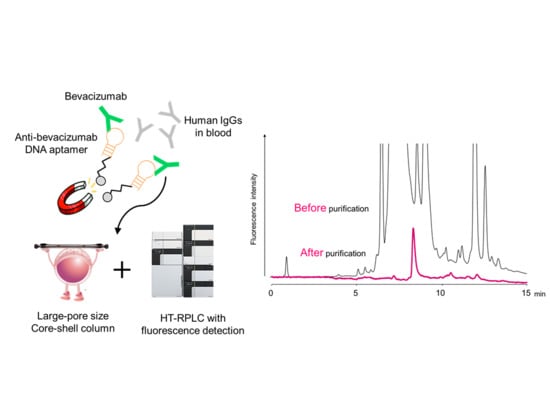
Anti-Idiotype DNA Aptamer Affinity Purification–High-Temperature Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography: A Simple, Accurate, and Selective Bioanalysis of Bevacizumab
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. HT-RPLC Separation of Bevacizumab
2.2. Selection of Affinity Support the Aptamer Affinity Magnetic Beads
2.3. Evaluation of Aptamer Affinity Purification
2.4. Method Validation
2.5. Determination of Bevacizumab in the Plasma Samples from Patients with Cancer
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents, Solutions, and Apparatus
3.2. Preparation of Aptamer Affinity Magnetic Beads Immobilized Anti-Bevacizumab DNA Aptamer
3.3. Evaluation of Aptamer Immobilization Amount on Three Different Magnetic Beads
3.4. Isolation of Bevacizumab from Plasma Samples Using Aptamer Affinity Magnetic Beads
3.5. HT-RPLC System and Conditions
3.6. Preparation of Stock Solutions, Calibration Standards, and Quality Control Samples
3.7. Method Validation
3.7.1. Precision
3.7.2. Accuracy
3.7.3. Calibration Curve
3.7.4. Recovery
3.8. Plasma Sample Collection from Patients with Cancer Treated with Bevacizumab
3.9. Immunoaffinity Purification using RT-HPLC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Urquhart, L. Market watch: Top drugs and companies by sales in 2017. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliwkowski, M.X.; Mellman, I. Antibody therapeutics in cancer. Science 2013, 341, 1192–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, L.M.; Surana, R.; Wang, S. Monoclonal antibodies: Versatile platforms for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbers, H.C.; van Meer, P.J.; Moors, E.H.M.; Mantel-Teeuwisse, A.K.; Leufkens, H.G.M.; Schellekens., H. Measures of biosimilarity in monoclonal antibodies in oncology: The case of bevacizumab. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rugo, H.S.; Linton, K.M.; Cervi, P.; Rosenberg, J.A.; Jacobs, I. A clinician’s guide to biosimilars in oncology. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2016, 46, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Den Broek, I.; Niessen, W.M.; van Dongen, W.D. Bioanalytical LC–MS/MS of protein-based biopharmaceuticals. J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 929, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todoroki, K.; Yamada, T.; Mizuno, H.; Toyo’oka, T. Current Mass Spectrometric Tools for the Bioanalyses of Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies and Antibody-Drug Conjugates. Anal. Sci. 2018, 34, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heudi, O.; Barteau, S.; Zimmer, D.; Schmidt, J.; Bill, K.; Lehmann, N.; Bauer, C.; Kretz, O. Towards absolute quantification of therapeutic monoclonal antibody in serum by LC−MS/MS using isotope-labeled antibody standard and protein cleavage isotope dilution mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 4200–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewles, M.; Mannu, R.; Fox, C.; Stanta, J.; Evans, G.; Goodwin, L.; Duffy, J.; Bell, L.; Estdale, S.; Firth, D. LC–MS/MS strategies for therapeutic antibodies and investigation into the quantitative impact of antidrug-antibodies. Bioanalysis 2016, 8, 2565–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legeron, R.; Xuereb, F.; Chaignepain, S.; Gadeau, A.P.; Claverol, S.; Dupuy, J.W.; Djabarouti, S.; Couffinhal, T.; Schmitter, J.M.; Breilh, D. A new reliable, transposable and cost-effective assay for absolute quantification of total plasmatic bevacizumab by LC–MS/MS in human plasma comparing two internal standard calibration approaches. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1070, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, N.; Shimada, T.; Umino, Y.; Aoki, C.; Aoki, Y.; Sato, T.A.; Hamada, A.; Nakagama, H. Selective detection of complementarity-determining regions of monoclonal antibody by limiting protease access to the substrate: Nano-surface and molecular-orientation limited proteolysis. Analyst 2014, 139, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, N.; Umino, Y.; Aoki, C.; Yamane, N.; Hamada, A.; Shimada, T. Fully validated LCMS bioanalysis of Bevacizumab in human plasma using nano-surface and molecular-orientation limited (nSMOL) proteolysis. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2016, 31, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Liu, L.; Saad, O.M.; Baudys, J.; Williams, L.; Leipold, D.; Shen, B.; Raab, H.; Junutula, J.R.; Kim, A.; et al. Characterization of intact antibody–drug conjugates from plasma/serum in vivo by affinity capture capillary liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 412, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, D.; Ng, C.; Khosraviani, M.; Yu, S.F.; Cosino, E.; Kaur, S.; Xu, K. Custom-designed affinity capture LC-MS F (ab’) 2 assay for biotransformation assessment of site-specific antibody drug conjugates. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 11340–11346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, J.R.; Cornec, D.; Dasari, S.; Ladwig, P.M.; Hummel, A.M.; Cheu, M.; Murray, D.L.; Willrich, M.A.; Snyder, M.R.; Hoffman, G.S.; et al. Using mass spectrometry to quantify rituximab and perform individualized immunoglobulin phenotyping in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6317–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todoroki, K.; Nakano, T.; Eda, Y.; Ohyama, K.; Hayashi, H.; Tsuji, D.; Min, J.Z.; Inoue, K.; Iwamoto, N.; Kawakami, A.; et al. Bioanalysis of bevacizumab and infliximab by high-temperature reversed-phase liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection after immunoaffinity magnetic purification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 916, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Hayes, M.; Fang, X.; Daley, M.P.; Ettenberg, S.; Tse, F.L. LC-MS/MS approach for quantification of therapeutic proteins in plasma using a protein internal standard and 2D-solid-phase extraction cleanup. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 9294–9301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casteele, N.V.; Buurman, D.J.; Sturkenboom, M.G.G.; Kleibeuker, J.H.; Vermeire, S.; Rispens, T.; van der Kleij, D.; Gils, A.; Dijkstra, G. Detection of infliximab levels and anti-infliximab antibodies: A comparison of three different assays. Aliment. Pharm. Ther. 2012, 36, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klussmann, S. The aptamer Handbook: Functional Oligonucleotides and their Applications; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kiel, J.L.; Kiel, A.L. Fundamental Performance Differences between Antibodies and Aptamers. In Biomedical Applications of Aptamers; Bruno, J.G., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Perret, G.; Boschetti, E. Aptamer affinity ligands in protein chromatography. Biochimie 2018, 145, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forier, C.; Boschetti, E.; Ouhammouch, M.; Cibiel, A.; Ducongé, F.; Nogré, M.; Tellier, M.; Bataille, D.; Bihoreau, N.; Santambien, P.; et al. DNA aptamer affinity ligands for highly selective purification of human plasma-related proteins from multiple sources. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1489, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikebukuro, K.; Saito, T.; Todoroki, K.; Nakano, T.; Toyo’oka, T. Detection method of aptamer and antibody. Japan patent P2018-027024A, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, T.; Saito, T.; Hill, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Tsukakoshi, K.; Mizuno, H.; Hayashi, H.; Ikebukuro, K.; Toyo’oka, T.; Todoroki, K. High-throughput bioanalysis of bevacizumab in human plasma based on enzyme-linked aptamer assay using anti-idiotype DNA aptamer. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3125–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillon, T.M.; Bondarenko, P.V.; Ricci, M.S. Development of an analytical reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography-electro spray ionization mass spectrometry method for characterization of recombinant antibodies. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1053, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Mizuno, H.; Min, J.Z.; Toyo’oka, T.; Todoroki, K. High Sensitivity and Precision High-Temperature Reversed-Phase LC Analysis of Bevacizumab for Intact Bioanalysis of Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies. Chromatography 2018, 39, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergsland, E.; Dickler, M.N. Maximizing the potential of bevacizumab in cancer treatment. Oncologist 2004, 9, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Department of Health and Human Services; Food and Drug Administration; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research; Center for Veterinary Medicine. Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical Method Validation; Rockville, MD, USA. 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/Guidances/ucm070107.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2019).
