Alkaloids from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and Their Anti-Inflammatory Effects on LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
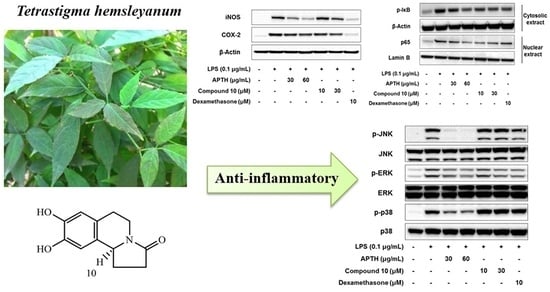
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Measurement of NO, PGE2, IL-1β and IL-6 Production and Cell Cytotoxicity
3.5. Western Blotting Analysis
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shao, Q.; Deng, Y.; Fang, H.; Zhao, X. Optimization of polysaccharides extraction from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum diels et gilg using response surface methodology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 958–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.-J.; Ding, G.-Q.; Fu, J.-Y.; Meng, J.; Zhang, R.-H.; Lou, X.-M. Immunoregulatory effects of ethyl-acetate fraction of extracts from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum diels et. Gilg on immune functions of icr mice. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2008, 21, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Wu, X.; Rao, L. Tetrastigma hemsleyanum (sanyeqing) root tuber extracts induces apoptosis in human cervical carcinoma hela cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 165, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Fan, Y.-W.; Liu, X.-R.; Deng, Z.-Y. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of phenolics in Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and their antioxidant and antiproliferative activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 10507–10515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.L.; Liu, X.G. Extraction of flavonoids from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum diels et gilg and their antioxidant activity. J. Food Process Preserv. 2015, 39, 2197–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Shah, M.D.; Gnanaraj, C.; Iqbal, M. In vitro total phenolics, flavonoids contents and antioxidant activity of essential oil, various organic extracts from the leaves of tropical medicinal plant Tetrastigma from Sabah. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2011, 4, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Hao, W.; Lin, X.; Fan, D.; Zhou, J. Antitumor activity of total flavonoids from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum diels et gilg is associated with the inhibition of regulatory t cells in mice. OncoTargets Ther. 2014, 7, 947–956. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Hui, Q.; Chen, R.; Li, H.; Peng, H.; Chen, F.; Deng, Z. Apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells induced by the phenolics of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum leaves and their antitumor effects in H22 tumor-bearing mice. J. Funct. Food. 2018, 40, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, G.M. A calculated response: Control of inflammation by the innate immune system. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Ahn, H.M.; Shen, T.; Yoon, K.; Jang, H.-J.; Lee, Y.J.; Yang, H.M.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, C.; Han, M.H. Anti-inflammatory activity of ethanol extract derived from Phaseolus angularis beans. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.J.; Moon, M.E.; Park, H.S.; Im, S.Y.; Kim, Y.H. Chitosan oligosaccharide (COS) inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory effects in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 358, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, K.-J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-B.; Lee, K.-W.; Jeong, S.-Y.; Park, H.-J.; Jung, H.-J.; Cho, Y.-W.; Yun, K.; Lee, K.-T. Inhibition of LPS-induced no and PGE2 production by asiatic acid via NF-κB inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages: Possible involvement of the IKK and MAPK pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroux, F.S.; Lefer, D.J.; Kawachi, S.; Scalia, R.; Cockrell, A.S.; Gray, L.; Van der Heyde, H.; Hoffman, J.M.; Grisham, M.B. Role of nitric oxide in the regulation of acute and chronic inflammation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2000, 2, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.-Q.; Pang, B.; Kiziltepe, T.; Trudel, L.J.; Engelward, B.P.; Dedon, P.C.; Wogan, G.N. Threshold effects of nitric oxide-induced toxicity and cellular responses in wild-type and p53-null human lymphoblastoid cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2006, 19, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pando, M.P.; Verma, I.M. Signal-dependent and-independent degradation of free and NF-κB-bound IκBα. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 21278–21286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, S.-J.; Chung, T.-W.; Son, M.-J.; Kim, S.-H.; Moon, T.C.; Son, K.H.; Kim, H.P.; Chang, H.W.; Kim, C.-H. The naturally occurring biflavonoid, ochnaflavone, inhibits LPS-induced iNOS expression, which is mediated by ERK1/2 via NF-κB regulation, in RAW264.7 cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2006, 447, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Suh, S.