Inhibition of Pancreatic α-amylase by Resveratrol Derivatives: Biological Activity and Molecular Modelling Evidence for Cooperativity between Viniferin Enantiomers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Preparation of Individual Resveratrol Derivatives
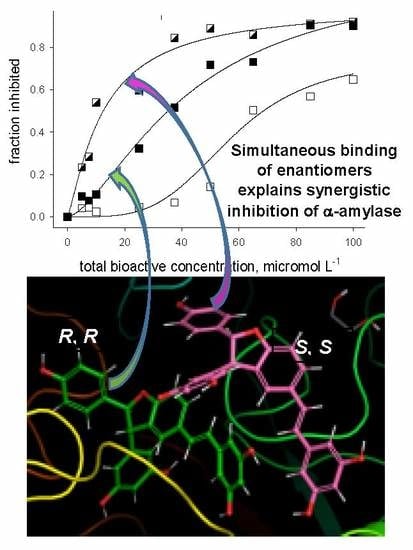
2.2. Alpha-amylase Inhibitory Activity
2.3. Molecular Docking Studies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
4.2. Enzymatic Inhibition
4.3. Computational Procedures
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazeem, M.I.; Raimi, O.G.; Balogun, R.M.; Ogundajo, A.L. Comparative study on the α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory potential of different extracts of Blighia sapida Koenig. Am. J. Res. Commun. 2013, 1, 178–192. [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa, T.; Ikegami, H.; Inoue, K.; Kawabata, Y.; Ogihara, T. Effect of two α-glucosidase inhibitors, voglibose and acarbose, on postprandial hyperglycemia correlates with subjective abdominal symptoms. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2005, 54, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Rai, P.K.; Jaiswal, D.; Watal, G. Evidence-based critical evaluation of glycemic potential of Cynodon dactylon. J. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2008, 6, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carrizzo, A.; Forte, M.; Damato, A.; Trimarco, V.; Salzano, F.; Bartolo, M.; Maciag, A.; Puca, A.A.; Vecchione, C. Antioxidant effects of resveratrol in cardiovascular, cerebral and metabolic diseases. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 61, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Ou, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Szkudelski, T.; Delmas, D.; Daglia, M.; Xiao, J. Dietary polyphenols and type 2 diabetes: Human Study and Clinical Trial. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinwumi, B.C.; Bordun, K.A.M.; Anderson, H.D. Biological Activities of Stilbenoids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyenihi, O.R.; Oyenihi, A.B.; Adeyanju, A.A.; Oguntibeju, O.O. Antidiabetic effects of resveratrol: The way forward in its clinical utility. J. Diabetes Res. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, E.; Arslan, A.K.K.; Yerer, M.B.; Bishayee, A. Resveratrol and diabetes: A critical review of clinical studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lucia, M.; Panzella, L.; Pezzella, A.; Napolitano, A.; d’Ischia, M. Plant catechols and their S-glutathionyl gonjugates as antinitrosating agents: Expedient synthesis and remarkable potency of 5-S-glutathionylpiceatannol. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 2407–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, M.; Muhlbauer, A.; Jagers, E.; Steglich, W. Studies on the biosynthesis of bovilactone-4,4 and related fungal meroterpenoids. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 20, 3544–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lu, J.; Xu, X.; Hu, R.; Pan, Y. pH-Switched HRP-catalysed dimerization of resveratrol: A selective biomimetic synthesis. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 3281–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulfson, E.N.; Halling, P.J.; Holland, H.L. Enzymes in Nonaqueous Solvents: Methods and Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Klibanov, A.M. Improving enzymes by using them in organic solvents. Nature 2001, 409, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Chen, P.; Liu, X.; Han, X. Concise synthesis of several oligostilbenes from the enzyme-promoted oxidation of brominated resveratrol. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 3056–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitrac, X.; Bornet, A.; Vanderlinde, R.; Valls, J.; Richard, T.; Delaunay, J.C.; Merillon, J.M.; Teissedre, P.L. Determination of stilbenes (delta-viniferin, trans-astringin, trans-piceid, cis- and trans-resveratrol, epsilon-viniferin) in Brazilian wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5664–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, G.; Martinez-Pinilla, E.; Ortiz, R.; Noe, V.; Ciudad, C.J.; Franco, R. Resveratrol and related stilbenoids, nutraceutical/dietary complements with health-promoting actions: Industrial production, safety, and the search for mode of action. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 808–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, P.; Capraro, J.; Scarafoni, A.; Bonomi, F.; Blandino, M.; Marengo, M.; Giordano, D.; Carpen, A.; Iametti, S. The bio-functional properties of pigmented cereals may involve synergies among different bioactive species. Plant. Foods Hum. Nutr. 2019, 74, 128–134. [Google Scholar]
