Endotoxin-Induced Inflammation Suppresses the Effect of Melatonin on the Release of LH from the Ovine Pars Tuberalis Explants—Ex Vivo Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
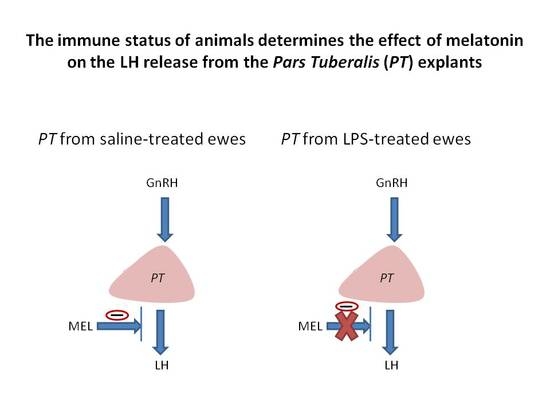
2.1. Influence of GnRH and Melatonin on LH Releasing
2.2. Influence of GnRH and Melatonin on LH Gene Expression
2.3. Effect of GnRH and Melatonin on the Gene Expression of GnRHR, MT1, and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Determination of the Relative Gene Expression
4.2. Radioimmunoassay for LH
4.3. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Todini, L.; Terzano, G.; Borghese, A.; Debenedetti, A.; Malfatti, A. Plasma melatonin in domestic female Mediterranean sheep (Comisana breed) and goats (Maltese and Red Syrian). Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 90, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardeland, R.; Pandi-Perumal, S.; Cardinali, D.P. Melatonin. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Boil. 2006, 38, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Brunet, A.; Santiago-Moreno, J.; Campo, A.D.; Malpaux, B.; Chemineau, P.; Tortonese, D.J.; Gonzalez-Bulnes, A.; López-Sebastián, A. Endogenous circannual cycles of ovarian activity and changes in prolactin and melatonin secretion in wild and domestic female sheep maintained under a long-day photoperiod. Biol. Reprod. 2008, 78, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malpaux, B.; Daveau, A.; Maurice, F.; Gayrard, V.; Thiery, J.-C. Short-day effects of melatonin on luteinizing hormone secretion in the ewe: Evidence for central sites of action in the mediobasal hypothalamus. Biol. Reprod. 1993, 48, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misztal, T.; Romanowicz, K.; Barcikowski, B. Melatonin-a modulator of the GnRH/LH axis in sheep. Reprod. Biol. 2002, 2, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lincoln, G. Effects of placing micro-implants of melatonin in the Pars Tuberalis, pars distalis and the lateral septum of the forebrain on the secretion of FSH and prolactin, and testicular size in rams. J. Endocrinol. 1994, 142, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malpaux, B.T.; Daveau, A.S.; Maurice-Mandon, F.O.; Duarte, G.; Chemineau, P. Evidence that melatonin acts in the premammillary hypothalamic area to control reproduction in the ewe: Presence of binding sites and stimulation of luteinizing hormone secretion by in situ microimplant delivery. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, P.J.; Williams, L.M. The Pars Tuberalis of the pituitary: A gateway for neuroendocrine output. Rev. Reprod. 1996, 1, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, M.; Blázquez, J.L.; Peruzzo, B.; Peláez, B.; Rodríguez, S.; Toranzo, D.; Pastor, F.; Rodríguez, E.M. Cell organization of the rat Pars Tuberalis. Evidence for open communication between Pars Tuberalis cells, cerebrospinal fluid and tanycytes. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 339, 359–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mignot, M.; Skinner, D.C. Colocalization of GH, TSH and prolactin, but not ACTH, with βLH-immunoreactivity: Evidence for pluripotential cells in the ovine pituitary. Cell Tissue Res. 2005, 319, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafarque, M.M.; Ezquer, M.; Aguado, L.I.; Oliveros, L.B. Bovine Pars Tuberalis secretions release growth hormone from rat pars distalis of pituitary gland. Neuroendocrinol. Lett. 2004, 25, 275–279. [Google Scholar]
