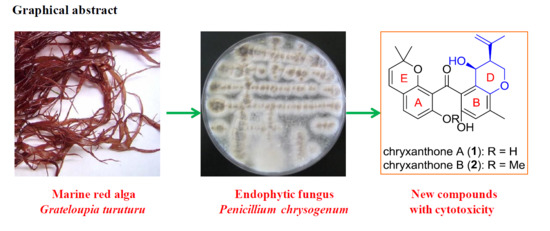
Benzophenone Derivatives from an Algal-Endophytic Isolate of Penicillium chrysogenum and Their Cytotoxicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structural Elucidation
2.2. Cytotoxic Activity of the New Compounds
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Fungal Material and Fermentation
3.3. Crude Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blunt, J.W.; Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 8–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Shao, C.L.; Meng, H.; She, Z.G.; Wang, C.Y. Anti-respiratory syncytial virus prenylated dihydroquinolone derivatives from the gorgonian-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. XS-20090B15. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2720–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imhoff, J.F. Natural products from marine fungi—Still an underrepresented resource. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, B.; Liu, X.; Mo, T.; Li, S.S.; Wang, J.; Shi, X.P.; Wang, X.H.; Zhu, Z.X.; Zhao, Y.F.; Jin, H.W.; et al. Nitric oxide inhibitory polyketides from Penicillium chrysogenum MT-12, an endophytic fungus isolated from Huperzia serrata. Fitoterapia 2017, 123, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.Q.; Li, D.; Peng, J.X.; Zhu, T.J.; Gu, Q.Q.; Li, D.H. Penicitols A–C and penixanacid A from the mangrove-derived Penicillium chrysogenum HDN11-24. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Zhou, L.M.; Chen, S.T.; Yang, B.; Liao, S.R.; Kong, F.D.; Lin, X.P.; Wang, F.Z.; Zhou, X.F.; Liu, Y.H. New chlorinated diphenyl ethers and xanthones from a deep-sea-derived fungus Penicillium chrysogenum SCSIO 41001. Fitoterapia 2018, 125, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.X.; Zhang, X.M.; Du, L.; Wang, W.; Zhu, T.J.; Gu, Q.Q.; Li, D.H. Sorbicatechols A and B, antiviral sorbicillinoids from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium chrysogenum PJX-17. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Wang, X.F.; Ren, G.W.; Yuan, X.L.; Deng, N.; Ji, G.X.; Li, W.; Zhang, P. Prenylated diphenyl ethers from the marine algal-derived endophytic fungus Aspergillus tennesseensis. Molecules 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.L.; Wang, D.; Tian, X.Y.; Cao, F.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhang, C.S. Anti-phytopathogenic and cytotoxic activities of crude extracts and secondary metabolites of marine-derived fungi. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chexal, K.K.; Fouweather, C.; Holker, J.S.E.; Simpson, T.J.; Young, K. The biosynthesis of fungal metabolites. Part III. Structure of shamixanthone and tajixanthone, metabolites of Aspergillus variecolor. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1974, 1584–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosophon, P.; Kanokmedhakul, S.; Kanokmedhakul, K.; Soytong, K. Prenylxanthones and a bicyclo[3.3.1]nona-2,6-diene derivative from the fungus Emericella rugulosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1442–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Fang, L.Z.; Liu, F.L.; Pang, X.J.; Qin, H.L.; Zhao, T.; Xu, L.L.; Yang, D.F.; Yang, X.L. New prenylxanthones, polyketide hemiterpenoid pigments from the endophytic fungus Emericella sp. XL029 and their anti-agricultural pathogenic fungal and antibacterial activities. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 31115–31122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Yang, M.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Shao, C.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Hu, L.D.; Cao, F.; Zhu, H.J. Absolute configurations of 14,15-hydroxylated prenylxanthones from a marine-derived Aspergillus sp. fungus by chiroptical methods. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10621–10630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.; Zhang, X.W.; Zhang, M.; Li, W.; Ma, Z.Y.; Zhu, H.J.; Cao, F. Aspergixanthones I–K, new anti-Vibrio prenylxanthones from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. ZA-01. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Wu, C.; Long, H.; Chen, R.; Liu, D.; Proksch, P.; Guo, P.; Lin, W. Varioxiranols A–G and 19-O-methyl-22-methoxypre-shamixanthone, PKS and hybrid PKS-derived metabolites from a sponge-associated Emericella variecolor fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, M.; Hamasaki, T.; Hatsuda, Y.; Fukuyama, K.; Tsukihara, T.; Katsube, Y. Epishamixanthone, a new metabolite from Aspergillus rugulosus. Agr. Biol. Chem. 1976, 40, 1051–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaussian 09, revision D.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2013.
