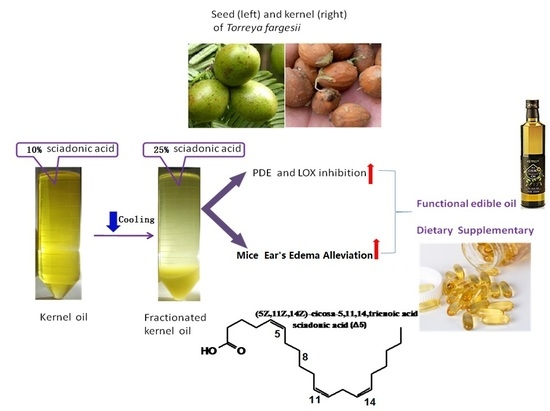
Fractionated Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Kernel Oil from Torreya fargesii
Abstract
:Abstract
Practical Applications
1. Introduction
2. Result and Discussion
2.1. Kernel Oil of T. fargesii and its Properties
2.2. Dewaxing and Fractionation
2.3. Stability of Fractionated Oil
2.4. Radical Scavenging Test
2.4.1. DPPH Scavenging Efficiency
2.4.2. ORAC Capacity
2.5. Anti-inflammatory Effect
2.5.1. PDE Inhibition
2.5.2. LOX Inhibition
2.5.3. Inhibition of Mouse Ear Edema
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Animals
4.3. Preparation of Kernel Oil of T. fargesii
4.4. Physicochemical Properties of Kernel Oil
4.4.1. Total Polyphenols Content
4.4.2. Squalene
4.5. Dewaxing and Fractionation
4.6. Stability of Fractionated Oil
4.7. DPPH and ORAC assays
4.7.1. DPPH
4.7.2. ORAC
4.8. Anti-inflammatory Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolff, R.L.; Bayard, C.C. Fatty acid composition of some pine seed oils. J. Am. Oil. Chem. Soc. 1995, 72, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrono, F.; Boulier-Monthean, N.; Biossel, F.; Ossemond, J.; Devehat, F.L. The Hypo triglyceridemic Effect of Sciadonic Acid is Mediated by the Inhibition of Δ9-Desaturase Expression and Activity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 62, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Gambelli, L.; Schmid, U. Use of a polyunsaturated fatty acid compound. US Patent No. 12/306,292, 13 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Destaillats, F.; Cruz-Hernandez, C.; Dionisi, F.; Masserey-Elmelegy, I.; Manuel-Oliveira, M.; Moulin, J. Sn-1(3) Monoacylglycerides and lipid absorption. US Patent US9000039B2, 7 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, Y.; Tsunokake, K.; Ikeda, I. Effects of non-methylene-interrupted polyunsaturated fatty acid, sciadonic (all-cis-5,11,14-eicosatrienoic acid) on lipid metabolism in rats. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 2009, 73, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.C.; Tsai, P.J.; Huang, Y.L.; Chen, S.N.; Chuang, L.T. PGE2 production is suppressed by chemically-synthesized Δ7-eicosatrienoic acid in macrophages through the competitive inhibition of COX-2. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 66, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.J.; Chuang, L.T.; Liao, J.S.; Huang, W.C.; Lin, H.H. Phospholipid Incorporation of Non-Methylene-Interrupted Fatty Acids (NMIFA) in Murine Microglial BV-2 Cells Reduces Pro-Inflammatory Mediator Production. Inflammation 2015, 38, 2133–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, R.L.; Pedronoa, F.; Marpeau, A.M.; Christie, W.W.; Gunstone, F.D. The seed fatty acid composition and the distribution of Δ5-olefinic acids in the triacylglycerols of some taxaceae (Taxus and Torreya). J. Am. Oil. Chem. Soc. 1998, 75, 1637–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, R.L.; Pedronoa, F.; Marpeau, A.M.; Gunstone, F.D. The seed fatty acid composition and the distribution of Δ5-olefinic acids in the triacylglycerols of some taxares (Cephalotaxus and Podocarpus). J. Am. Oil. Chem. Soc. 1999, 76, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.Y.; Zhu, H.D.; Li, W.L.; Zeng, M.M.; Wu, S.F.; Chen, S.W.; Qin, F.; Chen, J. Chemical components of cold pressed kernel oils from different Torreya grandis cultivars. Food Chem. 2016, 209, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.K.; Mao, J.H.; Zheng, L.; Zhao, C.W.; Jin, Q.Z.; Wang, X.G. Chemical characterization and free radical scavenging capacity of oils obtained from Torreya grandis Fort. ex. Lindl. and Torreya grandis Fort. var. Merrillii: A comparative study using chemometrics. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 115, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.K.; Zheng, L.; Mao, J.H.; Zhao, C.W.; Huang, J.H.; Liu, R.J.; Chang, M.; Jin, Q.Z.; Wang, X.G. Effects of the variety and oil extraction method on the quality, fatty acid composition and antioxidant capacity of Torreya grandis kernel oils. LWT Food Sci. 2018, 91, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Shao, X.F.; Li, H.S. Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction, fatty acid composition, oxidative stability, and antioxidant effect of Torreya grandis seed oil. J. Am. Oil. Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 817–825. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, L.; Shi, W.Y. Composition and free radical scavenging activity of kernel oil from Torreya grandis, Caryacathayensis, and Myricarubra. Iran. J. Pharma. Res. Ijpr. 2014, 13, 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.J.; Ni, S.; Wu, F.; Sang, G.W. Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Essential Oil from Torreya grandis cv. merrillii Arils. J. Essent. OilBear. Pl. 2016, 19, 1170–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, B.; Zhou, X.R.; Shang, J.; Wang, J.H.; Song, H.; Qin, M.Y.; Liu, X.N.; Wang, Q. Population structure and dynamics of Torreya fargesii Franch, a plant endemic to China. Acta. Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 1016–1027. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shang, J.; Wang, J.H.; Zhou, X.R.; Jiang, B.; Qin, M.Y. Ultrasound Extraction of Total Flavonoids from Torreya Fargesii Franch. and Its Antioxidant Activity Based on Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Fresen. Envir. Bull. 2017, 26, 611–617. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.R.; Shang, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, B.; Wang, Q. Antioxidant activity of extracts from the aril of Torreya fargesii Franch. And its protection on the oxidation of DHA algal oil. CyTA-J. Food 2018, 16, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cao, J.; Bai, X.P.; Zhang, F.F. Chemical composition and thermal properties of tilapia oil extracted by different methods. Inter. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, L.; Ortego, E.; Corzo-Martínez, M.; Reglero, G.; Torres, C.F. Stearidonic Acid Concentration by Urea Complexation from Echium Oil. J. Oleo. Sci. 2018, 67, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Alessio, H.M.; Cutler, R.G. Oxygen-radical absorbance capacity assay for antioxidants. Free Radical. Bio. Med. 1993, 14, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimamura, T.; Sumikura, Y.; Yamazaki, T.; Tada, A.; Kashiwagi, T.; Ishikawa, H.; Matsui, T.; Sugimoto, N.; Akiyama, H.; Ukeda, H. Applicability of the DPPH Assay for Evaluating the Antioxidant Capacity of Food Additives Inter-laboratory Evaluation Study. Anal. Sci. 2014, 30, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoo, M.; Regenstein, J.M.; Gavlighi, H.A. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) and its potential to preserve the quality and safety of foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. F. 2018, 17, 732–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, Y.; Hari, S.P.; Passwater, R., Jr.; Huang, D. Antioxidant activities of natural vitamin E formulations. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2003, 49, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odubanjo, V.O.; Olasehinde, T.A.; Oyeleye, S.I.; Oboh, G.; Boligon, A.A. Seed extracts from Myristicafragrans (nutmeg) and Moringa oleifera (drumstick tree) inhibits enzymes relevant to erectile dysfunction and metal-induced oxidative damage in rats’ penile tissues. J. Food Biochem. 