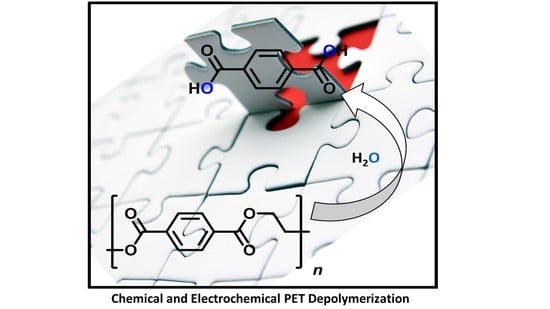
Chemical and Electrochemical Recycling of End-Use Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) Plastics in Batch, Microwave and Electrochemical Reactors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Methods
4.2. PET Depolymerization in Batch and Microwave
4.3. Microwave Experiments
4.4. Electrochemistry Experiments and Gas Chromatography
4.5. Identification of Plasticizers by GC-EI
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Advancing Sustainable Materials Management: 2016 and 2017 Tables and Figures; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Kuczenski, B.; Geyer, R. Material flow analysis of polyethylene terephthalate in the US, 1996–2007. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2010, 54, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emissions of Greenhouse Gases in the United States 2006 (DOE/EIA-0573); U.S. Energy Information Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2006.
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tabone, M.D.; Cregg, J.J.; Beckman, E.J.; Landis, A.E. Sustainability metrics: Life cycle assessment and green design in polymers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8264–8269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastas, P.T.; Warner, J.C. Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, D.L. Introduction to biopolymers from renewable resources. In Biopolymers from Renewable Resources; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ragaert, K.; Delva, L.; Van Geem, K. Mechanical and chemical recycling of solid plastic waste. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 24–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiounn, T.; Smith, R.C. Advances and approaches for chemical recycling of plastic waste. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 58, 1347–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awaja, F.; Pavel, D. Recycling of PET. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 1453–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Sheu, M.-F.; Chen, S.-M. Solid-state polymerization of poly(ethylene terephthalate). J. Appl. 1983, 28, 3289–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastin, H.; Ahmadi, Z.; Pakdel, A.S.; Saeb, M.R.; Abbasian, Y.; Liravi, M.; Eslahi, A. A physicochemical route for compensation of molecular weight loss during recycling of poly(ethylene terephthalate). J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2016, 22, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, S.A.; Zanin, M. PET recycling: Evaluation of the solid state polymerization process. J. Appl. 2006, 99, 2117–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitaroni, L.B.; De Oliveira, É.C.; Marcomini, A.L.; Paranhos, C.M.; Freitas, F.L.; Cruz, S.A. Reprocessing and Solid State Polymerization on Contaminated Post-consumer PET: Thermal and Crystallization Behavior. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doina Dimonie, R.S.; Pop, S.; Fierascu, I.; Fierascu, R.; Petra, C.; Zaharia, C.; Patrache, M. Overview on Mechanic Recycling by Chain Extension of POSTC-PET Bottles. In Material Recycling: Trends and Perspectives; Achilias, D.S., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Salem, S.; Lettieri, P.; Baeyens, J. Recycling and recovery routes of plastic solid waste (PSW): A review. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2625–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, U.; Mastellone, M.L. Particle Agglomeration during Energy Recovery from Plastic Wastes by Means of Fluidized Bed Reactors; Univ. Federico II of Naples: Napoli, Italy, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Institute, F. PET-Recyclate from Post-Consumer Waste. Available online: https://www.ivv.fraunhofer.de/en/recycling-environment/packaging-recycling/pet-recycling.html (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Carta, D.; Cao, G.; D’Angeli, C. Chemical recycling of poly (ethylene terephthalate)(PET) by hydrolysis and glycolysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2003, 10, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paszun, D.; Spychaj, T. Chemical recycling of poly (ethylene terephthalate). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1997, 36, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehanno, C.; Pérez-Madrigal, M.M.; Demarteau, J.; Sardon, H.; Dove, A.P. Organocatalysis for depolymerisation. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- George, N.; Kurian, T. Recent Developments in the Chemical Recycling of Postconsumer Poly(ethylene terephthalate) Waste. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 14185–14198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K.; Coulembier, O.; Lecuyer, J.M.; Almegren, H.A.; Alabdulrahman, A.M.; Alsewailem, F.D.; Mcneil, M.A.; Dubois, P.; Waymouth, R.M.; Horn, H.W. Organocatalytic depolymerization of poly (ethylene terephthalate). J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2011, 49, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.-C.; Oku, A.; Yamada, E.; Tomari, K. Alkali-decomposition of poly (ethylene terephthalate) in mixed media of nonaqueous alcohol and ether. Study on recycling of poly (ethylene terephthalate). Polym. J. 1997, 29, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshioka, T.; Sato, T.; Okuwaki, A. Hydrolysis of waste PET by sulfuric acid at 150 °C for a chemical recycling. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1994, 52, 1353–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Goje, A.; Zope, V. Chemical recycling, kinetics, and thermodynamics of poly (ethylene terephthalate)(PET) waste powder by nitric acid hydrolysis. Polym. React. Eng. 2003, 11, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.E. Peroxides and peroxide-forming compounds. Chem. Health Saf. 2001, 8, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, S.; Kadoma, Y.; Yokoe, I. Radical-scavenging activity of butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) and its metabolites. Chem. Phys. Lip. 2004, 130, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappe, C.O.; Dallinger, D. The impact of microwave synthesis on drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, M.N.; Achilias, D.S.; Redhwi, H.H.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Katsogiannis, K.A.G.; Karayannidis, G.P. Hydrolytic depolymerization of PET in a microwave reactor. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 295, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, O.R.; Blakemore, J.D.; Konezny, S.J.; Praetorius, J.M.; Schmeier, T.J.; Hunsinger, G.B.; Batista, V.S.; Brudvig, G.W.; Hazari, N.; Crabtree, R.H. Organometallic Ni pincer complexes for the electrocatalytic production of hydrogen. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 8704–8709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luca, O.R.; Konezny, S.J.; Blakemore, J.D.; Colosi, D.M.; Saha, S.; Brudvig, G.W.; Batista, V.S.; Crabtree, R.H. A tridentate Ni pincer for aqueous electrocatalytic hydrogen production. New J. Chem. 2012, 36, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mast, Z.J.; Myren, T.H.; Huntzinger, C.G.; Stinson, T.A.; Kharbouch, R.M.; Almanza, E.M.; Zygmont, S.E.; Miecznikowski, J.R.; Luca, O.R. Cu I SNS triazole and imidazole pincers as electrocatalyst precursors for the production of solar fuels. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 1012–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myren, T.H.; Lilio, A.M.; Huntzinger, C.G.; Horstman, J.W.; Stinson, T.A.; Donadt, T.B.; Moore, C.; Lama, B.; Funke, H.H.; Luca, O.R. Manganese N-heterocyclic carbene pincers for the electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide. Organometallics 2018, 38, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myren, T.H.; Alherz, A.; Thurston, J.R.; Stinson, T.A.; Huntzinger, C.G.; Musgrave, C.B.; Luca, O.R. Mn-Based Molecular Catalysts for the Electrocatalytic Disproportionation of CO2 into CO and CO32–. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, B.; Dzieciuch, M. New Approaches to the Study of Electrochemical Decarboxylation and the Kolbe Reaction: Part I. The Model Reaction with Formate. Can. J. Chem. 1963, 41, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conway, B.; Dzieciuch, M. New Approaches to the Study of Electrochemical Decarboxylation and the Kolbe Reaction: Part II. The Model Reaction with Trifluoroacetate and Comparisons with Aqueous Solution Behavior. Can. J. Chem. 1963, 41, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, R.J. Terephthalic Acid, Dimethyl Terephthalate, and Isophthalic Acid. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Guart, A.; Bono-Blay, F.; Borrell, A.; Lacorte, S. Migration of plasticizersphthalates, bisphenol A and alkylphenols from plastic containers and evaluation of risk. Food Addit. Contam. A 2011, 28, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of end-use PET plastic used in the study are available from the authors as well as reagents. |



| Reaction Entry | Conditions a | Reaction Time | Terephthalic Acid Yield% b |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MeOH, reflux | 4 h | 23 |
| 2 | MeOH, reflux | 12 h | 75 |
| 3 | Water, reflux | 48 h | 23 |
| Reaction Entry | Conditions a | Reaction Time | Terephthalic Acid Yield% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Water, 170 °C | 30 min | 0 |
| 2 | MeOH, 85 °C | 13 min | 55 |
| 3 | MeOH, 85 °C | 40 min | 65 |
| 4 | MeOH, 130 °C | 40 min | 65 |
| Reaction Entry | Conditions | Terephthalic Acid Yield% a | nCO2 * 10−6 b |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50% MeOH in water, −2.2 V | 16.9 | 7.89 ± 0.36 |
| 2 | Water, 0.1 M NaCl, −2.2 V | 0.51 | n/a c |
| Compound | Prob (%) |
|---|---|
| Dodecamethylcyclohexasiloxane | 86.89 |
| Tetradecamethylcyclohexasiloxane | 86.89 |
| Hexadecamethylcyclooctasiloxane | 75.73 |
| Octasiloxane | 66.82 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Myren, T.H.T.; Stinson, T.A.; Mast, Z.J.; Huntzinger, C.G.; Luca, O.R. Chemical and Electrochemical Recycling of End-Use Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) Plastics in Batch, Microwave and Electrochemical Reactors. Molecules 2020, 25, 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122742
Myren THT, Stinson TA, Mast ZJ, Huntzinger CG, Luca OR. Chemical and Electrochemical Recycling of End-Use Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) Plastics in Batch, Microwave and Electrochemical Reactors. Molecules. 2020; 25(12):2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122742
Chicago/Turabian StyleMyren, Tessa H. T., Taylor A. Stinson, Zachary J. Mast, Chloe G. Huntzinger, and Oana R. Luca. 2020. "Chemical and Electrochemical Recycling of End-Use Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) Plastics in Batch, Microwave and Electrochemical Reactors" Molecules 25, no. 12: 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122742
APA StyleMyren, T. H. T., Stinson, T. A., Mast, Z. J., Huntzinger, C. G., & Luca, O. R. (2020). Chemical and Electrochemical Recycling of End-Use Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) Plastics in Batch, Microwave and Electrochemical Reactors. Molecules, 25(12), 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122742