Catalytic Ozonation of Organics in Reverse Osmosis Concentrate with Catalysts Based on Activated Carbon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the Catalysts
2.2. Catalytic Ozonation of p-CBA in Water
2.3. The Removal of Organics in ROC by Catalytic Ozonation
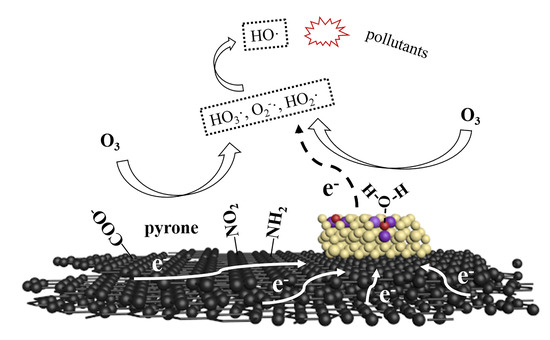
2.4. Possible Mechanism of Catalytic Ozonation in ROC
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of the Catalysts
3.3. Experimental Methods
3.4. Analytical Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van der Bruggen, B.; Lejon, L.; Vandecasteele, C. Reuse, treatment, and discharge of the concentrate of pressure-driven membrane processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 3733–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radjenovic, J.; Petrovic, M.; Ventura, F.; Barcelo, D. Rejection of pharmaceuticals in nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membrane drinking water treatment. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3601–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ternes, T.A.; Joss, A.; Siegrist, H. Scrutinizing pharmaceuticals and personal care products in wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 392A–399A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkinson, A.J.; Murby, E.J.; Costanzo, S.D. Removal of antibiotics in conventional and advanced wastewater treatment: Implications for environmental discharge and wastewater recycling. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4164–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Lim, T.-T.; Chin, S.-S.; Fane, A.G. Treatment of organics in reverse osmosis concentrate from a municipal wastewater reclamation plant: Feasibility test of advanced oxidation processes with/without pretreatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Gunten, U. Ozonation of drinking water: Part I. Oxidation kinetics and product formation. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1443–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.Y.; Zhou, Y.T.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Du, Y.; Hu, H.Y. Underestimated risk from ozonation of wastewater containing bromide: Both organic byproducts and bromate contributed to the toxicity increase. Water Res. 2019, 162, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.D.; Plewa, M.J.; Wagner, E.D.; Schoeny, R.; Demarini, D.M. Occurrence, genotoxicity, and carcinogenicity of regulated and emerging disinfection by-products in drinking water: A review and roadmap for research. Mutat Res. 2007, 636, 178–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Ziółek, M.; Nawrocki, J. Catalytic ozonation and methods of enhancing molecular ozone reactions in water treatment. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 46, 639–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghuge, S.P.; Saroha, A.K. Catalytic ozonation for the treatment of synthetic and industrial effluents-Application of mesoporous materials: A review. J. Environ. Manage 2018, 211, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lu, X.; Xu, K.; Qu, J.; Qiang, Z. Cerium incorporated MCM-48 (Ce-MCM-48) as a catalyst to inhibit bromate formation during ozonation of bromide-containing water: Efficacy and mechanism. Water Res. 2015, 86, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wu, D.; Wu, Y.; Li, L. Mechanism insight of pollutant degradation and bromate inhibition by Fe-Cu-MCM-41 catalyzed ozonation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 346, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Polo, M.; Salhi, E.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; von Gunten, U. Combination of Ozone with Activated Carbon as an Alternative to Conventional Advanced Oxidation Processes. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2006, 28, 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Polo, M.; von Gunten, U.; Rivera-Utrilla, J. Efficiency of activated carbon to transform ozone into OH radicals: Influence of operational parameters. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3189–3198. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, P.M.; Masa, F.J.; Jaramillo, J.; Beltran, F.J.; Gomez-Serrano, V. Kinetics of ozone decomposition by granular activated carbon. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 2545–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqer, S.M.; Kondarides, D.I.; Verykios, X.E. Catalytic oxidation of toluene over binary mixtures of copper, manganese and cerium oxides supported on γ-Al2O3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 103, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, P.; Cheng, Z.; Li, J.; Zuo, S. Ce-modified mesoporous γ-Al2O3 supported Pd-Pt nanoparticle catalysts and their structure-function relationship in complete benzene oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.; Li, L. Catalytic Ozonation of Oxalic Acid in the Presence of Fe2O3-Loaded Activated Carbon. