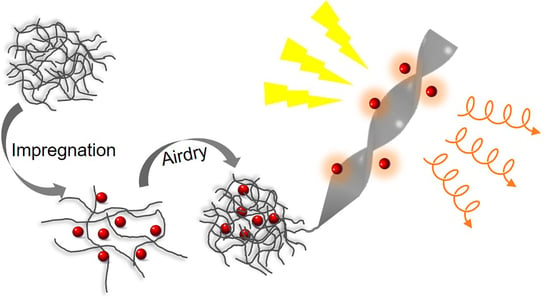
Bacterial Cellulose: A Versatile Chiral Host for Circularly Polarized Luminescence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Bacterial Cellulose-Luminophore Composited Films Exhibited CPL Property
2.2. CPL Property Effected by Film Thickness and Loading Amount
2.3. Structural Anisotropy in BC
2.4. The Universality of the Method
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of BC
3.3. Preparation of BCNC
3.4. Preparation of BC-X Composite Films
3.5. Preparation of BC-RhB-m Composite Films
3.6. Preparation of BC-RhB-n Composite Films
3.7. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuzyk, A.; Schreiber, R.; Fan, Z.; Pardatscher, G.; Roller, E.M.; Hogele, A.; Simmel, F.C.; Govorov, A.O.; Liedl, T. DNA-based self-assembly of chiral plasmonic nanostructures with tailored optical response. Nature 2012, 483, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerrero-Martinez, A.; Auguie, B.; Alonso-Gomez, J.L.; Dzolic, Z.; Gomez-Grana, S.; Zinic, M.; Cid, M.M.; Liz-Marzan, L.M. Intense optical activity from three-dimensional chiral ordering of plasmonic nanoantennas. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5499–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Han, L.; Duan, Y.; Asahina, S.; Terasaki, O.; Cao, Y.; Liu, B.; Ma, L.; Zhang, J.; Che, S. Synthesis of chiral TiO(2) nanofibre with electron transition-based optical activity. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, A.G.; Gibbs, J.G.; Lee, T.C.; Fischer, P. Hybrid nanocolloids with programmed three-dimensional shape and material composition. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Kuang, H.; Xu, L.; Ding, L.; Xu, C.; Wang, L.; Kotov, N.A. Attomolar DNA detection with chiral nanorod assemblies. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wagenknecht, C.; Li, C.M.; Reingruber, A.; Bao, X.H.; Goebel, A.; Chen, Y.A.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, K.; Pan, J.-W. Experimental demonstration of a heralded entanglement source. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; da Costa, R.C.; Fuchter, M.J.; Campbell, A.J. Circularly polarized light detection by a chiral organic semiconductor transistor. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffern, M.C.; Matosziuk, L.M.; Meade, T.J. Lanthanide Probes for Bioresponsive Imaging. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4496–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, J.; Yeom, B.; Chan, H.; Smith, K.W.; Dominguez-Medina, S.; Bahng, J.H.; Zhao, G.; Chang, W.S.; Chang, S.J.; Chuvilin, A.; et al. Chiral templating of self-assembling nanostructures by circularly polarized light. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Xu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.D.; Wang, L.H.; He, X.H.; Zhang, Q.J.; Hong, C.Y.; Zou, G. Circularly polarized light triggered enantioselective thiol-ene polymerization reaction. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 1735–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Sato, M.; Ishiguro, S.; Saito, T.; Morishita, Y.; Sato, I.; Nishino, H.; Inoue, Y.; Soai, K. Enantioselective Synthesis of Near Enantiopure Compound by Asymmetric Autocatalysis Triggered by Asymmetric Photolysis with Circularly Polarized Light. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 3274–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Li, W.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, S.X.-A.; Xu, Y. Uncovering the Circular Polarization Potential of Chiral Photonic Cellulose Films for Photonic Applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; He, H.; Gu, X.; Guo, L.; Wong, K.S.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Circularly Polarized Luminescence and a Reflective Photoluminescent Chiral Nematic Liquid Crystal Display Based on an Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogen. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2016, 4, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Jose, B.A.; Matsushita, S.; Akagi, K. Lyotropic Chiral Nematic Liquid Crystalline Aliphatic Conjugated Polymers Based on Disubstituted Polyacetylene Derivatives That Exhibit High Dissymmetry Factors in Circularly Polarized Luminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 19795–19807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, T.; Okazaki, Y.; Ueki, M.; Kuwahara, Y.; Takafuji, M.; Oda, R.; Ihara, H. Induction of Strong and Tunable Circularly Polarized Luminescence of Nonchiral, Nonmetal, Low-Molecular-Weight Fluorophores Using Chiral Nanotemplates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 2989–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, S.N.; Almeida, P.L.; Monge, N.; Aguirre, L.E.; Reis, D.; de Oliveira, C.L.; Neto, A.M.; Pieranski, P.; Godinho, M.H. Mind the Microgap in Iridescent Cellulose Nanocrystal Films. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Duan, P.; Jiao, T.; Peng, Q.; Liu, M. Self-Assembled Luminescent Quantum Dots To Generate Full-Color and White Circularly Polarized Light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12174–12178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keszthelyi, L. Asymmetries of nature and the origin of biomolecular handedness. Biosystems 1987, 20, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.E.; Ahn, H.Y.; Mun, J.; Lee, Y.Y.; Kim, M.; Cho, N.H.; Chang, K.; Kim, W.S.; Rho, J.; Nam, K.T. Amino-acid- and peptide-directed synthesis of chiral plasmonic gold nanoparticles. Nature 2018, 556, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jin, X.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, J.; Duan, P. Optically active quantum dots with induced circularly polarized luminescence in amphiphilic peptide dendron hydrogel. Nanoscale Adv. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Buldum, G.; Mantalaris, A.; Bismarck, A. More than meets the eye in bacterial cellulose: Biosynthesis, bioprocessing, and applications in advanced fiber composites. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 10–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.A. On an acetic ferment which forms cellulose. J. Am. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1886, 19, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.M.; Willison, J.H.; Richardson, C.L. Cellulose biosynthesis in Acetobacter xylinum: Visualization of the site of synthesis and direct measurement of the in vivo process. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 4565–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, G.S.; Shin, H.D.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Du, G.; Chen, J.; Liu, L. Metabolic engineering for amino-, oligo-, and polysugar production in microbes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2523–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannam, S.K.; Oehme, D.P.; Doblin, M.S.; Gidley, M.J.; Bacic, A.; Downton, M.T. Hydrogen bonds and twist in cellulose microfibrils. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usov, I.; Nystrom, G.; Adamcik, J.; Handschin, S.; Schutz, C.; Fall, A.; Bergstrom, L.; Mezzenga, R. Understanding nanocellulose chirality and structure-properties relationship at the single fibril level. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Yang, J.; Nie, Y.; Chen, C.; Sun, D. Recent advances in bacterial cellulose. Cellulose 2013, 21, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blok, P.M.L.; Dekkers, H.P.J.M. Measurement of the Circular Polarization of the Luminescence of Photoselected Samples under Artifact-Free Conditions. Appl. Spectrosc. 1990, 44, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehl, J.P.; Richardson, F.S. Circularly polarized luminescence spectroscopy. Chem. Rev. 1986, 86, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Wang, T.; Shi, L.; Tang, Z.; Liu, M. Strong circularly polarized luminescence from the supramolecular gels of an achiral gelator: Tunable intensity and handedness. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 4267–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Ju, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Li, M.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, S.X.-A.; Xu, Y. Circularly Polarized Luminescent Carbon Dot Nanomaterials of Helical Superstructures for Circularly Polarized Light Detection. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2018, 6, 1801246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Liu, Z.; Chen, H.; Sheng, L.; Zhang, S.X.-A.; Chiu, D.T.; Yin, S.; Wu, C.; Qin, W. Conjugated Polymer Dots for Ultra-Stable Full-Color Fluorescence Patterning. Small 2014, 10, 4270–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Williams, G.R.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Niu, S.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Zhu, L. Regenerated chitin fibers reinforced with bacterial cellulose nanocrystals as suture biomaterials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 180, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohira, A.; Okoshi, K.; Fujiki, M.; Kunitake, M.; Naito, M.; Hagihara, T. Versatile Helical Polymer Films: Chiroptical Inversion Switching and Memory with Re-Writable (RW) and Write-Once Read-Many (WORM) Modes. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1645–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, C.; Qu, D.; Jiang, H.; Lu, D.; Ma, X.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, Y. Bacterial Cellulose: A Versatile Chiral Host for Circularly Polarized Luminescence. Molecules 2019, 24, 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061008
Zou C, Qu D, Jiang H, Lu D, Ma X, Zhao Z, Xu Y. Bacterial Cellulose: A Versatile Chiral Host for Circularly Polarized Luminescence. Molecules. 2019; 24(6):1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061008
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Chen, Dan Qu, Haijing Jiang, Di Lu, Xiaoting Ma, Ziyi Zhao, and Yan Xu. 2019. "Bacterial Cellulose: A Versatile Chiral Host for Circularly Polarized Luminescence" Molecules 24, no. 6: 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061008
APA StyleZou, C., Qu, D., Jiang, H., Lu, D., Ma, X., Zhao, Z., & Xu, Y. (2019). Bacterial Cellulose: A Versatile Chiral Host for Circularly Polarized Luminescence. Molecules, 24(6), 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061008