Developing an Enzyme-Assisted Derivatization Method for Analysis of C27 Bile Alcohols and Acids by Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
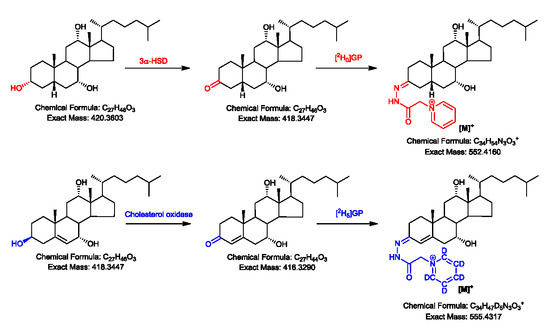
2.1. Oxidation Efficiency of 3α-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase (3α-HSD)
2.2. Girard P (GP)-Derivatisation of 3-Oxo Groups
2.3. LC-MS Analysis of Oxidised/Derivatised 3α-Hydroxy-5β-Hydrogen Substrates
2.4. MSn Fragmentation
2.4.1. Triols and Tetrols
2.4.2. Pentols
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Oxidation and Derivatization
4.2.2. LC-MS(MSn) Analysis
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fahy, E.; Subramaniam, S.; Brown, H.A.; Glass, C.K.; Merrill, A.H., Jr.; Murphy, R.C.; Raetz, C.R.; Russell, D.W.; Seyama, Y.; Shaw, W.; et al. A comprehensive classification system for lipids. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 839–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroepfer, G.J., Jr. Oxysterols: Modulators of cholesterol metabolism and other processes. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 361–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjovall, J. Fifty years with bile acids and steroids in health and disease. Lipids 2004, 39, 703–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorkhem, I. Rediscovery of cerebrosterol. Lipids 2007, 42, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, W.J.; Sjovall, J. Bile acids: Analysis in biological fluids and tissues. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shackleton, C.H. Role of a disordered steroid metabolome in the elucidation of sterol and steroid biosynthesis. Lipids 2012, 47, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Griffiths, W.J. Unravelling new pathways of sterol metabolism: Lessons learned from in-born errors and cancer. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2018, 21, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, W.J.; Gilmore, I.; Yutuc, E.; Abdel-Khalik, J.; Crick, P.J.; Hearn, T.; Dickson, A.; Bigger, B.W.; Wu, T.H.; Goenka, A.; et al. Identification of unusual oxysterols and bile acids with 7-oxo or 3beta,5alpha,6beta-trihydroxy functions in human plasma by charge-tagging mass spectrometry with multistage fragmentation. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, W.J.; Crick, P.J.; Meljon, A.; Theofilopoulos, S.; Abdel-Khalik, J.; Yutuc, E.; Parker, J.E.; Kelly, D.E.; Kelly, S.L.; Arenas, E.; et al. Additional pathways of sterol metabolism: Evidence from analysis of Cyp27a1-/- mouse brain and plasma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 191–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.M.; Kliewer, S.A.; Moore, L.B.; Smith-Oliver, T.A.; Oliver, B.B.; Su, J.L.; Sundseth, S.S.; Winegar, D.A.; Blanchard, D.E.; Spencer, T.A.; et al. Activation of the nuclear receptor LXR by oxysterols defines a new hormone response pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 3137–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Liao, S. Cholestenoic acid is a naturally occurring ligand for liver X receptor alpha. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 4180–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogundare, M.; Theofilopoulos, S.; Lockhart, A.; Hall, L.J.; Arenas, E.; Sjovall, J.; Brenton, A.G.; Wang, Y.; Griffiths, W.J. Cerebrospinal fluid steroidomics: Are bioactive bile acids present in brain? J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 4666–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theofilopoulos, S.; Griffiths, W.J.; Crick, P.J.; Yang, S.; Meljon, A.; Ogundare, M.; Kitambi, S.S.; Lockhart, A.; Tuschl, K.; Clayton, P.T.; et al. Cholestenoic acids regulate motor neuron survival via liver X receptors. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4829–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimaki-Mogami, T.; Une, M.; Fujino, T.; Sato, Y.; Tamehiro, N.; Kawahara, Y.; Shudo, K.; Inoue, K. Identification of intermediates in the bile acid synthetic pathway as ligands for the farnesoid X receptor. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 1538–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, B.; Gauthier, K.C.; Umetani, M.; Watson, M.A.; Lochansky, M.I.; Collins, J.L.; Leitersdorf, E.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Kliewer, S.A.; Repa, J.J. Identification of bile acid precursors as endogenous ligands for the nuclear xenobiotic pregnane X receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussault, I.; Yoo, H.D.; Lin, M.; Wang, E.; Fan, M.; Batta, A.K.; Salen, G.; Erickson, S.K.; Forman, B.M. Identification of an endogenous ligand that activates pregnane X receptor-mediated sterol clearance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroosh, P.; Wu, J.; Xue, X.; Song, J.; Sutton, S.W.; Sablad, M.; Yu, J.; Nelen, M.I.; Liu, X.; Castro, G.; et al. Oxysterols are agonist ligands of RORgammat and drive Th17 cell differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12163–12168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuSell, C.D.; Umetani, M.; Shaul, P.W.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; McDonnell, D.P. 27-hydroxycholesterol is an endogenous selective estrogen receptor modulator. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, X.V.; Wu, J.; Kuei, C.; Mani, N.S.; Zhang, L.; Yu, J.; Sutton, S.W.; Qin, N.; Banie, H.; et al. Oxysterols direct B-cell migration through EBI2. Nature 2011, 475, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannedouche, S.; Zhang, J.; Yi, T.; Shen, W.; Nguyen, D.; Pereira, J.P.; Guerini, D.; Baumgarten, B.U.; Roggo, S.; Wen, B.; et al. Oxysterols direct immune cell migration via EBI2. Nature 2011, 475, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, B.R.; Sever, N.; Chong, Y.C.; Kim, J.; Belani, J.D.; Rychnovsky, S.; Bazan, J.F.; Beachy, P.A. Hedgehog pathway modulation by multiple lipid binding sites on the smoothened effector of signal response. Dev. Cell 2013, 26, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raleigh, D.R.; Sever, N.; Choksi, P.K.; Sigg, M.A.; Hines, K.M.; Thompson, B.M.; Elnatan, D.; Jaishankar, P.; Bisignano, P.; Garcia-Gonzalo, F.R.; et al. Cilia-Associated Oxysterols Activate Smoothened. Mol. Cell 2018, 72, 316–327 e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, A.; Ikeda, Y.; Kwon, H.J.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. Sterol-regulated transport of SREBPs from endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi: Oxysterols block transport by binding to Insig. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6511–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorkhem, I. Five decades with oxysterols. Biochimie 2013, 95, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzeletovic, S.; Breuer, O.; Lund, E.; Diczfalusy, U. Determination of cholesterol oxidation products in human plasma by isotope dilution-mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 225, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, W.J.; Sjovall, J. Analytical strategies for characterization of bile acid and oxysterol metabolomes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 396, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heubi, J.E.; Setchell, K.D.; Bove, K.E. Inborn errors of bile acid metabolism. Semin. Liver Dis. 2007, 27, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, P.T. Disorders of bile acid synthesis. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2011, 34, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, F.M.; Ferdinandusse, S. Bile acid analysis in human disorders of bile acid biosynthesis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2017, 56, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quehenberger, O.; Armando, A.M.; Brown, A.H.; Milne, S.B.; Myers, D.S.; Merrill, A.H.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Jones, K.N.; Kelly, S.; Shaner, R.L.; et al. Lipidomics reveals a remarkable diversity of lipids in human plasma. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 3299–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.A.; Heckert, A.; Ulmer, C.Z.; Jones, C.M.; Koelmel, J.P.; Abdullah, L.; Ahonen, L.; Alnouti, Y.; Armando, A.M.; Asara, J.M.; et al. Harmonizing lipidomics: NIST interlaboratory comparison exercise for lipidomics using SRM 1950-Metabolites in Frozen Human Plasma. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 2275–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Sjovall, J.; Griffiths, W.J. Analysis of oxosteroids by nano-electrospray mass spectrometry of their oximes. Rapid. Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2000, 14, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.W.; ten Brink, H.J.; Jakobs, C. A rapid screening procedure for cholesterol and dehydrocholesterol by electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Lipid Res. 2001, 42, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Ory, D.S.; Han, X. Characterization of oxysterols by electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry after one-step derivatization with dimethylglycine. Rapid. Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2007, 21, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, A.; Yamashita, K.; Hara, T.; Ikegami, T.; Miyazaki, T.; Shirai, M.; Xu, G.; Numazawa, M.; Matsuzaki, Y. Highly sensitive quantification of key regulatory oxysterols in biological samples by LC-ESI-MS/MS. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, R.; Jiang, H.; Farhat, N.Y.; Carrillo-Carrasco, N.; Woolery, M.; Ottinger, E.; Porter, F.D.; Schaffer, J.E.; Ory, D.S.; Jiang, X. A validated LC-MS/MS assay for quantification of 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faqehi, A.M.M.; Cobice, D.F.; Naredo, G.; Mak, T.C.S.; Upreti, R.; Gibb, F.W.; Beckett, G.J.; Walker, B.R.; Homer, N.Z.M.; Andrew, R. Derivatization of estrogens enhances specificity and sensitivity of analysis of human plasma and serum by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2016, 151, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.W.; ten Brink, H.J.; Schuit, R.C.; Jakobs, C. Rapid and quantitative analysis of unconjugated C(27) bile acids in plasma and blood samples by tandem mass spectrometry. J. Lipid Res. 2001, 42, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- DeBarber, A.E.; Luo, J.; Giugliani, R.; Souza, C.F.; Chiang, J.P.; Merkens, L.S.; Pappu, A.S.; Steiner, R.D. A useful multi-analyte blood test for cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 47, 860–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Alvelius, G.; Liu, S.; Bodin, K.; Sjovall, J. Analysis of oxysterols by electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2006, 17, 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karu, K.; Hornshaw, M.; Woffendin, G.; Bodin, K.; Hamberg, M.; Alvelius, G.; Sjovall, J.; Turton, J.; Wang, Y.; Griffiths, W.J. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry utilizing multi-stage fragmentation for the identification of oxysterols. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 976–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Zakkar, M.; Karu, K.; Lidington, E.A.; Hamdulay, S.S.; Boyle, J.J.; Zloh, M.; Bauer, A.; Haskard, D.O.; Evans, P.C.; et al. Induction of the cytoprotective enzyme heme oxygenase-1 by statins is enhanced in vascular endothelium exposed to laminar shear stress and impaired by disturbed flow. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 18882–18892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberg-Larsen, H.; Strand, M.F.; Grimsmo, A.; Olsen, P.A.; Dembinski, J.L.; Rise, F.; Lundanes, E.; Greibrokk, T.; Krauss, S.; Wilson, S.R. High sensitivity measurements of active oxysterols with automated filtration/filter backflush-solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1255, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, W.J.; Crick, P.J.; Wang, Y.; Ogundare, M.; Tuschl, K.; Morris, A.A.; Bigger, B.W.; Clayton, P.T.; Wang, Y. Analytical strategies for characterization of oxysterol lipidomes: Liver X receptor ligands in plasma. Free Radic Biol. Med. 2013, 59, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crick, P.J.; William Bentley, T.; Abdel-Khalik, J.; Matthews, I.; Clayton, P.T.; Morris, A.A.; Bigger, B.W.; Zerbinati, C.; Tritapepe, L.; Iuliano, L.; et al. Quantitative charge-tags for sterol and oxysterol analysis. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crick, P.J.; Bentley, T.W.; Wang, Y.; Griffiths, W.J. Revised sample preparation for the analysis of oxysterols by enzyme-assisted derivatisation for sterol analysis (EADSA). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 5235–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soncini, M.; Corna, G.; Moresco, M.; Coltella, N.; Restuccia, U.; Maggioni, D.; Raccosta, L.; Lin, C.Y.; Invernizzi, F.; Crocchiolo, R.; et al. 24-Hydroxycholesterol participates in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6219–E6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Une, M.; Harada, J.; Mikami, T.; Hoshita, T. High-performance liquid chromatographic separation of ultraviolet-absorbing bile alcohol derivatives. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 1996, 682, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, O.H. The Girard Reagents. Chem. Educ. 1968, 45, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, W.J.; Liu, S.; Alvelius, G.; Sjovall, J. Derivatisation for the characterisation of neutral oxosteroids by electrospray and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation tandem mass spectrometry: The Girard P derivative. Rapid. Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2003, 17, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofilopoulos, S.; Wang, Y.; Kitambi, S.S.; Sacchetti, P.; Sousa, K.M.; Bodin, K.; Kirk, J.; Salto, C.; Gustafsson, M.; Toledo, E.M.; et al. Brain endogenous liver X receptor ligands selectively promote midbrain neurogenesis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Khalik, J.; Yutuc, E.; Crick, P.J.