2017, 1, e12452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Levenson, C.; Browning, J.C.; Becker, E.M.; Clements, I.; Castella, P. East Indian sandalwood oil is a phosphodiesterase inhibitor: A new therapeutic option in the treatment of inflammatory skin disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ahmady, S.H.; Ashour, M.L.; Wink, M. Chemical composition and anti-inflammatory activity of the essential oils of Psidiumguajava fruits and leaves. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2013, 25, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, F.; Karaca, N.; Tekin, M.; Demirci, B. Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial evaluation of Thymussipyleus boiss. subsp. sipyleus var. sipyleus essential oil against rhinosinusitis pathogens. Microb. Pathogenesis. 2018, 122, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Fan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, T.; Zhou, P.; Niu, X. Houttuyniacordata thunb. volatile oil exhibited anti-inflammatory effects in vivo and inhibited nitric oxide and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in LPS-stimulated mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro. Phytothe. Res. 2013, 27, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.L.M.; Nunes-Pinheiro, D.C.S.; Bezerra, B.M.O.; Leite, L.O.; Tomé, A.R.; Girão, V.C.C. Topical Anti-inflammatory Potential of Pumpkin (Cucurbitapepo L.) Seed Oil on Acute and Chronic Skin Inflammation in Mice. Acta Sci. Veter. 2013, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 19th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, H.L.N.; Puah, C.W.; Choo, Y.M.; Ma, A.N.; Cheng, H.C. Simultaneous quantification of free fatty acids, free sterols, squalene, and acylglycerol molecular species in palm oil by high-temperature gas chromatography-flame ionization detection. Lipids 2005, 40, 523–528. [Google Scholar]
- Yasamin, S.; Mohammad, A.S.; Mohsen, B. Influence of processing parameters on physicochemical properties of fractionated fish oil at low temperature crystallization. Nutr. Food Sci. 2015, 45, 2–19. [Google Scholar]
- Nayik, G.A.; Dar, B.N.; Nanda, V. Optimization of the process parameters to establish the quality attributes of DPPH radical scavenging activity, total phenolic content, and total flavonoid content of apple (Malusdomestica) honey using response surface methodology. Inter. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 1738–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segovia, F.J.; Hidalgo, G.I.; Villasante, J.; Ramis, X.; Almajano, M.P. Avocado Seed: A Comparative Study of Antioxidant Content and Capacity in Protecting Oil Models from Oxidation. Molecules 2018, 23, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamillapalli, R.; Haimovitz, R.; Ohad, M.; Shinitzky, M. Enhancement and inhibition of snake venom phosphodiesterase activity by Iysophospholipids. FEBSLett. 1998, 436, 256–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, A.; Ortiz-Ruiz, V.; Martinez-Gutierrez, R.; Tomas, V.; Tudela, J. Lavandulastoechas essential oil from Spain: Aromatic profile determined by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry, antioxidant and lipoxygenase inhibitory bioactivities. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 73, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhotnik, I.; Moati, D.; Shaoul, R.; Loberman, B.; Pollak, Y.; Schwartz, B. Quercetin prevents small intestinal damage and enhances intestinal recovery during methotrexate-induced intestinal mucositis of rats. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 62, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |





| T. fragesii Oil (UT Oil) | Fractionated T. fragesii Oil (FT Oil) | T. grandis Oil | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Color (Lovibond 1.0 inch) | Y30 + R1 | Y30 + R0.5 | - |
| Viscority 20 °C, mPa.s | 55–90 | 60–90 | - |
| Density, 20 °C, g/cm3 | 0.920–0.930 | 0.910–0.930 | - |
| Acid value (AV), mg KOH/g | 0.35 ± 0.01 a | 0.33 ± 0.01 a | 0.2–3 |
