Composition and Physicochemical Properties of Three Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) Starches: A Comparison Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and discussion
2.1. Compositions
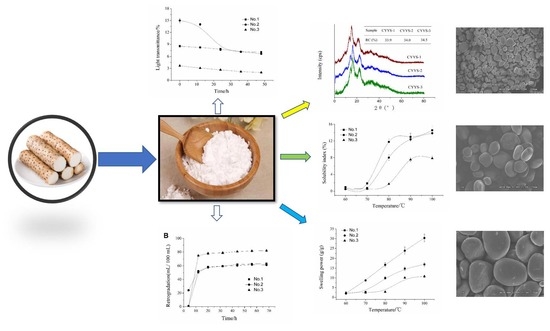
2.2. Morphological Properties
2.3. XRD
2.4. Swelling Power (SP), Solubility Index (SI), Paste Clarity, and Retrogradation
2.5. Freeze–Thaw Stability
2.6. Thermal Property
2.7. Pasting Properties
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Starch Isolation
3.3. Morphological Properties
3.4. XRD
3.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.6. Swelling Power (SP) and Solubility Index (SI) Determination
3.7. Paste Clarity and Retrogradation Evaluation
3.8. Freeze–Thaw Stability
3.9. Pasting Properties Determination
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CYYS | Chinese Yunlong yam starch |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| DSC | differential scanning calorimetry |
| SP | swelling power |
| SI | solubility index |
| PV | peck viscosity |
| BD | breakdown |
| SB | setback |
| FV | final viscosity |
References
- Jiang, Q.; Gao, W.; Shi, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Huang, L.; Xiao, P. Physicochemical properties and in vitro digestion of starches from different Dioscorea plants. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 32, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchiesi, J.; Velazquez, M.B.; Palopoli, N.; Iglesias, A.A.; Gomez-Casati, D.F.; Ballicora, M.A.; Busi, M.V. Starch Synthesis in Ostreococcus tauri: The Starch-Binding Domains of Starch Synthase III-B Are Essential for Catalytic Activity. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jyothi, A.N.; Sasikiran, K.; Sajeev, M.S.; Revamma, R.; Moorthy, S.N. Gelatinisation properties of cassava starch in the presence of salts, acids and oxidising agents. Starch-Stärke 2005, 57, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, N.; Buléon, A.; Kamenan, A.; Colonna, P. Variability in starch physicochemical and functional properties of yam (Dioscorea sp) cultivated in Ivory Coast. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2004, 84, 2085–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bircan, C.; Barringer, S.A. Salt-starch interactions as evidenced by viscosity and dielectric property measurements. J. Food Sci. 2010, 63, 983–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, S.; Ferrero, C.; Redigonda, V.; Beleia, A.P.; Grossmann, M.V.E.; Zaritzky, N.E. Influence of pH and hydrocolloids addition on yam (Dioscorea alata) starch pastes stability. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 36, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, W. Characterisation and preliminary lipid-lowering evaluation of starch from Chinese yam. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 176–181. [Google Scholar]
- Mandala, I.G.; Bayas, E. Xanthan effect on swelling, solubility and viscosity of wheat starch dispersions. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, K.; Riar, C.S.; Bala, A.; Sibian, M.S. Effect of ionic gums and dry heating on physicochemical, morphological, thermal and pasting properties of water chestnut starch. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; He, X.; Fu, X.; Luo, F.; Gao, Q. Effect of microwave radiation on the physicochemical properties of normal maize, waxy maize and amylomaize V starches. Starch-Stärke 2006, 58, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Gao, W.; Li, X.; Xia, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Xiao, P. Characterizations of starches isolated from five different Dioscorea L. species. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 29, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, L.; Blazek, J.; Salman, H.; Tang, M.C. Form and functionality of starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Gao, W. Study on physico-chemical properties of dialdehyde yam starch with different aldehyde group contents. Thermochim. Acta 2011, 512, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Chang, P.R.; Wang, S.; Yu, J.; Ma, X. Preparation and properties of halloysite nanotubes/plasticized Dioscorea opposita Thunb. starch composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nattapulwat, N.; Purkkao, N.; Suwithayapan, O. Preparation and application of carboxymethyl yam (Dioscorea esculenta) starch. AAPS Pharmscitech 2009, 10, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoover, R.; Ratnayake, W.S. Starch characteristics of black bean, chick pea, lentil, navy bean and pinto bean cultivars grown in Canada. Food Chem. 2002, 78, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, W.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Huang, L. Physicochemical, crystalline, and thermal properties of native, oxidized, acid, and enzyme hydrolyzed Chinese yam (Dioscorea opposite Thunb) starch. Starch-Stärke 2011, 63, 616–624. [Google Scholar]
- Jobling, S.A.; Westcott, R.J.; Tayal, A.; Jeffcoat, R.; Schwall, G.P. Production of a freeze–thaw-stable potato starch by antisense inhibition of three starch synthase genes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Fu, X.; Luo, Z.G. Effect of gum arabic on freeze-thaw stability, pasting and rheological properties of tapioca starch and its derivatives. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, A.I.; Chan, T.Y.; Chuang, G.C.C. Effect of water content and mucilage on physico-chemical characteristics of Yam (Discorea alata Purpurea) starch. J. Food Eng. 2009, 95, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, L.A.; Pedreschi, F.; Leiva, A.; Aguilera, J.M. Loss of birefringence and swelling behavior in native starch granules: Microstructural and thermal properties. J. Food Eng. 2015, 152, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhu, X.; Si, F.; Xiong, L. Effect of acid hydrolysis combined with heat moisture treatment on structure and physicochemical properties of corn starch. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, T.; Hoover, R.; Liu, Q.; Donner, E.; Chibbar, R.; Jaiswal, S. Composition, morphology, molecular structure, and physicochemical properties of starches from newly released chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) cultivars grown in Canada. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunyanart, T.; Charoenrein, S. Effect of sucrose on the freeze–thaw stability of rice starch gels: Correlation with microstructure and freezable water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muadklay, J.; Charoenrein, S. Effects of hydrocolloids and freezing rates on freeze-thaw stability of tapioca starch gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1268–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Baek, M.H.; Cha, D.S.; Park, H.J.; Lim, S.T. Freeze–thaw stabilization of sweet potato starch gel by polysaccharide gums. Food Hydrocoll. 2002, 16, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sae-kang, V.; Suphantharika, M. Influence of pH and xanthan gum addition on freeze-thaw stability of tapioca starch pastes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 65, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, T.; Takahata, Y.; Sato, T.; Suda, I.; Morishita, T.; Ishiguro, K.; Yamakawa, O. Relationships between chain length distribution of amylopectin and gelatinization properties within the same botanical origin for sweet potato and buckwheat. Carbohydr. Polym. 1998, 37, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, R.F.; Morrison, W.R. Swelling and gelatinization of cereal starches. I. effects of amylopectin, amylose, and lipids. Cereal Chem. 1990, 67, 551–557. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero, C.; Martino, M.N.; Zaritzky, N.E. Corn starch-xanthan gum interaction and its effect on the stability during storage of frozen gelatinized suspension. Starch-Stärke 1994, 46, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deffenbaugh, L.B.; Walker, C.E. Comparison of starch pasting properties in the Brabender Viscoamylograph and the Rapid Visco-Analyzer. Cereal Chem. 1989, 66, 493–499. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.M.; Huang, Q.; Fu, X.; Luo, F.X. Ultrasonic effect on the octenyl succinate starch synthesis and substitution patterns in starch granules. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohyama, K.; Nishinari, K. Effect of soluble sugars on gelatinization and retrogradation of sweet potato starch. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 1406–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; Walker, C.E. Changes in starch pasting properties due to sugars and emulsifiers as determined by viscosity measurement. J. Food Sci. 1992, 57, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deffenbaugh, L.B.; Walker, C.E. Use of the Rapid Visco-Analyzer to Measure Starch Pasting Properties part II: Effects of Emulsifiers and Sugar-Emulsifier Interactions. Starch-Stärke 1990, 42, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantaro, P.; Pongsawatmanit, R. Influence of sucrose on thermal and pasting properties of tapioca starch and xanthan gum mixtures. J. Food Eng. 2010, 98, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Oberoi, D.P.S.; Sogi, D.S.; Gill, B.S. Effect of sugar and gums on the pasting properties of cassava starch. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2009, 33, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H.; Wang, Y.S.; Leng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X. Effect of NaCl and sugar on physicochemical properties of flaxseed polysaccharide-potato starch complexes. Sci. Asia 2014, 40, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosten, D.B.J. Tentative hypothesis to explain how electrolytes affect the gelatinization temperature of starches in water. Starch-Stärke 1982, 34, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhong, L.; Chen, W.; Song, Y.; Qian, Z.; Cao, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Chen, H.; Chen, W. Preparation and characterization of pectin/chitosan beads containing porous starch embedded with doxorubicin hydrochloride: A novel and simple colon targeted drug delivery system. Food Hydrocolloids 2019, 95, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.K.; Rani, V.S.; Raja, K.C.M.; Moorthy, S.N. Physicochemical and enzyme susceptibility characteristics of starch extracted from chemically pretreated xanthosoma sagitifolium roots. Starch-Stärke 1999, 51, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.E.; Gray, D.A. Effect of sulphite and propyl gallate or ferulic acid on the thermal depolymerisation of food polysaccharides. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, L.S.; Mabesa, L.B.; Oates, C.G.; Corke, H. Bihon-type noodles from heat-moisture-treated sweet potato starch. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |





| Samples | Total starch (%) | Amylose (%) | Moisture (%) | Ash (%) | Protein (%) | Fat (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYYS-1 | 70.14 ± 0.35 b | 20.43 ± 0.25 c | 12.26 ± 0.28 a | 1.75 ± 0.06 c | 0.13 ± 0.01 b | 0.06 ± 0.01 a |
| CYYS-2 | 72.78 ± 1.06 a | 24.81 ± 0.20 a | 12.68 ± 0.31 a | 2.00 ± 0.02 b | 0.19 ± 0.01 a | 0.08 ± 0.01 a |
| CYYS-3 | 69.63 ± 0.83 b | 21.53 ± 0.11 b | 12.51 ± 0.24 a | 2.21 ± 0.03 a | 0.20 ± 0.01 a | 0.08 ± 0.01 a |
| Type | Syneresis (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cycle 1 | Cycle 2 | Cycle 3 | Cycle 4 | Cycle 5 | |
| CYYS-1 | 40.18 ± 0.61 a | 41.31 ± 0.45 b | 41.38 ± 0.38 b | 41.44 ± 0.39 b | 41.53 ± 0.21 b |