- Herman, A.; Romanowicz, K.; Tomaszewska-Zaremba, D. Effect of LPS on reproductive system at the level of the pituitary of anestrous ewes. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2010, 45, e351–e359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, A.P.; Krawczyńska, A.; Bochenek, J.; Antushevich, H.; Herman, A.; Tomaszewska-Zaremba, D. Involvement of prolactin in the meloxicam-dependent inflammatory response of the gonadotropic axis to prolonged lipopolysaccharide treatment in anoestrous ewes. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2016, 28, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, A.P.; Krawczyńska, A.; Bochenek, J.; Dobek, E.; Herman, A.; Tomaszewska-Zaremba, D. LPS-induced inflammation potentiates the IL-1-mediated reduction of LH secretion from the anterior pituitary explants. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 926937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, A.; Krawczyńska, A.; Bochenek, J.; Haziak, K.; Romanowicz, K.; Misztal, T.; Antushevich, H.; Herman, A.; Tomaszewska-Zaremba, D. The effect of rivastigmine on the LPS-induced suppression of GnRH/LH secretion during the follicular phase of the estrous cycle in ewes. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2013, 138, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, A.P.; Tomaszewska-Zaremba, D. Effect of endotoxin on the expression of GnRH and GnRHR genes in the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland of anestrous ewes. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2010, 120, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, J.; Abrams, M.; Wagner, C.; Whitlock, B.; Sartin, J. Endotoxin inhibition of luteinizing hormone in sheep. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2003, 25, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, E.; Marquette, C.; Sarrieau, A.; Fitzpatrick, F.; Fillion, G.; Milon, G.; Rostene, W.; Haour, F. Regulation of lnterleukin-1 receptor expression in mouse brain and pituitary by lipopolysaccharide and glucocorticoids. Neuroendocrinology 1993, 58, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnet, P.; Brunke, D.L.; Goujon, E.; Mainard, J.D.; Biragyn, A.; Arkins, S.; Dantzer, R.; Kelley, K.W. Molecular Identification of Two Types of lnterleukin-1 Receptors in the Murine Pituitary Gland. J. Neuroendocrinol. 1993, 5, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Król, K.; Tomaszewska-Zaremba, D.; Herman, A. Photoperiod-dependent effect of inflammation on nocturnal gene expression of proinflammatory cytokines and their receptors in Pars Tuberalis of ewe. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2016, 25, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, D.C.; Robinson, J.E. Luteinising hormone secretion from the perifused ovine Pars Tuberalis and pars distalis: Effects of gonadotropin-releasing hormone and melatonin. Neuroendocrinology 1997, 66, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, K.; Marubayashi, U.; McCann, S. Mediation of the short-loop negative feedback of luteinizing hormone (LH) on LH-releasing hormone release by melatonin-induced inhibition of LH release from the Pars Tuberalis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 7576–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanecek, J. Inhibitory effect of melatonin on GnRH-induced LH release. Rev. Reprod. 1999, 4, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanecek, J.; Watanabe, K. Mechanisms of melatonin action in the pituitary and SCN. In Melatonin after Four Decades: An Assessment Of Its Potential; Olcese, J., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 191–198. ISBN 978-0-306-46134-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ibáñez-Costa, A.; Córdoba-Chacón, J.; Gahete, M.D.; Kineman, R.D.; Castaño, J.P.; Luque, R.M. Melatonin regulates somatotrope and lactotrope function through common and distinct signaling pathways in cultured primary pituitary cells from female primates. Endocrinology 2014, 156, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forcada, F.; Abecia, J.; Casao, A.; Cebrian-Perez, J.; Muino-Blanco, T.; Palacin, I. Effects of ageing and exogenous melatonin on pituitary responsiveness to GnRH in ewes during anestrus and the reproductive season. Theriogenology 2007, 67, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servili, A.; Herrera-Pérez, P.; del Carmen Rendón, M.; Muñoz-Cueto, J.A. Melatonin inhibits GnRH-1, GnRH-3 and GnRH receptor expression in the brain of the European sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 7603–7616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, I.; Sridaran, R. GnRH-GnRH-Receptor System in the Mammalian Female Reproductive Tract. In Reproductive Endocrinology: A Molecular Approach; Chedrese, P.J., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 131–143. ISBN 978-0-387-88185-0. [Google Scholar]
