Antiprotozoal Activity of Triazole Derivatives of Dehydroabietic Acid and Oleanolic Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
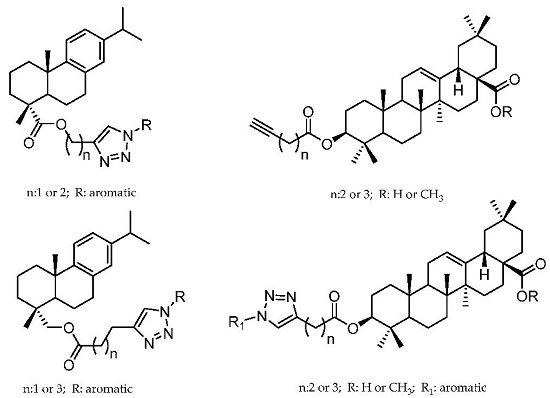
2.1. Dehydroabietic Acid Derivatives
2.2. Oleanolic Acid Derivatives
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Antiprotozoal Assays
3.3. Cytotoxicity
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan American Health Organization. Health in the Americas 2007. In Regional, Scientific and Technical Publication 622; Pan American Health Organization: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. First WHO Report on Neglected Tropical Diseases. Working to Overcome the Global Impact Neglected Tropical Diseases; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; ISBN 978-92-4-1564090. [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata, Y.; Nakagawa, J. Control of Chagas disease. Adv. Parasitol. 2006, 61, 129–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Health Estimates 2014 Summary Tables: DALY by Cause, Age and Sex, by WHO Region, 2000–2012. Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. Available online: http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/en/ (accessed on 21 November 2016).
- WHO. Chagas Disease (American Trypanosomiasis). Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs340/en/ (accessed on 12 December 2016).
- Senior, K. Chagas disease: Moving towards global elimination. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotez, P.J.; Bottazzi, M.E.; Franco-Paredes, C.; Ault, S.K.; Periago, M.R. The Neglected Tropical Diseases of Latin America and the Caribbean: A Review of Disease Burden and Distribution and a Roadmap for Control and Elimination. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2008, 2, e300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gascón, J. Epidemiology of Chagas disease in Europe and control programs in Spain. In Proceedings of the I Iberoamerican Workshop on Chagas Disease, Triatomine Vectors, T. cruzi, and Triatoma Virus, Lisboa, Portugal, 13–16 September 2010.
- Rassi, A.; Rassi, A.; Marcondes de Rezende, J. American Trypanosomiasis (Chagas Disease). Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 26, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, M.; Acosta, N.; Llewellyn, M.; Sanchez, H.; Adamson, S.; Miles, G.A.J.; Lopez, E.; Gonzalez, N.; Patterson, J.S.; Gaunt, M.W.; et al. Origins of Chagas disease: Didelphis species are natural hosts of Trypanosoma cruzi I and armadillos hosts of Trypanosoma cruzi II, including hybrids. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingales, B. Molecular epidemiology of Chagas disease: Gaps of knowledge and research priorities. Biomédica 2011, 31, 3–315. [Google Scholar]
- De Rojas Arias, A. Status of Chagas disease in the Americas. In Laboratorios Silanes; Enfermedad de Chagas: Estrategias en la Búsqueda de Nuevos Medicamentos, 1st ed.; Cerrteto, H., Gonzalez, M., Eds.; Una Visión Iberoamericana: Col. del Valle, Mexico, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 17–34. ISBN 978-607-95813-0-5. [Google Scholar]
- De Mello, T.F.; Bitencourt, H.R.; Pedroso, R.B.; Aristides, S.M.; Lonardoni, M.V.; Silveira, T.G. Leishmanicidal activity of synthetic chalcones in Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis. Exp. Parasitol. 2014, 136, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, J.V.; Maurício, S.; Bernardino, A.M.R.; Becker, K.M.; Machado, G.M.C.; Rodrigues, R.F.; Canto-Cavalheiro, M.M.; Leon, L.L. Synthesis and activity of novel tetrazole compounds and their pyrazole-4-carbonitrile precursors against Leishmania spp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 6310–6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinedo-Cancino, V.; Laurenti, M.D.; Kesper, N.; Umezawa, E.S. Evaluation of Leishmania (Leishmania) infantum excreted-secreted antigens for detection of canine leishmaniasis. Acta Trop. 2016, 161, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbina, J.; Docampo, R. Specific chemotherapy of Chagas disease: Controversies and advances. Trends Parasitol. 2003, 19, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarpenello, J. Enfermedad de Chagas (Tripanosomiasis Americana). Evid. Actual Pract. Ambul. 2004, 7, 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Kalil, J.; Cunha-Neto, E. Autoimmunity in Chagas disease cardiomyopathy: fullfilling the criteria at last? Parasitol. Today 1996, 12, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engman, D.M.; Leon, J.S. Pathogenesis of Chagas heart disease: Role of autoimmunity. Acta Trop. 2002, 81, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldos, V.; Nakayama, H.; Rolo, M.; Trucco, F.; Torres, S.; Vega, C.; Marrero-Ponce, Y.; Heguaburu, V.; Yaluff, G.; Go, A.; et al. Activity of a hydroxybibenzyl bryophyte constituent against Leishmania spp. and Trypanosoma cruzi: In silico, in vitro and in vivo activity studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 1797–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, C.; Rolón, M.; Martínez-Fernández, A.R.; Escario, J.A.; Gómez-Barrio, A. A new pharmacological screening assay with Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes expressing β-galactosidase. Parasitol. Res. 2005, 95, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepesheva, G.I. Design or screening of drugs for the treatment of Chagas disease: What shows the most promise? Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamim, M.; Domeneghini, L.; Rosaria, L.; Dias, S.; Kramer, L.; Regina, T.; Mascarello, A.; Steindel, M.; Augusto, R.; Carla, H.; et al. Trimethoxy-chalcone derivatives inhibit growth of Leishmania braziliensis: Synthesis, biological evaluation, molecular modeling and structure–activity relationship (SAR). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 5046–5052. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Research and Development to Meet Health Needs in Developing Countries; Report of the Consultative Expert Working Group on Research and Development: Strengthening Global Financing and Coordination; Financing and Coordination; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, H.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Al-Rawahi, A.; Green, I.R.; Gibbons, S. Fruitful decade for antileishmanial compounds from 2002 to late 2011. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10369–10428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, E.O.J.; Carvalho, P.B.; Avery, M.A.; Tekwani, B.L.; Labadie, G.R. Click chemistry decoration of amino sterols as promising strategy to developed new leishmanicidal drugs. Steroids 2014, 79, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diogo, E.B.T.; Dias, G.G.; Rodrigues, B.L.; Guimarães, T.T.; Valença, W.O.; Camara, C.A.; De Oliveira, R.N.; Da Silva, M.G.; Ferreira, V.F.; De Paiva, Y.G.; et al. Synthesis and anti-Trypanosoma cruzi activity of naphthoquinone-containing triazoles: Electrochemical studies on the effects of the quinoidal moiety. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 6337–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, E.N.; Menna-Barreto, R.F.S.; Pinto, M.d.C.F.R.; Silva, R.S.F.; Teixeira, D.V.; de Souza, M.C.B.V.; de Simone, C.A.; de Castro, S.L.; Ferreira, V.F.; Pinto, A.V. Naphthoquinoidal [1–3]-triazole, a new structural moiety active against Trypanosoma cruzi. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 1774–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, I.; Andrade, P.; Campo, V.L.; Guedes, P.M.M.; Sesti-Costa, R.; Silva, J.S.; Schenkman, S.; Dedola, S.; Hill, L.; Rejzek, M.; Nepogodiev, S.A.; et al. “Click chemistry” synthesis of a library of 1,2,3-triazole-substituted galactose derivatives and their evaluation against Trypanosoma cruzi and its cell surface trans-sialidase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 2412–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Andrade, P.; Galo, O.A.; Carvalho, M.R.; Lopes, C.D.; Carneiro, Z.A.; Sesti-Costa, R.; De Melo, E.B.; Silva, J.S.; Carvalho, I. 1,2,3-Triazole-based analogue of benznidazole displays remarkable activity against Trypanosoma cruzi. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 6815–6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samoylenko, V.; Dunbar, D.C.; Gafur, Md.A.; Khan, S.I.; Ross, S.A.; Mossa, J.S.; El-Feraly, F.S.; Tekwani, B.L.; Bossealaers, J.; Muhammad, I. Antiparasitic, nematicidal and antifouling constituents from Juniperus berries. Phyther. Res. 2008, 22, 1570–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmo, F.; Guardia, J.J.; Marin, C.; Messouri, I.; Rosales, M.J.; Urbanová, K.; Chayboun, I.; Chahboun, R.; Alvarez-Manzaneda, E.J.; Sánchez-Moreno, M. Prospects of an alternative treatment against Trypanosoma cruzi based on abietic acid derivatives show promising results in Balb/c mouse model. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahermo, M.; Krogerus, S.; Nasereddin, A.; Kaiser, M.; Brun, R.; Jaffe, C.L.; Yli-Kauhaluoma, J.; Moreira, V.M. Antiprotozoal activity of dehydroabietic acid derivatives against Leishmania donovani and Trypanosoma cruzi. Med. Chem. Comm. 2016, 7, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirttimaa, M.; Nasereddin, A.; Kopelyanskiy, D.; Kaiser, M.; Yli-Kauhaluoma, J.; Oksman-Caldentey, K.M.; Brun, R.; Jaffe, C.L.; Moreira, V.M.; Alakurtti, S. Abietane-type diterpenoid amides with highly potent and selective activity against Leishmania donovani and Trypanosoma cruzi. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dea-Ayuela, M.A.; Bilbao-Ramos, P.; Bolás-Fernández, F.; González-Cardenete, M.A. Synthesis and antileishmanial activity of C7- and C12-functionalized dehydroabietylamine derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 121, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, M.D.R.; Mata, R.; Castaneda, P.; Kirby, G.C.; Warhurst, D.C.; Croft, S.L.; Phillipson, J.D. Bioactive compounds from Celaenodendron mexicanum. Planta Med. 2000, 66, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauvain, M.; Kunesch, N.; Poisson, J.; Gantier, J.C.; Gayral, P.; Dedet, J.P. Isolation of leishmanicidal triterpenes and lignans from the amazonian liana Doliocarpus dentatus (Dilleniaceae). Phytother. Res. 1996, 10, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Santos, E.C.; Lopes, D.; Oliveira, R.R.; Carauta, J.P.P.; Falcao, C.A.B.; Kaplan, M.A.C.; Rossi-Bergmann, B. Antileishmanial activity of isolated triterpenoids from Pourouma guianensis. Phytomedicine 2004, 11, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, T.S.; Gattass, C.R.; Soares, D.C.; Cunha, M.R.; Ferreira, C.; Tavares, M.T.; Saraiva, E.; Parise-Filho, R.; Braden, H.; Delorenzi, J.C. Oleanolic acid (OA) as an antileishmanial agent: Biological evaluation and in silico mechanistic insights. Parasitol. Int. 2016, 65, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Hernández, D.; Barbosa, L.C.A.; Demuner, A.J.; de Almeida, R.M.; Fujiwara, R.T.; Ferreira, S.R. Highly potent anti-leishmanial derivatives of hederagenin, a triperpenoid from Sapindus saponaria L. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 124, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertino, M.W.; Verdugo, V.; Theoduloz, C.; Schmeda-Hirschmann, G. Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of some novel triazole derivatives from dehydroabietic acid. Molecules 2014, 19, 2523–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertino, M.W.; Lopez, C.; Theoduloz, C.; Schmeda-hirschmann, G. 1,2,3-Triazole-substituted oleanolic acid derivatives: Synthesis and antiproliferative activity. Molecules 2013, 18, 7661–7674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikus, J.; Steverding, D. A simple colorimetric method to screen drug cytotoxicity against Leishmania using the dye Alamar Blue. Parasitol. Int. 2000, 48, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolón, M.; Seco, E.M.; Vega, C.; Nogal, J.J.; Escario, A.; Gómez-Barrio, A.; Malpartida, F. Selective activity of polyene macrolides produced by genetically modified Streptomyces on Trypanosoma cruzi. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2006, 28, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1–34 are available from the authors.

| Compound | Leishmanicidal Activity on Promastigotes (µg/mL) | Antiepimastigote Activity of T. cruzi (µg/mL) | NCTC-Clone 929 Fibroblasts (µg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. braziliensis | L. infantum | T. cruzi | ||
| DHA | 44 | 72 | 212 | - |
| Dehydroabietinol | 63 | 40 | 66 | - |
| 1 | 53 | 60 | 46 | >256 |
| 2 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 3 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 4 | 64 | 64 | 61 | 189 |
| 5 | 218 | 193 | 223 | >256 |
| 6 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 7 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 8 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 9 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 10 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 11 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 12 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 13 | 242 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 14 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 15 | 89 | 53 | 69 | 232 |
| 16 | 71 | 73 | 199 | 129 |
| OA | >256 | >256 | >256 | - |
| 17 | >256 | >256 | 252 | 196 |
| 18 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 19 | 109 | 155 | >256 | >256 |
| 20 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 21 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 22 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 23 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 24 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 25 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 26 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 27 | >256 | >256 | 43 | >256 |
| 28 | >256 | >256 | 61 | >256 |
| 29 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 30 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 31 | >256 | 128 | >256 | >256 |
| 32 | >256 | >256 | >256 | - |
| 33 | >256 | >256 | >256 | - |
| 34 | >256 | >256 | >256 | - |
| Pentamidine | 3.3 | 3.3 | - | - |
| Benzimidazole | - | - | 15.0 | - |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pertino, M.W.; Vega, C.; Rolón, M.; Coronel, C.; Rojas de Arias, A.; Schmeda-Hirschmann, G. Antiprotozoal Activity of Triazole Derivatives of Dehydroabietic Acid and Oleanolic Acid. Molecules 2017, 22, 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030369
Pertino MW, Vega C, Rolón M, Coronel C, Rojas de Arias A, Schmeda-Hirschmann G. Antiprotozoal Activity of Triazole Derivatives of Dehydroabietic Acid and Oleanolic Acid. Molecules. 2017; 22(3):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030369
Chicago/Turabian StylePertino, Mariano Walter, Celeste Vega, Miriam Rolón, Cathia Coronel, Antonieta Rojas de Arias, and Guillermo Schmeda-Hirschmann. 2017. "Antiprotozoal Activity of Triazole Derivatives of Dehydroabietic Acid and Oleanolic Acid" Molecules 22, no. 3: 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030369
APA StylePertino, M. W., Vega, C., Rolón, M., Coronel, C., Rojas de Arias, A., & Schmeda-Hirschmann, G. (2017). Antiprotozoal Activity of Triazole Derivatives of Dehydroabietic Acid and Oleanolic Acid. Molecules, 22(3), 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030369