Synthesis and Evaluation of 3-Substituted-4-(quinoxalin-6-yl) Pyrazoles as TGF-β Type I Receptor Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Residual Activity in an Enzymatic Assay
2.3. p38a MAP Kinase Assay
2.4. ALK5 Inhibitory Activity in an Enzymatic Assay
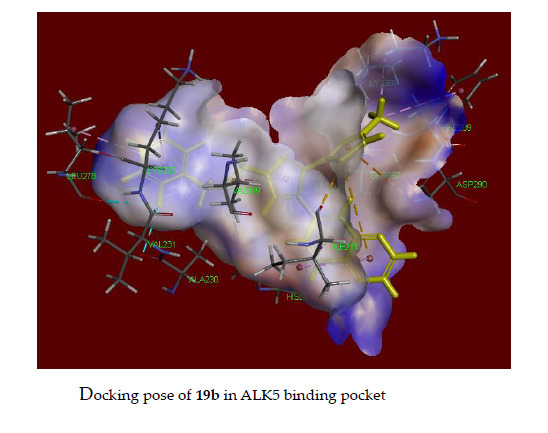
2.5. Docking Study of 18b and 19b in the Alk5 Active Site
2.6. ADMET Analysis
3. Experimental
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General procedure for the preparation of diphenyl ((6-(dimethylamino)pyridin-2-yl)(phenylamino)methyl)phosphonate (10a), Diphenyl ((4-methylthiazol-2-yl)(phenylamino)methyl)phosphonate (10b) and Diphenyl ((phenylamino)(pyrimidin-4-yl)methyl)phosphonate (21)
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Preparation of 1-(6-(Dimethylamino)pyridin-2-yl)-2-(quinoxalin-6-yl)ethanone (11a) 1-(4-Methylthiazol-2-yl)-2-(quinoxalin-6-yl)ethanone (11b) and 1-(Pyrimidin-4-yl)-2-(quinoxalin-6-yl)ethan-1-one (22)
3.1.3. General Procedure for the Preparation of N,N-Dimethyl-6-(4-(quinoxalin-6-yl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)pyridin-2-amine (12a) 4-Methyl-2-(4-(quinoxalin-6-yl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)thiazole (12b) and 6-(3-(Pyrimidin-4-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)quinoxaline (23)
3.1.4. General Procedure for the Preparation of 2-(3-(6-(Dimethylamino)pyridin-2-yl)-, 2-(3-(4-Methylthiazol-2-yl)- or 2-(3-(Pyrimidin-4-yl)-4-(quinoxalin-6-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)acetamide (14a–d, 16a–d, 25a, 25b, 25d) and 2-(5-(6-(Dimethylamino)pyridin-2-yl)-, 2-(5-(4-Methylthiazol-2-yl)- or 2-(5-(Pyrimidin-4-yl)-4-(quinoxalin-6-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-N-phenylacetamide (15a–d, 17a–d, 26a, 26b, 26d)
3.1.5. General Procedure for the Preparation of 2-(3-(6-(Dimethylamino)pyridin-2-yl)-4-(quinoxalin-6-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-N-phenylethanethioamide 18a–d, 2-(3-(4-Methylthiazol-2-yl)-4-(quinoxalin-6-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)-N-phenylethanethioamide 19a–d or N-Phenyl-2-(3-(pyrimidin-4-yl)-4-(quinoxalin-6-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)ethanethioamide (27b and 27d)
3.2. Kinase Assay
3.3. Docking Assay
3.4. Prediction of ADMET Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Derynck, R.; Zhang, Y.E. Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-β family signaling. Nature 2003, 425, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.; Zhu, Y.Z. Role of transforming growth factor-β in the progression of heart failure. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 2584–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.; Zhu, Y.J.; Yang, X.; Guo, Z.J.; Xu, W.B.; Tian, X.L. Effect of TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway on lung myofibroblast differentiation. Acta. Pharmacol. Sin. 2007, 28, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Hao, X.; Xu, L.; Cui, J.; Xue, L.; Tian, Z. Intestinal flora imbalance promotes alcohol-induced liver fibrosis by the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway in mice. Oncol Lett. 2017, 14, 4511–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, B.Y.; Park, S.R.; Cho, S.; Yu, S.L.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, C.G.; Kang, J.; Jung, D.Y.; Park, M.H.; Hwang, W.M.; et al. TGF-β-mediated NADPH oxidase 4-dependent oxidative stress promotes colistin-induce acute kidney injury. J. Antimicrob. Chemoth. 