Extraction of Acids and Bases from Aqueous Phase to a Pseudoprotic Ionic Liquid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
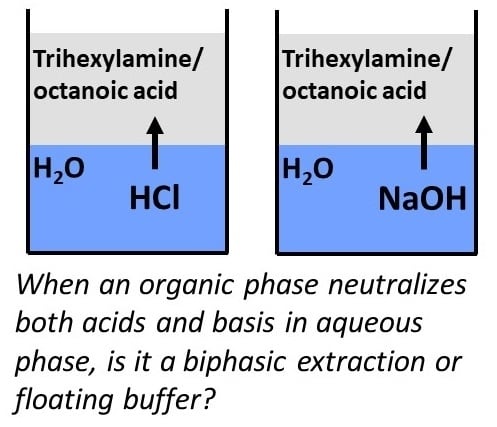
2.1. Extraction of Acids and Bases from Water
2.2. Mechanism of Extraction
2.3. Role of the Hofmeister Effect
2.4. Comparison to Other Acid Extraction Systems
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Methodology for Extraction Experiments
3.2. Methodology for Mechanism Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greaves, T.L.; Drummond, C.J. Protic ionic liquids: Evolving structure–property relationships and expanding applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11379–11448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greaves, T.L.; Drummond, C.J. Protic ionic liquids: Properties and applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 206–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Luo, H.; Jiang, D.; Li, H.; Dai, S. Carbon dioxide capture by superbase-derived protic ionic liquids. Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 6114–6117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Huang, J.-F.; Dai, S. Solvent extraction of Sr2+ and Cs+ using protic amide-based ionic liquids. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 1679–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuara-Diaz, E.; Brisard, G.; Trejo, G.; Meas, Y.; Ortega-Borges, R. Nickel Electrodeposition from protic ionic liquids based on carboxylate anions as electrolyte: I. Electrodeposition from 2-hydroxyethyl ammonium formate. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 12856–12869. [Google Scholar]
- Lü, H.; Wang, S.; Deng, C.; Ren, W.; Guo, B. Oxidative desulfurization of model diesel via dual activation by a protic ionic liquid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 279, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshizawa, M.; Xu, W.; Angell, C.A. Ionic liquids by proton transfer: Vapor pressure, conductivity, and the relevance of ΔpKa from aqueous solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 15411–15419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanzaki, R.; Doi, H.; Song, X.; Hara, S.; Ishiguro, S.I.; Umebayashi, Y. Acid-base property of N-methylimidazolium-based protic ionic liquids depending on anion. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 14146–14152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, H.; Song, X.; Minofar, B.; Kanzaki, R.; Takamuku, T.; Umebayashi, Y. A new proton conductive liquid with no ions: Pseudo-protic ionic liquids. Chem. A Eur. J. 2013, 19, 11522–11526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazet, A.; Buchner, R. Dielectric response and transport properties of alkylammonium formate ionic liquids. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 193836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Janssen, C.H.C.; Macías-Ruvalcaba, N.A.; Aguilar-Martínez, M.; Kobrak, M.N. Copper extraction using protic ionic liquids: Evidence of the Hofmeister effect. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 168, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobrak, M.N.; Yager, K.G. X-Ray scattering and physicochemical studies of trialkylamine/carboxylic acid mixtures: Nanoscale structure in pseudoprotic ionic liquids and related solutions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 18539–18646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, F.; Atrops, H.; Kalali, H.; Liebermann, E.; Wilhelm, E.; Ratkovics, F.; Salamon, T. Molecular interactions in mixtures of carboxylic acids with amines. 1. Melting curves and viscosities. J. Phys. Chem. 1981, 85, 2520–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, F.; Gopal, R.; Goetze, G.; Atrops, H.; Demeriz, M.A.; Liebermann, E.; Wilhelm, E.; Ratkovics, F.; Palagyi, B. Molecular interactions in mixtures of carboxylic acids with amines. 2. Volumetric, conductimetric, and NMR properties. J. Phys. Chem. 1981, 85, 2524–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, F.; Liebermann, E.; Miksch, G.; Kainz, C. Thermodynamics of the acetic acid-triethylamine system. J. Phys. Chem. 1972, 76, 2764–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salis, A.; Ninham, B.W. Models and mechanisms of Hofmeister effects in electrolyte solutions, and colloid and protein systems revisited. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7358–7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grinstead, R.R.; Davis, J.C. Base strengths of amine-amine hydrochloride systems in toluene. J. Phys. Chem. 