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Warner, M.; Roman, G.; Talbot, K.; Gray, E.; Griffiths, W.J.; Turner, M.R.; et al. Defective cholesterol metabolism in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, W.J. Tandem mass spectrometry in the study of fatty acids, bile acids, and steroids. Mass. Spectrom. Rev. 2003, 22, 81–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilarinho, S.; Sari, S.; Mazzacuva, F.; Bilguvar, K.; Esendagli-Yilmaz, G.; Jain, D.; Akyol, G.; Dalgic, B.; Gunel, M.; Clayton, P.T.; et al. ACOX2 deficiency: A disorder of bile acid synthesis with transaminase elevation, liver fibrosis, ataxia, and cognitive impairment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11289–11293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Sidhu, R.; Mydock-McGrane, L.; Hsu, F.F.; Covey, D.F.; Scherrer, D.E.; Earley, B.; Gale, S.E.; Farhat, N.Y.; Porter, F.D.; et al. Development of a bile acid-based newborn screen for Niemann-Pick disease type C. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 337ra63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, N.; Yu, S.; Adams, S.H.; Ronis, M.J.; Badger, T.M. Profiling of urinary bile acids in piglets by a combination of enzymatic deconjugation and targeted LC-MRM-MS. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 1917–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorkhem, I. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2013, 24, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, A.; Salen, G.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Batta, A.K.; Xu, G.; Leitersdorf, E.; Tint, G.S.; Erickson, S.K.; Tanaka, N.; Shefer, S. Side chain hydroxylations in bile acid biosynthesis catalyzed by CYP3A are markedly up-regulated in Cyp27-/- mice but not in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 34579–34585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, A.; Salen, G.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Batta, A.K.; Xu, G.; Leitersdorf, E.; Tint, G.S.; Erickson, S.K.; Tanaka, N.; Shefer, S. Differences in hepatic levels of intermediates in bile acid biosynthesis between Cyp27(-/-) mice and CTX. J. Lipid Res. 2001, 42, 291–300. [Google Scholar]
- Duane, W.C.; Pooler, P.A.; Hamilton, J.N. Bile acid synthesis in man. In vivo activity of the 25-hydroxylation pathway. J. Clin. Investig. 1988, 82, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoda, J.; Axelson, M.; Sjovall, J. Synthesis of potential C27-intermediates in bile acid biosynthesis and their deuterium-labeled analogs. Steroids 1993, 58, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds C-3α,7α,12α-triol, C-3α,7α,12α,25-tetrol, C-3α,7α,12α,26-tetrol, C-3α,7α,12α,24R,25-pentol, C-3α,7α,12α,24S,25-pentol, C-3α,7α,12α,25,26-pentol, C-3α,7α,12α,26,27-pentol and C-3α,7α,12α,23,25-pentol are available from the authors. |














| Ion | Composition | C-triol | [2H7]C-triol | C-tetrol | C-pentol | CA-triol | BA-triol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m/z | m/z | m/z | m/z | m/z | m/z | ||
| [M]+ | [M]+ | 552.4160 | 559.4599 | 568.4109 | 584.4058 | 582.3901 | 540.3432 |
| [M-79]+ | [M-Py]+ | 473.3738 | 480.4177 | 489.3687 | 505.3636 | 503.3479 | 461.3010 |
| [M-79-18]+ | [M-Py-H2O]+ | 455.3632 | 462.4071 | 471.3581 | 487.3530 | 485.3373 | 443.2904 |
| [M-79-28]+ | [M-Py-CO]+ | 445.3789 | 452.4228 | 461.3738 | 477.3687 | 475.3530 | 433.3061 |
| [M-79-36]+ | [M-Py-(H2O)2]+ | 437.3526 | 444.3965 | 453.3475 | 469.3424 | 467.3267 | 425.2798 |
| [M-79-28-18]+ | [M-Py-CO-H2O]+ | 427.3683 | 434.4122 | 443.3632 | 459.3581 | 457.3424 | 415.2955 |
| [M-79-36-18]+ | [M-Py-(H2O)3]+ | 419.3421 | 426.3860 | 435.3370 | 451.3319 | 449.3162 | 407.2693 |
| [M-79-28-18-15]+ | [M-Py-CO-H2O-NH]+ | 412.3574 | 419.4013 | 428.3523 | 444.3472 | 442.3315 | 400.2846 |
| [M-79-28-18-17]+ | [M-Py-CO-H2O-NH3]+ | 410.3417 | 417.3856 | 426.3366 | 442.3315 | 440.3158 | 398.2689 |
| [M-79-28-36]+ | [M-Py-CO-(H2O)2]+ | 409.3577 | 416.4016 | 425.3526 | 441.3475 | 439.3318 | 397.2849 |
