Insight into the Synthesis and Characterization of Organophosphorus-Based Bridged Triazine Compounds
Abstract
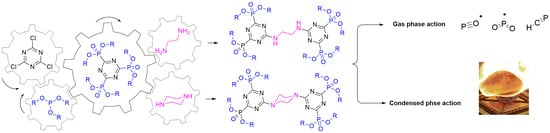
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of Chemicals
2.2. Characterization of the Molecular Structure of Chemicals
2.3. Thermal Characteristics and Chemical Composition of the Resulting Chars
2.4. Direct Insertion Probe Mass Spectrometry (DIP-MS) Measurements
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Thermal Characterization, DIP-MS, SEM-EDX, Elemental Analysis, and NMR Spectrometer
3.3. Single Crystal X-Ray Structure Determination
3.4. Synthesis
3.4.1. Synthesis of 2,4,6-Trisdiethoxyphosphinyl-1,3,5-Triazine (HEPT)

3.4.2. Synthesis of N,N′-Bis[4,6-Bis(diethylphosphono)-1,3,5-Triazin-yl]-1,2-Diaminoethane (EDA-bis-TEPT)

3.4.3. Synthesis of N,N′-Bis[4,6-Bis(diethylphosphono)-1,3,5-Triazin-yl]-Piperazine (Pip-bis-TEPT)

4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prokhorov, A.M.; Prokhorova, P.E. Triazines and tetrazines. Prog. Heterocycl. Chem. 2015, 27, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Brown, D.R.; Weerapana, E. Recent developments in the synthesis of bioactive 2,4,6-trisubstituted 1,3,5-triazines. Synlett 2013, 24, 1599–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blotny, G. Recent applications of 2,4,6-trichloro-1,3,5-triazine and its derivatives in organic synthesis. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 9507–9522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst, D.A.; Hanson, P.R.; Barda, D.A. Cyanuric chloride. In e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 2874–2878. [Google Scholar]
- Senier, A. Contributions to the history of cyanuric chloride and cyanuric acid. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1886, 49, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretterbauer, K.; Schwarzinger, C. Melamine derivatives. A review on synthesis and application. Curr. Org. Synth. 2012, 9, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Jeught, S.; Stevens, C.V. Direct Phosphonylation of Aromatic Azaheterocycles. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 2672–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huthmacher, K.; Most, D. Cyanuric acid and cyanuric chloride. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Hao, J.; Gaan, S. Recent studies on the decomposition and strategies of smoke and toxicity suppression for polyurethane based materials. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 74742–74756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cipolli, R.; Masarati, E.; Rossi, C.; Oriani, R.; Nucida, G. Self-extinguishing polymeric compositions. EP551154A1, 14 July 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, P. Synthesis of a formaldehyde-free phosphorus-nitrogen flame retardant with multiple reactive groups and its application in cotton fabrics. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 120, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.C.; Condon, B.; Nguyen, T.-M.; Graves, E.; Smith, J. Antiflammable properties of capable phosphorus-nitrogen-containing triazine derivatives on cotton. ACS Symp. Ser. 2012, 1118, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.C.; Condon, B.; Graves, E.; Uchimiya, M.; Fortier, C.; Easson, M.; Wakelyn, P. Flame retardant properties of triazine phosphonates derivative with cotton fabric. Fibers Polym. 2011, 12, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-M.D.; Chang, S.; Condon, B.; Slopek, R. Synthesis of a novel flame retardant containing phosphorus-nitrogen and its comparison for cotton fabric. Fibers Polym. 2012, 13, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easson, M.; Condon, B.; Yoshioka-Tarver, M.; Childress, S.; Slopek, R.; Bland, J.; Nguyen, T.-M.; Chang, S.C.; Graves, E. Cyanuric chloride derivatives for cotton textile treatment-synthesis, analysis, and flammability testing. AATCC Rev. 2011, 11, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, C.; Ciesielski, M.; Greiner, L.; Doering, M. Novel organophosphorus flame retardants and their synergistic application in novolac epoxy resin. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 158, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Huo, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, J. Preparation and flame retardancy of a compounded epoxy resin system composed of phosphorus/nitrogen-containing active compounds. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 121, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, G.; Cheng, Z.; Tang, Y.; He, H. Functional Group Effect on Char Formation, Flame Retardancy and Mechanical Properties of Phosphonate–Triazine-based Compound as Flame Retardant in Epoxy Resin. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 7309–7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Ni, A.; Ding, A.; Han, X.; Sun, Z. The effects of a macromolecular charring agent with gas phase and condense phase synergistic flame retardant capability on the properties of PP/IFR composites. Materials 2018, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Li, J. Synthesis of a bio-based triazine derivative and its effects on flame retardancy of polypropylene composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Yan, H. A novel hyperbranched poly(phosphorodiamidate) with high expansion degree and carbonization efficiency used for improving flame retardancy of APP/PP composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 142, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.-D.; Liu, S.-M.; Sheng, Q. Synthesis and application in polypropylene of a novel of phosphorus-containing intumescent flame retardant. Molecules 2010, 15, 7593–7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatt, M. Nitrogen-based flame retardants. In Non-Halogenated Flame Retardant Handbook; Morgan, A.B., Wilkie, C.A., Eds.; Scrivener Publishing LLC: Beverly, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 143–168. [Google Scholar]
- Salmeia, K.A.; Fage, J.; Liang, S.; Gaan, S. An Overview of Mode of Action and Analytical Methods for Evaluation of Gas Phase Activities of Flame Retardants. Polymers 2015, 7, 504–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salmeia, K.A.; Gaan, S. An overview of some recent advances in DOPO-derivatives: Chemistry and flame retardant applications. Polym. Degrad. Stability 2015, 113, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-P.; Li, W.-Y.; Wang, Y.-Z. Synthesis and characterization of a novel nitrogen-containing flame retardant. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 94, 1556–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Dong, E. Development of environmental friendly flame retardants for wood plastic composites (WPC). Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 332–334, 1880–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikroyannidis, J.A. Synthesis, physical, and thermal properties of linear poly(dialkoxyphosphinyl-s-triazines). J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1988, 26, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.M.; Al-Abdul-Wahid, M.S.; Fontenot, K.R.; Graves, E.E.; Chang, S.C.; Condon, B.D.; Grimm, C.C.; Lorigan, G.A. Understanding the mechanism of action of triazine-phosphonate derivatives as flame retardants for cotton fabric. Molecules 2015, 20, 11236–11256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, D.C. sym-Triazinetriphosphonic acid esters. J. Org. Chem. 1957, 22, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewertson, W.; Shaw, R.A.; Smith, B.C. 313. 1,3,5-Triazines. Part III. Arbuzov reactions of chlorotriazines. J. Chem. Soc. 1963, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewertson, W.; Shaw, R.A.; Smith, B.C. 197. 1,3,5-Triazines. Part IV. Phosphino-1,3,5-triazines. J. Chem. Soc. 1964, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreher, T.; Costisella, B.; Kirschke, K.; Bartoszek, M.; Quaiser, S.; Fischer, M. Dynamic NMR studies of phosphorylated diamine-coupled bis-1,3,5-triazines. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 1998, 141, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmeia, K.; Gaan, S.; Bruehwiler, M. Flame retardants. WO2018069249A1, 19 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, J.P.; Chance, L.H. New method for preparing alkyl (amino-s-triazinyl) phosphonates. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1970, 15, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta. Crystallogr. A 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spek, A.L. Single-crystal structure validation with the program PLATON. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Song, L.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Xing, W. Flame retardation and char formation mechanism of intumescent flame retarded polypropylene composites containing melamine phosphate and pentaerythritol phosphate. Polym. Degrad. Stability 2008, 93, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Yi, Y.; Tao, J.; Qi, H.; Li, D. Synergistic effect between a novel triazine charring agent and ammonium polyphosphate on flame retardancy and thermal behavior of polypropylene. Polym. Degrad. Stability 2014, 105, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.S.; Karak, N. s-Triazine containing flame retardant hyperbranched polyamines: Synthesis, characterization and properties evaluation. Polym. Degrad. Stability 2007, 92, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Hemberger, P.; Neisius, N.M.; Bodi, A.; Gruetzmacher, H.; Levalois-Gruetzmacher, J.; Gaan, S. Elucidating the Thermal Decomposition of Dimethyl Methylphosphonate by Vacuum Ultraviolet (VUV) Photoionization: Pathways to the PO Radical, a Key Species in Flame-Retardant Mechanisms. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds HEPT, EDA-bis-TEPT, and Pip-bis-TEPT are available from the authors. |







