Discovery of Selective Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) Inhibitors through a Combination of Computational Studies and Biological Evaluations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
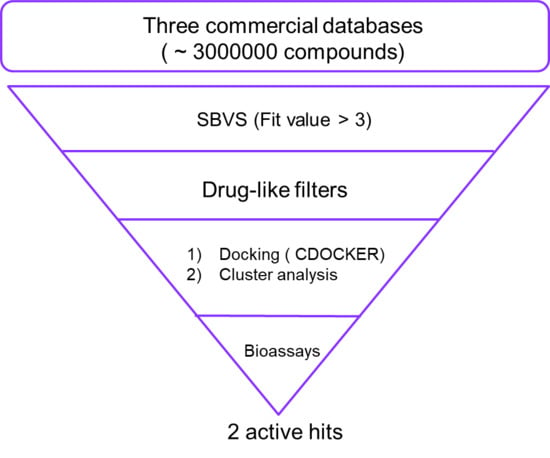
2.1. Virtual Screening
2.2. ChEs Inhibitory Activities of Hit Compounds
2.3. Kinetic Studies
2.4. Docking Simulation of Hit Compounds
2.5. Molecular Dynamics
2.6. Cell Viability Assay
2.7. Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, and Toxicity (ADMET) in Silico Prediction
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Virtual Screening
3.2. Biological Evaluation
3.3. Kinetic Study
3.4. Binding Mode Prediction
3.5. Molecular Dynamics
3.6. Cell Viability Assay
3.7. ADMET in Silico Prediction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lane, C.A.; Hardy, J.; Schott, J.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hu, J.; Yang, X.; Feng, X.; Li, X.; Huang, L.; Chan, A.S.C. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Orally Bioavailable Quinoline−Indole Derivatives as Innovative Multitarget-Directed Ligands: Promotion of Cell Proliferation in the Adult Murine Hippocampus for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 1871–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzheimer’s Disease International. Available online: https://www.alz.co.uk/research/world-report-2018 (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- Więckowska, A.; Wichur, T.; Godyń, J.; Bucki, A.; Marcinkowska, M.; Siwek, A.; Więckowski, K.; Zaręba, P.; Knez, D.; Głuch-Lutwin, M.; et al. Novel Multitarget-Directed Ligands Aiming at Symptoms and Causes of Alzheimer’ s Disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 1195–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wu, D.; Luo, H. Novel Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors for Cognitive Improvement in Alzheimer ’ s Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 5467–5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cline, E.N.; Bicca, M.A.; Viola, K.L.; Klein, W.L. The Amyloid-β Oligomer Hypothesis: Beginning of the Third Decade. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 64, S567–S610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, G.; Distefano, D.A.; Parlascino, P.; Fresta, C.G.; Lazzarino, G.; Lunte, S.M.; Nicoletti, V.G. Receptor-mediated toxicity of human amylin fragment aggregated by short- and long-term incubations with copper ions. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 425, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julien, C.; Tomberlin, C.; Roberts, C.M.; Akram, A.; Stein, G.H.; Silverman, M.A.; Link, C.D. In vivo induction of membrane damage by β-amyloid peptide oligomers. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Wang, X.; Geng, M. Alzheimer’s disease hypothesis and related therapies. Transl. Neurodegener. 2018, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanabria-Castro, A.; Alvarado-Echeverra, I.; Monge-Bonilla, C. Molecular Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: An Update. Ann. Neurosci. 2017, 24, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; He, S.Y.; Chen, Y.; Feng, F.; Qu, W.; Sun, H.P. Donepezil-based Multi-functional Cholinesterase Inhibitors for Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contestabile, A. The history of the cholinergic hypothesis. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 221, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, M.; Yu, L.B.; Ju, Y. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters Synthesis and binding ability of 1, 2, 3-triazole-based triterpenoid receptors for recognition of Hg2+ ion. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4342–4345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Csuk, R.; Albert, S.; Kluge, R.; StrÖhl, D. Resveratrol Derived Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitors. Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. 2013, 346, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, P.; Kumar, A.; Panda, G. Anti-cholinesterase hybrids as multi-target-directed ligands against Alzheimer’s disease (1998–2018). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 895–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dighe, S.N.; Deora, G.S.; Mora, E.D.; Nachon, F.; Chan, S.; Parat, M.; Brazzolotto, X.; Ross, B.P. Discovery and Structure−Activity Relationships of a Highly Selective Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitor by Structure-Based Virtual Screening. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 7683–7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt, T.; Bigl, V.; Walther, F.; Sonntag, M. Decreased Ratio of CSF Acetylcholinesterase to Butyrylcholinesterase Activity in Alzheimer’s Disease. Lancet 1984, 323, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, H.Y.; Chen, Y.; Sun, H.P. Recent progress in the identification of selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 132, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesulam, M.M.; Guillozet, A.; Shaw, P.; Levey, A.; Duysen, E.G.; Lockridge, O. Acetylcholinesterase knockouts establish central cholinergic pathways and can use butyrylcholinesterase to hydrolyze acetylcholine. Neuroscience 2002, 110, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greig, N.H.; Utsuki, T.; Ingram, D.K.; Wang, Y.; Pepeu, G.; Scali, C.; Yu, Q.; Mamczarz, J.; Holloway, H.W.; Giordano, T.; et al. Selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibition elevates brain acetylcholine, augments learning and lowers Alzheimer β-amyloid peptide in rodent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 17213–17218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Pan, Y.; Muzyka, J.L.; Zhan, C.G. Active site gating and substrate specificity of butyrylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase: Insights from molecular dynamics simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 8797–8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Košak, U.; Brus, B.; Knez, D.; Šink, R.; Žakel, S.; Trontelj, J.; Pišlar, A.; Šlenc, J.; Gobec, M.; Živin, M.; et al. Development of an in-vivo active reversible butyrylcholinesterase inhibitor. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Košak, U.; Brus, B.; Knez, D.; Žakel, S.; Trontelj, J.; Pišlar, A.; Šink, R.; Jukič, M.; Živin, M.; Podkowa, A.; et al. The Magic of Crystal Structure-Based Inhibitor Optimization: Development of a Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitor with Picomolar Affinity and in Vivo Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Candia, M.; Zaetta, G.; Denora, N.; Tricarico, D.; Majellaro, M.; Cellamare, S.; Altomare, C.D. New azepino [4,3-b] indole derivatives as nanomolar selective inhibitors of human butyrylcholinesterase showing protective effects against NMDA-induced neurotoxicity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 125, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawatzky, E.; Wehle, S.; Kling, B.; Wendrich, J.; Bringmann, G.; Sotri, C.A.; Heilmann, J.; Decker, M. Discovery of Highly Selective and Nanomolar Carbamate-Based Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitors by Rational Investigation into Their Inhibition Mode. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 2067–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Košak, U.; Kenz, D.; Coquelle, N.; Brus, B.; Pišlar, A.; Nachon, F.; Brazzolotto, X.; Kos, J.; Colletier, J.P.; Gobec, S. N-Propargylpiperidines with naphthalene-2-carboxamide or naphthalene-2-sulfonamide moieties: Potential multifunctional anti-Alzheimer’s agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brus, B.; Košak, U.; Turk, S.; Pišlar, A.; Coquelle, N.; Kos, J.; Stojan, J.; Colletier, J.P.; Gobec, S. Discovery, biological evaluation, and crystal structure of a novel nanomolar selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 8167–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meden, A.; Knez, D.; Jukič, M.; Brazzolotto, X.; Gršič, M.; Pišlar, A.; Zahirović, A.; Kos, J.; Nachon, F.; Svete, J.; et al. Tryptophan-derived butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors as promising leads against Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 3765–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.S.; Ge, Y.X.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Tao, H.R.; Zhu, K.K.; Zhang, H. Discovery of New Selective Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) Inhibitors with Anti-Aβ Aggregation Activity: Structure-Based Virtual Screening, Hit Optimization and Biological Evaluation. Molecules 2019, 24, 2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atatreh, N.; Al Rawashdah, S.; Al Neyadi, S.S.; Abuhamdah, S.M.; Ghattas, M.A. Discovery of new butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors via structure-based virtual screening. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beesu, M.; Caruso, G.; Salyer, A.C.D.; Khetani, K.K.; Sil, D.; Weerasinghe, M.; Tanji, H.; Ohto, U.; Shimizu, T.; David, S.A. Structure-Based Design of Human TLR8-Specific Agonists with Augmented Potency and Adjuvanticity. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 7833–7849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, B.J.; Braga, R.C.; Melo-Filho, C.C.; Moreira-Filho, J.T.; Muratov, E.N.; Andrade, C.H. QSAR-based virtual screening: Advances and applications in drug discovery. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beesu, M.; Caruso, G.; Salyer, A.C.D.; Shukla, N.M.; Khetani, K.K.; Smith, L.J.; Fox, L.M.; Tanji, H.; Ohto, U.; Shimizu, T.; et al. Identification of a Human Toll-Like Receptor (TLR) 8-Specific Agonist and a Functional Pan-TLR Inhibitor in 2-Aminoimidazoles. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 3311–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Yang, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, F.; Liu, W.; Guo, Q.; Sun, H. Expansion of the scaffold diversity for the development of highly selective butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) inhibitors: Discovery of new hits through the pharmacophore model generation, virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulation. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 85, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A. Drug-like properties and the causes of poor solubility and poor permeability. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2000, 44, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.L.; Fu, T.M.; Li, W.; Xu, X.L.; Sun, H.P. Discovery of new acetylcholinesterase inhibitors with small core structures through shape-based virtual screening. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3442–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankovic, Z. CNS drug design: Balancing physicochemical properties for optimal brain exposure. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 2584–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, A.K.; Herbertz, T.; Hudkins, R.L.; Dorsey, B.D.; Mallamo, J.P. Knowledge-based, central nervous system (CNS) lead selection and lead optimization for CNS drug discovery. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2012, 3, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belinskaya, D.; Juffer, A.; Shestakova, N. The role of electrostatic interactions in the absorption of ligands to the active sites of cholinesterases, as indicated by molecular modeling data. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2010, 36, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachon, F.; Carletti, E.; Ronco, C.; Trovaslet, M.; Nicolet, Y.; Jean, L.; Renard, P.-Y. Crystal structures of human cholinesterases in complex with huprine W and tacrine: Elements of specificity for anti- Alzheimer’s drugs targeting acetyl-and butyryl-cholinesterase. Biochem. J. 2013, 453, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberry, T.L.; Id, X.B.; Macdonald, I.R.; Wandhammer, M.; Trovaslet-leroy, M.; Darvesh, S.; Nachon, F. Comparison of the Binding of Reversible Inhibitors to Human Butyrylcholinesterase and Acetylcholinesterase: A Crystallographic, Kinetic and Calorimetric Study. Molecules 2017, 22, 2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Feng, L.J.; Huang, Y.; Wu, D.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, Y.; Luo, H.B. Discovery of novel phosphodiesterase-2A inhibitors by structure-based virtual screening structural optimization, and bioassay. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, Z.; Pan, W.; Wang, K.; Ma, Q.; Yu, L.; Yang, Y.; Bai, P.; Leng, C.; Xu, Q.; Li, X.; et al. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel ferulic acid- O -alkylamine derivatives as potential multifunctional agents for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 130, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, H.; Yang, H.; Tan, R.; Bian, Y.; Fu, T.; Li, W.; Wu, L.; Pei, Y.; Sun, H. Discovery of new acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors through structure-based virtual screening. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 3429–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Yang, H.; Jiang, X.; Lin, H.; Chen, Y.; Qu, W.; Feng, F.; Bian, Y.; et al. Investigation of multi-target-directed ligands (MTDLs) with (IDO1) inhibition: The design, synthesis of miconazole analogues targeting Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 1665–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.A.; Betz, R.M.; Cerutti, D.S.; Cheatham, T.E., III; Darden, T.A.; Duke, R.E.; Giese, T.J.; Gohlke, H.; Goetz, A.W.; Homeyer, N.; et al. AMBER 2016; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Hou, T.; Qiao, X.; Xu, X. Parameters for the Generalized Born Model Consistent with RESP Atomic Partial Charge Assignment Protocol. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 9071–9078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornak, V.; Abel, R.; Okur, A.; Strockbine, B.; Roitberg, A.; Simmerling, C. Comparison of Multiple Amber Force Fields and Development of Improved Protein Backbone Parameters. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2006, 65, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roe, D.R.; Cheatham, T.E. PTRAJ and CPPTRAJ: Software for Processing and Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Trajectory Data. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 3084–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.R.; Mcgee, T.D.; Swails, J.M.; Homeyer, N.; Gohlke, H.; Roitberg, A.E. MMPBSA.py: An Efficient Program for End-State Free Energy Calculations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 3314–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of compounds 5–19 are available from the authors. |









| Compound | BChE | AChE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IR a (%) | IC50 b (μM) | IR c (%) | IC50 (μM) | |
| 5 | 7.2 ± 0.6 | nd. d | −0.31 ± 0.5 | nd. |
| 6 | 8.5 ± 0.3 | nd. | −1.5 ± 0.5 | nd. |
| 7 | 16.3 ± 1.1 | nd. | 0.6 ± 0.6 | nd. |
| 8 | 68.6 ± 0.7 | 1.1 ± 0.6 | 58.5 ± 1.2 | 43.2 ± 17.6 |
| 9 | 15.5 ± 1.6 | nd. | 16.0 ± 1.5 | nd. |
| 10 | 9.9 ± 1.0 | nd. | 7.8 ± 0.7 | nd. |
| 11 | 14.8 ± 1.3 | nd. | −0.7 ± 0.7 | nd. |
| 12 | −1.8 ± 1.1 | nd. | 1.1 ± 1.0 | nd. |
| 13 | 20.1 ± 1.2 | nd. | 11.3 ± 1.3 | nd. |
| 14 | 3.4 ± 0.4 | nd. | 10.9 ± 0.8 | nd. |
| 15 | −0.6 ± 0.5 | nd. | 0.6 ± 1.0 | nd. |
| 16 | 26.4 ± 1.1 | nd. | 38.7 ± 1.7 | nd. |
| 17 | 11.8 ± 1.2 | nd. | 2.9 ± 0.5 | nd. |
| 18 | 58.4 ± 0.9 | 6.3 ± 2.0 | 11.1 ± 1.5 | nd. |
| 19 Tacrine | 61.2 ± 1.8 100 | 2.4 ± 1.0 0.003 ± 0.004 | 53.2 ± 0.6 95.2 ± 0.3 | 13.8 ± 6.0 0.01 ± 0.003 |
| Compound | Kic a | Kiu b |
|---|---|---|
| 8 | 0.88 ± 0.07 µM | 3.61 ± 0.24 µM |
| 18 | 0.93 ± 0.13 µM | 2.31 ± 0.32 µM |
| Energy Terms (kcal/mol) | 8 | 18 |
|---|---|---|
| VDWAALS a | −43.3 ± 5.8 | −52.2 ± 3.5 |
| EEL b | −51.3 ± 16.8 | −142 ± 24.0 |
| EGB c | 57.6 ± 15.0 | 153 ± 21.3 |
| ESURF d | −5.9 ± 1.0 | −7.1 ± 0.7 |
| DELTA G gas e | −94.6 ± 19.1 | −195 ± 24.6 |
| DELTA G solv f | 51.7 ± 14.2 | 146 ± 20.8 |
| DELTA TOTAL g | −42.9 ± 9.4 | −48.2 ± 6.1 |
| Comp. | AlogP98 a | PSA-2D b | Solubility Level c | Absorption Level d | BBB Level e | PPB f | CYP2D6 g | Hepatotoxic h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 3.53 | 53.589 | 3 | 0 | 1 | true | true | false |
| 18 | 3.514 | 63.209 | 3 | 0 | 2 | true | false | false |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Lu, X.; Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Tang, Z.; Cheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; et al. Discovery of Selective Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) Inhibitors through a Combination of Computational Studies and Biological Evaluations. Molecules 2019, 24, 4217. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234217
Zhou Y, Lu X, Yang H, Chen Y, Wang F, Li J, Tang Z, Cheng X, Yang Y, Xu L, et al. Discovery of Selective Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) Inhibitors through a Combination of Computational Studies and Biological Evaluations. Molecules. 2019; 24(23):4217. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234217
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, You, Xin Lu, Hongyu Yang, Yao Chen, Feng Wang, Jifu Li, Zhiran Tang, Xifei Cheng, Yingbin Yang, Li Xu, and et al. 2019. "Discovery of Selective Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) Inhibitors through a Combination of Computational Studies and Biological Evaluations" Molecules 24, no. 23: 4217. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234217
APA StyleZhou, Y., Lu, X., Yang, H., Chen, Y., Wang, F., Li, J., Tang, Z., Cheng, X., Yang, Y., Xu, L., & Xia, Q. (2019). Discovery of Selective Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) Inhibitors through a Combination of Computational Studies and Biological Evaluations. Molecules, 24(23), 4217. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234217