2018, 73, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heldin, C.H.; Miyazono, K.; Ten Dijke, P. TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD proteins. Nature 1997, 390, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Blobe, G.C. Role of transforming growth factor-β in hematologic malignancies. Blood 2006, 107, 4589–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrik, U.; Frank, G.; Roland, K.; Utz, S.; Hendrik, L.; Bernhard, H.R. Signaling Crosstalk of TGF-β/ALK5 and PAR2/PAR1: A Complex Regulatory Network Controlling Fibrosis and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, B.; Benjamin, R.; Dirk, R.; Roland, K.; Harald, B.; Hendrik, L.; Frank, G.; Hendrik, U. Dasatinib blocks transcriptional and promigratory responses to transforming growth factor-beta in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells through inhibition of Smad signaling: Implications for in vivo mode of action. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 199/1–199/12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byfield, S.D.; Major, C.; Laping, N.J.; Roberts, A.B. SB-505124 is a selective inhibitor of transforming growth factor-β type I receptors ALK4, ALK5, and ALK7. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 65, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhl, M.; Aulwurm, S.; Wischhusen, J.; Weiler, M.; Ma, J.Y.; Almirez, R.; Mangadu, R.; Liu, Y.W.; Platten, M.; Herrlinger, U.; et al. SD-208, a novel transforming growth factor β receptor I kinase inhibitor, inhibits growth and invasiveness and enhances immunogenicity of murine and human glioma cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7954–7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, L.; De Alwis, D.P.; Pitou, C.; Yingling, J.; Lahn, M.; Glatt, S. Semi-mechanistic modeling of the tumor growth inhibitory effects of LY2157299, a new type I receptor TGF-β kinase antagonist, in mice. Eur. J. Cancer 2008, 44, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.H.; Krishnaiah, M.; Sreenu, D.; Subrahmanyam, V.B.; Rao, K.S.; Lee, H.J.; Park, S.J.; Park, H.J.; Lee, K.; Sheen, Y.Y.; et al. Discovery of N-((4-([1,2,4]triazolo- [1,5-a]pyridin-6-yl)-5-(6-methylpyridin- 2-yl)-1H-imidazol-2-yl)methyl)-2-fluoroaniline (EW-7197): A highly potent, selective, and orally bioavailable inhibitor of TGF-β type I receptor kinase as cancer immunotherapeutic/antifibrotic agent. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4213–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.H.; Sreenu, D.; Krishnaiah, M.; Subrahmanyam, V.B.; Rao, K.S.; Mohan, A.V.N.; Park, C.V.; Son, J.Y.; Son, D.H.; Park, H.J.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 1-substituted-3(5)- (6-methylpyridin-2-yl)-4-(quinoxalin-6-yl)pyrzoles as transforming growth factor-β type I receptor kinase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 3917–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tojo, M.; Hamashima, Y.; Hanyu, A.; Kajimoto, T.; Saitoh, M.; Miyazono, K.; Node, M.; Imamura, T. The ALK-5 inhibitor A-83-01 inhibits Smad signaling and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by transforming growth factor-β. Cancer Sci. 2005, 96, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewang, P.M.; Kim, D.K. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 2-pyridyl-substituted pyrazoles and imidazoles as transforming growth factor-β type I receptor kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4228–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belveren, S.; Ali Dondas, H.; Ulger, M.; Poyraz, S.; Garcia, M.E.; Saperas, M.F.; Sansano, J.M. Synthesis of highly functionalized 2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)thiazole frameworks with interesting antibacterial and antimycobacterial activity. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 6718–6727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, N.; Correia-Branco, A.; Patricio, B.; Duarte, D.; Martel, F. In vitro studies on the inhibition of colon cancer by amino acid derivatives of bromothiazole. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 3507–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, J.M.; Carda, M.; Crespo, B.; Cunat, A.C.; Cozar, C.; Leon, M.L.; Marco, J.A.; Roda, N.; Cervera, J.F.S. Design, synthesis and antimalarial evaluation of novel thiazole derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 3938–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, G.; Jin, J.; Chen, H.; Cao, R.; Chen, X.; Xu, B. Synthesis and biological evaluation of pyrimidine derivatives as novel human Pin1 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2186–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, I.; Koshio, H.; Kuramochi, T.; Saitoh, C.; Inamura, H.Y.; Nozawa, C.K.; Yamamoto, E.; Yatsu, T.; Shimada, Y.; Sakamoto, S.; et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of amide derivatives of (4,4-difluoro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-5H- benzazepin-5- ylidene)acetic as selective arginine vasopressin V2 receptor agonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 3130–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concepcion, P.M.; Ana, B.S.M.; Benedicto del, R.; Pelaez, R.; Caballero, E.; Medarde, M. A new family of quinolone and quinoxaline analogues of combretastatins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 3771–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.H.; Krishnaiah, M.; Sreenu, D.; Rao, K.S.; Subrahmanyam, V.B.; Park, C.Y.; Son, J.Y.; Sheen, Y.Y.; Kim, D.K. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 1-substituted-3(5)-(6-methylpyridin- 2-yl)-4-(quinolin-6-yl)pyrazoles as transforming growth factor-β type I receptor kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 2633–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraldi, P.G.; Preti, D.; Tabrizi, M.A.; Fruttarolo, F.; Saponaro, G.; Baraldi, S.; Romagnoli, R.; Moorman, A.R.; Gessi, S.; Varani, K.; et al. N6-[(Hetero)aryl/(cyclo)alkyl-carbamoyl- methoxy-phenyl]-(2-chloro)-5’-N-ethylcarboxamido-adenosines: The first example of adenosine-related structures with potent agonist activity at the human A2B adenosine receptor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 2514–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Leng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Liu, H. Benzamide derivatives as dual-action hypoglycemic agents that inhibit glycogen phosphorylase and activate glucokinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 7301–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanyam, C.; Wager, T.T. Novel Compounds as Casein Kinase Inhibitors. U.S. Patent US2011,0098,272,A1, 28 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Eyers, P.A.; Craxton, M.; Morrice, N.; Cohen, P.; Goedert, M. Conversion of SB 203580-insensitive MAP kinase family members to drug-senstive forms by a single amino-acid substitution. Chem. Biol. 1998, 5, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.C.; Qin, Y.J.; Wang, P.F.; Yang, Y.A.; Wen, Q.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, H.Y.; Duan, Y.T.; Wang, Y.T.; Sang, Y.L.; et al. Sulfonamides containing coumarin moieties selectively and potently inhibit carbonic anhydrases II and IX: Design, synthesis, inhibitory activity and 3D-QSAR analysis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 66, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellibert, F.; Fouchet, M.H.; Nguyen, V.L.; Wang, R.; Krysa, G.; Gouvile, A.C.; Huet, S.; Dodic, N. Design of novel quinazoline deirivatives and related analogues as potent and selective ALK5 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 2277–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.M.; Feng, Y.D.; Lu, X.; Nie, J.B.; Li, W.; Wang, L.N.; Tian, L.J.; Liu, Q.H. Isosteroidal alkaloids as potent dual-binding site inhibitors of both acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase from the bulbs of Fritillaria walujewii. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 137, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, T.S.; Vanparia, S.F.; Patel, U.H.; Dixit, R.B.; Chudasama, C.J.; Patel, B.D.; Dixit, B.C. Novel 2,3-disubstituted quinazoline-4(3)-one derived from amino acid linked sulphonamide as a potent malarial antifolates for DHFR inhibition. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 129, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 18a–d, 19a–d, 25a, 25b, 25d, 27b, and 27d are available from the authors. |









| Compounds | R | X | Residual Activity a (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p38α b | ALK5 c | |||
| 14a | H | O | 110 | 85 |
| 14b | o-F | O | 118 | 84 |
| 14c | m-F | O | 121 | 37 |
| 14d | m-CN | O | 121 | 95 |
| 15a | H | 118 | 95 | |
| 15b | o-F | 117 | 87 | |
| 15c | m-F | 109 | 88 | |
| 15d | m-CN | 109 | 94 | |
| 18a | H | S | 119 | 29 |
| 18b | o-F | S | 125 | 70 |
| 18c | m-F | S | 165 | 29 |
| 18d | m-CN | S | 119 | 54 |
| 16a | H | O | 98 | 5 |
| 16b | o-F | O | 103 | 5 |
| 16c | m-F | O | 101 | 3 |
| 16d | m-CN | O | 108 | 3 |
| 17a | H | 68 | 46 | |
| 17b | o-F | 54 | 73 | |
| 17c | m-F | 66 | 69 | |
| 17d | m-CN | 97 | 58 | |
| 19a | H | S | 102 | 5 |
| 19b | o-F | S | 92 | 2 |
| 19c | m-F | S | 109 | 2 |
| 19d | m-CN | S | 105 | 13 |
| 3 (LY-2157299) | 4 | 1 | ||

| Compounds | R | X | IC50 (µM) | Selectivity Index c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p38α a | ALK5 b | ||||
| 18a | H | S | >10 | 5.75 | >2 |
| 18b | o-F | S | >10 | >10 | |
| 18c | m-F | S | >10 | 5.00 | >2 |
| 18d | m-CN | S | >10 | >10 | |
| 19a | H | S | >10 | 0.57 | >17 |
| 19b | o-F | S | >10 | 0.28 | >35 |
| 19c | m-F | S | >10 | 0.33 | >30 |
| 19d | m-CN | S | >10 | 0.37 | >27 |
| 25a | H | O | >10 | 5.03 | >2 |
| 25b | o-F | O | >10 | 3.66 | >3 |
| 25d | m-CN | O | >10 | 4.12 | >2 |
| 27b | o-F | S | >10 | >10 | |
| 27d | m-CN | S | >10 | 2.26 | >4 |
| 3 (LY-2157299) | 0.49 | 0.12 | 4 | ||
| Compounds | Absorption a | Solubility b | BBB c | CYP2D6 d | PPB e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19a | 0 | −5.72 | 1 | False | True |
| 19b | 0 | −5.998 | 1 | False | True |
| 19c | 0 | −5.997 | 1 | False | True |
| 19d | 0 | −5.541 | 4 | False | True |
| 3 | 0 | −5.415 | 2 | False | True |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.-M.; Guo, Z.; Xue, Y.-J.; Min, J.Z.; Zhu, W.-J.; Li, X.-Y.; Piao, H.-R.; Jin, C.H. Synthesis and Evaluation of 3-Substituted-4-(quinoxalin-6-yl) Pyrazoles as TGF-β Type I Receptor Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules 2018, 23, 3369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123369
Zhao L-M, Guo Z, Xue Y-J, Min JZ, Zhu W-J, Li X-Y, Piao H-R, Jin CH. Synthesis and Evaluation of 3-Substituted-4-(quinoxalin-6-yl) Pyrazoles as TGF-β Type I Receptor Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules. 2018; 23(12):3369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123369
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Li-Min, Zhen Guo, Yi-Jie Xue, Jun Zhe Min, Wen-Jing Zhu, Xiang-Yu Li, Hu-Ri Piao, and Cheng Hua Jin. 2018. "Synthesis and Evaluation of 3-Substituted-4-(quinoxalin-6-yl) Pyrazoles as TGF-β Type I Receptor Kinase Inhibitors" Molecules 23, no. 12: 3369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123369
APA StyleZhao, L. -M., Guo, Z., Xue, Y. -J., Min, J. Z., Zhu, W. -J., Li, X. -Y., Piao, H. -R., & Jin, C. H. (2018). Synthesis and Evaluation of 3-Substituted-4-(quinoxalin-6-yl) Pyrazoles as TGF-β Type I Receptor Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules, 23(12), 3369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123369