Formation and Characterization of Lactoferrin-Hyaluronic Acid Conjugates and Their Effects on the Storage Stability of Sesamol Emulsions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. SDS-PAGE Analysis
2.2. Structural Characterization of LF-HA Systems
2.2.1. FTIR
2.2.2. Fluorescence Spectra
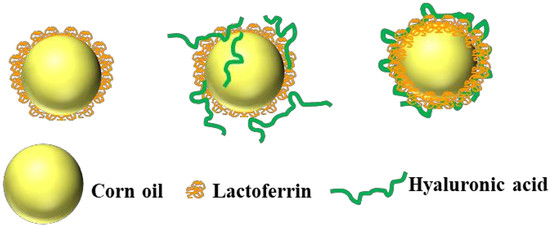
2.3. Proposed Formation Mechanism of LF-HA Conjugates
2.4. Emulsion Particle Size and ζ-Potential Analysis
2.5. Changes in Physical State of Different Emulsions During Storage
2.6. Chemical Stability of Sesamol Emulsions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of LF-HA Mixtures and Conjugates
3.3. SDS-PAGE
3.4. Characterization of Particles LF-HA Systems
3.4.1. FTIR
3.4.2. Fluorescence Spectrum Analysis
3.5. Preparation of Sesamol Emulsions
3.6. Measurements of Droplet Size and ζ-potential of Sesamol Emulsions
3.7. Storage Stability of Sesamol-Loaded Emulsions
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Oliveira, F.C.; dos Reis Coimbra, J.S.; de Oliveira, E.B.; Giraldo Zuniga, A.D.; Garcia Rojas, E.E. Food protein-polysaccharide conjugates obtained via the Maillard reaction: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1108–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ma, C.; Gao, Y.; McClements, D.J. Food-grade covalent complexes and their application as nutraceutical delivery systems: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. F 2017, 16, 76–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wei, T.; Wei, Z.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Influence of soybean soluble polysaccharides and beet pectin on the physicochemical properties of lactoferrin-coated orange oil emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 44, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Interfacial structure and stability of food emulsions as affected by protein-polysaccharide interactions. Soft Matter. 2008, 4, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Zhao, M.; McClements, D.J. Improving the stability of wheat protein-stabilized emulsions: Effect of pectin and xanthan gum addition. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.; Ding, R. Covalently cross-linked proteins & polysaccharides: Formation, characterisation and potential applications. Curr Opin Colloid In 2017, 28, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Jan, K.-C.; Ho, C.-T.; Hwang, L.S. Bioavailability and tissue distribution of sesamol in rat. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2008, 56, 7032–7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Li, H.; Fu, G.; Chen, X.; Chen, F.; Xie, M. The relationship of antioxidant components and antioxidant activity of sesame seed oil. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2571–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, K.-C.; Ho, C.-T.; Hwang, L.S. Elimination and metabolism of sesamol, a bioactive compound in sesame oil, in rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, S36–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Khullar, N.; Kakkar, V.; Kaur, I.P. Sesamol loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: A promising intervention for control of carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, Y.; Choe, E. Effects of sesamol, sesamin, and sesamolin extracted from roasted sesame oil on the thermal oxidation of methyl linoleate. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1871–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galano, A.; Raul Alvarez-Idaboy, J.; Francisco-Marquez, M. Physicochemical insights on the free radical scavenging activity of sesamol: Importance of the acid/base equilibrium. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 13101–13109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, X. Recent development of lactoferrin-based vehicles for the delivery of bioactive compounds: Complexes, emulsions, and nanoparticles. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 79, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Park, H.J. Stability investigation of hyaluronic acid based nanoemulsion and its potential as transdermal carrier. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencherif, S.A.; Srinivasan, A.; Horkay, F.; Hollinger, J.O.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Washburn, N.R. Influence of the degree of methacrylation on hyaluronic acid hydrogels properties. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.Y.; Lee, S.; Park, K.; Kim, K.; Park, J.H.; Kwon, I.C.; Jeong, S.Y. Preparation and characterization of hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2008, 69, 1591–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Chen, X.; Park, H. Design and investigation of nanoemulsified carrier based on amphiphile-modified hyaluronic acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Wang, R.; He, Y.; Dang, X. Fabrication, structure and surface charges of albumin-chitosan hybrids. Sci. China Chem. 2012, 55, 1788–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Mao, L.; Dai, L.