Engineering the l-Arabinose Isomerase from Enterococcus Faecium for d-Tagatose Synthesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
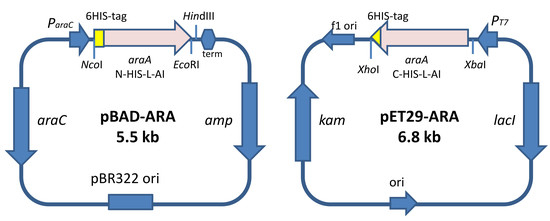
2.1. Design of the Recombinant l-AIs for Their Overproduction in E. coli
2.2. Production and Extraction of the Recombinant Enzymes
2.3. Purification of the Recombinant l-AIs Using Nickel and Copper Metal-Affinity Chromatography
2.4. Analysis of Recombinant l-AI Quaternary Structure by Ultracentrifugation
2.5. Effect of pH and Temperature on the Activity and Stability of Recombinant HisTagged l-AIs
2.6. d-Tagatose Conversion by Recombinant l-AIs in Solution
2.7. Determination of the Kinetic Models for Both Recombinants l-AIs Using d-Galactose As Substrate
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Genetic Engineering Procedures
3.3. Synthesis of the Gene Encoding the N-Terminal His-Tagged l-AI. Expression under the Control of the ParaC-Inducible Promoter
3.4. Synthesis of the Gene Encoding the C-Terminal His-Tagged l-AI. Expression Under the Control of PT7—Inducible Promoter
3.5. Enzyme Production
3.6. Protein Analyses
3.7. l-AI Assay
3.8. Preparation of Affinity Supports
3.9. Purification of the Recombinant l-AI by Metal-Affinity Chromatography
3.10. Estimation of Kinetic Parameters
3.11. Bioconversion Assays
3.12. Analytical Ultracentrifugation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, J.H.; Chung, S.J. Sweetness potency and sweetness synergism of sweeteners in milk and coffee systems. Food Res. Int. 2015, 74, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.H.; Lee, D.W.; Lee, S.J.; Choe, E.A.; Kim, S.B.; Lee, Y.H.; Cheigh, C.I.; Pyun, Y.R. Production of d-tagatose at high temperatures using immobilized Escherichia coli cells expressing l-arabinose isomerase from Thermotoga neapolitana. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Li, S.; Feng, X.; Liang, J.; Xu, H. l-Arabinose isomerase and its use for biotechnological production of rare sugars. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 8869–8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, L.D.; Bell, L.N. Physical and chemical stability of tagatose powder. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouhi, M.; Mohammadi, R.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Sarlak, Z. Combined effects of replacement of sucrose with d-tagatose and addition of different probiotic strains on quality characteristics of chocolate milk. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2015, 95, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudebbouze, S.; Maguin, E.; Rhimi, M. Bacterial l-arabinose isomerases: Industrial application for d-tagatose production. Recent Pat. DNA Gene Seq. 2011, 5, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghizalba, O.; Meyer, H.P.; Wohlgemuth, R. Industrial Biotransformation. In Encyclopedia of Industrial Biotechnology: Bioprocess, Bioseparation, and Cell Technology; Flickinger, M.C., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon, R.A.; van Pelt, S. Enzyme immobilisation in biocatalysis: Why, what and how. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6223–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.K. Tagatose: Properties, applications, and biotechnological processes. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2007, 76, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.; Chen, M.; Liu, X.; Zhai, Y.; Liu, X.W.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, M.; Wang, P. Bioconversion of d-galactose to d-tagatose: Continuous packed bed reaction with an immobilized thermostable l-arabinose isomerase and efficient purification by selective microbial degradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, P.R.; Manzo, R.M.; Rubiolo, A.C.; Batista-Viera, F.D.; Mammarella, E.J. Purification of an l-arabinose isomerase from Enterococcus faecium DBFIQ E36 employing a biospecific affinity strategy. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2014, 102, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, X.G.; Tseng, W.C.; Liu, S.M.; Tzou, W.S.; Fang, T.Y. Characterization of a thermophilic l-arabinose isomerase from Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum NTOU1. Biochem. Eng. J. 2014, 83, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Kang, Z.; Izumori, K.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Y. Enzymatic conversion of d-galactose to d-tagatose: Cloning, overexpression and characterization of l-arabinose isomerase from Pediococcus pentosaceus PC-5. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.F.; Cavalcante, K.F.; de Freitas, M.F.M.; Rodrigues, T.H.S.; Rocha, M.V.P.; Gonçalves, L.R.B. Comparative biochemical characterization of soluble and chitosan immobilized β-galactosidase from Kluyveromyces lactis NRRL Y1564. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, R.M.; Simonetta, A.C.; Rubiolo, A.C.; Mammarella, E.J. Screening and selection of wild strains for l-arabinose isomerase production. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Choe, E.A.; Kim, S.B.; Eom, S.H.; Hong, Y.H.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, D.Y.; Pyun, Y.R. Distinct metal dependence for catalytic and structural functions in the l-arabinose isomerase from the mesophilic Bacillus halodurans and the thermophilic Geobacillus stearothermophilus. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 434, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, D.W.; Choe, E.A.; Hong, Y.H.