Optimisation of Sporosori Purification and Protein Extraction Techniques for the Biotrophic Protozoan Plant Pathogen Spongospora subterranea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
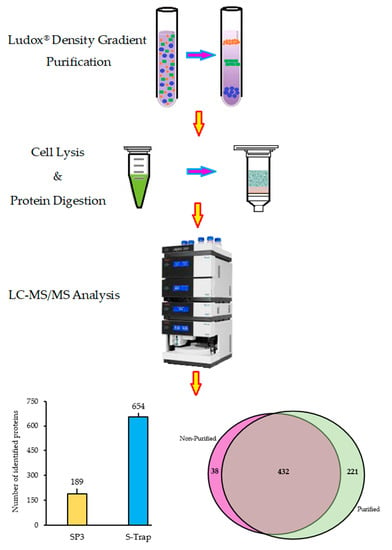
2.1. Sporosori Purification
2.2. Optimisation of Protein Preparation for Mass Spectrometry
2.3. Quantitative Efficiency of Ludox® Purification for Protein Analysis of Resting Spores
2.4. Major Metabolic Pathways and Cellular Processes of S. subterranea Resting Spores Revealed by a Bioinformatics Approach
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Pathogen Source
3.2. Ludox® Density Gradient Centrifugation for Sporosori Purification
3.3. Spore Viability
3.4. Protein Extraction and Digestion
3.4.1. Single-Pot Solid-Phase-Enhanced Sample Preparation (SP3 Method)
3.4.2. Suspension-Trapping (S-Trap Method)
3.5. LC–MS/MS Analysis
3.6. Data Processing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neuhauser, S.; Huber, L.; Kirchmair, M. Sorosphaera viticola, a plasmodiophorid parasite of grapevine. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2009, 48, 136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balendres, M.; Tegg, R.; Wilson, C. Key events in pathogenesis of Spongospora diseases in potato: A review. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2016, 45, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.; Swaby, A.; Jones, P. Confirmation of the transmission of barley yellow mosaic virus (BaYMV) by the fungus Polymyxa graminis. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1988, 112, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, I.; Parodi, E.; Westermeier, R.; Müller, D.G. Maullinia ectocarpii gen. et sp. nov.(Plasmodiophorea), an intracellular parasite in Ectocarpus siliculosus (Ectocarpales, Phaeophyceae) and other filamentous brown algae. Protist 2000, 151, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamada, T.; Asher, M.J. The Plasmodiophorid Protist Polymyxa Betae. In Rhizomania; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 135–153. [Google Scholar]
- Robbins, R.K.; Braselton, J.P. Ultrastructure and classification of the genus Sorodiscus (Plasmodiophoromycetes). Mycotaxon (USA) 1997, 61, 327–334. [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood, W.A. Extension of the host range of Octomyxa brevilegniae. J. Elisha. Mitchell. Sci. Soc. 1968, 84, 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Dylewski, D.P.; Miller, C.E. The ultrastructure of meiosis in Woronina pythii (Plasmodiophoromycetes). Mycologia 1984, 76, 1075–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Gupta, P.; Suseela, M. Ultrastructure of the parasitic infection of Marsilea minuta by Ligniera verrucosa. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant. Prot. 1995, 30, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falloon, R.E.; Merz, U.; Lister, R.A.; Wallace, A.R.; Hayes, S.P. Morphological enumeration of resting spores in sporosori of the plant pathogen Spongospora subterranea. Acta. Protozool. 2011, 50, 121. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, C. Plant pathogens–the great thieves of vegetable value. Acta Hortic. 2016, 1123, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsror, L.; Lebiush, S.; Hazanovsky, M.; Erlich, O. Control of potato powdery scab caused by Spongospora subterranea by foliage cover and soil application of chemicals under field conditions with naturally infested soil. Plant. Pathol. 2020, 69, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falloon, R.; Merz, U.; Butler, R.; Curtin, D.; Lister, R.; Thomas, S. Root infection of potato by Spongospora subterranea: Knowledge review and evidence for decreased plant productivity. Plant. Pathol. 2016, 65, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balendres, M.A.; Tegg, R.S.; Wilson, C.R. Resting spore dormancy and infectivity characteristics of the potato powdery scab pathogen Spongospora subterranea. J. Phytopathol. 2017, 165, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakke, M.K. Density gradient centrifugation: A new separation technique1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 1847–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, B.T.; Nixon, H. Purification and electron microscopy of three soil-borne plant viruses. Virology 1960, 12, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castlebury, L.; Maddox, J.; Glawe, D. A technique for the extraction and purification of viable Plasmodiophora brassicae resting spores from host root tissue. Mycologia 1994, 86, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Du, Y.; Lei, Y.; Dai, R. A practical method of Ludox density gradient centrifugation combined with protargol staining for extracting and estimating ciliates in marine sediments. Eur. J. Protistol. 