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Martin, A.; Oliveras-Ferraros, C.; Cufi, S.; Del Barco, S.; Martin-Castillo, B.; Menendez, J.A. Metformin regulates breast cancer stem cell ontogeny by transcriptional regulation of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) status. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 3807–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Cheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Han, R.; Li, L.; Xiang, T.; He, L.; Long, H.; Zhu, B.; He, Y. Metformin inhibits the IL-6-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and lung adenocarcinoma growth and metastasis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, C.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, J.; He, Z. Metformin reverses multidrug resistance and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) via activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in human breast cancer cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2014, 386, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.C.; Lee, K.H.; Lai, I.L.; Wang, D.; Mo, X.; Kulp, S.K.; Shapiro, C.L.; Chen, C.S. AMPK reverses the mesenchymal phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the Akt-MDM2-Foxo3a signaling axis. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 4783–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.F.; Shim, J.S. Existing drugs and their application in drug discovery targeting cancer stem cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2015, 38, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, K.N.; Sim, W.J.; Racine, V.; Lee, S.Y.; Goh, B.C.; Thiery, J.P. A cell-based small molecule screening method for identifying inhibitors of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33183. [Google Scholar]
- Aref, A.R.; Huang, R.Y.; Yu, W.; Chua, K.N.; Sun, W.; Tu, T.Y.; Bai, J.; Sim, W.J.; Zervantonakis, I.K.; Thiery, J.P.; et al. Screening therapeutic EMT blocking agents in a three-dimensional microenvironment. Integr. Biol. 2013, 5, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Tu, T.Y.; Kim, C.; Thiery, J.P.; Kamm, R.D. Identification of drugs as single agents or in combination to prevent carcinoma dissemination in a microfluidic 3D environment. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 36603–36614. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.; Feng, S.; Wei, L.; Wang, Z.; Hong, D.; Wang, Q. Evodiamine, a novel inhibitor of the Wnt pathway, inhibits the self-renewal of gastric cancer stem cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Hu, C.; Liang, S.J.; Fei, X.C.; Yan, N.N.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, F.C. WNT pathway inhibitor pyrvinium pamoate inhibits the self-renewal and metastasis of breast cancer stem cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busaranon, K.; Plaimee, P.; Sritularak, B.; Chanvorachote, P. Moscatilin inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and sensitizes anoikis in human lung cancer H460 cells. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 70, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.R.; Zhang, P.; Wang, H.; Hou, D.M.; Li, W.T.; Xiao, G.S.; Li, C.W. Inhibitory effects of metformin at low concentration on epithelial-mesenchymal transition of CD44(+)CD117(+) ovarian cancer stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, G.; Xu, F.; Qin, T.; Zheng, Q.F.; Shi, D.B.; Xia, W.; Tian, Y.; Tang, Y.L.; Wang, J.S.; Xiao, X.S.; et al. Palbociclib inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in breast cancer via c-Jun/COX-2 signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 41794–41808. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Jiang, C.W.; Han, H.X.; Liu, H.; Tang, M.; Liu, L.X.; Ji, W.Y.; Lu, X.C.; Yang, X.L.; Zhang, Y.X.; et al. Icaritin inhibits the invasion and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of glioblastoma cells by targeting EMMPRIN via PTEN/AKt/HIF-1 alpha signalling. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Phys. 2015, 42, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Wu, G.; Chang, C.; Zhu, F.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Q.H.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, L.L. Disulfiram inhibits TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem-like features in breast cancer via ERK/NF-kappa B/Snail pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 40907–40919. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hseu, Y.C.; Huang, Y.C.; Korivi, M.; Wu, J.J.; Way, T.D.; Ou, T.T.; Chiu, L.W.; Lee, C.C.; Lin, M.L.; Yang, H.L. Zerumbone attenuates TGF-beta 1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition via upregulated E-cadherin expression and downregulated Smad2 signalling pathways in non-small cell lung cancer (A549) cells. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, S.Z.; Che, X.F.; Hou, K.Z.; Ma, Y.J.; Li, C.; Wen, T.; Fan, Y.B.; Hu, X.J.; Liu, Y.P.; et al. Bufalin inhibits TGF-beta-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and migration in human lung cancer A549 cells by downregulating TGF-beta receptors. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004, 431, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, F.H.; Li, Y.W.; Wang, Z.W.; Kong, D.J.; Ali, S. Implication of microRNAs in drug resistance for designing novel cancer therapy. Drug Resist. Update 2010, 13, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.W.; Li, Y.W.; Ahmad, A.; Azmi, A.S.; Kong, D.J.; Banerjee, S.; Sarkar, F.H. Targeting miRNAs involved in cancer stem cell and EMT regulation: An emerging concept in overcoming drug resistance. Drug Resist. Update 2010, 13, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, P.A.; Bert, A.G.; Paterson, E.L.; Barry, S.C.; Tsykin, A.; Farshid, G.; Vadas, M.A.; Khew-Goodall, Y.; Goodall, G.J. The mir-200 family and mir-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.M.; Gaur, A.B.; Lengyel, E.; Peter, M.E. The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Gene Dev. 2008, 22, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellner, U.; Schubert, J.; Burk, U.C.; Schmalhofer, O.; Zhu, F.; Sonntag, A.; Waldvogel, B.; Vannier, C.; Darling, D.; zur Hausen, A.; et al. The EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, U1487–U236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burk, U.; Schubert, J.; Wellner, U.; Schmalhofer, O.; Vincan, E.; Spaderna, S.; Brabletz, T. A reciprocal repression between ZEB1 and members of the miR-200 family promotes EMT and invasion in cancer cells. EMBO Rep. 2008, 9, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishijima, N.; Seike, M.; Soeno, C.; Chiba, M.; Miyanaga, A.; Noro, R.; Sugano, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Kubota, K.; Gema, A. miR-200/ZEB axis regulates sensitivity to nintedanib in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Fang, B.B.; Zeng, F.P.; Ma, C.; Pang, H.J.; Cheng, L.; Shi, Y.; Wang, H.; Yin, B.; Xia, J.; et al. Down-regulation of miR-223 reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 1740–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Lu, X.H.; Zhao, Z.L.; Zhu, L.H.; Chen, S.L.; Wu, Q.; Chen, C.J.; Wang, Z.W. MiR-125b regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition via targeting Sema4C in paclitaxel-resistant breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3268–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Shen, H.; Yin, X.; Long, L.; Xie, C.; Liu, Y.; Hui, L.; Lin, X.; Fang, Y.; Cao, Y.; et al. miR-186 regulation of Twist1 and ovarian cancer sensitivity to cisplatin. Oncogene 2016, 35, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yao, Q.; Tao, Z. miR-15b regulates cisplatin resistance and metastasis by targeting PEBP4 in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 2015, 22, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Li, Y.M.; Hou, Y.Y.; Yang, Q.L.; Chen, S.L.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.S.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.J.; Wang, Z.W.; et al. The PDGF-D/miR-106a/Twist1 pathway orchestrates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gemcitabine resistance hepatoma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7000–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.Z.; Bai, Y.F.; Qiu, S.C.; Zheng, L.; Huang, L.Y.; Liu, T.Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.T.; Xu, N.B.; Yan, X.H.; et al. MiR-203 downregulation is responsible for chemoresistance in human glioblastoma by promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition via SNAI2. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 8914–8928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, A.; Balwierz, A.; Zhang, J.D.; Kublbeck, M.; Pawitan, Y.; Hielscher, T.; Wiemann, S.; Sahin, O. Re-expression of microRNA-375 reverses both tamoxifen resistance and accompanying EMT-like properties in breast cancer. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.P.; Wang, Y.P.; Song, Y.L.; Fu, Z.M.; Yu, W.J. miR-27a regulates cisplatin resistance and metastasis by targeting RKIP in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; He, D.X.; Yang, D.T.; Chen, Z.; Pan, Q.X.; Mao, A.Q.; Cai, Y.F.; Li, X.Y.; Xing, H.; Shi, M.; et al. MiR-489 regulates chemoresistance in breast cancer via epithelial mesenchymal transition pathway. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.H.; Fu, Y.B.; Chen, L.; Lee, W.; Lai, Y.L.; Rezaei, K.; Tabbara, S.; Latham, P.; Teal, C.B.; Man, Y.G.; et al. miR-671–5p inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by downregulating FOXM1 expression in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.H. Cancer stem cells and chemoresistance: The smartest survives the raid. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 160, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, K. Companies waver in efforts to target transforming growth factor beta in cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 1664–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderton, M.J.; Mellor, H.R.; Bell, A.; Sadler, C.; Pass, M.; Powell, S.; Steele, S.J.; Roberts, R.R.A.; Heier, A. Induction of heart valve lesions by small-molecule ALK5 inhibitors. Toxicol. Pathol. 2011, 39, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbertz, S.; Sawyer, J.S.; Stauber, A.J.; Gueorguieva, I.; Driscoll, K.E.; Estrem, S.T.; Cleverly, A.L.; Desaiah, D.; Guba, S.C.; Benhadji, K.A.; et al. Clinical development of galunisertib (LY2157299 monohydrate), a small molecule inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 4479–4499. [Google Scholar]