- Haziak, K.; Herman, A.; Tomaszewska-Zaremba, D. The effect of LPS on LH release and gene expression of LH-β, GnRH-R and TLR4 in the anterior pituitary of follicular phase ewes–an in vitro study. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2013, 22, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, A.; Bochenek, J.; Skipor, J.; Król, K.; Krawczyńska, A.; Antushevich, H.; Pawlina, B.; Marciniak, E.; Tomaszewska-Zaremba, D. Interleukin-1 β Modulates Melatonin Secretion in Ovine Pineal Gland: Ex Vivo Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 526464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, A.P.; Herman, A.; Skipor, J.; Krawczyńska, A.; Bochenek, J.; Tomaszewska-Zaremba, D. Caffeine stimulates in vitro pituitary LH secretion in lipopolysaccharide-treated ewes. Reprod. Boil. 2015, 15, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spangelo, B.L.; Judd, A.M.; Isakson, P.C.; MacLeod, R.M. Interleukin-6 stimulates anterior pituitary hormone release in vitro. Endocrinology 1989, 125, 575–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsagarakis, S.; Kontogeorgos, G.; Kovacs, K. The role of cytokines in the normal and neoplastic pituitary. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 1998, 28, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.Y. Prolactin suppresses luteinizing hormone secretion and pituitary responsiveness to luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone by a direct action at the anterior pituitary. Endocrinology 1983, 113, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turzillo, A.; Nolan, T.; Nett, T. Regulation of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) Receptor Gene Expression in Sheep: Interaction of GnRH and Estradiol** A preliminary report has appeared in the abstracts of the 30th Annual Meeting of The Society for the Study of Reproduction. This work was supported by USDA Grant 95-37203-1997 (to TMN). Endocrinology 1998, 139, 4890–4894. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.Y.; Harris, T.G.; Battaglia, D.F.; Viguié, C.; Karsch, F.J. Endotoxin inhibits pituitary responsiveness to gonadotropin-releasing hormone. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 1915–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Conn, P.M. Transcriptional Activation of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) Receptor Gene by GnRH: Involvement of Multiple Signal Transduction Pathways** This study was supported by NIH Grants HD-19899, RR-00163 and HD-18185. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Kim, S.; Leonhardt, S.; Jarry, H.; Wuttke, W.; Kim, K. Effect of interleukin-1b on gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and GnRH receptor gene expression in castrated male rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2000, 12, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciechanowska, M.; Łapot, M.; Malewski, T.; Mateusiak, K.; Misztal, T.; Przekop, F. Effects of corticotropin-releasing hormone and its antagonist on the gene expression of gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and GnRH receptor in the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland of follicular phase ewes. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2011, 23, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lohrer, P.; Gloddek, J.; Nagashima, A.C.; Korali, Z.; Hopfner, U.; Pereda, M.P.; Arzt, E.; Stalla, G.; Renner, U. Lipopolysaccharide Directly Stimulates the Intrapituitary Interleukin-6 Production by Folliculostellate Cells via Specific Receptors and the p38α Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase/Nuclear Factor-κB Pathway** Supported by a grant from the DFG: Sta 285/7–3. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 4457–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuel, K.F.; Kougias, P.; Rice, P.J.; Wei, D.; De Ponti, K.; Wang, J.; Laffan, J.J.; Li, C.; Kalbfleisch, J.; Williams, D.L. Anterior pituitary cells express pattern recognition receptors for fungal glucans: Implications for neuroendocrine immune involvement in response to fungal infections. Neuroimmunomodulation 2004, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongprayoon, P.; Govitrapong, P. Melatonin attenuates methamphetamine-induced neuroinflammation through the melatonin receptor in the SH-SY5Y cell line. Neurotoxicology 2015, 50, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barjavel, M.J.; Mamdouh, Z.; Raghbate, N.; Bakouche, O. Differential expression of the melatonin receptor in human monocytes. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tenn, C.; Niles, L.P. Physiological regulation of melatonin receptors in rat suprachiasmatic nuclei: Diurnal rhythmicity and effects of stress. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1993, 98, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.-E.; Wright, I.K.; Wyse, C.; Samson-Desvignes, N.; Le Blanc, P.; Laroche, S.; Hazlerigg, D.G.; Johnston, J.D. Regulation of pituitary MT1 melatonin receptor expression by gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and early growth response factor-1 (Egr-1): In vivo and in vitro studies. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnston, J.D.; Messager, S.; Ebling, F.J.; Williams, L.M.; Barrett, P.; Hazlerigg, D.G. Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone drives melatonin receptor down-regulation in the developing pituitary gland. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2831–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero, H.Y.; Gauer, F.; Schuster, C.; Pévet, P.; Masson-Pévet, M. Melatonin regulates the mRNA expression of the mt1 melatonin receptor in the rat Pars Tuberalis. Neuroendocrinology 2000, 71, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markus, R.P.; Cecon, E.; Pires-Lapa, M.A. Immune-pineal axis: Nuclear factor κB (NF-kB) mediates the shift in the melatonin source from pinealocytes to immune competent cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10979–10997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molpeceres, V.; Mauriz, J.L.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; González, P.; Barrio, J.P.; González-Gallego, J. Melatonin is able to reduce the apoptotic liver changes induced by aging via inhibition of the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2007, 62, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.G.; Tang, S.T.; Tseng, H.P.; Wu, K.K. Melatonin suppresses macrophage cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by inhibiting p52 acetylation and binding. Blood 2006, 108, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowes, D.A.; Webster, N.R.; Murphy, M.P.; Galley, H.F. Antioxidants that protect mitochondria reduce interleukin-6 and oxidative stress, improve mitochondrial function, and reduce biochemical markers of organ dysfunction in a rat model of acute sepsis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 110, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, E.; Agrawal, R.; Nath, C.; Shukla, R. Effect of melatonin on neuroinflammation and acetylcholinesterase activity induced by LPS in rat brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 640, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, R. Quantification on the LightCycler. In Rapid Cycle Real-Time PCR, Methods and Applications; Meuer, S., Wittwer, C., Nakagawara, K.-I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; Volume 1, pp. 21–34. ISBN 978-3-540-66736-0. [Google Scholar]
- Herman, A.P.; Krawczyńska, A.; Bochenek, J.; Antushevich, H.; Herman, A.; Tomaszewska-Zaremba, D. Peripheral injection of SB203580 inhibits the inflammatory-dependent synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines in the hypothalamus. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 475152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupnicki, R.; Madej, A. Radioimmunoassay of LH in blood plasma of farm animals. Endokrinologie 1976, 68, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |

| Gene | Animals | Group of Pars Tuberalis Explants | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | GnRH | Melatonin | GnRH + Melatonin | ||
| LHβ | Saline-treated | 1.00 ± 0.09 A | 1.57 ± 0.28 B | 1.04 ± 0.14 A | 0.74 ±0.10 A |
| LPS-treated | 1.44 ± 0.18 A,B | 1.40 ± 0.22 A,B | 1.18 ± 0.27 A,B | 1.29 ± 0.19 A,B | |
| GnRHR | Saline-treated | 1.00 ± 0.11 B | 1.36 ± 0.20 B | 1.28 ± 0.10 B | 1.40 ± 0.21 B |
| LPS-treated | 0.56 ± 0.06 A | 0.77 ± 0.11 A | 0.72 ± 0.06 A | 0.79 ± 0.12 A | |
| MT1 | Saline-treated | 1.00 ±0.40 C | 0.50 ± 0.14 B | 0.38 ± 0.06 B | 0.36 ± 0.07 B |
| LPS-treated | 0.18 ± 0.02 A | 0.25 ± 0.05 A | 0.46 ± 0.20 A,B | 0.18 ± 0.02 A | |
| IL-1β | Saline-treated | 1.00 ± 0.08 D | 0.99 ± 0.04 D | 0.52 ± 0.06 A | 0.92 ± 0.14 B,C,D |
| LPS-treates | 0.85 ± 0.06 B,C,D | 0.68 ± 0.08 B,C,D | 0.91 ± 0.07 C,D | 0.65 ± 0.07 A,B | |
| IL-6 | Saline-treated | 1 ± 0.06 B | 0.78 ± 0.12 A,B | 0.49 ± 0.04 A | 0.64 ± 0.06 A,B |
| LPS-treates | 1.87 ± 0.22 C,D | 1.83 ± 0.21 C,D | 2.21 ± 0.27 D | 1.39 ± 0.23 B,C | |
| TNFα | Saline-treated | 1 ± 0.06 C | 0.92 ± 0.07 B,C | 0.65 ± 0.10 A | 0.89 ± 0.09 A,B,C |
| LPS-treates | 0.75 ± 0.07 A,B | 0.75 ± 0.08 A,B | 0.91 ± 0.07 B,C | 0.74 ± 0.10 A,B | |
| GenBank Acc. No. | Gene | Amplicon Size [bp] | Forward/Reverse | Sequence 5’→3’ | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NM_001034034 | GAPDH | 134 | forward | AGAAGGCTGGGGCTCACT | [16] |
| glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | reverse | GGCATTGCTGACAATCTTGA | |||
| U39357 | ACTB | 168 | forward | CTTCCTTCCTGGGCATGG | [16] |
| beta actin | reverse | GGGCAGTGATCTCTTTCTGC | |||
| NM_001076910 | PPIC | 131 | forward | ACGGCCAAGGTCTTCTTTG | [16] |
| cyclophilin C | reverse | TATCCTTTCTCTCCCGTTGC | |||
| X52488 | LHβ | 184 | forward | AGATGCTCCAGGGACTGCT | [16] |
| luteinizing hormone beta-subunit | reverse | TGCTTCATGCTGAGGCAGTA | |||
| NM-001009397 | GnRHR | 150 | forward | TCTTTGCTGGACCACAGTTAT | [16] |
| gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor | reverse | GGCAGCTGAAGGTGAAAAAG | |||
| U02517 | GnRH | 123 | forward | GCCCTGGAGGAAAGAGAAAT | [16] |
| gonadotropin-releasing hormone | reverse | GAGGAGAATGGGACTGGTGA | |||
| XM_614283.6 | MT1 | 114 | forward | GCCTCCATCCTCATCTTCAC | Originally designed |
| Melatotonin receptor type I | reverse | GCTCACCACAAACACATTCC | |||
| NM_001130938 | MT2 | 107 | forward | CTCCGGAACGCAGGTAAC | Originally designed |
| Melatotonin receptor type II | reverse | CAGCCGTCGTGGAAGATG | |||
| X54796.1 | IL1B | 137 | forward | CAGCCGTGCAGTCAGTAAAA | [54] |
| interleukin 1 beta | reverse | GAAGCTCATGCAGAACACCA | |||
| NM_001009392.1 | IL6 | 165 | forward | GTTCAATCAGGCGATTTGCT | [54] |
| interleukin 6 | reverse | CCTGCGATCTTTTCCTTCAG | |||
| NM_001024860 | TNF | 153 | forward | CAAATAACAAGCCGGTAGCC | [54] |
| tumor necrosis factor | reverse | AGATGAGGTAAAGCCCGTCA |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wojtulewicz, K.; Tomaszewska-Zaremba, D.; Herman, A.P. Endotoxin-Induced Inflammation Suppresses the Effect of Melatonin on the Release of LH from the Ovine Pars Tuberalis Explants—Ex Vivo Study. Molecules 2017, 22, 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111933
Wojtulewicz K, Tomaszewska-Zaremba D, Herman AP. Endotoxin-Induced Inflammation Suppresses the Effect of Melatonin on the Release of LH from the Ovine Pars Tuberalis Explants—Ex Vivo Study. Molecules. 2017; 22(11):1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111933
Chicago/Turabian StyleWojtulewicz, Karolina, Dorota Tomaszewska-Zaremba, and Andrzej Przemysław Herman. 2017. "Endotoxin-Induced Inflammation Suppresses the Effect of Melatonin on the Release of LH from the Ovine Pars Tuberalis Explants—Ex Vivo Study" Molecules 22, no. 11: 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111933
APA StyleWojtulewicz, K., Tomaszewska-Zaremba, D., & Herman, A. P. (2017). Endotoxin-Induced Inflammation Suppresses the Effect of Melatonin on the Release of LH from the Ovine Pars Tuberalis Explants—Ex Vivo Study. Molecules, 22(11), 1933. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111933