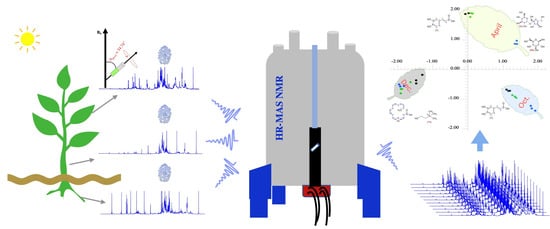
High-Resolution Magic Angle Spinning (HR-MAS) NMR-Based Fingerprints Determination in the Medicinal Plant Berberis laurina
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. 1H HR-MAS NMR-Based Chemical Composition of the Leaves of Berberis laurina
2.2. 1H HR-MAS NMR-Based Chemical Composition of Stems and Roots of Berberis laurina
2.3. 1H HR-MAS NMR-Based Insight into the Leaves Metabolic Patterns
2.4. Principal Component Analysis-Based Metabolic Pattern Discrimination in the Leaves
3. Experimental
3.1. Botanical Materials
3.2. 1H HR-MAS NMR
3.3. Liquid-State (2D) NMR
3.4. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhardwaj, D.; Kaushik, N. Phytochemical and pharmacological studies in genus Berberis. Phytochem. Rev. 2012, 11, 523–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrum, L.R. Revision of Berberis (Berberidaceae) in Chile and adjacent southern argentina. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1999, 86, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, D.P.; Collins, J.H.P.; Lama, B.; Zeng, H.; Nguyen, T.; Keller, G.; Febo, M.; Long, J. Characterization of brain metabolism by nuclear magnetic resonance. ChemPhysChem 2018, 20, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzakis, E. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy in food science: A comprehensive review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 189–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaneko, G.; Ushio, H.; Ji, H. Application of magnetic resonance technologies in aquatic biology and seafood science. Fish. Sci. 2019, 85, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Kuhn, L.T.; Balbach, J. In-cell NMR: Analysis of protein–small molecule interactions, metabolic processes, and protein phosphorylation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nikitin, K.; O’Gara, R. Mechanisms and beyond: Elucidation of fluxional dynamics by exchange NMR spectroscopy. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 4551–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pautler, B.G.; Simpson, A.J.; Simpson, M.J.; Tseng, L.-H.; Spraul, M.; Dubnick, A.; Sharp, M.J.; Fitzsimons, S.J. Detection and structural identification of dissolved organic matter in antarctic glacial ice at natural abundance by SPR-W5-WATERGATE 1H NMR spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4710–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudszuck, T.; Förster, E.; Nirschl, H.; Guthausen, G. Low-field NMR for quality control on oils. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2019, 57, 777–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignoli, A.; Ghini, V.; Meoni, G.; Licari, C.; Takis, P.G.; Tenori, L.; Turano, P.; Luchinat, C. High-throughput metabolomics by 1D NMR. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 968–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-M.; Jeon, J.-Y.; Lee, B.-J.; Lee, H.; Choi, H.-K. Application of metabolomics to quality control of natural product derived medicines. Biomol. Ther. 2017, 25, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simmler, C.; Graham, J.G.; Chen, S.-N.; Pauli, G.F. Integrated analytical assets aid botanical authenticity and adulteration management. Fitoterapia 2018, 129, 401–414. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, D.-Y.; Kang, Y.-G.; Kim, E.-H.; Kim, M.; Park, N.-H.; Choi, H.-T.; Go, G.H.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Hong, Y.-S. Metabolomics approach for understanding geographical dependence of soybean leaf metabolome. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuballa, T.; Brunner, T.S.; Thongpanchang, T.; Walch, S.G.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Application of NMR for authentication of honey, beer and spices. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 19, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Wei, L.; Xie, Z.; Guan, B. Effects of hypoxia in the gills of the Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum using NMR-based metabolomics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanatta, M.; Simon, N.M.; dos Santos, F.P.; Corvo, M.C.; Cabrita, E.J.; Dupont, J. Correspondence on “preorganization and cooperation for highly efficient and reversible capture of low-concentration CO2 by ionic liquids”. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, B.; Simpson, A.J. Direct 1H NMR spectroscopy of dissolved organic matter in natural waters. Analyst 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.; Lucas-Torres, C. High-resolution magic-angle spinning (HR-MAS) NMR spectroscopy. In NMR-Based Metabolomics; Keun, H.C., Ed.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2018; pp. 133–150. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, I.S.; Martinelli, B.C.B.; Pinto, V.S.; Queiroz, L.H.K.; Lião, L.M. Important issues in plant tissues analyses by HR-MAS NMR. Phytochem. Anal. 2019, 30, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jensen, H.M.; Bertram, H.C. The magic angle view to food: Magic-angle spinning (MAS) NMR spectroscopy in food science. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, T.M.; Jenkins, J.E. HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy in material science. In Advanced Aspects of Spectroscopy; Farrukh, M.A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 279–306. [Google Scholar]
- Farooq, H.; Courtier-Murias, D.; Soong, R.; Bermel, W.; Kingery, W.; Simpson, A. HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy: A practical guide for natural samples. Curr. Org. Chem. 2013, 17, 3013–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzei, P.; Piccolo, A.; Valentini, M. Intact food analysis by means of HRMAS-NMR spectroscopy. In Modern Magnetic Resonance; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1503–1518. [Google Scholar]
- Gribbestad, I.S.; Aursand, M.; Martinez, I. High-resolution 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy of whole fish, fillets and extracts of farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) for quality assessment and compositional analyses. Aquaculture 2005, 250, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, T.; Aursand, M.; Hirata, Y.; Gribbestad, I.S.; Wada, S.; Nonaka, M. Nondestructive quantitative determination of docosahexaenoic acid and n−3 fatty acids in fish oils by high-resolution 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2000, 77, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, A.B.; Lamichhane, S.; Castejón, D.; Cambero, M.I.; Bertram, H.C. 1H HR-MAS NMR-based metabolomics analysis for dry-fermented sausage characterization. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhu, V.V.; Nguyen, T.B.; Cui, Y.; Oh, Y.-E.; Piao, Y.-H.; Baek, H.-M.; Kim, J.J.-Y.; Shin, K.-H.; Kim, J.J.-Y.; Lee, K.-H.; et al. Metabolite signature associated with stress susceptibility in socially defeated mice. Brain Res. 2019, 1708, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, Q.; Dutta Majumdar, R.; Wu, B.; Lane, D.; Tabatabaei-Anraki, M.; Soong, R.; Simpson, M.J.; Simpson, A.J. Improvements in lipid suppression for 1H NMR-based metabolomics: Applications to solution-state and HR-MAS NMR in natural and in vivo samples. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2019, 57, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocampos, F.M.M.; Menezes, L.R.A.; Dutra, L.M.; Santos, M.F.C.; Ali, S.; Barison, A. NMR in chemical ecology: An overview highlighting the main NMR approaches. In eMagRes; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2017; Volume 6, pp. 325–342. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.D.C.; Fonseca, F.A.; Lião, L.M.; Alcantara, G.B.; Barison, A. High-resolution magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance in foodstuff analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 73, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumez, J.-N. Spatial encoding and spatial selection methods in high-resolution NMR spectroscopy. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2018, 109, 101–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampaio, B.L.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; da Costa, F.B. Effect of the environment on the secondary metabolic profile of Tithonia diversifolia: A model for environmental metabolomics of plants. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Rensburg, H.C.J.; van den Ende, W.; Signorelli, S. Autophagy in plants: Both a puppet and a puppet master of sugars. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahbazy, M.; Moradi, P.; Ertaylan, G.; Zahraei, A.; Kompany-Zareh, M. FTICR mass spectrometry-based multivariate analysis to explore distinctive metabolites and metabolic pathways: A comprehensive bioanalytical strategy toward time-course metabolic profiling of Thymus vulgaris plants responding to drought stress. Plant Sci. 2020, 290, 110257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fait, A.; Batushansky, A.; Shrestha, V.; Yobi, A.; Angelovici, R. Can metabolic tightening and expansion of co-expression network play a role in stress response and tolerance? Plant Sci. 2020, 293, 110409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarı, Z.K.A. Phytochemical investigations on chemical constituents of taraxacum bessarabicum (Hornem.) hand.-mazz. subsp. bessarabicum (Hornem.) hand.-mazz. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Luo, L.; Zheng, L. Lignins: Biosynthesis and biological functions in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boerjan, W.; Ralph, J.; Baucher, M. Lignin biosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2003, 54, 519–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, V.; Aswal, J.S.; Dobhal, R.; Uniyal, D.P. A review on pharmacological potential of berberine; an active component of himalayan berberis aristata. J. Phytopharm. 2017, 6, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia, A.; Tripathi, T.; Singh, S.; Bisht, H.; Behl, H.M.; Roy, R.; Sidhu, O.P. Comprehensive metabolite profiling in distinct chemotypes of Commiphora wightii. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, D.W.; Yoder, T.J.; Reiter, W.D.; Gibson, S.I. Fumaric acid: An overlooked form of fixed carbon in Arabidopsis and other plant species. Planta 2000, 211, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shakya, A.; Singh, G.; Chatterjee, S.; Kumar, V. Role of fumaric acid in anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of a Fumaria indica extracts. J. Intercult. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 3, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, K.; Triantis, T.; Dimotikali, D.; Nikokavouras, J. Evaluation of food antioxidant activity by photostorage chemiluminescence. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 433, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Peralta, M.A.; Robles-Zepeda, R.E.; Garibay-Escobar, A.; Ruiz-Bustos, E.; Alvarez-Berber, L.P.; Gálvez-Ruiz, J.C. In vitro anti-proliferative activity of Argemone gracilenta and identification of some active components. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, S.; Srivastava, M.; Misra, A.; Pandey, G.; Rawat, A. A review on biological and chemical diversity in Berberis (Berberidaceae). EXCLI J. 2015, 14, 247–267. [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto, T.; Yoshitomi, T.; Maruyama, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hakamatsuka, T.; Uchiyama, N. 13C-NMR-based metabolic fingerprinting of Citrus-type crude drugs. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 161, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A.M.; Duarte, I.F.; Delgadillo, I.; Colquhoun, I.J.; Casuscelli, F.; Humpfer, E.; Spraul, M. Study of the compositional changes of mango during ripening by use of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1524–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuramalingam, P.; Krishnan, S.R.; Pandian, S.; Mareeswaran, N.; Aruni, W.; Pandian, S.K.; Ramesh, M. Global analysis of threonine metabolism genes unravel key players in rice to improve the abiotic stress tolerance. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenka, S.K.; Katiyar, A.; Chinnusamy, V.; Bansal, K.C. Comparative analysis of drought-responsive transcriptome in Indica rice genotypes with contrasting drought tolerance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 9, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barison, A.; da Silva, C.W.P.; Campos, F.R.R.; Simonelli, F.; Lenz, C.A.A.; Ferreira, A.G. A simple methodology for the determination of fatty acid composition in edible oils through 1H NMR spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2010, 48, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, K.; Maltese, F.; Zyprian, E.; Rex, M.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. NMR metabolic fingerprinting based identification of grapevine metabolites associated with downy mildew resistance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9599–9606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. NMR-based metabolomic analysis of plants. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Azmat, R.; Haider, S.; Nasreen, H.; Aziz, F.; Riaz, M. A viable alternative mechanism in adapting the plants to heavy metal environment. Pakistan J. Bot. 2009, 41, 2729–2738. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, M.; Mushta, M.Y.; Ali, K.; Korthout, H.A.A.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Cardozo, M.L.; Ordoñez, R.M.; Isla, M.I.; Choi, Y.H. NMR Spectroscopy Coupled with Multivariate Data Analysis to Assess Antiinflammatory Activities of Eugenia Uniflora Fruits in Different Developmental Stages. Ph.D. Thesis, Leiden University, Leiden, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ravaglia, L.M.; Pizzotti, A.B.C.; Alcantara, G.B. NMR-based and chemometric approaches applicable to adulteration studies for assessment of the botanical origin of edible oils. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neag, M.A.; Mocan, A.; Echeverría, J.; Pop, R.M.; Bocsan, C.I.; Crişan, G.; Buzoianu, A.D.; Crisan, G.; Buzoianu, A.D.; Crişan, G. Berberine: Botanical occurrence, traditional uses, extraction methods, and relevance in cardiovascular, metabolic, hepatic, and renal disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, R.; Bohra, A.; Pandey, A.K.; Pandey, M.K.; Kumar, A. Metabolomics for plant improvement: Status and prospects. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pavarini, D.P.; Pavarini, S.P.; Niehues, M.; Lopes, N.P. Exogenous influences on plant secondary metabolite levels. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2012, 176, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wen, K.S.; Ruan, X.; Zhao, Y.X.; Wei, F.; Wang, Q. Response of plant secondary metabolites to environmental factors. Molecules 2018, 23, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ncube, B.; Finnie, J.F.; Van Staden, J. Quality from the field: The impact of environmental factors as quality determinants in medicinal plants. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2012, 82, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jahangir, M.; Nuringtyas, T.R.; Ali, K.; Wilson, E.G.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. NMR-based metabolomics: Understanding plant chemistry and identification of biologically active compounds. In NMR-Based Metabolomics; Keun, H.C., Ed.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2018; pp. 246–263. [Google Scholar]
- Emwas, A.-H.; Saccenti, E.; Gao, X.; McKay, R.T.; dos Santos, V.A.P.M.; Roy, R.; Wishart, D.S. Recommended strategies for spectral processing and post-processing of 1D 1H-NMR data of biofluids with a particular focus on urine. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ebrahimi, P.; Viereck, N.; Bro, R.; Engelsen, S.B. Chemometric analysis of NMR spectra. In Modern Magnetic Resonance; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2018; pp. 1649–1668. ISBN 9783319283883. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, J.; Gerretzen, J.; Szymańska, E.; Jansen, J.J.; Downey, G.; Blanchet, L.; Buydens, L.M.C. Breaking with trends in pre-processing? Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 50, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds were identified directly on the botanical material. |












| Compound | Position | Current Work a | Literature b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (mult. J, Hz) | δC | LRJH-C (HMBC) | δH (mult. J, Hz) | δC | ||
| Caffeic Acid (1) | 1 | - | 127.8 | - | - | 127.2 |
| 2 | 7.04 (d, 1.9) | 115.2 | 149.5; 147.0; 122.7 | 7.07 (d, 2) | 114.1 | |
| 3 | - | 147.0 | - | - | 145.5 | |
| 4 | - | 149.5 | - | - | 148.5 | |
| 5 | 6.76 (d, 8.1) | 116.3 | 149.5; 147.0; 127.8; 122.7 | 6.77 (d, 7.8) | 115.2 | |
| 6 | 6.95 (dd, 8.1;1.9) | 122.7 | 149.5; 115.2 | 6.95 (dd, 7.9; 1.9) | 121.7 | |
| 7 | 7.55 (d, 15.9) | 146.8 | 168.8; 122.7; 115.2 | 7.62 (d, 16.1) | 145.7 | |
| 8 | 6.27 (d, 15.9) | 115.2 | 168.8; 127.8 | 6.42 (d, 16.1) | 115.0 | |
| 9 | - | 168.8 | - | - | 167.8 | |
| Sucrose (2a) | α-H-1 | 5.38 (d, 3.8) | 93.4 | 105.4; 74.5 | 5.37 (d, 3.8) | 95.4 |
| 2 | 3.42 (dd, 9.8; 3.8) | 74.5 | 74.8 | 3.40 (dd, 9.8; 3.8) | 75.0 | |
| 3 | 3.70 (t, 9.5) | 74.8 | 71.3 | 3.68 (t, 9.6) | 76.4 | |