2010, 46, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Hebert, A.S.; Coon, J.J.; Hull, C.M. Protein composition of infectious spores reveals novel sexual development and germination factors in Cryptococcus. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voltersen, V.; Blango, M.G.; Herrmann, S.; Schmidt, F.; Heinekamp, T.; Strassburger, M.; Krüger, T.; Bacher, P.; Lother, J.; Weiss, E.; et al. Proteome analysis reveals the conidial surface protein CcpA essential for virulence of the pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. MBio. 2018, 9, e01557-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lai, E.-M.; Phadke, N.D.; Kachman, M.T.; Giorno, R.; Vazquez, S.; Vazquez, J.A.; Maddock, J.R.; Driks, A. Proteomic analysis of the spore coats of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus anthracis. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 1443–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Mei, H.; Qian, H.; Tang, Q.; Liu, X.; Yu, Z.; He, J. Expression profile and regulation of spore and parasporal crystal formation-associated genes in Bacillus thuringiensis. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 5487–5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xia, Q.; Li, Y. Label free-based proteomic analysis of proteins in Bacillus cereus spores regulated by high pressure processing and slightly acidic electrolyzed water treatment. Food Control. 2018, 90, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Adams, R.M.; Chourey, K.; Hurst, G.B.; Hettich, R.L.; Pan, C. Systematic comparison of label-free, metabolic labeling, and isobaric chemical labeling for quantitative proteomics on LTQ Orbitrap Velos. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 1582–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Wariishi, H. Development of a sample preparation method for fungal proteomics. Fems Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 247, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hughes, C.S.; Moggridge, S.; Müller, T.; Sorensen, P.H.; Morin, G.B.; Krijgsveld, J. Single-pot, solid-phase-enhanced sample preparation for proteomics experiments. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zougman, A.; Selby, P.J.; Banks, R.E. Suspension trapping (STrap) sample preparation method for bottom-up proteomics analysis. Proteomics 2014, 14, 1006–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.R.; Schroll, M.M.; Hummon, A.B. Comparison of in-solution, FASP, and S-trap based digestion methods for bottom-up proteomic studies. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2480–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayoun, K.; Gouveia, D.D.; Grenga, L.; Pible, O.; Armengaud, J. Evaluation of sample preparation methods for fast proteotyping of microorganisms by tandem mass spectrometry. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doellinger, J.; Schneider, A.; Hoeller, M.; Lasch, P. Sample Preparation by Easy Extraction and Digestion (SPEED)-A Universal, Rapid, and Detergent-free Protocol for Proteomics based on Acid Extraction. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2020, 19, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balendres, M.A.; Nichols, D.S.; Tegg, R.S.; Wilson, C.R. Metabolomes of potato root exudates: Compounds that stimulate resting spore germination of the soil-borne pathogen Spongospora subterranea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7466–7474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.; Searle, R.; Williams, N. Powdery scab disease of potato—a review. Plant. Pathol. 1997, 46, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elinger, D.; Gabashvili, A.; Levin, Y. Suspension trapping (S-Trap) is compatible with typical protein extraction buffers and detergents for bottom-up proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 1441–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.S.; Kim, S.G.; Chung, W.S.; Bae, H.; Jeong, S.W.; Shin, S.C.; Jeong, M.-J.; Park, S.-C.; Kwak, Y.-S.; Bae, D.