Quinoline-Based Hybrid Compounds with Antimalarial Activity
Abstract
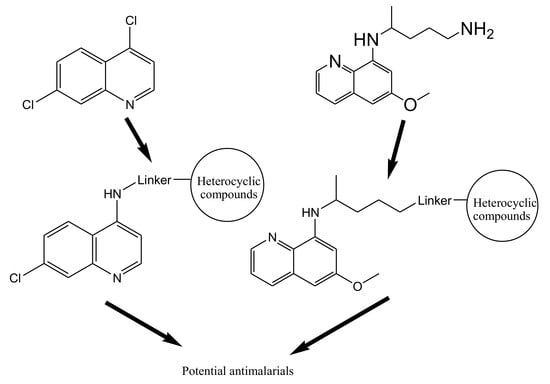
:1. Introduction
2. Classes of Antimalarial Drugs
3. Mechanism of Antimalarial Drug Resistance
3.1. Mechanism of Resistance in Quinolines
3.2. Mechanism of Resistance in Artemisinins
3.3. Mechanism of Resistance to 4-Quinolinemethanols
3.4. Mechanism of Resistance to Hydroxynaphthoquinones and Diaminopyrimidines
3.5. Mechanism of Resistance to Sulphonamides
4. Hybrid Compounds
4.1. Quinoline–Artemisinin Derivatives Hybrid Compounds
4.2. Quinoline–Ferrocene Hybrid Compounds
4.3. Quinoline-Trioxolanes Hybrid Compounds
4.4. Hybrid Compounds Containing Quinoline Derivatives and Antibacterial Agents
4.5. Quinoline-Mercaptopurine Hybrid
4.6. Quinoline-Pyrimidine Hybrid Compounds
4.7. Quinoline–Sulfonamide Hybrids
4.8. Hybrid Compounds Containing Quinoline and Other Ring Systems
5. Lipinski Rules
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reddy, P.L.; Khan, S.I.; Ponnan, P.; Tripathi, M.; Rawat, D.S. Synthesis and evaluation of 4-aminoquinoline-purine hybrids as potential antiplasmodial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 126, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, S.S.; Khan, S.I.; Bahuguna, A.; Kumar, D.; Rawat, D.S. Synthesis, antimalarial activity, heme binding and docking studies of N-substituted 4-aminoquinoline-pyrimidine molecular hybrids. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 129, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Kumar, V. 4-Aminoquinoline-ferrocenyl-chalcone conjugates: Synthesis and anti-plasmodial evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 125, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.A.; Panda, S.S.; Hall, C.D. Quinine conjugates and quinine analogues as potential antimalarial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 335–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugan, K.; Raichurkar, A.V.; Rahman, F.; Khan, N.; Iyer, P.S. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of novel 8-aminoquinoline—Pyrazolopyrimidine hybrids as potent antimalarial agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar]
- White, N.J.; Pukrittayakamee, S.; Hien, T.T.; Faiz, M.A.; Mokuolu, O.A.; Dondorp, A.M. Malaria. Lancet 2014, 383, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.; Land, K.M.; Kumar, V. 4-Aminoquinoline-hybridization en route towards the development of rationally designed antimalarial agents. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 82676–82698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Agarwal, D.; Sharma, K.; Sharma, M.; Nielsen, M.A.; Alifrangis, M.; Singh, A.K.; Gupta, R.D.; Awasthi, S.K. 4-Aminoquinoline derivatives: Synthesis, in vitro and in vivo antiplasmodial activity against chloroquine-resistant parasites. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 122, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira Pedrosa, M.; da Cruz, D.; Marques, R.; Viana, O.; de Moura, R.O.; Ishiki, H.M.; Barbosa, F.; Maria, J.; Diniz, M.F.; Scotti, M.T.; et al. Hybrid Compounds as Direct Multitarget Ligands: A Review. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1044–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antimalarial Drugs. Available online: http://www.malariasite.com/malaria-drugs (accessed on 16 October 2017).
- Sevene, E.; González, R.; Menéndez, C. Current knowledge and challenges of antimalarial drugs for treatment and prevention in pregnancy. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2010, 11, 1277–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Classification of Antimalarial Drugs. Available online: http://www.medworldonline.com/classification-anti-malarial-drugs (accessed on 16 October 2017).