Sample Availability: Not available. |





| Spiked Concentration (μg/mL) | Precision (%) | Accuracy (Bias, %) | Recovery (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-Day | Inter-Day | |||
| 1 | 5.5 | 6.2 | 14.2 | 99.9 |
| 5 | 3.4 | 3.2 | 4.0 | 100.3 |
| 10 | 2.3 | 3.0 | −2.9 | 101.4 |
| 20 | 3.2 | 3.1 | −3.6 | 100.3 |
| 30 | 2.4 | 3.5 | −0.9 | 99.3 |
| 40 | 2.5 | 3.4 | −2.2 | 96.7 |
| 50 | 2.5 | 3.9 | −4.9 | 95.4 |
| Number | Age | Height (cm) | Weight (kg) | Disease Status | Date of Administration and Blood Collection | Bevacizumab Concentration (μg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Present Method | Immunoaffinity Purification–HT-RPLC [16] | ||||||
| 1 | 58 | 166.0 | 70.1 | IV | 17/05/09 17/05/27 | 174.4 | 188.4 |
| 2 | 69 | 162.9 | 74.5 | IV | 17/03/14 17/04/04 | 205.1 | 202.2 |
| 3 | 65 | 174.6 | 66.5 | IIB | 17/05/09 17/06/01 | 172.9 | 171.1 |
| 4 | 55 | 173.0 | 71.2 | IV | 17/05/30 17/06/20 | 312.7 | 324.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamada, T.; Saito, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Tsukakoshi, K.; Hayashi, H.; Mizuno, H.; Tsuji, D.; Yamamoto, K.; Itoh, K.; Toyo’oka, T.; et al. Anti-Idiotype DNA Aptamer Affinity Purification–High-Temperature Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography: A Simple, Accurate, and Selective Bioanalysis of Bevacizumab. Molecules 2019, 24, 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050857
Yamada T, Saito T, Shimizu Y, Tsukakoshi K, Hayashi H, Mizuno H, Tsuji D, Yamamoto K, Itoh K, Toyo’oka T, et al. Anti-Idiotype DNA Aptamer Affinity Purification–High-Temperature Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography: A Simple, Accurate, and Selective Bioanalysis of Bevacizumab. Molecules. 2019; 24(5):857. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050857
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamada, Tomohiro, Taro Saito, Yutaka Shimizu, Kaori Tsukakoshi, Hideki Hayashi, Hajime Mizuno, Daiki Tsuji, Keisuke Yamamoto, Kunihiko Itoh, Toshimasa Toyo’oka, and et al. 2019. "Anti-Idiotype DNA Aptamer Affinity Purification–High-Temperature Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography: A Simple, Accurate, and Selective Bioanalysis of Bevacizumab" Molecules 24, no. 5: 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050857
APA StyleYamada, T., Saito, T., Shimizu, Y., Tsukakoshi, K., Hayashi, H., Mizuno, H., Tsuji, D., Yamamoto, K., Itoh, K., Toyo’oka, T., Ikebukuro, K., & Todoroki, K. (2019). Anti-Idiotype DNA Aptamer Affinity Purification–High-Temperature Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography: A Simple, Accurate, and Selective Bioanalysis of Bevacizumab. Molecules, 24(5), 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050857