-W. Proteomic analysis of Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 sclerotia maturation. Fungal Biol. 2014, 118, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Akhal, M.R.; Colby, T.; Cantoral, J.M.; Harzen, A.; Schmidt, J.; Fernández-Acero, F.J. Proteomic analysis of conidia germination in Colletotrichum acutatum. Arch. Microbiol. 2013, 195, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mappa, C.; Pible, O.; Armengaud, J. Assessing the ratio of Bacillus spores and vegetative cells by shotgun proteomics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mares, J.H.; Gramacho, K.P.; Santos, E.C.; da Silva Santiago, A.; Santana, J.O.; de Sousa, A.O.; Alvim, F.C.; Pirovani, C.P. Proteomic analysis during of spore germination of Moniliophthora perniciosa, the causal agent of witches’ broom disease in cacao. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- González-Rodríguez, V.E.; Liñeiro, E.; Colby, T.; Harzen, A.; Garrido, C.; Cantoral, J.M.; Schmidt, J.; Fernández-Acero, F.J. Proteomic profiling of Botrytis cinerea conidial germination. Arch. Microbiol. 2015, 197, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryngelsson, T.; Gustafsson, M.; Green, B.; Lind, C. Uptake of host DNA by the parasitic fungus Plasmodiophora brassicae. Physiol. Mol. Plant. Pathol. 1988, 33, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Xu, K.; He, Y. Application of the Ludox-QPS method for estimating ciliate diversity in soil and comparison with direct count and DNA fingerprinting. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2012, 49, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubitz, A.; Bauer, B.; Heesemann, J.; Ebel, F. Role of respiration in the germination process of the pathogenic mold Aspergillus fumigatus. Curr. Microbiol. 2007, 54, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novodvorska, M.; Stratford, M.; Blythe, M.J.; Wilson, R.; Beniston, R.G.; Archer, D.B. Metabolic activity in dormant conidia of Aspergillus niger and developmental changes during conidial outgrowth. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2016, 94, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sephton-Clark, P.C.; Muñoz, J.F.; Ballou, E.R.; Cuomo, C.A.; Voelz, K. Pathways of Pathogenicity: Transcriptional Stages of Germination in the Fatal Fungal Pathogen Rhizopus delemar. mSphere 2018, 3, e00403–e00418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernandez Maldonado, M.L.; Falloon, R.E.; Butler, R.C.; Conner, A.J.; Bulman, S.R. Spongospora subterranea root infection assessed in two potato cultivars differing in susceptibility to tuber powdery scab. Plant. Pathol. 2013, 62, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balendres, M.; Clark, T.; Tegg, R.; Wilson, C. Germinate to exterminate: Chemical stimulation of Spongospora subterranea resting spore germination and its potential to diminish soil inoculum. Plant. Pathol. 2018, 67, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Csordas, A.; Bai, J.; Bernal-Llinares, M.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Inuganti, A.; Griss, J.; Mayer, G.; Eisenacher, M. The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: Improving support for quantification data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D442–D450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balotf, S.; Wilson, R.; Tegg, R.S.; Nichols, D.S.; Wilson, C.R. Optimisation of Sporosori Purification and Protein Extraction Techniques for the Biotrophic Protozoan Plant Pathogen Spongospora subterranea. Molecules 2020, 25, 3109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25143109
Balotf S, Wilson R, Tegg RS, Nichols DS, Wilson CR. Optimisation of Sporosori Purification and Protein Extraction Techniques for the Biotrophic Protozoan Plant Pathogen Spongospora subterranea. Molecules. 2020; 25(14):3109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25143109
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalotf, Sadegh, Richard Wilson, Robert S. Tegg, David S. Nichols, and Calum R. Wilson. 2020. "Optimisation of Sporosori Purification and Protein Extraction Techniques for the Biotrophic Protozoan Plant Pathogen Spongospora subterranea" Molecules 25, no. 14: 3109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25143109
APA StyleBalotf, S., Wilson, R., Tegg, R. S., Nichols, D. S., & Wilson, C. R. (2020). Optimisation of Sporosori Purification and Protein Extraction Techniques for the Biotrophic Protozoan Plant Pathogen Spongospora subterranea. Molecules, 25(14), 3109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25143109