| [M-79-36-36]+ | [M-Py-(H2O)4]+ | 401.3315 | 408.3754 | 417.3264 | 433.3213 | 431.3056 | 389.2587 |
| [M-79-28-15-31]+ | [M-Py-CO-NH-CH2NH3]+ | 399.3258 | 406.3697 | 415.3207 | 431.3156 | 429.2999 | 387.2530 |
| [M-79-36-36-2]+ | [M-Py-(H2O)4-H2]+ | 399.3159 | 406.3598 | 415.3108 | 431.3057 | 429.2900 | 387.2431 |
| [M-79-28-36-15]+ | [M-Py-CO-(H2O)2-NH]+ | 394.3468 | 401.3907 | 410.3417 | 426.3366 | 424.3209 | 382.2740 |
| [M-79-28-36-17]+ | [M-Py-CO-(H2O)2-NH3]+ | 392.3312 | 399.3751 | 408.3261 | 424.3210 | 422.3053 | 380.2584 |
| [M-79-28-36-18]+ | [M-Py-CO-(H2O)3]+ | 391.3472 | 398.3911 | 407.3421 | 423.3370 | 421.3213 | 379.2744 |
| [M-79-28-18-15-31]+ | [M-Py-CO-H2O-NH-CH2NH3]+ | 381.3152 | 388.3591 | 397.3101 | 413.3050 | 411.2893 | 369.2424 |
| [M-79-36-36-18-2]+ | [M-Py-(H2O)5-H2]+ | 381.3053 | 388.3492 | 397.3002 | 413.2951 | 411.2794 | 369.2325 |
| [M-79-28-36-15-18+2]+ | [M-Py-CO-(H2O)3-NH+H2]+ | 378.3519 | 385.3958 | 394.3468 | 410.3417 | 408.3260 | 366.2791 |
| [M-79-28-36-15-18]+ | [M-Py-CO-(H2O)3-NH]+ | 376.3363 | 383.3802 | 392.3312 | 408.3261 | 406.3104 | 364.2635 |
| [M-79-28-36-17-18]+ | [M-Py-CO-(H2O)3-NH3]+ | 374.3206 | 381.3645 | 390.3155 | 406.3104 | 404.2947 | 362.2478 |
| [M-79-28-36-15-31]+ | [M-Py-CO-(H2O)2-NH-CH2NH3]+ | 363.3046 | 370.3485 | 379.2995 | 395.2944 | 393.2787 | 351.2318 |
| [M-79-28-36-15-36+2]+ | [M-Py-CO-(H2O)4-NH+H2]+ | 360.3414 | 367.3853 | 376.3363 | 392.3312 | 390.3155 | 348.2686 |
| [M-79-28-36-15-31-18]+ | [M-Py-CO-(H2O)3-NH-CH2NH3]+ | 345.2941 | 352.3380 | 361.2890 | 377.2839 | 375.2682 | 333.2213 |
| M-79-28-36-15-31-36]+ | [M-Py-CO-(H2O)4-NH-CH2NH3]+ | 327.2835 | 334.3274 | 343.2784 | 359.2733 | 357.2576 | 315.2107 |
| [A3+H-36]+ | [A3+H-(H2O)2]+ | 313.2890 | 320.3329 | 329.2839 | 345.2788 | 343.2631 | 301.2162 |
| [A3-H-36]+ | [A3-H-(H2O)2]+ | 311.2733 | 318.3172 | 327.2682 | 343.2631 | 341.2474 | 299.2005 |
| [A3-H-36-18]+ | [A3-H-(H2O)3]+ | 293.2628 | 300.3067 | 309.2577 | 325.2526 | 323.2369 | 281.1900 |
| [A3-H-26]+ | 285.2577 | 292.3016 | 301.2526 | 317.2475 | 315.2318 | 273.1849 | |
| [A3-H-36-36]+ | [A3-H-(H2O)4]+ | 275.2522 | 282.2961 | 291.2471 | 307.2420 | 305.2263 | 263.1794 |
| [ABCD-Δx5-H]+ | 249.1638 | 249.1638 | 249.1638 | 249.1638 | 249.1638 | 249.1638 | |
| [ABC-Δx5-H]+ | 209.1325 | 209.1325 | 209.1325 | 209.1325 | 209.1325 | 209.1325 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdel-Khalik, J.; Crick, P.J.; Yutuc, E.; Wang, Y.; Griffiths, W.J. Developing an Enzyme-Assisted Derivatization Method for Analysis of C27 Bile Alcohols and Acids by Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2019, 24, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030597
Abdel-Khalik J, Crick PJ, Yutuc E, Wang Y, Griffiths WJ. Developing an Enzyme-Assisted Derivatization Method for Analysis of C27 Bile Alcohols and Acids by Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry. Molecules. 2019; 24(3):597. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030597
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdel-Khalik, Jonas, Peter J. Crick, Eylan Yutuc, Yuqin Wang, and William J. Griffiths. 2019. "Developing an Enzyme-Assisted Derivatization Method for Analysis of C27 Bile Alcohols and Acids by Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry" Molecules 24, no. 3: 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030597
APA StyleAbdel-Khalik, J., Crick, P. J., Yutuc, E., Wang, Y., & Griffiths, W. J. (2019). Developing an Enzyme-Assisted Derivatization Method for Analysis of C27 Bile Alcohols and Acids by Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry. Molecules, 24(3), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030597