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Characterization of chitosan-ferulic acid conjugates and their application in the design of beta-carotene bilayer emulsions with propylene glycol alginate. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 80, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shin, G.H.; Chen, X.; Park, H.J. Modified curcumin with hyaluronic acid: Combination of pro-drug and nano-micelle strategy to address the curcumin challenge. Food Res. Int. 2015, 69, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Liu, F.; Xu, C.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Molecular interaction between (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and bovine lactoferrin using multi-spectroscopic method and isothermal titration calorimetry. Food Res. Int. 2014, 64, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, M.; Ren, J.; Yang, B. Improvement of functional properties of peanut protein isolate by conjugation with dextran through Maillard reaction. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooster, T.J.; Augustin, M.A. Beta-lactoglobulin-dextran Maillard conjugates: Their effect on interfacial thickness and emulsion stability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 303, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, D.J. Emulsion design to improve the delivery of functional lipophilic components. In Annual Review of Food Science and Technology; Doyle, M.P., Klaenhammer, T.R., Eds.; 2010; Volume 1, pp. 241–269. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Wang, D.; Sun, C.; McClements, D.J.; Gao, Y. Utilization of interfacial engineering to improve physicochemical stability of beta-carotene emulsions: Multilayer coatings formed using protein and protein-polyphenol conjugates. Food Chem. 2016, 205, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasanphan, W.; Chirachanchai, S. Conjugation of gallic acid onto chitosan: An approach for green and water-based antioxidant. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 72, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Sun, C.; Yang, W.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Structural characterization and functional evaluation of lactoferrin-polyphenol conjugates formed by free-radical graft copolymerization. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 15641–15651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ma, C.; McClements, D.J.; Gao, Y. A comparative study of covalent and non-covalent interactions between zein and polyphenols in ethanol-water solution. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Mao, L. Characterization and stability evaluation of beta-carotene nanoemulsions prepared by high pressure homogenization under various emulsifying conditions. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ax, K.; Mayer-Miebach, E.; Link, B.; Schuchmann, H.; Schubert, H. Stability of lycopene in oil-in-water emulsions. Eng. Life Sci. 2003, 3, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alencar, J.; Gosset, G.; Rahmouni, H.; Culcasi, M.; Robin, M.; Reynier, J.-P.; Piccerelle, P.; Pietri, S. Development of spray- and freeze-dried high-concentration sesamol emulsions and antioxidant evaluation in fibroblasts and UV-Exposed rat skin slices. Drug Dev. Res. 2008, 69, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not Available. |







© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, C.; Duan, X.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, X.; Liu, F. Formation and Characterization of Lactoferrin-Hyaluronic Acid Conjugates and Their Effects on the Storage Stability of Sesamol Emulsions. Molecules 2018, 23, 3291. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123291
Liu R, Zhang J, Zhao C, Duan X, McClements DJ, Liu X, Liu F. Formation and Characterization of Lactoferrin-Hyaluronic Acid Conjugates and Their Effects on the Storage Stability of Sesamol Emulsions. Molecules. 2018; 23(12):3291. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123291
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Runhua, Jinhong Zhang, Caicai Zhao, Xiang Duan, David Julian McClements, Xuebo Liu, and Fuguo Liu. 2018. "Formation and Characterization of Lactoferrin-Hyaluronic Acid Conjugates and Their Effects on the Storage Stability of Sesamol Emulsions" Molecules 23, no. 12: 3291. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123291
APA StyleLiu, R., Zhang, J., Zhao, C., Duan, X., McClements, D. J., Liu, X., & Liu, F. (2018). Formation and Characterization of Lactoferrin-Hyaluronic Acid Conjugates and Their Effects on the Storage Stability of Sesamol Emulsions. Molecules, 23(12), 3291. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123291