- Sanchez, J.F.; Entwistle, R.; Hung, J.H.; Yaegashi, J.; Jain, S.; Chiang, Y.M.; Wang, C.C.C.; Oakley, B.R. Genome-based deletion analysis reveals the prenyl xanthone biosynthesis pathway in Aspergillus nidulans. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 4010–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holker, J.S.E.; Lapper, R.D.; Simpson, T.J. The biosynthesis of fungal metabolites. Part IV. Tajixanthone: 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum and feedings with [1-13C]- and [2-13C]-acetate. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1974, 2135–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralj, A.; Kehraus, S.; Krick, A.; Eguereva, E.; Kelter, G.; Maurer, M.; Wortmann, A.; Fiebig, H.H.; König, G.M. Arugosins G and H: prenylated polyketides from the marine-derived fungus Emericella nidulans var. acristata. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, X.M.; Teuscher, F.; Li, D.L.; Diesel, A.; Ebel, R.; Proksch, P.; Wang, B.G. Chaetopyranin, a benzaldehyde derivative, and other related metabolites from Chaetomium globosum, an endophytic fungus derived from the marine red alga Polysiphonia urceolata. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1622–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.L.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X.M.; Du, Y.M.; Hou, X.D.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, Z.F. Cytological assessments and transcriptome profiling demonstrate that evodiamine inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in a renal carcinoma cell line. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12572–12583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1 and 2 are available from the authors. |




| Compound 1 | Compound 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | δH (mult, J in Hz) | δC, type | δH (mult, J in Hz) | δC, type |
| 1 | 154.1, C | 150.9, C | ||
| 2 | 112.3, C | 115.0, C | ||
| 3 | 7.12, d (8.4) | 132.4, CH | 7.04, d (8.4) | 128.1, CH |
| 4 | 6.39, d (8.4) | 108.6, CH | 6.55, d (8.4) | 104.3, CH |
| 5 | 6.58, s | 117.6, CH | 6.52, s | 118.7, CH |
| 6 | 128.3, C | 130.3, C | ||
| 7 | 144.1, C | 144.5, C | ||
| 8 | 113.8, C | 124.3, C | ||
| 9 | 121.5, C | 121.2, C | ||
| 10 | 161.7, C | 158.1, C | ||
| OH-10/ OCH3-10 | 12.20, s | 3.69, s | 56.3, CH3 | |
| 11 | 146.9, C | 150.0, C | ||
| OH-11 | 8.88, s | 9.07, s | ||
| 12 | 126.4, C | 127.0, C | ||
| 13 | 200.6, C | 198.1, C | ||
| 14 | 6.26, d (9.8) | 121.3, CH | 6.31, d (9.8) | 121.8, CH |
| 15 | 5.44, d (9.8) | 126.7, CH | 5.51, d (9.8) | 129.0, CH |
| 16 | 76.7, C | 76.6, C | ||
| 17 | 0.98, s | 27.2, CH3 | 1.13, s | 28.2, CH3 |
| 18 | 0.92, s | 26.6, CH3 | 0.79, s | 26.6, CH3 |
| 19a 19b | 4.18, m 4.13, m | 62.8, CH2 | 4.26, dd (10.1, 3.0) 4.20, dd (11.0, 10.1) | 63.1, CH2 |
| 20 | 2.34, br d (11.0) | 44.4, CH | 2.37, br d (11.0) | 43.7, CH |
| 21 | 142.1, C | 142.6, C | ||
| 22a 22b | 4.83, s 4.61, s | 111.6, CH2 | 4.87, s 4.65, s | 111.9, CH2 |
| 23 | 1.70, s | 22.1, CH3 | 1.76, s | 22.5, CH3 |
| 24 | 2.10, s | 16.0, CH3 | 2.07, s | 16.9, CH3 |
| 25 | 4.53, br s | 61.5, CH | 4.59, br s | 62.4, CH |
| OH-25 | − | 4.14, br s | ||
| A549 a | BT-549 a | HeLa a | HepG2 a | MCF-7 a | THP-1 a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 41.7 ± 1.9 | 20.4 ± 1.2 | 23.5 ± 0.2 | 33.6 ± 1.4 | 46.4 ± 1.2 | >50 |
| 2 | 20.4 ± 0.9 | >50 | >50 | >50 | >50 | 41.1 ± 0.5 |
| Epirubicin b | 7.2 ± 0.11 | 5.3 ± 0.02 | 2.9 ± 0.04 | 4.6 ± 0.11 | 5.2 ± 0.02 | 5.5 ± 0.04 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, D.-L.; Yuan, X.-L.; Du, Y.-M.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Zhang, P. Benzophenone Derivatives from an Algal-Endophytic Isolate of Penicillium chrysogenum and Their Cytotoxicity. Molecules 2018, 23, 3378. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123378
Zhao D-L, Yuan X-L, Du Y-M, Zhang Z-F, Zhang P. Benzophenone Derivatives from an Algal-Endophytic Isolate of Penicillium chrysogenum and Their Cytotoxicity. Molecules. 2018; 23(12):3378. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123378
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Dong-Lin, Xiao-Long Yuan, Yong-Mei Du, Zhong-Feng Zhang, and Peng Zhang. 2018. "Benzophenone Derivatives from an Algal-Endophytic Isolate of Penicillium chrysogenum and Their Cytotoxicity" Molecules 23, no. 12: 3378. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123378
APA StyleZhao, D. -L., Yuan, X. -L., Du, Y. -M., Zhang, Z. -F., & Zhang, P. (2018). Benzophenone Derivatives from an Algal-Endophytic Isolate of Penicillium chrysogenum and Their Cytotoxicity. Molecules, 23(12), 3378. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123378