Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activity and Machine Learning Classification Analysis of Essential Oils from Different Mediterranean Plants against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. EO Extraction
2.3. GC–MS Analysis
2.4. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
2.5. Determination of Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
2.6. Static Biofilm Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis of Biological Evaluation
2.8. Machine Learning Binary Classification
2.8.1. General Methods
2.8.2. Validation
2.8.3. Accuracy (ACC)
2.8.4. Precision, Positive Predictive Values (PPV)
2.8.5. Recall, Sensitivity, True Positive Rate (TPR)
2.8.6. TNR
2.8.7. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve
2.8.8. Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC)
3. Results
3.1. EO Extraction
3.2. GC-MS Analysis of EOs
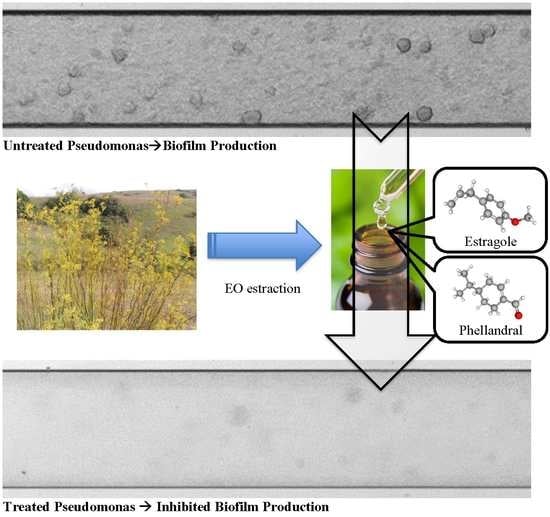
3.3. Qualitative Analysis of EOs Effect on Biofilm Formation of P. aeruginosa
3.4. Application of Machine Learning Algorithms
4. Discussion
4.1. Chemical Quantitative Composition–Activity Relationships
4.2. Gradient Boosting Binary Classification Model
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davies, D. Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Alam, A.; Rani, M.; Ehtesham, N.Z.; Hasnain, S.E. Biofilms: Survival and defense strategy for pathogens. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 307, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Estrada, S.; Borgatta, B.; Rello, J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa ventilator-associated pneumonia management. Infect. Drug Resist. 2016, 9, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cag, Y.; Caskurlu, H.; Fan, Y.; Cao, B.; Vahaboglu, H. Resistance mechanisms. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetti, M.; Righi, E.; Viscoli, C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa serious infections: Mono or combination antimicrobial therapy? Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanc, D.S.; Francioli, P.; Zanetti, G. Molecular Epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Intensive Care Units—A Review. Open Microbiol. J. 2007, 1, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulcahy, L.R.; Isabella, V.M.; Lewis, K. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in disease. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 68, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjarnsholt, T.; Kirketerp-Moller, K.; Jensen, P.O.; Madsen, K.G.; Phipps, R.; Krogfelt, K.; Hoiby, N.; Givskov, M. Why chronic wounds will not heal: A novel hypothesis. Wound Repair. Regen. 2008, 16, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradeep Kumar, S.S.; Easwer, H.V.; Maya Nandkumar, A. Multiple drug resistant bacterial biofilms on implanted catheters—A reservoir of infection. J. Assoc. Phys. India 2013, 61, 702–707. [Google Scholar]
- Papa, R.; Selan, L.; Parrilli, E.; Tilotta, M.; Sannino, F.; Feller, G.; Tutino, M.L.; Artini, M. Anti-Biofilm Activities from Marine Cold Adapted Bacteria Against Staphylococci and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bozovic, M.; Pirolli, A.; Ragno, R. Mentha suaveolens Ehrh. (Lamiaceae) Essential Oil and Its Main Constituent Piperitenone Oxide: Biological Activities and Chemistry. Molecules 2015, 20, 8605–8633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozovic, M.; Ragno, R. Calamintha nepeta (L.) Savi and its Main Essential Oil Constituent Pulegone: Biological Activities and Chemistry. Molecules 2017, 22, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langeveld, W.T.; Veldhuizen, E.J.A.; Burt, S.A. Synergy between essential oil components and antibiotics: A review. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 40, 76–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stringaro, A.; Vavala, E.; Colone, M.; Pepi, F.; Mignogna, G.; Garzoli, S.; Cecchetti, S.; Ragno, R.; Angiolella, L. Effects of Mentha suaveolens Essential Oil Alone or in Combination with Other Drugs in Candida albicans. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freires, A.I.; Denny, C.; Benso, B.; de Alencar, M.S.; Rosalen, L.P. Antibacterial Activity of Essential Oils and Their Isolated Constituents against Cariogenic Bacteria: A Systematic Review. Molecules 2015, 20, 7329–7358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoharan, R.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Kim, S.I.; Lee, J. Inhibitory effects of the essential oils-longipinene and linalool on biofilm formation and hyphal growth of Candida albicans. Biofouling 2017, 33, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, P.S.; Rai, R.V. Inhibition of quorum-sensing-controlled virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Murraya koenigii essential oil: A study in a Caenorhabditis elegans infectious model. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 1528–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanovic-Radic, Z.; Pejcic, M.; Stojanovic, N.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Stankovic, N. Potential of Ocimum basilicum L. and Salvia officinalis L. essential oils against biofilms of P. aeruginosa clinical isolates. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 62, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bozovic, M.; Garzoli, S.; Sabatino, M.; Pepi, F.; Baldisserotto, A.; Andreotti, E.; Romagnoli, C.; Mai, A.; Manfredini, S.; Ragno, R. Essential Oil Extraction, Chemical Analysis and Anti-Candida Activity of Calamintha nepeta (L.) Savi subsp. glandulosa (Req.) Ball-New Approaches. Molecules 2017, 22, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozovic, M.; Navarra, A.; Garzoli, S.; Pepi, F.; Ragno, R. Esential oils extraction: A 24-hour steam distillation systematic methodology. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 2387–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzoli, S.; Bozovic, M.; Baldisserotto, A.; Sabatino, M.; Cesa, S.; Pepi, F.; Vicentini, C.B.; Manfredini, S.; Ragno, R. Essential oil extraction, chemical analysis and anti-Candida activity of Foeniculum vulgare Miller—New approaches. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzoli, S.; Pirolli, A.; Vavala, E.; Di Sotto, A.; Sartorelli, G.; Bozovic, M.; Angiolella, L.; Mazzanti, G.; Pepi, F.; Ragno, R. Multidisciplinary Approach to Determine the Optimal Time and Period for Extracting the Essential Oil from Mentha suaveolens Ehrh. Molecules 2015, 20, 9640–9655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Tipping, M.E.; Bishop, C.M. Probabilistic principal component analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1999, 61, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, P.; Brunak, S.; Chauvin, Y.; Andersen, C.A.F.; Nielsen, H. Assessing the accuracy of prediction algorithms for classification: An overview. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metz, C.E. Basic principles of ROC analysis. Semin. Nucl. Med. 1978, 8, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-Vector Networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.K. The random subspace method for constructing decision forests. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1998, 20, 832–844. [Google Scholar]
- Vert, J.-P. Kernel methods in genomics and computational biology. In Medical Informatics: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications; Idea Group, Inc.: Hershey, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramanian, D.; Schneper, L.; Kumari, H.; Mathee, K. A dynamic and intricate regulatory network determines Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of listed essential oils are available from the authors. |



