All Solid-State Poly (Vinyl Chloride) Membrane Potentiometric Sensor Integrated with Nano-Beads Imprinted Polymers for Sensitive and Rapid Detection of Bispyribac Herbicide as Organic Pollutant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
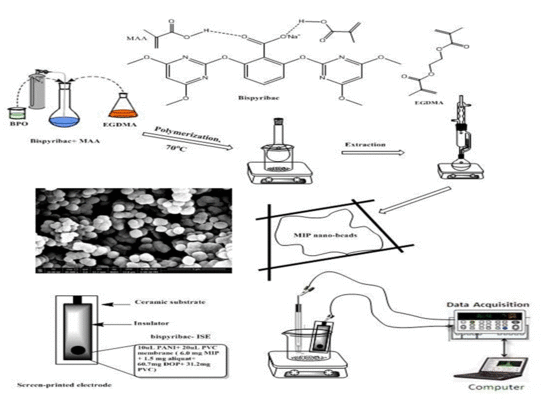
2.1. Characterization of MIP Particles
2.2. Characteristics of the Proposed Sensors
2.3. Potential Stability
2.4. Electrochemical Impedance Spectrometry
2.5. Selectivity
2.6. Analytical Applications and Sample Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. MIPs Synthesis
3.3. Sensors Preparation and EMF Measurements
3.4. Adsorption Isotherm
3.5. Applications to Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; Asensio-Ramos, M.; Herna’ndez-Borges, J.; Rodrıguez-Delgado, M.A. Pesticides and herbicides: Types, uses, and determination of herbicides. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Finglas, P.M., Toldrá, F., Eds.; Academic: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 326–332. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, A.J.; Ateh, C.M.; Bayer, D.E.; Hill, J.E. Herbicide-resistant Echinochloaoryzoides and E. phyllopogon in California Oryza sativa fields. Weed Sci. 2000, 48, 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, A.J.; Bayer, D.E.; Carriere, M.D. Mechanisms of resistance to bispyribac-sodium in an Echinochloaphyllopogon accession. Pesticide Biochem. Physiol. 2000, 68, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.W. Re-evaluating the role of herbicides in contemporary urban horticulture. Acta Hortic. 1997, 496, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barceló, D.; Hennion, M.C. Trace Determination of Pesticides and Their Degradation Products in Water, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kuster, M.; Alda, M.L.; Barceló, D. Analysis of pesticides in water by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric techniques. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2006, 25, 900–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamilselvan, C.; Joseph, S.J.; Angayarkanni, V. Determination of bispyribac sodium 10% SC (herbicide) residue level in straw, grain and soil using HPLC method. Int. Lett. Nat. Sci. 2014, 12, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Roy, S.; Das, T.K.; Bhattacharyya, A. Dissipation kinetics of a new mixture formulation of bispyribac-sodium and metamifop in rice. J. Crop Weed 2016, 12, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Mei, J. Analysis of the herbicide bispyribac-sodium in rice by slid phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 86, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurz, M.H.S.; Gonçalves, F.F.; Martel, S. Rapid and accurate HPLC-DAD method for the determination of the herbicide bispyribac-sodium in surface water, and its validation. Química Nova 2009, 32, 1457–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramprakash, T.; Madhavi, M.; Yakadri, M.; Srinivas, A. Bispyribac sodium persistence in soil, plant and grain in direct seeded rice and its effect on soil properties. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2015, 14, 605–609. [Google Scholar]
- Parej, L.; Cesio, V.; Heinzen, H.; Fernandez-Alb, A.R. Evaluation of various QuEChERS based methods for the analysis of herbicides and other commonly used pesticides in polished rice by LC-MS/MS. Talanta 2011, 83, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, S.; Bai, A.; Pan, C. Dissipation and residues of bispyribac-sodium in rice and environment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 9743–9749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niell, S.; Pareja, L.; Asteggiante, L.G.; Roehrs, R.; Pizzutti, I.R.; Garcia, C.; Heinzen, H.; Cesio, M.V. Development of methods for multiresidue analysis of rice post-emergence herbicides in loam soil and their possible applications to soils of different composition. J. AOAC Int. 2010, 93, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kamel, A.H.; Galal, H.R.; Awwad, N.S. Cost-effective and handmade paper-based potentiometric sensing platform for piperidine determination. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 5406–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, G.A. Recent advances in ion-selective membrane electrodes for in situ environmental water analysis. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 245, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuartero, M.; Crespo, G.A. All-solid-state potentiometric sensors: A new wave for in situ aquatic research. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2018, 10, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.H.; El-Naggar, A.M.; Argig, A.A.A. Response characteristics of lead-selective membrane sensors based on a newly synthesized quinoxaline derivatives as neutral carrier ionophores. Ionics 2017, 23, 3497–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kosasy, A.M.; Kamel, A.H.; Hussin, L.A.; Ayad, M.F.; Fares, N.V. Mimicking new receptors based on molecular imprinting and their application to potentiometric assessment of 2,4-dichlorophenol as a food Taint. Food Chem. 2018, 250, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, A.H.; Hassan, A.M.E. Solid contact potentiometric sensors based on host-tailored molecularly imprinted polymers for creatine assessment. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 8938–8949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liang, R.; Yang, X.; Qin, W. Imprinted nanobead-based disposable screen-printed potentiometric sensor for highly sensitive detection of 2-naphthoic acid. Mater. Lett. 2018, 225, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.H.; Jiang, X.; Li, P.; Liang, R. A paper-based potentiometric sensing platform based on molecularly imprinted nanobeads for determination of bisphenol A. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 3890–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinova, N.; Chumbimuni-Torres, K.Y.; Bakker, E. Solid-contact potentiometric polymer membrane microelectrodes for the detection of silver ions at the femtomole level. Sens. Actuators B 2007, 121, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindner, E.; Gyurcsányi, R.J. Quality control criteria for solid-contact, solvent polymeric membrane ion-selective electrodes. Solid State Electrochem. 2009, 13, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutter, J.; Radu, A.; Peper, S.; Bakker, E.; Pretsch, E. Solid-contact polymeric membrane electrodes with detection limits in the subnanomolar range. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 523, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.N.; Song, D.A.; Zhang, R.M.; Qin, W. Potentiometric sensing of neutral species based on a uniform-sized molecularly imprinted polymer as a receptor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 2556–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobacka, J. Potential stability of all-solid-state ion-selective electrodes using conducting polymers as ion-to-electron transducers. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 4932–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvai, G.; Graf, E.; Toth, K.; Pungor, E.; Buck, R.P. Plasticized poly(vinyl chloride) properties and characteristics of valinomycin electrodes. 1. High-frequency resistances and dielectric properties. Anal. Chem. 1986, 58, 2735–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobacka, J.; McCarrick, M.; Lewenstam, A.; Ivaska, A. All-solid-state poly(vinyl chloride) membrane ion–selective electrodes with poly(3-octylthiophene) solid internal contact. Analyst 1994, 119, 1985–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E. Determination of improved selectivity coefficients of polymer membrane ion-selective electrodes by conditioning with a discriminated ion. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, L83–L85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Anwar, F.S.; Firdous, S.; Da-Chuan, Y.; Iqbal, S. Biodegradation of bispyribac sodium by a novel bacterial consortium BDAM: Optimization of degradation conditions using response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mat. 2018, 349, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaata, S.; Bhale, A.; Fukunaga, Y.; Murata, H. Copper(II)-selective electrode using thiuram disulfide neutral carriers. Anal. Chem. 1988, 60, 2464–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |







| Interfering Ion | * Log Kpotx,y | |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor I | Sensor II | |
| Diquate | −5.05 ± 0.2 | −5.04 ± 0.5 |
| Acetampirid | −4.73 ± 0.4 | −4.63 ± 0.2 |
| Dinotefuran | −5.17 ± 0.5 | −3.12 ± 0.3 |
| Imidachloprid | −5.32 ± 0.3 | −5.98 ± 0.8 |
| Cyromazine | −5.32 ± 0.7 | −5.35 ± 0.1 |
| Flucarbazone | −2.51 ± 0.1 | −0.24 ± 0.05 |
| Cl− | −5.05 ± 0.4 | −4.75 ± 0.5 |
| Br− | −5.15 ± 0.2 | −2.97 ± 0.4 |
| SO42− | −5.57 ± 0.3 | −5.08 ± 0.3 |
| CH3COO− | −3.96 ± 0.2 | −4.21 ± 0.1 |
| NO3− | −4.25 ± 0.6 | −3.06 ± 0.2 |
| Commercial Product | Label (w/v %) | a Found | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potentiometry | RSD, % | HPLC [28] | RSD, % | ||
| Nomenee-kz, Kafr El-Zayat Pesticides& Chemicals Company (Gharbia, Egypt) | 3 | 2.97 ± 0.02 | 99.0 | 2.99 ± 0.05 | 99.6 |
| Sample | Amount of Bispyribac (µg/g) | |
|---|---|---|
| Potentiometry | HPLC [28] a | |
| Sample 1 | 8.8 ± 0.9 | 9.2 ± 0.2 |
| Sample 2 | 10.4 ± 0.4 | 9.7 ± 0.1 |
| Sample 3 | 14.3 ± 0.7 | 13.1 ± 0.3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdalla, N.S.; Youssef, M.A.; Algarni, H.; Awwad, N.S.; Kamel, A.H. All Solid-State Poly (Vinyl Chloride) Membrane Potentiometric Sensor Integrated with Nano-Beads Imprinted Polymers for Sensitive and Rapid Detection of Bispyribac Herbicide as Organic Pollutant. Molecules 2019, 24, 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040712
Abdalla NS, Youssef MA, Algarni H, Awwad NS, Kamel AH. All Solid-State Poly (Vinyl Chloride) Membrane Potentiometric Sensor Integrated with Nano-Beads Imprinted Polymers for Sensitive and Rapid Detection of Bispyribac Herbicide as Organic Pollutant. Molecules. 2019; 24(4):712. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040712
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdalla, Nashwa S., Maha A. Youssef, H. Algarni, Nasser S. Awwad, and Ayman H. Kamel. 2019. "All Solid-State Poly (Vinyl Chloride) Membrane Potentiometric Sensor Integrated with Nano-Beads Imprinted Polymers for Sensitive and Rapid Detection of Bispyribac Herbicide as Organic Pollutant" Molecules 24, no. 4: 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040712
APA StyleAbdalla, N. S., Youssef, M. A., Algarni, H., Awwad, N. S., & Kamel, A. H. (2019). All Solid-State Poly (Vinyl Chloride) Membrane Potentiometric Sensor Integrated with Nano-Beads Imprinted Polymers for Sensitive and Rapid Detection of Bispyribac Herbicide as Organic Pollutant. Molecules, 24(4), 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040712