- Connolly, E.C.; Freimuth, J.; Akhurst, R.J. Complexities of TGF-beta targeted cancer therapy. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 964–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Kang, Y. Probing the fifty shades of EMT in metastasis. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, J.H.; Donaher, J.L.; Murphy, D.A.; Chau, S.; Yang, J. Spatiotemporal regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition is essential for squamous cell carcinoma metastasis. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brabletz, T. EMT and MET in metastasis: Where are the cancer stem cells? Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 699–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biddle, A.; Gammon, L.; Liang, X.; Costea, D.E.; Mackenzie, I.C. Phenotypic plasticity determines cancer stem cell therapeutic resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma. EBioMedicine 2016, 4, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Drugs | Target Genes | Function | Cancer | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curcumin | BMI1, SUZ12 and EZH2 | Inhibits EMT and reverses 5-fluorouracil resistance | Colorectal cancer | [71] |
| Mocetinostat | HDAC | Induces sensitivity against chemotherapy | Pancreatic cancer | [72] |
| Zidovudine | Akt-GSK3 beta-Snail pathway | Inhibits EMT and reverses gemcitabine resistance | Pancreatic cancer | [73] |
| Evodiamine | WNT pathway | Inhibits EMT and reverses oxaliplatin resistance | Gastric cancer | [86] |
| Pyrvinium pamoate | WNT pathway | Inhibits EMT | Breast cancer | [87] |
| Moscatilin | Vimentin, Slug, and Snail | Inhibits EMT and sensitizes anoikis | Lung cancer | [88] |
| Metformin | ZEB1, Slug, Twist and Vimentin | Inhibits EMT | Breast cancer Ovarian cancer | [78,89] |
| Palbociclib | c-Jun/COX-2 | Inhibits EMT | Breast cancer | [90] |
| Icaritin | PTEN/Akt/HIF-1α pathway | Inhibits EMT | Glioblastoma | [91] |
| Disulfiram | ERK/NF-kappa B/Snail pathway | Inhibits EMT and stem cell-like features | Breast cancer | [92] |
| Zerumbone | TGFβ pathway | Inhibits EMT | Non-small cell lung cancer | [93] |
| Bufalin | TGFβ pathway | Inhibits EMT | Lung cancer | [94] |
| miRNA | Target Gene | Function | Cancer | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-200 | ZEB1, ZEB2 | Inhibits EMT and reverses nintedanib resistance | Non-small cell lung cancer | [104] |
| miR-223 | Fbw7 | Induces EMT and confers gemcitabine-resistance | Pancreatic cancer | [105] |
| miR-125b | Sema4C | Inhibits EMT and reverses paclitaxel-resistance | Breast cancer | [106] |
| miR-186 | Twist1 | Inhibits EMT and reverses cisplatin-resistance | Ovarian cancer | [107] |
| miR-15b | PEBP4 | Induces EMT and confers cisplatin resistance | Lung adenocarcinoma | [108] |
| miR-106a | Twist1 | Inhibits EMT and reverses gemcitabine resistance | Hepatocellular carcinoma | [109] |
| miR-203 | Slug | Inhibits EMT and reverses imatinib resistance | Glioblastoma | [110] |
| miR-375 | MTDH | Inhibits EMT and reverses tamoxifen resistance | Breast cancer | [111] |
| miR-27a | RKIP | Induces EMT and confers cisplatin resistance | Lung adenocarcinoma | [112] |
| miR-489 | Smad3 | Inhibits EMT and reverses chemoresistance | Breast cancer | [113] |
| miR-671-5p | FOXM1 | Inhibits EMT and reverses cisplatin resistance | Breast cancer | [114] |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, B.; Shim, J.S. Targeting Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) to Overcome Drug Resistance in Cancer. Molecules 2016, 21, 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070965
Du B, Shim JS. Targeting Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) to Overcome Drug Resistance in Cancer. Molecules. 2016; 21(7):965. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070965
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Bowen, and Joong Sup Shim. 2016. "Targeting Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) to Overcome Drug Resistance in Cancer" Molecules 21, no. 7: 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070965
APA StyleDu, B., & Shim, J. S. (2016). Targeting Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) to Overcome Drug Resistance in Cancer. Molecules, 21(7), 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070965