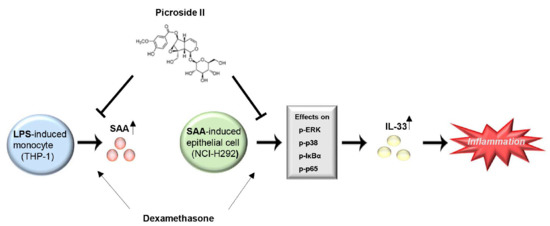
Picroside II Isolated from Pseudolysimachion rotundum var. subintegrum Inhibits Glucocorticoid Refractory Serum Amyloid A (SAA) Expression and SAA-induced IL-33 Secretion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Picroside II Inhibits LPS-Induced SAA1 Expression in Human Monocytes
2.2. SAA Induces Expression and Secretion of IL-33 in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
2.3. The MAP Kinases (p38/ERK1/2) and NF-κB Play a Critical Role in SAA-Induced IL-33 Secretion in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
2.4. IL-33 Secretion by SAA Is Mediated by TLR2/4 in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
2.5. Picroside II Inhibits SAA-Induced Expression/Secretion of IL-33 via TLR2 in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
2.6. Picroside II Inhibits SAA-Induced Activation of MAP Kinase and NF-κB Pathway in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Preparation of Picroside II
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Cell Survival Assay
4.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.6. RNA Extraction, RT-PCR and Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| COPD | chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| DEX | dexamethason |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-κB |
| Pam3 | Pam 3CSK4 |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt |
| PMB | polymyxin B |
| SAA | serum amyloid A |
References
- Pauwels, R.A.; Rabe, K.F. Burden and clinical features of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Lancet 2004, 364, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, K.F.; Hurd, S.; Anzueto, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Buist, S.A.; Calverley, P.; Fukuchi, Y.; Jenkins, C.; Rodriguez-Roisin, R.; van Weel, C.; et al. Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung, D., Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 532–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burney, P.G.; Patel, J.; Newson, R.; Minelli, C.; Naghavi, M. Global and regional trends in COPD mortality, 1990-2010. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. New anti-inflammatory targets for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J.; Adcock, I.M. Glucocorticoid resistance in inflammatory diseases. Lancet 2009, 373, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozinovski, S.; Uddin, M.; Vlahos, R.; Thompson, M.; McQualter, J.L.; Merritt, A.S.; Wark, P.A.; Hutchinson, A.; Irving, L.B.; Levy, B.D.; et al. Serum amyloid A opposes lipoxin A(4) to mediate glucocorticoid refractory lung inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, R.D.; Sun, L. Emerging functions of serum amyloid A in inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 98, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, A.; Bellettato, C.M.; Braccioni, F.; Romagnoli, M.; Casolari, P.; Caramori, G.; Fabbri, L.M.; Johnston, S.L. Infections and airway inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease severe exacerbations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozinovski, S.; Hutchinson, A.; Thompson, M.; Macgregor, L.; Black, J.; Giannakis, E.; Karlsson, A.S.; Silvestrini, R.; Smallwood, D.; Vlahos, R.; et al. Serum amyloid a is a biomarker of acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, J.R.; Perera, W.R.; Wilkinson, T.M.; Donaldson, G.C.; Wedzicha, J.A. Systemic and upper and lower airway inflammation at exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Shepard, L.W.; Chen, J.; Pan, Z.K.; Ye, R.D. Serum amyloid A is an endogenous ligand that differentially induces IL-12 and IL-23. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 4072–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migita, K.; Izumi, Y.; Jiuchi, Y.; Kozuru, H.; Kawahara, C.; Nakamura, M.; Nakamura, T.; Agematsu, K.; Masumoto, J.; Yasunami, M.; et al. Serum amyloid A induces NLRP-3-mediated IL-1beta secretion in neutrophils. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Sang, H.; Ye, R.D. Serum amyloid A induces IL-8 secretion through a G protein-coupled receptor, FPRL1/LXA4R. Blood 2003, 101, 1572–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byers, D.E.; Alexander-Brett, J.; Patel, A.C.; Agapov, E.; Dang-Vu, G.; Jin, X.; Wu, K.; You, Y.; Alevy, Y.; Girard, J.P.; et al. Long-term IL-33-producing epithelial progenitor cells in chronic obstructive lung disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3967–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saglani, S.; Lui, S.; Ullmann, N.; Campbell, G.A.; Sherburn, R.T.; Mathie, S.A.; Denney, L.; Bossley, C.J.; Oates, T.; Walker, S.A.; et al. IL-33 promotes airway remodeling in pediatric patients with severe steroid-resistant asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 676–685.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oh, S.R.; Lee, M.Y.; Ahn, K.; Park, B.Y.; Kwon, O.K.; Joung, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Suppressive effect of verproside isolated from Pseudolysimachion longifolium on airway inflammation in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.U.; Sung, M.H.; Ryu, H.W.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.S.; In, H.J.; Ahn, K.S.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, H.K.; Shin, D.H.; et al. Verproside inhibits TNF-alpha-induced MUC5AC expression through suppression of the TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB pathway in human airway epithelial cells. Cytokine 2016, 77, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.G.; Hwang, D.K.; Jeong, H.U.; Ji, H.Y.; Oh, S.R.; Lee, Y.; Yoo, J.S.; Shin, D.H.; Lee, H.S. In vitro and in vivo metabolism of verproside in rats. Molecules 2012, 17, 11990–12002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Choi, B.K.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, J.W.; Park, H.A.; Ryu, H.W.; Lee, S.U.; Hwang, K.W.; Yun, W.K.; Kim, H.C.; et al. Picroside II Attenuates Airway Inflammation by Downregulating the Transcription Factor GATA3 and Th2-Related Cytokines in a Mouse Model of HDM-Induced Allergic Asthma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urieli-Shoval, S.; Meek, R.L.; Hanson, R.H.; Eriksen, N.; Benditt, E.P. Human serum amyloid A genes are expressed in monocyte/macrophage cell lines. Am. J. Pathol. 1994, 145, 650–660. [Google Scholar]