| Peroxide value (PV), meq/g | 0.56 ± 0.05 a | 0.49 ± 0.04 a | 0.1–1 |
| Iodine value (IV), g I2/100g | 145 ± 1.8 a | 161 ± 2.0 b | 130–150 |
| Saponification value, mg KOH/g | 186 ± 2.3 a | 188 ± 2.6 a | 180–200 |
| Unsaponifiable matter, % | 0.82 ± 0.05 a | 0.76 ± 0.05 a | - |
| Wax, % | 2.12 ± 0.25 a | 0.05 ± 0.00 b | - |
| C16:0, % by GC, same as below | 9.68 ± 0.35 a | 2.62 ± 0.25 b | 7–10 |
| C18:0 | 5.32 ± 0.23 a | 3.21 ± 0.21 b | 2–4 |
| C18:1 | 29.36 ± 0.7 a | 20.62 ± 0.8 b | 17–33 |
| C18:2 | 39.95 ± 0.3 a | 50.68 ± 0.2 b | 40–47 |
| C18:3 9c 12c 15c | 1.65 ± 0.10 a | 2.58 ± 0.31 b | 0.4–1 |
| C20:2 11c 14c | 1.98 ± 0.14 a | 2.35 ± 0.16 a | 2–4 |
| C20:3 5c 1c 14c | 11.23 ± 0.43 a | 25.23 ± 0.45 b | 9–18 |
| SFA ** | 15.00 ± 0.51 a | 5.83 ± 0.48 b | 10–12 |
| MUFA ** | 29.36 ± 1.0 a | 23.62 ± 1.2 b | 19–35 |
| PUFA ** | 56.64 ± 1.5 a | 77.76 ± 1.4 b | 53–67 |
| UFA ** | 85.00 ± 1.9 a | 94.17 ± 1.3 b | 87–89 |
| Total tocopherols, mg/Kg | 1830 ± 25 a | 2020 ± 32 b | 1400–2300 |
| Total polyphenols, mg GAE**/kg | 5.6 ± 0.4 a | 2.3 ±0.3 b | 3.7–31.1 |
| Squalene, mg/kg | 15.6 ± 0.05 a | 16.2 ± 0.06 a | 16–35 |
| Total phytosterols, mg/kg | 2020 ± 80 a | 1980 ± 75 a | 1200–2200 |
| Dewaxing/Fractionation Condition | Yield of Liquid Fraction % | Sciadonic Acid % | Melting Range (Liquid Fraction) | Solid Fat Content (25 °C, Liquid Fraction) | Wax% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UT oil, original | - | 11.2 ± 0.8 a | 13.5 d–16.8 d | 10.9 ± 1.3 c | 2.12 ± 0.25 e |
| WP 2 °C/h (40–25 °C), filtration | 96.8 ± 1.6 d | 11.5 ± 1.3 a | 12.3 d–15.6 d | 10.5 ± 1.6 c | 0.45 ± 0.09 d |
| FP1 0.5 °C/h, (30–5 °C), 2 rpm | 76.6 ± 1.3 a | 19.7 ± 0.8 d | 4.3 b–7.8 b | 2.1 ± 0.8 a | 0.06 ± 0.00 a |
| FP2 1 °C/h, (30–5 °C), 2 rpm | 80.7 ± 1.8 b | 15.3 ± 0.9 c | 4.6 b–8.3 b | 2.6 ± 0.6 b | 0.12 ± 0.02 b |
| FP 3 (FT oil) 1 °C/h, (30–15 °C), 0.5 °C/h, (15–5 °C), 2 rpm | 75.2 ± 1.7 a | 25.2 ± 0.9 d | 3.2 a–5.6 a | 1.9 ± 0.8 a | 0.05 ± 0.00 a |
| FP4 1 °C /h, (30–15 °C), 0.5 °C/h, (15–5 °C), 4 rpm | 88.6 ± 2.3 c | 13.9 ± 1.5 b | 5.5 c–9.2 c | 2.5 ± 0.3 b | 0.18 ± 0.02 c |
| UT Oil | FT Oil | EGCG** | T. grandis Oil | BHT | NDGA** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORAC μmol TE/100 g | 445 ± 12 a | 458 ± 10 a | 8000 ± 124 | 260–435 | - | - |
| DPPH μmol TE/100 g | 485 ± 15 a | 502 ± 18 a | - | 422–509 | - | - |
| DPPH IC50 μg/ml | 6.12 ± 0.05 a | 5.90 ± 0.12 a | 90 | - | 1.75 ± 0.03 | - |
| LOX-5 IE% (Concentration of oil) | 32.1 ± 2.3 a (66.7 μg/mL) | 65.2 ± 3.1 b (66.7μg/mL) | - | - | - | 100 ± 0 (10 μg/mL) |
| LOX-5 IC50 μg/ml | - | 47.8 ± 1.3 | - | - | - | 2.95 ± 0.21 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Shang, J.; Qin, M.; Wang, J.; Jiang, B.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y. Fractionated Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Kernel Oil from Torreya fargesii. Molecules 2019, 24, 3402. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183402
Zhou X, Shang J, Qin M, Wang J, Jiang B, Yang H, Zhang Y. Fractionated Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Kernel Oil from Torreya fargesii. Molecules. 2019; 24(18):3402. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183402
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xianrong, Jin Shang, Mingyi Qin, Jianhua Wang, Bo Jiang, Hui Yang, and Yan Zhang. 2019. "Fractionated Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Kernel Oil from Torreya fargesii" Molecules 24, no. 18: 3402. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183402
APA StyleZhou, X., Shang, J., Qin, M., Wang, J., Jiang, B., Yang, H., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Fractionated Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Kernel Oil from Torreya fargesii. Molecules, 24(18), 3402. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183402