-J.; Kwak, C.-H.; Kwon, K.-M.; Seo, C.-S.; Li, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, X.; Hwang, S.-L.; Kwon, O. Saucerneol F, a new lignan, inhibits iNOS expression via MAPKs, NF-κB and AP-1 inactivation in LPS-induced RAW264. 7 cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 12, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Lafuente, A.; Guillamón, E.; Villares, A.; Rostagno, M.A.; Martínez, J.A. Flavonoids as anti-inflammatory agents: Implications in cancer and cardiovascular disease. Inflamm. Res. 2009, 58, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamieńska-Trela, K.; Kania, L.; Bechcicka, M. 13C NMR studies on the structure of 5H- and 6H-indolo-[2,3-b] quinolines and the related compounds. J. Mol. Struct. 2003, 661, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hämäläinen, A.; Tois, J.; Franzén, R. Preparation of indole-phosphine oxazoline (indphox) ligands and their application in allylic alkylation. Tetrahedron-Asymmetry 2010, 21, 2376–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Kim, W.-C.; Jeon, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-W.; Joo, G.-J.; Rhee, I.-K.; Song, K.-S. Growth inhibitors of soybean seedling from Bacillus sp. IJ-31. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2003, 46, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Sauleau, P.; Martin, M.-T.; Dau, M.-E.T.H.; Youssef, D.T.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.-L. Hyrtiazepine, an azepino-indole-type alkaloid from the red sea marine sponge Hyrtios erectus. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1676–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, I.K.; Lee, K.H.; Choi, S.U.; Lee, K.R. A new flavonol glycoside from Hylomecon vernalis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- OuYang, J.; Zhou, W.N.; Li, G.; Wang, X.Y.; Ding, C.X.; Suo, Y.R.; Wang, H.L. Three new alkaloids from Hippophae rhamnoides Linn. subsp. sinensis Rousi. Helv. Chim. Acta 2015, 98, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueoend, R.M.; Walker, J.; Neier, R.W. Assessment of the active-site requirements of 5-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase: Evaluation of substrate and product analogs as competitive inhibitors. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 5005–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, N.; Matsuda, M.; Uenishi, J. Stereoselective synthesis of tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids: (−)-trolline, (+)-crispin A, (+)-oleracein E. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 8648–8653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, S.; Hirasawa, H.; Shiga, H.; Nakanishi, K.; Matsuda, K.-I.; Nakamua, M. Sequential measurement of IL-6 blood levels in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome (sirs)/sepsis. Cytokine 2005, 29, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, Y.-C.; Jeong, Y.H.; Cho, W.-K.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Ma, J.Y. Inhibitory effects of dianthi herba ethanolic extract on inflammatory and nociceptive responses in murine macrophages and mouse models of abdominal writhing and ear edema. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 211, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portanova, J.P.; Zhang, Y.; Anderson, G.D.; Hauser, S.D.; Masferrer, J.L.; Seibert, K.; Gregory, S.A.; Isakson, P.C. Selective neutralization of prostaglandin E2 blocks inflammation, hyperalgesia, and interleukin 6 production in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 184, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guay, J.; Bateman, K.; Gordon, R.; Mancini, J.; Riendeau, D. Carrageenan-induced paw edema in rat elicits a predominant prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) response in the central nervous system associated with the induction of microsomal PGE2 synthase-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 24866–24872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funk, C.D. Prostaglandins and leukotrienes: Advances in eicosanoid biology. Science 2001, 274, 1871–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tursun, X.; Zhao, Y.; Talat, Z.; Xin, X. Anti-inflammatory effect of Rosa rugosa flower extract in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264. 7 macrophages. Biomol. Ther. 2016, 24, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, J.K.; Surh, Y.J. Inflammation: Gearing the journey to cancer. Mutat. Res. 2008, 659, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Redington, A.E.; Meng, Q.H.; Springall, D.R.; Evans, T.J.; Créminon, C.; Maclouf, J.; Holgate, S.T.; Howarth, P.H.; Polak, J.M. Increased expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclo-oxygenase-2 in the airway epithelium of asthmatic subjects and regulation by corticosteroid treatment. Thorax 2001, 56, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garg, A.D.; Kaczmarek, A.; Krysko, O.; Vandenabeele, P.; Krysko, D.V.; Agostinis, P. ER stress-induced inflammation: Does it aid or impede disease progression? Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Chen, J.; Ye, J.; Zhai, X.; Song, J.; Jiang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Jia, X.; Zhu, F. Anti-inflammatory effect of the six compounds isolated from Nauclea officinalis pierrc ex pitard, and molecular mechanism of strictosamide via suppressing the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathway in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 196, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Cao, G.; Han, L.; Ye, Y.; SiMa, Y.; Ge, W. Flavonoids from Radix Tetrastigmae inhibit TLR4/MD-2 mediated JNK and NF-κB pathway with anti-inflammatory properties. Cytokine 2016, 84, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Léguillette, R.; Tohver, T.; Bond, S.L.; Nicol, J.A.; McDonald, K.J. Effect of Dexamethasone and Fluticasone on Airway Hyperresponsiveness in Horses With Inflammatory Airway Disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huebner, K.D.; Shrive, N.G.; Frank, C.B. Dexamethasone inhibits inflammation and cartilage damage in a new model of post-traumatic osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Res. 2014, 32, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davoudi, Z.; Peroutka-Bigus, N.; Bellaire, B.; Wannemuehler, M.; Barrett, T.A.; Narasimhan, B.; Wang, Q. Intestinal organoids containing poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles for the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2018, 106, 876–886. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.X.; Huang, L.; Gauthier, M.; Yang, G.; Wang, Q. Recent advances in liposome surface modification for oral drug delivery. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 1169–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakase, H.; Okazaki, K.; Tabata, Y.; Uose, S.; Ohana, M.; Uchida, K.; Matsushima, Y.; Kawanami, C.; Oshima, C.; Ikada, Y.; et al. Development of an oral drug delivery system targeting immune-regulating cells in experimental inflammatory bowel disease: A new therapeutic strategy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 292, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.-J.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.-J.; Lim, H.-J.; Jung, K.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, S.W.; Rho, M.-C. Anti-inflammatory activity of eudesmane-type sesquiterpenoids from Salvia plebeia. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2666–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.-J.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, C.Y.; Lee, S.; Jung, K.; Hwang, J.T.; Choi, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S.W.; Rho, M.-C. Effect of sunlight radiation on the growth and chemical constituents of Salvia plebeia R. Br. Molecules 2017, 22, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.-J.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, S.; Jung, K.; Lee, S.W.; Rho, M.-C. Acyclic Triterpenoids from Alpinia katsumadai inhibit IL-6-induced STAT3 activation. Molecules 2017, 22, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |





| Compounds | IC50 (µM) | Compounds | IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | >50 | 6 | 31.92 ± 0.01 * |
| 2 | >50 | 7 | 25.16 ± 0.41 * |
| 3 | >50 | 8 | >50 |
| 4 | >50 | 9 | >50 |
| 5 | >50 | 10 | 6.28 ± 0.45 * |
| Dexamethasoneb | 0.009 ± 0.001 * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.Y.; Jang, H.-J.; Han, Y.K.; Su, X.D.; Lee, S.W.; Rho, M.-C.; Wang, H.-S.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, Y.H. Alkaloids from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and Their Anti-Inflammatory Effects on LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061445
Wang CY, Jang H-J, Han YK, Su XD, Lee SW, Rho M-C, Wang H-S, Yang SY, Kim YH. Alkaloids from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and Their Anti-Inflammatory Effects on LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells. Molecules. 2018; 23(6):1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061445
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Cai Yi, Hyun-Jae Jang, Yoo Kyong Han, Xiang Dong Su, Seung Woong Lee, Mun-Chual Rho, Heng-Shan Wang, Seo Young Yang, and Young Ho Kim. 2018. "Alkaloids from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and Their Anti-Inflammatory Effects on LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells" Molecules 23, no. 6: 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061445
APA StyleWang, C. Y., Jang, H. -J., Han, Y. K., Su, X. D., Lee, S. W., Rho, M. -C., Wang, H. -S., Yang, S. Y., & Kim, Y. H. (2018). Alkaloids from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and Their Anti-Inflammatory Effects on LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells. Molecules, 23(6), 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061445