| EO (mg/mL) | R3 | R12 | CJM3 | CAM4 | CSM2 | FS1 | FSM5 | FOM4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 55.11 | 50.62 | 36.71 | 59.48 | 28.23 | 30.84 | 47.38 | 28.31 |
| 12.5 | 41.41 | 45.18 | 37.10 | 54.56 | 41.36 | 38.83 | 49.12 | 25.48 |
| 6.25 | 37.77 | 57.44 | 34.64 | 55.82 | 37.79 | 30.16 | 49.51 | 25.01 |
| 3.125 | 42.25 | 57.42 | 40.09 | 71.80 | 40.48 | 38.40 | 54.16 | 25.62 |
| 1.55 | 48.49 | 65.06 | 38.80 | 69.33 | 44.34 | 44.93 | 90.16 | 30.44 |
| 0.78 | 47.81 | 64.60 | 50.05 | 67.19 | 51.65 | 38.67 | 78.74 | 37.15 |
| 0.39 | 49.49 | 61.97 | 54.87 | 72.45 | 42.97 | 84.39 | 76.10 | 39.34 |
| 0.18 | 57.39 | 66.48 | 53.90 | 69.42 | 49.18 | 60.02 | 80.81 | 32.54 |
| 0.09 | 60.37 | 61.83 | 48.00 | 72.80 | 43.08 | 59.75 | 78.51 | 38.32 |
| 0.0488 | 70.65 | 59.05 | 52.99 | 83.24 | 50.26 | 42.44 | 88.71 | 38.28 |
| 0.0244 | 45.12 | 63.91 | 41.65 | 73.93 | 34.01 | 47.96 | 59.63 | 39.47 |
| 0.0122 | 64.81 | 66.11 | 46.59 | 73.19 | 40.02 | 57.26 | 75.63 | 38.29 |
| 0.0061 | 65.40 | 59.87 | 50.14 | 82.00 | 37.86 | 27.50 | 143.53 | 37.34 |
| 0.00305 | 63.06 | 78.37 | 45.22 | 69.05 | 35.44 | 38.70 | 117.45 | 39.75 |
| 0.00152 | 60.94 | 70.11 | 44.76 | 79.77 | 40.72 | 44.94 | 104.92 | 47.53 |
| 0.00076 | 61.95 | 65.18 | 40.29 | 73.17 | 37.14 | 37.13 | 112.35 | 53.00 |
| 0.0003814 | 61.13 | 62.05 | 49.74 | 76.76 | 47.15 | 42.07 | 113.75 | 37.23 |
| 0.0001907 | 56.98 | 65.80 | 48.48 | 83.21 | 49.49 | 36.59 | 90.67 | 57.15 |
| 0.00009535 | 72.29 | 65.27 | 45.52 | 71.44 | 52.18 | 39.25 | 79.33 | 46.41 |
| 0.000047675 | 64.71 | 74.79 | 44.19 | 91.78 | 46.23 | 43.30 | 99.52 | 68.74 |
| Statistical Parameter | At 48.8 µg/mL | At 3.125 mg/mL |
|---|---|---|
| ACC CV | 0.90 | 0.72 |
| MCC CV | 0.64 | 0.51 |
| Precision–Recall AUC | 0.84 | 0.72 |
| ROC AUC | 0.80 | 0.68 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Artini, M.; Patsilinakos, A.; Papa, R.; Božović, M.; Sabatino, M.; Garzoli, S.; Vrenna, G.; Tilotta, M.; Pepi, F.; Ragno, R.; et al. Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activity and Machine Learning Classification Analysis of Essential Oils from Different Mediterranean Plants against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecules 2018, 23, 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020482
Artini M, Patsilinakos A, Papa R, Božović M, Sabatino M, Garzoli S, Vrenna G, Tilotta M, Pepi F, Ragno R, et al. Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activity and Machine Learning Classification Analysis of Essential Oils from Different Mediterranean Plants against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecules. 2018; 23(2):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020482
Chicago/Turabian StyleArtini, Marco, Alexandros Patsilinakos, Rosanna Papa, Mijat Božović, Manuela Sabatino, Stefania Garzoli, Gianluca Vrenna, Marco Tilotta, Federico Pepi, Rino Ragno, and et al. 2018. "Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activity and Machine Learning Classification Analysis of Essential Oils from Different Mediterranean Plants against Pseudomonas aeruginosa" Molecules 23, no. 2: 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020482
APA StyleArtini, M., Patsilinakos, A., Papa, R., Božović, M., Sabatino, M., Garzoli, S., Vrenna, G., Tilotta, M., Pepi, F., Ragno, R., & Selan, L. (2018). Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activity and Machine Learning Classification Analysis of Essential Oils from Different Mediterranean Plants against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecules, 23(2), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020482