- Chinappi, M.; Via, A.; Marcatili, P.; Tramontano, A. On the mechanism of chloroquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogstad, D.J.; Gluzman, I.Y.; Kyle, D.E.; Oduola, A.M.J.; Martin, S.K.; Milhous, W.K. Schlesinger PHEfflux of chloroquine from Plasmodium falciparum: Mechanism of chloroquine resistance. Science 1987, 238, 1283–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, P.G.; Janneh, O.; Ward, S.A. Chloroquine uptake and activity is determined by binding to ferriprotoporphyrin IX in Plasmodium falciparum. Novartis Found. Symp. 1999, 226, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cooper, R.A.; Hartwig, C.L.; Ferdig, M.T. pfcrt is more than the Plasmodium falciparum chloroquine resistance gene: A functional and evolutionary perspective. Acta Trop. 2005, 94, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbengue, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Pandharkar, T.; Liu, H.; Estiu, G.; Stahelin, R.V.; Rizk, S.S.; Njimoh, D.L.; Ryan, Y.; Chotivanich, K.; et al. A molecular mechanism of artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Nature 2015, 520, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dassonville-Klimpt, A.; Jonet, A.; Pillon, M.; Mullié, C.; Sonnet, P. Mefloquine derivatives: Synthesis, mechanisms of action, antimicrobial activities. In Science against Microbial Pathogens: Communicating Current Research and Technological Advances; Méndez-Vilas, A., Ed.; Formatex Publishers: Badarjoz, Spain, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Price, R.N.; Nosten, F.; Luxemburger, C.; Kham, A.; Brockman, A.; Chongsuphajaisiddhi, T.; White, N.J. Artesunate versus artemether in combination with mefloquine for the treatment of multidrug-resistant falciparum malaria. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1995, 89, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoon, B.A.; Singh, K.P.; Varshney, M.; Gupta, S.K.; Shukla, Y.; Gupta, S.K. Understanding the mechanism of atovaquone drug resistance in Plasmodium falciparum cytochrome b mutation Y268S using computational methods. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirichaiwat, C.; Intaraudom, C.; Kamchonwongpaisan, S.; Vanichtanankul, J.; Thebtaranonth, Y.; Yuthavong, Y. Target guided synthesis of 5-benzyl-2,4-diamonopyrimidines: Their antimalarial activities and binding affinities to wild type and mutant dihydrofolate reductases from Plasmodium falciparum. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinayak, S.; Alam, M.T.; Mixson-Hayden, T.; McCollum, A.M.; Sem, R.; Shah, N.K.; Lim, P.; Muth, S.; Rogers, W.O.; Fandeur, T.; et al. Origin and evolution of sulfadoxine resistant Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloland, P.B. Drug Resistance in Malaria; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- White, N. Antimalarial drug resistance and combination chemotherapy. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1999, 354, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lödige, M.; Hiersch, L. Design and synthesis of novel hybrid molecules against malaria. Int. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 2015, 458319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muregi, F.W.; Ishih, A. Next-generation antimalarial drugs: Hybrid molecules as a new strategy in drug design. Drug Dev. Res. 2010, 71, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Wicht, K.J.; Shaban, E.; Ngoc, T.A.; Wang, M.Q.; Hayashi, I.; Hossain, M.I.; Takemasa, Y.; Kaiser, M.; El Sayed, I.E.; et al. Synthesis and evaluation of artesunate–indoloquinoline hybrids as antimalarial drug candidates. MedChemComm 2014, 5, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombard, M.C.; N’Da, D.D.; Breytenbach, J.C.; Kolesnikova, N.I.; Van Ba, C.T.; Wein, S.; Norman, J.; Denti, P.; Vial, H.; Wiesner, L. Antimalarial and anticancer activities of artemisinin–quinoline hybrid-dimers and pharmacokinetic properties in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 47, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, J.J.; Coughlan, D.; Heneghan, N.; Gaynor, C.; Bell, A. A novel artemisinin–quinine hybrid with potent antimalarial activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 3599–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombard, M.C.; N’Da, D.D.; Breytenbach, J.C.; Smith, P.J.; Lategan, C.A. Synthesis, in vitro antimalarial and cytotoxicity of artemisinin-aminoquinoline hybrids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 1683–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombard, M.C.; N’Da, D.D.; Van Ba, C.T.; Wein, S.; Norman, J.; Wiesner, L.; Vial, H. Potent in vivo anti-malarial activity and representative snapshot pharmacokinetic evaluation of artemisinin-quinoline hybrids. Malar. J. 2013, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Capela, R.; Cabal, G.G.