Development of an Impedimetric Aptasensor for Label Free Detection of Patulin in Apple Juice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
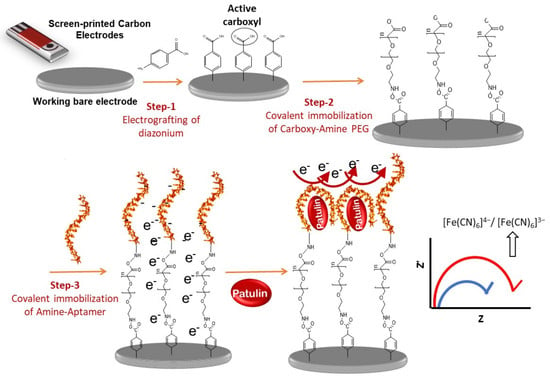
2.1. Design and Working Principle of Impedimetric Aptasensor
2.2. Electrochemical Characterization of the Aptasensors
2.2.1. Cyclic Voltammetry Characterization
2.2.2. Impedance Characterizations
2.3. Optimization of Experimental Parameters
2.4. Analytical Performance of the Aptasensors
2.5. Selectivity of the Aptasensors
2.6. Application to Spiked Apple Juice Sample
3. Experimental
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. Experimental Protocol
3.3.1. Covalent Immobilization of Aptamer onto the SPCEs
3.3.2. Detection of Patulin
3.3.3. Apple Juice Sample Preparation
3.4. Impedimetric Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
References
- Xia, X.; He, Q.; Dong, Y.; Deng, R.; Li, J. Aptamer-based Homogeneous Analysis for Food Control. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2018, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Mahato, D.K.; Kumar, P. Biosensor Technology—Advanced Scientific Tools, With Special Reference to Nanobiosensors and Plant- and Food-Based Biosensors. In Nanomaterials in Plants, Algae and Microorganisms; Elsevier Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 287–303. [Google Scholar]
- Vasilescu, A.; Marty, J.L. Electrochemical aptasensors for the assessment of food quality and safety. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laganà, A. Introduction to the Toxins Special Issue on LC-MS/MS Methods for Mycotoxin Analysis; Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute: Basel, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Moss, M. Fungi, quality and safety issues in fresh fruits and vegetables. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 1239–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ioi, J.D.; Zhou, T.; Tsao, R.; Marcone, M.F. Mitigation of patulin in fresh and processed foods and beverages. Toxins 2017, 9, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwahashi, Y.; Hosoda, H.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Suzuki, Y.; Kitagawa, E.; Murata, S.M.; Jwa, N.-S.; Gu, M.-B.; Iwahashi, H. Mechanisms of patulin toxicity under conditions that inhibit yeast growth. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 1936–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaser, N.; Stopper, H. Patulin: Mechanism of genotoxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 1796–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahfoud, R.; Maresca, M.; Garmy, N.; Fantini, J. The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: Mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2002, 181, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Commission, E. Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 364, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; He, S.; Gao, Z.; Di, Y.; Lu, K.; Li, K.; Wang, J. Aptamer-DNA Concatamer-Quantum Dots Based Electrochemical Biosensing Strategy for Green and Ultrasensitive Detection of Tumor Cells via Mercury-Free Anodic Stripping Voltammetry. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 126, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadok, I.; Szmagara, A.; Staniszewska, M.M. The validated and sensitive HPLC-DAD method for determination of patulin in strawberries. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, G.S.; Leggott, N.L. Chromatographic determination of the mycotoxin patulin in fruit and fruit juices. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 882, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takino, M.; Daishima, S.; Nakahara, T. Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometric determination of patulin in apple juice using atmospheric pressure photoionization. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 17, 1965–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimeno, A. Thin layer chromatographic determination of aflatoxins, ochratoxins, sterigmatocystin, zearalenone, citrinin, T-2 toxin, diacetoxyscirpenol, penicillic acid, patulin, penitrem A. J. Assoc. 1979, 62, 579–585. [Google Scholar]
- Beltrán, E.; Ibáñez, M.; Sancho, J.V.; Hernández, F. Determination of patulin in apple and derived products by UHPLC–MS/MS. Study of matrix effects with atmospheric pressure ionisation sources. Food Chem. 2014, 142, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grabowska, I.; Sharma, N.; Vasilescu, A.; Iancu, M.; Badea, G.; Boukherroub, R.; Ogale, S.; Szunerits, S. Electrochemical Aptamer-Based Biosensors for the Detection of Cardiac Biomarkers. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 12010–12018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goud, K.Y.; Hayat, A.; Catanante, G.; Satyanarayana, M.; Gobi, K.V.; Marty, J.L. An electrochemical aptasensor based on functionalized graphene oxide assisted electrocatalytic signal amplification of methylene blue for aflatoxin B1 detection. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 244, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhouati, A.; Catanante, G.; Nunes, G.; Hayat, A.; Marty, J.-L. Label-free aptasensors for the detection of mycotoxins. Sensors 2016, 16, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xiong, E.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J. Nanomaterials as signal amplification elements in DNA-based electrochemical sensing. Nano Today 2014, 9, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wu, J.; Zheng, L.; Qian, H.; Xue, F.; Wu, Y.; Pan, D.; Adeloju, S.B.; Chen, W. Rolling chain amplification based signal-enhanced electrochemical aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of ochratoxin A. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 10842–10849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Dong, X. Aptamer based voltammetric patulin assay based on the use of ZnO nanorods. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Xu, E.; Jin, Z.; Irudayaraj, J. An ultrasensitive aptasensor based on fluorescent resonant energy transfer and exonuclease-assisted target recycling for patulin detection. Food Chem. 2018, 249, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, A.; Andreescu, S.; Marty, J.-L. Design of PEG-aptamer two piece macromolecules as convenient and integrated sensing platform: Application to the label free detection of small size molecules. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 45, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Duan, N.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Z. Screening and development of DNA aptamers as capture probes for colorimetric detection of patulin. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 508, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahouche-Chergui, S.; Gam-Derouich, S.; Mangeney, C.; Chehimi, M.M. Aryl diazonium salts: A new class of coupling agents for bonding polymers, biomacromolecules and nanoparticles to surfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4143–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| PAT Added (ng/mL) | PAT Found (ng/mL) | RSD % | RE % | R % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 7.5 | 92.5 |
| 10 | 9.6 | 4.1 | 4 | 96 |
| 20 | 18.8 | 4.8 | 6 | 94 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, R.; Ben Aissa, S.; Sherazi, T.A.; Catanante, G.; Hayat, A.; Marty, J.L. Development of an Impedimetric Aptasensor for Label Free Detection of Patulin in Apple Juice. Molecules 2019, 24, 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061017
Khan R, Ben Aissa S, Sherazi TA, Catanante G, Hayat A, Marty JL. Development of an Impedimetric Aptasensor for Label Free Detection of Patulin in Apple Juice. Molecules. 2019; 24(6):1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061017
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Reem, Sondes Ben Aissa, Tauqir A. Sherazi, Gaelle Catanante, Akhtar Hayat, and Jean Louis Marty. 2019. "Development of an Impedimetric Aptasensor for Label Free Detection of Patulin in Apple Juice" Molecules 24, no. 6: 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061017
APA StyleKhan, R., Ben Aissa, S., Sherazi, T. A., Catanante, G., Hayat, A., & Marty, J. L. (2019). Development of an Impedimetric Aptasensor for Label Free Detection of Patulin in Apple Juice. Molecules, 24(6), 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061017