- Lamkanfi, M.; Dixit, V.M. IL-33 raises alarm. Immunity 2009, 31, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, B.A.; D’Armiento, J.M. Emerging role of MAP kinase pathways as therapeutic targets in COPD. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2006, 1, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Liang, Q.; Balzar, S.; Wenzel, S.; Gorska, M.; Alam, R. Cell-specific activation profile of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2, Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases in asthmatic airways. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 893–902.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, N.; He, R.; Tian, J.; Ye, P.P.; Ye, R.D. Cutting edge: TLR2 is a functional receptor for acute-phase serum amyloid A. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, S.; Rodriguez, D.; Gomes, E.; Monteiro, H.P.; Russo, M.; Campa, A. Is serum amyloid A an endogenous TLR4 agonist? J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niemi, K.; Teirila, L.; Lappalainen, J.; Rajamaki, K.; Baumann, M.H.; Oorni, K.; Wolff, H.; Kovanen, P.T.; Matikainen, S.; Eklund, K.K. Serum amyloid A activates the NLRP3 inflammasome via P2 × 7 receptor and a cathepsin B-sensitive pathway. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 6119–6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhu, Z.; Cheng, N.; Yan, Q.; Ye, R.D. Serum amyloid A induces interleukin-33 expression through an IRF7-dependent pathway. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 2153–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussion, C.; Ortega, N.; Girard, J.P. The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is constitutively expressed in the nucleus of endothelial cells and epithelial cells in vivo: A novel ‘alarmin’? PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hristova, M.; Habibovic, A.; Veith, C.; Janssen-Heininger, Y.M.; Dixon, A.E.; Geiszt, M.; van der Vliet, A. Airway epithelial dual oxidase 1 mediates allergen-induced IL-33 secretion and activation of type 2 immune responses. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1545–1556.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenuki, Y.; Matsushita, K.; Futatsugi-Yumikura, S.; Ishii, K.J.; Kawagoe, T.; Imoto, Y.; Fujieda, S.; Yasuda, M.; Hisa, Y.; Akira, S.; et al. A critical role of IL-33 in experimental allergic rhinitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 184–194.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, K.; Iijima, K.; Elias, M.K.; Seno, S.; Tojima, I.; Kobayashi, T.; Kephart, G.M.; Kurabayashi, M.; Kita, H. Airway uric acid is a sensor of inhaled protease allergens and initiates type 2 immune responses in respiratory mucosa. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 4032–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eklund, K.K.; Niemi, K.; Kovanen, P.T. Immune functions of serum amyloid A. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 32, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gon, Y.; Asai, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Mizumura, K.; Jibiki, I.; Machino, T.; Ra, C.; Horie, T. A20 inhibits toll-like receptor 2- and 4-mediated interleukin-8 synthesis in airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2004, 31, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, M.R.; Bartlett, N.W.; Clarke, D.; Birrell, M.; Belvisi, M.; Johnston, S.L. Targeting the NF-kappaB pathway in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 121, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, F.Y.; Girard, J.P.; Turnquist, H.R. Interleukin-33 in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.; Choi, J.; Choi, B.K.; Gu, Y.-M.; Ryu, H.W.; Oh, S.-R.; Lee, H.-J. Picroside II Isolated from Pseudolysimachion rotundum var. subintegrum Inhibits Glucocorticoid Refractory Serum Amyloid A (SAA) Expression and SAA-induced IL-33 Secretion. Molecules 2019, 24, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24102020
Lee K, Choi J, Choi BK, Gu Y-M, Ryu HW, Oh S-R, Lee H-J. Picroside II Isolated from Pseudolysimachion rotundum var. subintegrum Inhibits Glucocorticoid Refractory Serum Amyloid A (SAA) Expression and SAA-induced IL-33 Secretion. Molecules. 2019; 24(10):2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24102020
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Kiram, Jin Choi, Bo Kyong Choi, Young-Mi Gu, Hyung Won Ryu, Sei-Ryang Oh, and Hyun-Jun Lee. 2019. "Picroside II Isolated from Pseudolysimachion rotundum var. subintegrum Inhibits Glucocorticoid Refractory Serum Amyloid A (SAA) Expression and SAA-induced IL-33 Secretion" Molecules 24, no. 10: 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24102020
APA StyleLee, K., Choi, J., Choi, B. K., Gu, Y. -M., Ryu, H. W., Oh, S. -R., & Lee, H. -J. (2019). Picroside II Isolated from Pseudolysimachion rotundum var. subintegrum Inhibits Glucocorticoid Refractory Serum Amyloid A (SAA) Expression and SAA-induced IL-33 Secretion. Molecules, 24(10), 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24102020