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, B.C.; Pyun, Y.R. Characterization of a thermoacidophilic l-arabinose isomerase from Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius: Role of Lys-269 in pH optimum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 7888–7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, B.; Pan, B. Purification and characterization of l-arabinose Isomerase from Lactobacillus plantarum producing d-tagatose. World J. Microb. Biotechnol. 2007, 23, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, S.; Fu, F.; Li, G.; Feng, X.; Xu, H.; Ouyang, P. Production of d-tagatose, a functional sweetener, utilizing alginate immobilized Lactobacillus fermentum CGMCC2921 cells. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 166, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Xu, L.; Feng, X.; Xu, H. Coexpression of β-d-galactosidase and l-arabinose isomerase in the production of d-tagatose: A functional sweetener. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2412–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, J.; Kimb, S.B.; Parkb, S.W.; Hanb, J.K.; Kima, P. Characterization of l-Arabinose isomerase in Bacillus subtilis, a gras host, for the production of edible tagatose. Food Biotechnol. 2009, 23, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudigl, P.; Haltrich, D.; Peterbauer, C.K. l-Arabinose isomerase and d-xylose isomerase from Lactobacillus reuteri: Characterization, coexpression in the food grade host Lactobacillus plantarum, and application in the conversion of d-galactose and d-glucose. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Jang, H.J.; Choe, E.A.; Kim, B.C.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, S.B.; Hong, Y.H.; Pyun, Y.R. Characterization of a thermostable l-arabinose (d-galactose) isomerase from the hyperthermophilic eubacterium Thermotoga maritima. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, J.C. Heterologous expression and characterization of Bacillus coagulans l-arabinose isomerase. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 2205–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, Y.W.; Roh, H.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Cha, J.H.; Park, K.H.; Park, C.S. Production of tagatose by a recombinant thermostable l-arabinose isomerase from Thermus sp. IM6501. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 963–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhimi, M.; Messaoud, E.B.; Borgi, M.A.; Khadra, K.B.; Bejar, S. Co-expression of l-arabinose isomerase and d-glucose isomerase in E. coli and development of an efficient process producing simultaneously d-tagatose and d-fructose. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2007, 40, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhimi, M.; Bajic, G.; Ilhammami, R.; Boudebbouze, S.; Maguin, E.; Haser, R.; Aghajari, N. The acid-tolerant l-arabinose isomerase from the mesophilic Shewanella sp. ANA-3 is highly active at low temperatures. Microb. Cell Fact. 2011, 10, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrick, J.W.; Lee, N. Subunit Structure of Arabinose Isomerase from Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1969, 244, 4277–4283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.M.; Lee, Y.J.; Cao, T.P.; Shin, S.M.; Park, M.K.; Lee, H.S.; Luccio, E.; Kim, S.B.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, S.J.; et al. Structure of the thermophilic l-Arabinose isomerase from Geobacillus kaustophilus reveals metal-mediated intersubunit interactions for activity and thermostability. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 596, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamatu, T.; Yamanaka, K. Crystallization and properties of l-arabinose isomerase from Lactobacillus gayonii. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Enzymol. 1969, 178, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, N.; Nyyssölä, A.; Salonen, K.; Turunen, O. Bifidobacterium longum l-arabinose isomerase—Overexpression in Lactococcus lactis, purification, and characterization. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 168, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhimi, M.; Juy, M.; Aghajari, N.; Haser, R.; Bejar, S. Probing the essential catalytic residues and substrate affinity in the thermoactive Bacillus stearothermophilus US100 l-arabinose isomerase by site-directed mutagenesis. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 3556–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.Y.; Wiegel, J.; Gherardini, F.C. Purification and cloning of a thermostable xylose (glucose) isomerase with an acidic pH optimum from Thermoanaerobacterium strain JW/SL-YS 489. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 5938–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricard, J.A. Cornish-Bowden A. Co-operative and allosteric enzymes: 20 Years on. Eur. J. Biochem. 1987, 166, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, O.O.; Spradlin., J.E. Process for Manufacturing d-tagatose. U.S. Patent 6,057,135, 2 May 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rhimi, M.; Bejar, S. Cloning, purification and biochemical characterization of metallic-ions independent and thermoactive l-arabinose isomerase from the Bacillus stearothermophilus US100 strain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1760, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codon Optimization—Integrated DNA Technologies. Available online: http://eu.idtdna.com/CodonOpt (accessed on 14 November 2017).