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertocci, U.; Rolandi, G. Equilibria between tri-n-octylamine and some mineral acids. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1961, 23, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jeon, H.S.; Lee, M.S. Extraction of hydrochloric acid with binary mixtures of tertiary amine and organophosphorus acid and analysis of the interaction between the constituents of these mixtures. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 155, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, F.L. Long-chain amines: Versatile acid extractants. Anal. Chem. 1957, 29, 1660–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyal, A.; Baniel, A. Extraction of strong mineral acids by organic acid-base couples. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 1982, 21, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyal, A.M. Acid extraction by acid-base-coupled extractants. In Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange; Marinsky, J.A., Marcus, Y., Eds.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 13, pp. 31–93. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, E.; González-Pérez, A.; Ruso, J.M.; Pedrido, R.; Prieto, G.; Sarmiento, F. A comparative study of the physicochemical properties of perfluorinated and hydrogenated amphiphiles. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2005, 288, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietz, M.L.; Dzielawa, J.A.; Laszak, I.; Young, B.A.; Jensen, M.P. Influence of solvent structural variations on the mechanism of facilitated ion transfer into room-temperature ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2003, 5, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, C.A.; Garvey, S.L.; Dietz, M.L. Structural variations in room-temperature ionic liquids: Influence on metal ion partitioning modes and extraction selectivity. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 89, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, J.A. Lange’s Handbook of Chemistry, 15th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Romsted, L.S. Introduction to Surfactant Self-Assembly. In Supramolecular Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2012; ISBN 9780470661345. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, R.L. How Hofmeister ion interactions affect protein stability. Biophys. J. 1996, 71, 2056–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, J.M.; Diaz, A.R.; Fortin, D.T.; Friedle, J.M.; Piper, S.D. Influence of the Hofmeister series on the retention of amines in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 4927–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available. |


| Acid | Base |
|---|---|
| HBr | KOH |
| HCl | NaOH |
| HClO4 | |
| HI | |
| HNO3 |
| Acid | Initial Aqueous pH | Final Aqueous pH | Dacid |
|---|---|---|---|
| HClO4 | 1.0 | 6.2 | 1.6 × 105 |
| HNO3 | 1.2 | 5.4 | 1.5 × 104 |
| HBr | 1.3 | 5.0 | 5.3 × 103 |
| HCl | 1.2 | 4.7 | 3.2 × 103 |
| HClO4 | 2.0 | 6.2 | 1.9 × 104 |
| HI | 2.2 | 6.2 | 1.1 × 104 |
| HNO3 | 2.2 | 5.9 | 6.0 × 103 |
| HBr | 2.2 | 5.8 | 4.2 × 103 |
| HCl | 2.1 | 5.5 | 2.4 × 103 |
| Organic Phase | Final Aqueous [Na+(aq)] (M) | [OH−(aq)] (M) |
|---|---|---|
| Trihexylamine | 1.18 +/− 0.01 | 1.1 |
| Octanoic Acid | 0.0893 +/− 0.001 | 5.0 × 10−8 |
| T6A OA | 0.76 +/− 0.01 | 2.5 × 10−6 |
| Organic Phase | Final Aqueous [Cl−(aq)] (M) | [H+(aq)] (M) |
|---|---|---|
| Trihexylamine | 1.09 × 10−4 +/− 1 × 10−6 | 4.9 × 10−5 |
| Octanoic Acid | 1.0 +/− 0.1 | 1.0 |
| T6A OA | 0.056 +/− 0.001 | 6.5 × 10−5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patsos, N.; Lewis, K.; Picchioni, F.; Kobrak, M.N. Extraction of Acids and Bases from Aqueous Phase to a Pseudoprotic Ionic Liquid. Molecules 2019, 24, 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050894
Patsos N, Lewis K, Picchioni F, Kobrak MN. Extraction of Acids and Bases from Aqueous Phase to a Pseudoprotic Ionic Liquid. Molecules. 2019; 24(5):894. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050894
Chicago/Turabian StylePatsos, Nikolas, Karin Lewis, Francesco Picchioni, and Mark N. Kobrak. 2019. "Extraction of Acids and Bases from Aqueous Phase to a Pseudoprotic Ionic Liquid" Molecules 24, no. 5: 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050894
APA StylePatsos, N., Lewis, K., Picchioni, F., & Kobrak, M. N. (2019). Extraction of Acids and Bases from Aqueous Phase to a Pseudoprotic Ionic Liquid. Molecules, 24(5), 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050894