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, B.; Huang, R.; Li, L.; Yan, H.; Liao, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q. Catalytic ozonation of p-chlorobenzoic acid in aqueous solution using Fe-MCM-41 as catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Quan, X.; Chen, S.; Yu, H.; Liu, G. Enhanced catalytic ozonation by highly dispersed CeO2 on carbon nanotubes for mineralization of organic pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 368, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Sanchez-Polo, M. Ozonation of 1,3,6-naphthalenetrisulphonic acid catalysed by activated carbon in aqueous phase. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2002, 39, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Xing, L.; Wu, G.; Xie, Y.; Shi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Minakata, D.; Crittenden, J.C. Promoting effect of nitration modification on activated carbon in the catalytic ozonation of oxalic acid. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 146, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, T.F.; Chedeville, O.; Fauduet, H.; Cagnon, B. Use of ozone/activated carbon coupling to remove diethyl phthalate from water: Influence of activated carbon textural and chemical properties. Desalination 2011, 276, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, S.; Quan, X.; Lu, S. Catalytic performance and an insight into the mechanism of CeO2 nanocrystals with different exposed facets in catalytic ozonation of p-nitrophenol. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 248, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Méndez-Díaz, J.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; Ferro-García, M.A.; Bautista-Toledo, I. Removal of the surfactant sodium dodecylbenzenesulphonate from water by simultaneous use of ozone and powdered activated carbon: Comparison with systems based on O3 and O3/H2O2. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, M.; Kawashima, K.; Kozawa, K.; Sakai, H.; Kaneko, K. Amination of activated carbon and adsorption characteristics of its aminated surface. Langmuir 2000, 16, 5059–5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jans, U.; Hoigné, J. Activated Carbon and Carbon Black Catalyzed Transformation of Aqueous Ozone into OH-Radicals. Ozone Sci. Eng. 1998, 20, 67–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, P.C.C.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Pereira, M.F.R. Activated carbon and ceria catalysts applied to the catalytic ozonation of dyes and textile effluents. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 88, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, P.C.C.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Pereira, M.F.R. Activated carbon catalytic ozonation of oxamic and oxalic acids. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 79, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, M.C.; Buffle, M.O.; Von Gunten, U. Oxidation of antibacterial molecules by aqueous ozone: Moiety-specific reaction kinetics and application to ozone-based wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1969–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.; Costa, R.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M.; Martins, R.C. Application of ozonation for pharmaceuticals and personal care products removal from water. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Not available. |






| Catalysts | AC-A | AC-NO2 | AC-NH2 | Ce/AC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBET (m2/g) | 1037.85 | 1030.32 | 1072.84 | 865.49 |
| dp (nm) | 0.8573 | 0.8364 | 0.8368 | 0.8162 |
| Catalysts | AC-A | AC-NO2 | AC-NH2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acid Groups (μeq/g) | 194.0 | 313.4 | 74.6 |
| Base Groups (μeq/g) | 153.9 | 57.7 | 283.7 |
| AOPs | Reaction Constant (×10−3·min−1) | Contribution Rate (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | kTBA | ·OH | Non ·OH | |
| O3 + AC-A | 8.20 | 5.28 | 35.6 | 64.4 |
| O3 + AC-NO2 | 14.59 | 4.24 | 70.9 | 29.1 |
| O3 + AC-NH2 | 8.54 | 5.37 | 37.1 | 62.9 |
| O3 + Ce/AC | 51.52 | 4.42 | 91.4 | 8.6 |
| COD (mg/L) | TOC (mg/L) | UV254 (cm−1) | pH | Conductivity (S/cm), 25 °C | TDS (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31.44~41.86 | 9.28~10.69 | 0.19±0.05 | 6.5±0.5 | 1896 | 948 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Xia, Z.; Li, L.; Huang, Q.; He, C.; Wang, J. Catalytic Ozonation of Organics in Reverse Osmosis Concentrate with Catalysts Based on Activated Carbon. Molecules 2019, 24, 4365. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234365
Xu X, Xia Z, Li L, Huang Q, He C, Wang J. Catalytic Ozonation of Organics in Reverse Osmosis Concentrate with Catalysts Based on Activated Carbon. Molecules. 2019; 24(23):4365. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234365
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xieyang, Zhilin Xia, Laisheng Li, Qi Huang, Can He, and Jianbing Wang. 2019. "Catalytic Ozonation of Organics in Reverse Osmosis Concentrate with Catalysts Based on Activated Carbon" Molecules 24, no. 23: 4365. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234365
APA StyleXu, X., Xia, Z., Li, L., Huang, Q., He, C., & Wang, J. (2019). Catalytic Ozonation of Organics in Reverse Osmosis Concentrate with Catalysts Based on Activated Carbon. Molecules, 24(23), 4365. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234365