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Gut, J.; Mota, M.M.; Moreira, R.; Lopes, F.; Prudêncio, M. Design and evaluation of primaquine-artemisinin hybrids as a multistage antimalarial strategy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4698–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barends, M.; Jaidee, A.; Khaohirun, N.; Singhasivanon, P.; Nosten, F. In vitro activity of ferroquine (SSR 97193) against Plasmodium falciparum isolates from the Thai-Burmese border. Malar. J. 2007, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biot, C.; Taramelli, D.; Forfar-Bares, I.; Maciejewski, L.; Boyce, M.; Nowogrocki, G.; Brocard, J.; Basilico, N.; Olliaro, P.; Egan, T.J. Insights into the mechansims of action of ferroquine. Relationship between physicochemical properties and antiplasmodial activity. Mol. Pharm. 2005, 2, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Domarle, O.; Blampain, G.; Agnaniet, H.; Nzadiyabi, T.; Lebibi, J.; Brocard, J.; Maciejewski, L.; Biot, C.; Georges, A.J.; Millet, P. In vitro antimalarial activity of a new organometallic analog, ferrocene-chloroquine. Antimicrob. Agents Chem. 1998, 42, 540–544. [Google Scholar]
- Biot, C.; Dessolin, J.; Ricard, I.; Dive, D. Easily synthesized antimalarial ferrocene triazacyclononane quinoline conjugates. J. Organomet. Chem. 2004, 689, 4678–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’Da, D.D.; Smith, P.J. Synthesis, in vitro antiplasmodial and antiproliferative activities of a series of quinoline–ferrocene hybrids. Med. Chem. Res. 2014, 23, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biot, C.; Daher, W.; Chavain, N.; Fandeur, T.; Khalife, J.; Dive, D.; De Clercq, E. Design and synthesis of hydroxyferroquine derivatives with antimalarial and antiviral activities. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biot, C.; Pradines, B.; Sergeant, M.H.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Chibale, K. Design, synthesis, and antimalarial activity of structural chimeras of thiosemicarbazone and ferroquine analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 6434–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavain, N.; Davioud-Charvet, E.; Trivelli, X.; Mbeki, L.; Rottmann, M.; Brun, R.; Biot, C. Antimalarial activities of ferroquine conjugates with either glutathione reductase inhibitors or glutathione depletors via a hydrolyzable amide linker. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 8048–8059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellot, F.; Coslédan, F.; Vendier, L.; Brocard, J.; Meunier, B.; Robert, A. Trioxaferroquines as new hybrid antimalarial drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4103–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, C.; Salas, P.F.; Cawthray, J.F.; de Kock, C.; Patrick, B.O.; Smith, P.J.; Adam, M.J.; Orvig, C. 1,1′-Disubstituted ferrocenyl carbohydrate chloroquine conjugates as potential antimalarials. Organometallics 2012, 31, 5736–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, C.; Salas, P.F.; Patrick, B.O.; Kock, C.D.; Smith, P.J.; Adam, M.J.; Orvig, C. Modular synthesis of 1,2- and 1,1′-disubstituted ferrocenyl carbohydrate chloroquine and mefloquine conjugates as potential antimalarial agents. Organometallics 2012, 31, 5748–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, P.F.; Herrmann, C.; Cawthray, J.F.; Nimphius, C.; Kenkel, A.; Chen, J.; de Kock, C.; Smithm, P.J.; Patrick, B.O.; Adam, M.J.; et al. Structural characteristics of chloroquine-bridged ferrocenophane analogues of ferroquine may obviate malaria drug-resistance mechanisms. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1596–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biot, C.; Nosten, F.; Fraisse, L.; Ter-Minassian, D.; Khalife, J.; Dive, D. The antimalarial ferroquine: From bench to clinic. Parasite 2011, 18, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, D.N.; Breytenbach, J.C.; Smith, P.J.; Lategan, C. Synthesis and in vitro antiplasmodial activity of quinoline-ferrocene esters. Arzneimittelforschung 2011, 61, 358–365. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, N.C.; Barton, V.; Jones, M.; Stocks, P.A.; Ward, S.A.; Davies, J.; Bray, P.G.; Shone, A.E.; Cristiano, M.L.; O’Neill, P.M. Semi-synthetic and synthetic 1,2,4-trioxaquines and 1,2,4-trioxolaquines: Synthesis, preliminary SAR and comparison with acridine endoperoxide conjugates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 2038–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meunier, B. Hybrid molecules with a dual mode of action: Dream or reality? Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 41, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousejra-El Garah, F.; Claparols, C.; Benoit-Vical, F.; Meunier, B.; Robert, A. The antimalarial trioxaquine DU1301 alkylates heme in malaria-infected mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chem. 2008, 52, 2966–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, D.; Capela, R.; Albuquerque, I.S.; Meireles, P.; Paiva, I.; Nogueira, F.; Amewu, R.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Oliveira, R.; et al. Novel endoperoxide-based transmission-blocking antimalarials with liver-and blood-schizontocidal activities. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, B.; Teixeira, C.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Gomes, J.R.; Gomes, P. Cinnamic Acid/Chloroquinoline Conjugates as Potent Agents against Chloroquine-Resistant Plasmodium falciparum. Chem. Med. Chem. 2012, 7, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yardley, S.C.; Keller-Maerki, S.; Rottmann, M.; Brun, R.; Coletta, M.; Marini, S.; Guiso, G.; Caccia, S.; Fattorusso, C. Combining 4-aminoquinoline-and clotrimazole-based pharmacophores toward innovative and potent hybrid antimalarials. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 502–513. [Google Scholar]
- Gemma, S.; Camodeca, C.; Coccone, S.S.; Joshi, B.P.; Bernetti, M.; Moretti, V.; Brogi, S.; Bonache de Marcos, M.C.; Savini, L.; Taramelli, D.; et al. Optimization of 4-aminoquinoline/clotrimazole-based hybrid antimalarials: Further structure–activity relationships, in vivo studies, and preliminary toxicity profiling. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 5, 6948–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S.S.; Bajaj, K.; Meyers, M.J.; Sverdrup, F.M.; Katritzky, A.R. Quinine bis-conjugates with quinolone antibiotics and peptides: Synthesis and antimalarial bioassay. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 8985–8993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, B.C.; Teixeira, C.; Figueiras, M.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Gomes, J.R.; Gomes, P. Novel cinnamic acid/4-aminoquinoline conjugates bearing non-proteinogenic amino acids: Towards the development of potential dual action antimalarials. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 54, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, B.C.; Teixeira, C.; Albuquerque, I.S.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Gomes, J.R.; Prudêncio, M.; Gomes, P. N-Cinnamoylated chloroquine analogues as dual-stage antimalarial leads. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Singh, P.; Kumar, M.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Kumar, K.; Kumar, V.; Mahajan, M.P.; Bisetty, K. Synthesis, docking and in vitro antimalarial evaluation of bifunctional hybrids derived from β-lactams and 7-chloroquinoline using click chemistry. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, R.; Biot, C.; Carrère-Kremer, S.; Kremer, L.; Guérardel, Y.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Kumar, V. 4-Aminoquinoline-β-Lactam Conjugates: Synthesis, Antimalarial, and Antitubercular Evaluation. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2014, 83, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Raj, R.; Singh, P.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Kumar, V. Urea/oxalamide tethered β-lactam-7-chloroquinoline conjugates: Synthesis and in vitro antimalarial evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 71, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellotti de Souza, N.; Carvalhaes, R.; Maria Lino do Carmo, A.; Jose Martins Alves, M.; Soares Coimbra, E.; Maria Neumann Cupolilo, S.; Abramo, C.; David Da Silva, A. Synthesis and In Vivo Antimalarial Activity of Quinoline/Mercaptopurine Conjugates. Lett. Drug. Des. Discov. 2012, 9, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Khan, S.I.; Ponnan, P.; Kholiya, R.; Rawat, D.S. Aminoquinoline-Pyrimidine-Modified Anilines: Synthesis, In Vitro Antiplasmodial Activity, Cytotoxicity, Mechanistic Studies and ADME Predictions. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 9074–9083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, S.; Rajesh, U.C.; Khan, S.I.; Tekwani, B.L.; Rawat, D.S. Novel 4-aminoquinoline-pyrimidine based hybrids with improved in vitro and in vivo antimalarial activity. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Khan, S.I.; Tekwani, B.L.; Ponnan, P.; Rawat, D.S. 4-Aminoquinoline-Pyrimidine hybrids: Synthesis, antimalarial activity, heme binding and docking studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Khan, S.I.; Tekwani, B.L.; Ponnan, P.; Rawat, D.S. Synthesis, antimalarial activity, heme binding and docking studies of 4-aminoquinoline–pyrimidine based molecular hybrids. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 63655–63669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.B.; Valand, N.N.; Sutariya, P.G.; Menon, S.K. Design, synthesis and characterization of quinoline–pyrimidine linked calix [4] arene scaffolds as anti-malarial agents. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2016, 84, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Balzarini, J.; de Kock, C.; Smith, P.J.; Chibale, K.; Singh, K. Synthesis, antiplasmodial activity and mechanistic studies of pyrimidine-5-carbonitrile and quinoline hybrids. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 101, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, A.; Khan, S.I.; Rawat, D.S. Synthesis of piperazine tethered 4-aminoquinoline-pyrimidine hybrids as potent antimalarial agents. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 20729–20736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Kaur, H.; Chibale, K.; Balzarini, J.; Little, S.; Bharatam, P.V. 2-aminopyrimidine based 4-aminoquinoline anti-plasmodial agents. Synthesis, biological activity, structure–activity relationship and mode of action studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 52, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretorius, S.I.; Breytenbach, W.J.; De Kock, C.; Smith, P.J.; N’Da, D.D. Synthesis, characterization and antimalarial activity of quinoline–pyrimidine hybrids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, L.C.; Boechat, N.; Maria de Lourdes, G.F.; Júnior, C.C.; Jesus, A.M.; Leite, M.M.; Souza, N.B.; Krettli, A.U. Anti-Plasmodium falciparum activity of quinoline–sulfonamide hybrids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 5979–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Pandey, S.; Agarwal, P.; Verma, P.; Deshpande, S.; Saxena, J.K.; Srivastava, K.; Chauhan, P.M.; Prabhakar, Y.S. N-(7-Chloroquinolinyl-4-aminoalkyl) arylsulfonamides as antimalarial agents: Rationale for the activity with reference to inhibition of hemozoin formation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 25584–25593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, R.R.; da Silva, J.M.; Carlos, B.C.; da Fonseca, C.C.; de Souza, L.S.; Lopes, F.V.; de Paula Dias, R.M.; Moreira, P.O.; Abramo, C.; Viana, G.H.; et al. New quinoline derivatives demonstrate a promising antimalarial activity against Plasmodium falciparum in vitro and Plasmodium berghei in vivo. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 2308–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, G.M.; Tanpure, R.P.; Douchez, A.; Andrews, K.T.; Poulsen, S.A. Synthesis and Evaluation of Antimalarial Properties of Novel 4-Aminoquinoline Hybrid Compounds. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2014, 84, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salahuddin, A.; Inam, A.; van Zyl, R.L.; Heslop, D.C.; Chen, C.T.; Avecilla, F.; Agarwal, S.M.; Azam, A. Synthesis and evaluation of 7-chloro-4-(piperazin-1-yl) quinoline-sulfonamide as hybrid antiprotozoal agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 3080–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njogu, P.M.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Chibale, K. Design, Synthesis, and Antiplasmodial Activity of Hybrid Compounds Based on (2R,3S)-N-Benzoyl-3-phenylisoserine. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 4, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andayi, W.A.; Egan, T.J.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Chibale, K. Synthesis, Antiplasmodial Activity, and β-Hematin Inhibition of Hydroxypyridone–Chloroquine Hybrids. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, A.; Chetia, D.; Rudrapal, M. Synthesis, Antimalarial Activity Evaluation and Drug likeness Study of Some New Quinoline-Lawsone Hybrids. Ind. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 78, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Chetia, D.; Puri, S.K.; Srivastava, K.; Prakash, A. Synthesis and in vitro and in vivo antimalarial activity of novel 4-anilinoquinoline Mannich base derivatives. Med. Chem. Res. 2011, 20, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inam, A.; Van Zyl, R.L.; van Vuuren, N.J.; Chen, C.T.; Avecilla, F.; Agarwal, S.M.; Azam, A. Chloroquinoline–acetamide hybrids: A promising series of potential antiprotozoal agents. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 48368–48381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, J.; Fortuin, E.E.; Taylor, D.; Smith, P.J.; Malan, S.F. Pentacycloundecylamines and conjugates thereof as chemosensitizers and reversed chloroquine agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 5516–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.J.; Selzer, A.; Kelly, J.X.; Smilkstein, M.J.; Riscoe, M.K.; Peyton, D.H. A chloroquine-like molecule designed to reverse resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 5623–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S.; Burgess, S.J.; Skaalrud, D.; Kelly, J.X.; Peyton, D.H. Reversal agent and linker variants of reversed chloroquines: Activities against Plasmodium falciparum. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 53, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, C.J.; Kumar, S.P.; Gut, J.; Goncalves, L.M.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Moreira, R.; Santos, M.M. Squaric acid/4-aminoquinoline conjugates: Novel potent antiplasmodial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 69, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparatore, A.; Basilico, N.; Parapini, S.; Romeo, S.; Novelli, F.; Sparatore, F.; Taramelli, D. 4-Aminoquinoline quinolizidinyl-and quinolizidinylalkyl-derivatives with antimalarial activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 5338–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, V.R.; Haq, W.; Srivastava, K.; Puri, S.K.; Katti, S.B. Synthesis and antimalarial activity of side chain modified 4-aminoquinoline derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.F.; Levi, M.S.; Tekwani, B.L.; Wilson, N.H.; Borne, R.F. Synthesis of isoquinuclidine analogs of chloroquine: Antimalarial and antileishmanial activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 3919–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornut, D.; Lemoine, H.; Kanishchev, O.; Okada, E.; Albrieux, F.; Beavogui, A.H.; Bienvenu, A.L.; Picot, S.; Bouillon, J.P.; Médebielle, M. Incorporation of a 3-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-γ-hydroxy-γ-lactam motif in the side chain of 4-aminoquinolines. Syntheses and antimalarial activities. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunduru, N.; Sharma, M.; Srivastava, K.; Rajakumar, S.; Puri, S.K.; Saxena, J.K.; Chauhan, P.M. Synthesis of oxalamide and triazine derivatives as a novel class of hybrid 4-aminoquinoline with potent antiplasmodial activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6451–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musonda, C.C.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Yardley, V.; De Souza, R.C.; Chibale, K. Application of multicomponent reactions to antimalarial drug discovery. Part 2: New antiplasmodial and antitrypanosomal 4-aminoquinoline γ- and δ-lactams via a ‘catch and release’ protocol. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 5605–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunico, W.; Cechinel, C.A.; Bonacorso, H.G.; Martins, M.A.; Zanatta, N.; de Souza, M.V.; Freitas, I.O.; Soares, R.P.; Krettli, A.U. Antimalarial activity of 4-(5-trifluoromethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-chloroquine analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wilkinson, B. Drug discovery beyond the ‘rule-of-five’. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doak, B.C.; Kihlberg, J. Drug discovery beyond the rule of 5-Opportunities and challenges. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2017, 12, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Chetia, D.; Rudrapal, M. Design, synthesis and antimalarial activity of some new 2-hydroxy-1, 4-naphthoquinone-4-hydroxyaniline hybrid mannich bases. Asian J. Chem. 2016, 28, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, F.A.; Kouznetsov, V.V. Property-based design and synthesis of new chloroquine hybrids via simple incorporation of 2-imino-thiazolidin-4-one or 1h-pyrrol-2,5-dione fragments on the 4-amino-7-chloroquinoline side chain. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2011, 22, 1774–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Khan, S.I.; Ponnan, P.; Rawat, D.S. Triazine–pyrimidine based molecular hybrids: Synthesis, docking studies and evaluation of antimalarial activity. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 5087–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nqoro, X.; Tobeka, N.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Quinoline-Based Hybrid Compounds with Antimalarial Activity. Molecules 2017, 22, 2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122268
Nqoro X, Tobeka N, Aderibigbe BA. Quinoline-Based Hybrid Compounds with Antimalarial Activity. Molecules. 2017; 22(12):2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122268
Chicago/Turabian StyleNqoro, Xhamla, Naki Tobeka, and Blessing A. Aderibigbe. 2017. "Quinoline-Based Hybrid Compounds with Antimalarial Activity" Molecules 22, no. 12: 2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122268
APA StyleNqoro, X., Tobeka, N., & Aderibigbe, B. A. (2017). Quinoline-Based Hybrid Compounds with Antimalarial Activity. Molecules, 22(12), 2268. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122268