- Pessela, B.C.C.; Vian, A.; Mateo, C.; Lafuente, R.; García, J.L.; Guisan, J.M.; Carrascosa, A.V. Overproduction of Thermus sp. strain T2 beta-galactosidase in Escherichia coli and preparation by using tailor-made metal chelate supports. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2003, 69, 1967–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.F.; Russell, D. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural protein during the assembly of the heat of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dische, Z.; Borenfreund, E. A new spectrophotometric method for the detection and determination of keto sugars and trioses. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 192, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bolívar, J.M.; Rocha-Martin, J.; Godoy, C.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Guisán, J.M. Complete reactivation of immobilized derivatives of a trimeric glutamate dehydrogenase from Thermus thermophillus. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armisén, P.; Mateo, C.; Cortés, E.; Barredo, J.L.; Salto, F.; Diez, B.; Rodés, L.; García, J.L.; Fernández-Lafuente, R.; Guisan, J.M. Selective adsorption of poly-His tagged glutaryl acyiase on tailor-made metal chelate supports. J. Chomatogr. A 1999, 848, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessela, B.C.C.; Mateo, C.; Carrascosa, A.V.; Vian, A.; García, J.L.; Rivas, G.; Alfonso, C.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. One-step purification, covalent immobilization, and additional stabilization of a thermophilic poly-His tagged‚ β-galactosidase from Thermus sp. Strain T2 by using novel heterofunctional chelate-epoxy sepabeads. Biomacromolecules. 2003, 4, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |






| Extracts | Activity (U mL−1) | Protein Concentration (mg mL−1) | Specific Activity (U mg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Luria Bertani (LB) medium | N-His-l-AI | 6.21 | 40 | 0.154 |
| C-His-l-AI | 3.01 | 31 | 0.097 | |
| Terrific Broth (TB) medium | N-His-l-AI | 10.09 | 298 | 0.034 |
| C-His-l-AI | 5.29 | 145 | 0.036 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Sousa, M.; Manzo, R.M.; García, J.L.; Mammarella, E.J.; Gonçalves, L.R.B.; Pessela, B.C. Engineering the l-Arabinose Isomerase from Enterococcus Faecium for d-Tagatose Synthesis. Molecules 2017, 22, 2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122164
De Sousa M, Manzo RM, García JL, Mammarella EJ, Gonçalves LRB, Pessela BC. Engineering the l-Arabinose Isomerase from Enterococcus Faecium for d-Tagatose Synthesis. Molecules. 2017; 22(12):2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122164
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Sousa, Marylane, Ricardo M. Manzo, José L. García, Enrique J. Mammarella, Luciana R. B. Gonçalves, and Benevides C. Pessela. 2017. "Engineering the l-Arabinose Isomerase from Enterococcus Faecium for d-Tagatose Synthesis" Molecules 22, no. 12: 2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122164
APA StyleDe Sousa, M., Manzo, R. M., García, J. L., Mammarella, E. J., Gonçalves, L. R. B., & Pessela, B. C. (2017). Engineering the l-Arabinose Isomerase from Enterococcus Faecium for d-Tagatose Synthesis. Molecules, 22(12), 2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122164