| HEPT | EDA-bis-TEPT | Pip-bis-TEPT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atoms | Distances (Å) | Atoms | Distances (Å) | Atoms | Distances (Å) |
| P1–C1 | 1.846 (4) | P1–C3 | 1.827 (5) | P1–C1 | 1.826 (3) |
| N1–C1 | 1.337 (6) | P2–C4 | 1.834 (6) | P2–C2 | 1.830 (3) |
| N3–C3 | 1.355 (8) | N1–C1 | 1.344 (4) | ||
| N3–C4 | 1.354 (7) | N1–C2 | 1.347 (4) | ||
| N4–C4 | 1.323 (8) | N2–C2 | 1.323 (4) | ||
| N4–C2 | 1.361 (8) | N2–C3 | 1.353 (4) | ||
| N2–C3 | 1.309 (8) | N3–C1 | 1.326 (4) | ||
| N2–C2 | 1.366 (7) | N3–C3 | 1.354 (4) | ||
| N1–C2 | 1.335 (8) | N4–C3 | 1.343 (4) | ||
| Sample | Tonset (°C) | Tmax a (°C) | Char Residue (wt%) at 800 °C | N:P (wt%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2 | O2 | N2 | O2 | N2 | O2 | ||
| HEPT | 265 ± 1 | 265 ± 0.5 | 270 | 271 | 27 ± 0.5 | 20 ± 0.5 | 0.45 |
| EDA-bis-TEPT | 253 ± 0.5 | 252 ± 0.5 | 263 | 263 | 36 ± 1 | 25 ± 0.5 | 0.90 |
| Pip-bis-TEPT | 277 ± 3 | 261 ± 1 | 283 | 272 | 33 ± 1 | 25 ± 1 | 0.90 |
| Sample | EDX (wt%) | Elemental Loss (wt%) a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | C | N | P | C | N | |
| HEPT | 37 ± 2 | 24 ± 1 | 15 ± 1 | 61 | 87 | 65 |
| EDA-bis-EPT | 28 ± 2 | 26 ± 1 | 15 ± 0.5 | 57 | 83 | 74 |
| Pip-bis-TEPT | 27 ± 1 | 29 ± 2 | 18 ± 3 | 57 | 82 | 68 |
| Identification Code | HEPT | EDA-bis-TEPT | Pip-bis-TEPT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Empirical formula | C15H30N3O9P3 | C24H46N8O12P4 | C26H48N8O12P4 |
| Formula weight | 489.33 | 762.57 | 788.60 |
| Temp/K | 293 | 173 | 293 |
| Crystal system | Hexagonal | Triclinic | Triclinic |
| Space group | P63/m | P-1 | P-1 |
| a (Å) | 13.5150 (15) | 7.463 (5) | 7.3620 (9) |
| b (Å) | 13.5150 (15) | 21.171 (13) | 11.8117 (16) |
| c (Å) | 7.6602 (10) | 21.200 (12) | 12.4732 (16) |
| α (°) | 90 | 118.49 (4) | 106.602 (10) |
| β (°) | 90 | 95.68 (5) | 103.435 (10) |
| γ (°) | 120 | 97.27 (5) | 104.434 (10) |
| V (Å3) | 1211.7 (4) | 2858 (3) | 951.2 (2) |
| Z | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| Dcalc (g.cm−3) | 1.341 | 1.329 | 1.377 |
| Absorption coefficient (mm−1) | 0.293 | 0.262 | 0.264 |
| F(000) | 516 | 1206 | 416 |
| Crystal size /mm3 | 0.4 × 0.45 × 0.5 | 0.5 × 0.45 × 0.4 | 0.5 × 0.45 × 0.4 |
| Radiation (Å) | MoKα (λ = 71073) | MoKα (λ = 0.71073) | MoKα (λ = 0.71073) |
| 2θ range for data collection (°) | 1.7 to 25.7 | 1.931 to 26.273 | 3.606 to 51.326 |
| Index ranges | −16 ≤ h ≤ 14, −16 ≤ k ≤ 16, and −9 ≤ l ≤ 9 | −8 ≤ h ≤ 9, −25 ≤ k ≤ 25, and −25 ≤ l ≤ 25 | −8 ≤ h ≤ 8, −14 ≤ k ≤ 12, and −15 ≤ l ≤ 15 |
| Reflections collected | 5013 | 19228 | 8103 |
| Independent reflections | 5013 (Rint = 0.071) | 10234 (Rint = 0.0906) | 3528 (Rint = 0.0964) |
| Data/restraints/parameters | 820/0/85 | 10,234/18/582 | 3528/0/225 |
| Goodness of fit on F2 | 1.145 | 1.024 | 1.093 |
| Final R indexes (I ≥ 2σ (I)) | R1 = 0.0672, wR2 = 0.2142 | R1 = 0.0947, wR2 = 0.2612 | R1 = 0.0573, wR2 = 0.1588 |
| Final R indexes (all data) | R1a = 0.0853, wR2b = 0.2379 | R1a = 0.1662, wR2b = 0.3192 | R1a = 0.0700, wR2b = 0.1804 |
| Largest diff. peak/hole ( e Å-3) | 0.64/−0.27 | 0.632/−0.793 | 0.97/−0.88 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salmeia, K.A.; Neels, A.; Parida, D.; Lehner, S.; Rentsch, D.; Gaan, S. Insight into the Synthesis and Characterization of Organophosphorus-Based Bridged Triazine Compounds. Molecules 2019, 24, 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24142672
Salmeia KA, Neels A, Parida D, Lehner S, Rentsch D, Gaan S. Insight into the Synthesis and Characterization of Organophosphorus-Based Bridged Triazine Compounds. Molecules. 2019; 24(14):2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24142672
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalmeia, Khalifah A., Antonia Neels, Dambarudhar Parida, Sandro Lehner, Daniel Rentsch, and Sabyasachi Gaan. 2019. "Insight into the Synthesis and Characterization of Organophosphorus-Based Bridged Triazine Compounds" Molecules 24, no. 14: 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24142672
APA StyleSalmeia, K. A., Neels, A., Parida, D., Lehner, S., Rentsch, D., & Gaan, S. (2019). Insight into the Synthesis and Characterization of Organophosphorus-Based Bridged Triazine Compounds. Molecules, 24(14), 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24142672