- Akkarachiyasit, S.; Charoenlertkul, P.; Yibchok-anun, S.; Adisakwattana, A. Inhibitory activities of cyanidin and its glycosides and synergistic effect with acarbose against intestinal alpha-glucosidase and pancreatic alpha-amylase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 3387–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Lee, B.W.; Kim, M.R.; Jun, J.G. Syntheses of resveratrol and its hydroxylated derivatives as radical scavenger and tyrosinase inhibitor. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasutto, L.; Marotta, E.; Mattarei, A.; Beltramello, S.; Calicet, P.; Salmaso, S.; Bernkop-Schnurch, A.; Garbisa, S.; Zoratti, M.; Paradisi, C. Absorption and metabolism of resveratrol carboxyesters. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 24, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernini, R.; Barontini, M.; Spatafora, C. New lipophilic piceatannol derivatives exhibiting antioxidant activity prepared by aromatic hydroxylation with 2-iodoxybenzoic acid (IBX). Molecules 2009, 14, 4669–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Choi, D.H. Efficient total synthesis of piceatannol via (E)-selective Wittig-Horner reaction. Synth. Commun. 2009, 39, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar]
- Pezet, R.; Perret, C.; Jean-Denis, J.B.; Tabacchi, R.; Gindro, K.; Viret, O. δ-Viniferin, a resveratrol dehydrodimer: One of the major stilbenes synthesized by stressed grapevine leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 5488–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, D.D.; Elofsson, M. Total synthesis of viniferifuran, resveratrol-piceatannol hybrid, anigopreissin A and analogues – Investigation of demethylation. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2016, 358, 4085–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, S.A.; Breazzano, S.P.; Ross, A.G.; Lin, Y.; Zografos, A.L. Total synthesis of diverse carbogenic complexity within the resveratrol class from a common building block. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1753–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velu, S.S.; Buniyamin, I.; Ching, L.K. Regio- and stereoselective biomimetic synthesis of oligostilbenoid dimers from resveratrol analogues. Chem. - Eur. J. 2008, 14, 11376–11384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, B.; Planchestainer, M.; Contente, M.L.; Laurenzi, T.; Eberini, I.; Gourlay, L.J.; Romano, D.; Paradisi, F.; Molinari, F. Strategic single point mutation yields a solvent- and salt-stable transaminase from Virgibacillus sp. in soluble form. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, ID 16441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Omo, G.; Crescenti, D.; Vantaggiato, C.; Parravicini, C.; Borroni, A.P.; Rizzi, N.; Pinto, A.; Recordati, C.; Scanziani, E.; Bassi, F.D.; et al. Inhibition of SIRT1 deacetylase and p53 activation uncouples the anti-inflammatory and chemopreventive actions of NSAIDs. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 3–10 are available from the authors. |










© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mattio, L.M.; Marengo, M.; Parravicini, C.; Eberini, I.; Dallavalle, S.; Bonomi, F.; Iametti, S.; Pinto, A. Inhibition of Pancreatic α-amylase by Resveratrol Derivatives: Biological Activity and Molecular Modelling Evidence for Cooperativity between Viniferin Enantiomers. Molecules 2019, 24, 3225. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183225
Mattio LM, Marengo M, Parravicini C, Eberini I, Dallavalle S, Bonomi F, Iametti S, Pinto A. Inhibition of Pancreatic α-amylase by Resveratrol Derivatives: Biological Activity and Molecular Modelling Evidence for Cooperativity between Viniferin Enantiomers. Molecules. 2019; 24(18):3225. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183225
Chicago/Turabian StyleMattio, Luce M., Mauro Marengo, Chiara Parravicini, Ivano Eberini, Sabrina Dallavalle, Francesco Bonomi, Stefania Iametti, and Andrea Pinto. 2019. "Inhibition of Pancreatic α-amylase by Resveratrol Derivatives: Biological Activity and Molecular Modelling Evidence for Cooperativity between Viniferin Enantiomers" Molecules 24, no. 18: 3225. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183225
APA StyleMattio, L. M., Marengo, M., Parravicini, C., Eberini, I., Dallavalle, S., Bonomi, F., Iametti, S., & Pinto, A. (2019). Inhibition of Pancreatic α-amylase by Resveratrol Derivatives: Biological Activity and Molecular Modelling Evidence for Cooperativity between Viniferin Enantiomers. Molecules, 24(18), 3225. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183225