A Novel Fluoroimmunoassay for Detecting Ruscogenin with Monoclonal Antibodies Conjugated with CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
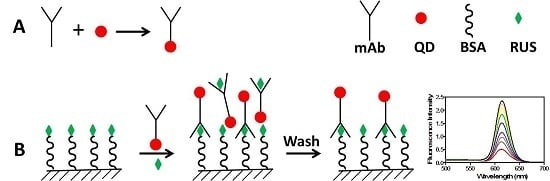
2.1. The Conjugation
2.2. Binding Affinity of the Conjugated mAb
2.3. FLISA Method
2.3.1. The Calibration Curve
2.3.2. The Comparison of the FLISA and ELISA
2.3.3. The Cross Reactivity
2.3.4. The Recovery, Precision, Accuracy in Plasma and Tissues of Rats
2.4. RUS Distribution Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Apparatus
3.3. Animals
3.4. Conjugation of QDs with Anti-RUS Monoclonal Antibody
3.5. Identification of the Conjugates
3.6. Binding Affinity of the Conjugated mAb
3.7. FLISA Procedure and Assessment of Method
3.7.1. The FLISA Procedure
3.7.2. Competition Curves
3.7.3. The Comparison of the FLISA and ELISA
3.7.4. Cross Reaction of the Analogues of RUS
3.7.5. The Method Assessment
Recovery Analysis
The Intra- and Inter-Day Precision and Accuracy
The LOD
3.8. The Tissue Distribution Study
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, G.; Jiang, N.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Yin, M.; Ma, X.; Zhou, K.; Qi, J.; Yu, B.; et al. Ruscogenin Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction by Suppressing TXNIP/NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and the MAPK Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, E1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zheng, Y.F.; Li, C.Y.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Wang, D.Q.; Wu, Z.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.G.; Li, P.B.; Peng, W.; et al. Discovery of Anti-inflammatory Ingredients in Chinese Herbal Formula Kouyanqing Granule based on Relevance Analysis between Chemical Characters and Biological Effects. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.-Y. Exploration on the Modern Research Methodology of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Based on the Systemic Research of Radix Ophiopogonis. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2007, 5, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, J.; Tian, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yan, J.; Yu, B. Antithrombotic Activities of Aqueous Extract from Radix Ophiopogon japonicus and Its Two Constituents. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 1267–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, L.Q.; Zhu, R.; Kong, H.; Wu, S.L.; Li, N.; Zuo, X.R.; Zhou, S.M.; Kou, J.P.; Yu, B.Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Ruscogenin attenuates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 16, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Bi, L.; Kong, H.; Xie, W.; Hong, Y.; Wang, H. Ruscogenin exerts beneficial effects on monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension by inhibiting NF-κB expression. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 12169–12176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Chen, L.; Gao, M.; Jiang, W.; Shao, F.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Kou, J.; Yu, B. Ruscogenin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice: involvement of tissue factor, inducible NO synthase and nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 12, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feihua, W.; Jingsong, C.; Jieyun, J.; Yu, B.; Xu, Q. Ruscogenin glycoside (Lm-3) isolated fromLiriope muscariimproves liver injury by dysfunctioning liver-infiltrating lymphocytes. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2000, 53, 681–688. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Wen, X.; Liu, J.; Liang, M.; Zeng, H.; Lin, Y.; Yu, B. Determination of ruscogenin in crude Chinese medicines and biological samples by immunoassay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 386, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güvenç, A.; Şatır, E.; Coşkun, M. Determination of Ruscogenin in Turkish Ruscus L. Species by UPLC. Chromatographia 2007, 66 (Suppl. 1), 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, T.; Liu, Q.; Qian, Y.; Yang, H.; Kong, J.; Kou, J.; Yu, B. Ruscogenin reduces cerebral ischemic injury via NF-kappaB-mediated inflammatory pathway in the mouse model of experimental stroke. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 714, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.N.; Jia, R.; Liu, Y.H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.L.; Kou, J.P.; Yu, B.Y. Ruscogenin suppresses mouse neutrophil activation: Involvement of protein kinase A pathway. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 154, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-H.; Li, M.L.; Feng, Y.-Q.; Hu, Y.-J.; Yu, B.-Y.; Jin, Q. Determination of Ruscogenin in Ophiopogonis Radix by High-performance Liquid Chromatography-evaporative Light Scattering Detector Coupled with Hierarchical Clustering Analysis. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2016, 12, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ji, P.Y.; Li, Z.W.; Yang, Q.; Wu, R. Rapid determination of ruscogenin in rat plasma with application to pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2015, 985, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, S.J.; Chang, J.C.; Kovtun, O.; McBride, J.R.; Tomlinson, I.D. Biocompatible quantum dots for biological applications. Chem. Biol. 2011, 18, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteve-Turrillas, F.A.; Abad-Fuentes, A. Applications of quantum dots as probes in immunosensing of small-sized analytes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.J. Optical sensing with quantum dots. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 520A–526A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Beier, R.C.; Xu, F.; Shen, J.; Ding, S. Simultaneous detection of multiple chemical residues in milk using broad-specificity antibodies in a hybrid immunosorbent assay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2716–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Chen, J.; Jiang, H.; He, J.; Shi, W.; Zhao, W.; Shen, J. Application of Quantum Dot—Antibody Conjugates for Detection of Sulfamethazine Residue in Chicken Muscle Tissue. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6139–6142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Xu, F.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Z.; Tong, J.; Guo, P.; Ding, S. Characterization and application of quantum dot nanocrystal-monoclonal antibody conjugates for the determination of sulfamethazine in milk by fluoroimmunoassay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 2243–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Arguelles, M.T.; Costa-Fernandez, J.M.; Pereiro, R.; Sanz-Medel, A. Simple bio-conjugation of polymer-coated quantum dots with antibodies for fluorescence-based immunoassays. Analyst 2008, 133, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Tao, G.; Meng, Y. A Novel CdSe/CdS Quantum Dot-based Competitive Fluoroimmunoassay for the Detection of Clenbuterol Residue in Pig Urine Using Megnetic Core/Shell Fe3o4/Au Nanoparticals as a Solid Carrier. Anal. Sci. Dec. 2009, 25, 1409–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ren, H.L.; Liu, N.; Sai, N.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Gao, Z.; Ning, B. A fluoroimmunoassay based on quantum dot-streptavidin conjugate for the detection of chlorpyrifos. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8895–8903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Han, Y.; Lin, L.; Deng, N.; Chen, B.; Liu, Y. Development of Quantum Dots-Labeled Antibody Fluorescence Immunoassays for the Detection of Morphine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 1290–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.; Zhu, L.; Yu, H. Dual-label quantum dot-based immunoassay for simultaneous determination of Carbadox and Olaquindox metabolites in animal tissues. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Xing, G.; Han, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, F.; Deng, R.; Hu, X.; Zhang, G. Novel fluoroimmunoassays for detecting ochratoxin A using CdTe quantum dots. J. Biophotonics 2017, 10, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, S.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.; Yu, R.; Lai, W.; Xiong, Y. Ultrasensitive direct competitive FLISA using highly luminescent quantum dot beads for tuning affinity of competing antigens to antibodies. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 972, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medintz, I.L.; Clapp, A.R.; Mattoussi, H.; Goldman, E.R.; Fisher, B.; Mauro, J.M. Self-assembled nanoscale biosensors based on quantum dot FRET donors. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Hu, X.; Ding, X. Monoclonal antibody-quantum dots CdTe conjugate-based fluoroimmunoassay for the determination of aflatoxin B1 in peanuts. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, J.-H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, B.-Y. A monoclonal antibody-based competitive ELISA for the determination of ruscogenin in Chinese traditional medicines and biological samples. Chin. J. Natl. Med. 2014, 12, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Gao, X. Engineering monovalent quantum dot-antibody bioconjugates with a hybrid gel system. Bioconj. Chem. 2011, 22, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Xiong, Y.; Lai, W.; Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Xie, M. A homogeneous immunosensor for AFB1 detection based on FRET between different-sized quantum dots. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 56, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.; Zheng, Y.; Long, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Yuan, J.; Cheng, F. Fluorescent immunosorbent assay for the detection of alpha lactalbumin in dairy products with monoclonal antibody bioconjugated with CdSe/ZnS quantum dots. Food Chem. 2014, 150, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.A.; Wang, S.; Allan, R.D.; Kennedy, I.R. A Rapid Aflatoxin B1 ELISA: Development and Validation with Reduced Matrix Effects for Peanuts, Corn, Pistachio, and Soybeans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2746–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |








| LOD (ng/mL) | IC50 (ng/mL) | Linear Range (ng/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA | 5.43 | 433.4 | 1–5000 |
| FLISA | 0.016 | 9.59 | 0.1–10,000 |
| Compounds | Cross Reactivities (%) |
|---|---|
| Sarsasapogenin | <0.1 |
| Diammonium glycyrrhizinate | <0.1 |
| Diosgenin | 22.39 |
| NotoginsenosideR1 | <0.1 |
| Oleanolic acid | <0.1 |
| Ruscogenin | 100 |
| Biological Sample | Calibration Curve | R2 | Concentration Range (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heart | Y = −0.7633X + 1.817 | 0.993 | 0.05–5000 |
| Liver | Y = −1.154X + 3.859 | 0.9862 | 0.05–5000 |
| Spleen | Y = −1.638X + 5.298 | 0.9902 | 0.05–5000 |
| Lung | Y = −1.749X + 6.163 | 0.9906 | 0.05–5000 |
| Kidney | Y = −0.9799X + 3.623 | 0.9887 | 0.05–5000 |
| Brain | Y = −0.8733X + 3.184 | 0.9957 | 0.05–5000 |
| Muscle | Y = −0.8592X + 3.589 | 0.9928 | 0.05–5000 |
| Fat | Y = −1.241X + 3.997 | 0.9871 | 0.05–5000 |
| Stomach | Y = −1.201X + 5.095 | 0.9917 | 0.05–5000 |
| Plasma | Y = −1.154X + 3.804 | 0.9952 | 0.05–5000 |
| Samples | Spiked (ng/mL) | Recovery | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (%) | RSD (%) | ||
| Heart | 1500 | 85.6 | 4.94 |
| 100 | 95.87 | 4.59 | |
| 10 | 91.22 | 6.04 | |
| Liver | 1500 | 86.98 | 3.32 |
| 100 | 92.15 | 6.38 | |
| 10 | 91.9 | 6.17 | |
| spleen | 1500 | 87.67 | 3.16 |
| 100 | 87.53 | 6.89 | |
| 10 | 93.34 | 7.93 | |
| Lung | 1500 | 93.35 | 5.16 |
| 100 | 87.55 | 8.54 | |
| 10 | 93.59 | 4.45 | |
| kidey | 1500 | 87.38 | 3.18 |
| 100 | 95.07 | 3.63 | |
| 10 | 91.45 | 6.32 | |
| Brain | 1500 | 94.19 | 5.05 |
| 100 | 91.39 | 6.12 | |
| 10 | 95.36 | 4.16 | |
| Muscle | 1500 | 92.59 | 5.26 |
| 100 | 85.39 | 3.41 | |
| 10 | 88.47 | 8.45 | |
| Fat | 1500 | 98.83 | 4.13 |
| 100 | 82.26 | 9.27 | |
| 10 | 91.26 | 8.76 | |
| Stomach | 1500 | 91.78 | 7.02 |
| 100 | 95.46 | 4.3 | |
| 10 | 100.22 | 0.87 | |
| Plasma | 1500 | 88.77 | 2.38 |
| 100 | 106.95 | 13.99 | |
| 10 | 94.75 | 9.29 | |
| Matrix | Accuracy RE (%) | Intra-Day RSD (%) | Inter-Day RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heart | −14.4 | 4.94 | 5.16 |
| −4.13 | 4.59 | 7.49 | |
| −8.78 | 6.04 | 1.87 | |
| Liver | −13.02 | 3.32 | 3.48 |
| −7.85 | 6.38 | 1.07 | |
| −8.1 | 6.17 | 2.5 | |
| Spleen | −12.33 | 3.16 | 1.4 |
| −12.47 | 6.89 | 6.49 | |
| −6.66 | 7.93 | 8.9 | |
| Lung | −6.65 | 5.16 | 3.68 |
| −12.45 | 8.54 | 5.12 | |
| −6.41 | 4.45 | 4.19 | |
| Kidney | −12.63 | 3.18 | 2.59 |
| −4.93 | 3.63 | 2.1 | |
| −8.55 | 6.32 | 2.67 | |
| Brain | −5.81 | 5.05 | 4.12 |
| −8.61 | 6.12 | 1.83 | |
| −4.64 | 4.16 | 6.41 | |
| Muscle | −7.41 | 5.26 | 6.72 |
| −14.61 | 3.41 | 3.92 | |
| −11.53 | 8.45 | 6.98 | |
| Fat | −1.17 | 4.13 | 6 |
| −7.74 | 9.27 | 4.58 | |
| −8.74 | 8.78 | 2.38 | |
| Stomach | −8.22 | 7.02 | 3.95 |
| −4.54 | 4.3 | 2.32 | |
| 0.22 | 0.89 | 9.33 | |
| Plasma | −11.23 | 2.39 | 6.5 |
| 6.95 | 13.99 | 5.11 | |
| −5.25 | 9.28 | 7.88 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Xu, T.; Gao, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Yu, B. A Novel Fluoroimmunoassay for Detecting Ruscogenin with Monoclonal Antibodies Conjugated with CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots. Molecules 2017, 22, 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22081250
Zhang H, Xu T, Gao L, Liu X, Liu J, Yu B. A Novel Fluoroimmunoassay for Detecting Ruscogenin with Monoclonal Antibodies Conjugated with CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots. Molecules. 2017; 22(8):1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22081250
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hongwei, Tao Xu, Lan Gao, Xiufeng Liu, Jihua Liu, and Boyang Yu. 2017. "A Novel Fluoroimmunoassay for Detecting Ruscogenin with Monoclonal Antibodies Conjugated with CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots" Molecules 22, no. 8: 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22081250
APA StyleZhang, H., Xu, T., Gao, L., Liu, X., Liu, J., & Yu, B. (2017). A Novel Fluoroimmunoassay for Detecting Ruscogenin with Monoclonal Antibodies Conjugated with CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots. Molecules, 22(8), 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22081250