TiO2-Based Hybrid Nanocomposites Modified by Phosphonate Molecules as Selective PAH Adsorbents
Abstract
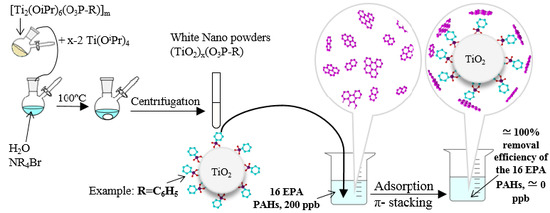
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Heteroleptic Precursors Synthesis
2.2. Hybrid Nanomaterials Synthesis
2.2.1. Syntheses and Characterization of (TiO2)x(VPA) Samples (Ti/P ratio (x) = 2–200)
2.2.2. Syntheses and Characterizations of (TiO2)100(O3P-R) Samples
2.3. Kinetic PAH Adsorption Studies of (TiO2)100(O3P-R) Samples
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Information
3.2. Product Characterizations
3.3. Synthesis of Titanium Precursors
3.3.1. Synthesis of [Ti2(OiPr)6(O3PC2H3)]m (1)
3.3.2. Synthesis of [Ti2(OiPr)6(O3PC6H5)]m (2)
3.3.3. Synthesis of [Ti2(OiPr)6(O3PCH2CH2NHCH2(C10H7)]m (3)
3.3.4. Synthesis of [Ti2(OiPr)6(O3PCH2CH2(NC9H10)]m (4)
3.4. Synthesis of Hybrid Nanomaterials (TiO2)x(O3P-R)
3.4.1. Preparation of (TiO2)x(VPA) nanoparticles
3.4.2. Preparation of (TiO2)100(PPA) Nanoparticles
3.4.3. Preparation of (TiO2)100(O3P-R) Nanoparticles: R = CH2CH2NHCH2(C10H7) (NMAPA), CH2CH2(NC9H10) (HQPA)
3.5. PAH Batch Adsorption Test Procedure
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contribution
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shuttleworth, K.L.; Cerniglia, E. Environmental aspects of PAH biodegradation. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 1995, 54, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashin, Y.V.; Bakhitova, L.M. Mutagenic and carcinogenic properties of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ. Health Perspect. 1979, 30, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Clemente, A.; Torres-Palma, R.A.; Peñuela, G.A. Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous environment by chemical treatments: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 478, 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ncube, S.; Madikizela, L.; Cukrowska, E.; Chimuka, L. Recent advances in the adsorbents for isolation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from environmental sample solutions. TrAC-Trend Anal. Chem. 2018, 99, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, S.; Bal Krishna, K.C.; Sarukkalige, R.; Lamichhane, S.; Bal Krishna, K.C.; Sarukkalige, R. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) removal by sorption: A review. Chemosphere 2016, 148, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Q.; Wu, Q.; Kuo, D.T.F.; Chen, S.; Hu, X.; Deng, M.; Zhang, H.; Luo, M. Removal efficiency and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a typical municipal wastewater treatment facility in Guangzhou, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougherty, D.A. The Cation−π Interaction. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janiak, C.; Janiak, C. A critical account on π–π stacking in metal complexes with aromatic nitrogen-containing ligands†. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton 2000, 21, 3885–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, J.W.G.; Wheeler, S.E. Taking the aromaticity out of aromatic interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 123, 7993–7995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Sánchez, B.; Wang, J. Micromotors for environmental applications: A review. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutin, P.H.; Guerrero, G.; Vioux, A.; Mutin, P.H.; Guerrero, G.; Vioux, A. Hybrid materials from organophosphorus coupling molecules. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, G.; Alauzun, J.G.; Granier, M.; Laurencin, D.; Mutin, P.H.; Guerrero, G.; Alauzun, J.G.; Granier, M.; Laurencin, D.; Mutin, P.H. Phosphonate coupling molecules for the control of surface/interface properties and the synthesis of nanomaterials. Dalton T. 2013, 42, 12569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.A.; Jaffé, P.R.; Chiou, C.T. Effect of Ten Quaternary Ammonium Cations on Tetrachloromethane Sorption to Clay from Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1990, 24, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutailler, G.; Guillard, C.; Daniele, S.; Hubert-Pfalzgraf, L.G. Low temperature and aqueous sol-gel deposit of photocatalytic active nanoparticulate TiO2. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 13, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidowski, S.K.; Holland, G.P. Solid-State NMR Characterization of Mixed Phosphonic Acid Ligand Binding and Organization on Silica Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2016, 32, 3253–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandary, R.; Alauzun, J.G.; Hesemann, P.; Stocco, A. Phase transfer of TiO2 nanoparticles from water to ionic liquid triggered by phosphonic acid grafting. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 8023–8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodard-Severac, F.; Guerrero, G.; Maquet, J.; Florian, P.; Gervais, C.; Mutin, P.H. High-Field 17 O MAS NMR Investigation of Phosphonic Acid Monolayers on Titania. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 5191–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Stellacci, F. Mixed-ligand nanoparticles as supramolecular receptors. Small 2011, 7, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cychosz, K.A.; Guillet-Nicolas, R.; García-Martínez, J.; Thommes, M. Recent advances in the textural characterization of hierarchically structured nanoporous materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 389–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balati, A.; Shahbazi, A.; Amini, M.M.; Hashemi, S.H. Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from wastewater by using silica-based organic–inorganic nanohybrid material. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2015, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, C.B.; Barros, A.L.; Moura, C.P.; de Lima, A.C.A.; Dias, F.S.; Vasconcellos, L.C.G.; Fechine, P.B.A.; Nascimento, R.F. Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from aqueous solutions by modified periodic mesoporous organosilica. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2011, 357, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, J.A.S.; Garcia, A.C.F.S.; Santos, D.O.; Sarmento, V.H.V.; de Mesquita, M.E.; Romão, L.P.C. Applications of inorganic–organic mesoporous materials constructed by self-assembly processes for removal of benzo[k]fluoranthene and benzo[b]fluoranthene. J. Sol.-Gel Sci. Technol. 2015, 75, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiStasio, R.A.; von Helden, G.; Steele, R.P.; Head-Gordon, M. On the T-shaped structures of the benzene dimer. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2007, 437, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahal, R.; Annani, F.; Pellet-Rostaing, S.; Arrachart, G.; Daniele, S. Surface modification of titanium oxide nanoparticles with chelating molecules: New recognition devices for controlling the selectivity towards lanthanides ionic separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 147, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bou Orm, N.; Dkhissi, Y.; Daniele, S.; Djakovitch, L.; Bou Orm, N.; Dkhissi, Y.; Daniele, S.; Djakovitch, L. Synthesis of 2-(arylamino)ethyl phosphonic acids via the aza-Michael addition on diethyl vinylphosphonate. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |











| Different Phosphonic Acids | Structures | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl phosphonic acid (VPA) |  | ||
| Phenyl phosphonic acid (PPA) |  | ||
| (2-{[(Naphthalen-2-yl) methyl] amino} ethyl) phosphonic acid (NMAPA) |  | ||
| [2-(3,4-Dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl) ethyl]phosphonic acid (HQPA) |  | ||
| Theoretical Ti/P Ratio | Experimental | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| % Ti | % P | Ti/P Ratio | |
| 25 | 50.69 | 1.03 | 32 |
| 50 | 51.29 | 0.72 | 46 |
| 75 | 82.00 | 0.82 | 65 |
| 100 | 50.03 | 0.35 | 92 |
| 125 | 68.43 | 0.36 | 123 |
| 150 | 79.84 | 0.35 | 148 |
| 200 | 106.31 | 0.36 | 190 |
| R Group | PPA | NMAPA | HQPA |
|---|---|---|---|
| % Ti | 54.52 | 59.62 | 59.06 |
| % P | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 |
| Ti/P | 98 | 106 | 105 |
| Ti/P (Molar Ratio) | 2 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 200 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (mmol) | 6.711 | 0.165 | 0.165 | 0.165 | 0.165 | 0.165 | 0.165 | 0.165 |
| y (mmol) | 0.00 | 3.81 | 7.95 | 6.05 | 8.11 | 10.21 | 12.26 | 16.4 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bou Orm, N.; Trieu, Q.A.; Daniele, S. TiO2-Based Hybrid Nanocomposites Modified by Phosphonate Molecules as Selective PAH Adsorbents. Molecules 2018, 23, 3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23113046
Bou Orm N, Trieu QA, Daniele S. TiO2-Based Hybrid Nanocomposites Modified by Phosphonate Molecules as Selective PAH Adsorbents. Molecules. 2018; 23(11):3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23113046
Chicago/Turabian StyleBou Orm, Nadine, Quoc An Trieu, and Stephane Daniele. 2018. "TiO2-Based Hybrid Nanocomposites Modified by Phosphonate Molecules as Selective PAH Adsorbents" Molecules 23, no. 11: 3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23113046
APA StyleBou Orm, N., Trieu, Q. A., & Daniele, S. (2018). TiO2-Based Hybrid Nanocomposites Modified by Phosphonate Molecules as Selective PAH Adsorbents. Molecules, 23(11), 3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23113046