| CYYS-2 | 60.23 ± 1.04 a | 64.74 ± 1.21 b | 68.13 ± 0.68 c | 68.98 ± 0.83 c | 69.06 ± 0.88 c |
| CYYS-3 | 58.36 ± 0.43 a | 60.52 ± 0.81 b | 61.37 ± 1.13 b | 61.39 ± 1.00 b | 61.55 ± 0.75 b |
| Samples | To (°C) | TP (°C) | TC (°C) | ΔH (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYYS-1 | 68.4 ± 0.1 b | 73.8 ± 0.2 b | 82.4 ± 0.1 c | 12.3 ± 0.2 c |
| CYYS-2 | 67.6 ± 0.4 c | 73.4 ± 0.1 c | 85.1 ± 0.2 b | 12.9 ± 0.3 b |
| CYYS-3 | 81.1 ± 0.2 a | 84.8 ± 0.2 a | 91.2 ± 0.3 a | 14.1 ± 0.5 a |
| Samples | PV (BU) | TV (BU) | BDV (BU) | FV (BU) | SBV (BU) | P-Time (min) | P-Temp (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYYS-1 (6%) | 1729 | 1354 | 375 | 2179 | 825 | 4.67 | 80.2 |
| CYYS-2 (6%) | 1957 | 1581 | 376 | 2477 | 896 | 5.13 | 81.8 |
| CYYS-3 (6%) | 1572 | 1490 | 82 | 2041 | 551 | 6.53 | 85.4 |
| CYYS-1 + 3% sucrose | 1873 | 1444 | 429 | 2272 | 828 | 4.73 | 81.00 |
| CYYS-1 + 6% sucrose | 1995 | 1510 | 485 | 2354 | 844 | 4.73 | 81.05 |
| CYYS-1 + 9% sucrose | 2154 | 1633 | 521 | 2519 | 886 | 4.80 | 81.75 |
| CYYS-2 + 3% sucrose | 1830 | 1554 | 276 | 2432 | 878 | 5.20 | 82.60 |
| CYYS-2 + 6% sucrose | 1878 | 1585 | 293 | 2505 | 920 | 5.20 | 82.55 |
| CYYS-2 + 9% sucrose | 2063 | 1704 | 359 | 2675 | 971 | 5.20 | 83.45 |
| CYYS-3 + 3% sucrose | 1692 | 1616 | 76 | 2204 | 588 | 6.33 | 86.00 |
| CYYS-3 + 6% sucrose | 1871 | 1778 | 93 | 2410 | 632 | 6.40 | 86.70 |
| CYYS-3 + 9% sucrose | 1941 | 1864 | 97 | 2420 | 656 | 7.00 | 88.40 |
| CYYS-1 + 2% NaCl | 1938 | 1767 | 121 | 2964 | 1197 | 5.40 | 85.85 |
| CYYS-1 + 3% NaCl | 2063 | 1931 | 132 | 3198 | 1267 | 5.60 | 86.75 |
| CYYS-1 + 5% NaCl | 2219 | 2066 | 153 | 3453 | 1387 | 5.93 | 88.40 |
| CYYS-1 + 7% NaCl | 2344 | 2259 | 185 | 3675 | 1416 | 6.20 | 88.35 |
| CYYS-2 + 2% NaCl | 1705 | 1578 | 127 | 2646 | 1068 | 6.00 | 86.75 |
| CYYS-2 + 3% NaCl | 1711 | 1684 | 27 | 2707 | 1023 | 6.13 | 88.40 |
| CYYS-2 + 5% NaCl | 1829 | 1769 | 60 | 2890 | 1121 | 6.47 | 89.05 |
| CYYS-2 + 7% NaCl | 1932 | 1909 | 23 | 3046 | 1137 | 6.53 | 89.90 |
| CYYS-3 + 2% NaCl | 851 | 738 | 120 | 1026 | 311 | 6.77 | 91.60 |
| CYYS-3 + 3% NaCl | 912 | 792 | 113 | 1103 | 288 | 6.89 | 93.30 |
| CYYS-3 + 5% NaCl | 939 | 839 | 100 | 1108 | 269 | 7.13 | 94.00 |
| CYYS-3 + 7% NaCl | 1098 | 1003 | 95 | 1250 | 267 | 7.28 | 94.90 |
| CYYS-1 (pH = 4) | 1667 | 1262 | 405 | 2011 | 749 | 4.67 | 80.15 |
| CYYS-1 (pH = 6) | 1783 | 1572 | 211 | 2651 | 1079 | 5.07 | 81.80 |
| CYYS-2 (pH = 4) | 1614 | 1035 | 579 | 1542 | 507 | 5.00 | 80.85 |
| CYYS-2 (pH = 6) | 1674 | 1431 | 243 | 2247 | 816 | 5.13 | 81.65 |
| CYYS-3 (pH = 4) | 1601 | 1514 | 87 | 2053 | 539 | 6.53 | 85.85 |
| CYYS-3 (pH = 6) | 1043 | 957 | 86 | 1290 | 333 | 7.00 | 86.70 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Hu, Z.; Liu, D.; Li, C.; Liu, S. Composition and Physicochemical Properties of Three Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) Starches: A Comparison Study. Molecules 2019, 24, 2973. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162973
Chen H, Hu Z, Liu D, Li C, Liu S. Composition and Physicochemical Properties of Three Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) Starches: A Comparison Study. Molecules. 2019; 24(16):2973. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162973
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Haiming, Zhen Hu, Dongli Liu, Congfa Li, and Sixin Liu. 2019. "Composition and Physicochemical Properties of Three Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) Starches: A Comparison Study" Molecules 24, no. 16: 2973. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162973
APA StyleChen, H., Hu, Z., Liu, D., Li, C., & Liu, S. (2019). Composition and Physicochemical Properties of Three Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) Starches: A Comparison Study. Molecules, 24(16), 2973. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162973