| 4 | 3.36 (t, 9.5) | 71.3 | 74.8; 71.6; 62.1 | 3.34 (t, 9.4) | 73.0 | |
| 5 | - | - | - | - | 76.1 | |
| 6 | - | - | - | 3.70 (dd, 7.9; 4.0) | 63.9 | |
| 1’ | 3.62 (d, 5.1) | 63.8 | 105.4; 79.2 | 3.58 (d, 12.3) | 65.7 | |
| 2’ | - | 105.4 | - | - | 107.1 | |
| β-H-3’ | 4.10 (d, 8.3) | 79.2 | 75.6; 63.8 | 4.08 (d, 8.2) | 81.0 | |
| 4’ | 4.0 (m) | 75.6 | 63.4 | 4.01 (t, 7.7) | 77.4 | |
| 5’ | 3.69-3.87 (m) | 83.9 | 83.9; 75.6 | 3.72-3.83 | 85.6 | |
| 6’ | - | 63.4 | - | 3.83-3.72 | 65.1 | |
| β-glucose (2b) | β-H-1 | 4.47 (d, 7.8) | 98.2 | - | 4.45 (d, 7.8) | 99.99 |
| 2 | 3.11 (d, 7.8) | 77.9 | - | - | 78.1 | |
| 3 | - | 74.6 | - | - | 79.8 | |
| 4 | - | 77.9 | - | - | 72.2 | |
| 5 | - | 74.6 | - | - | 79.9 | |
| 6 | - | - | - | - | 64.6 | |
| α-glucose (2b) | α-H-1 | 5.12 (d, 3.7) | 93.5 | - | 5.09 (d, 3.7 Hz) | 95.7 |
| 2 | 3.36 (d, 3.7) | 71.4 | - | - | - | |
| 3 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 4 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 5 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 6 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Threonine (3) | 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | - | - | - | 3.51 (d, 12.0) | - | |
| 3 | 4.29 (br, m) | - | - | 4.27 (m) | - | |
| 4 | 1.32 (d, 7.0) | 30.2 | - | 1.32 (d, 7.0) | - | |
| Fatty Acids (4) | 1 | 0.97 (t, 7.6) | 18.3 | 132.8 | 0.95 (t, 7.5) | - |
| 2, 11 | 2.1 (m) | 28.1 | 129.2; 30.8 | - | - | |
| -HC = CH- | 5.34 (m) | 129.3\72.0 | 26.6 | - | - | |
| 5, 8 | 2.81 (m) | 26.3 | 129.2; 44.1 | - | - | |
| 12-15 | 1.30 (br, d) | 30.5 | 30.5 | - | - | |
| 16 | 1.60 (m) | 26.1 | 30.5 | - | - | |
| 17 | 2.32 (m) | 35.2 | 174.8; 30.5; 26.1 | - | - | |
| 18 | - | 174.8 | - | - | - | |
| Arginine (5) | 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | 3.27 (m) | 71.4 | - | 3.25 | - | |
| 3 | 1.77 (m) | - | - | 1.77 | - | |
| 4 | 1.60 (m) | 26.0 | - | 1.59 | - | |
| 5 | 1.92 (m) | 38.7 | - | 1.91 | - | |
| 6 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Alanine (6) | 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 3 | 1.48 (d, 7.20) | - | - | 1.48 (d, 7.20) | - | |
| 3-hydorxybutyric acid (7) | 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 3 | 4.18 (brs) | - | - | 4.19 | - | |
| 4 | 1.21 (brs) | - | - | 1.20 | - | |
| Valine (8) | 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 3 | - | - | - | 2.27 (m) | - | |
| 4 | - | - | - | 0.99 (d) | - | |
| 5 | 1.03 (d, 2.7) | - | - | 1.04 (d) | - | |
| Trimethylamine (9) | 1 | 2.90 (s) | 40.2 | - | 2.89 (s) | - |
| Glutamic acid (10) | 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | 2.45 (m) | - | - | 2.37 (m) | - | |
| 3 | 2.0 (m) | - | - | - | - | |
| Fumaric acid (11) | 2,3 | 6.54 (s) | 120.9 | - | 6.52 (s) | - |
| Dihydroxy shikimate (12) | 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | 6.38 (s) | 115.4 | 127.8 | 6.39 (s) | - | |
| 3 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 4 | - | 127.8 | - | - | - | |
| 5 | 3.15-3.08 (m) | 71.1 | - | 3.07 (m) | - | |
| 6 | 2.66 (m) | 63.5 | 192.5 | 2.62 (m) | - | |
| 7 | - | 192.5 | - | - | - | |
| Choline (13) | 1 | 3.22 (s) N-(CH3)3 | 55.0 | 77.8; 55.0 | 3.21 (s) N-(CH3)3 | - |
| 2 | - | 77.8 | - | - | - | |
| 3 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Creatine (14) | - | 3.02 (s) N-CH3 | 43.9 | - | - | - |
| Berberine (15) | 1 | 7.63 (s) | 107.7 | 152.1; 149.9; 139.6; 131.8 | 7.45 (s) | 106.5 |
| 2 | - | 152.1 | - | - | 152 | |
| 2,3-OCH2O | 6.11 (s) | 104.7 | 152.1; 149.9 | 6.13 (s, -OCH3) | 103.6 | |
| 3 | - | 149.9 | - | - | 149.9 | |
| 4a | - | 121.8 | - | - | 121.9 | |
| 4 | 6.96 (s) | 110.7 | 152.1; 149.9; 121.8; 28.6 | 6.89 (s) | 109.3 | |
| 5 | 3.26 (t, J = 6.3 Hz) | 28.6 | 131.8; 121.8; 110.7; 58.3 | 3.26 (t, 5.6 Hz) | 28.2 | |
| 6 | 4.92 (t, J = 6.3 Hz) | 58.3 | 147.3; 139.6; 131.8; 28.6 | 4.95 (t, 5.6) | 57.1 | |
| 7 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 8a | - | 135.3 | - | - | 135.1 | |
| 8 | 9.74 (s) | 147.3 | 145.8; 139.6; 135.3; 58.3 | 9.78 (s) | 146.4 | |
| 9 | - | 145.8 | - | - | 145.7 | |
| H3CO-9 | 4.11 (s) | 58.8 | 152.0 | 4.12 (s, -OCH3) | 54.6 | |
| 10 | - | 152.0 | - | - | 152 | |
| H3CO-10 | 4.20 (s) | 63.6 | 145.8 | 4.35 (s, -OCH3) | 62.5 | |
| 11 | 8.11 (d, 9.1 Hz) | 129.3 | 145.8; 135.3 | 8.00 (d, 7.98 Hz) | 128 | |
| 12a | - | 123.3 | - | - | 123.3 | |
| 12 | 8.0 (d, 9.1 Hz) | 125.4 | 152.0; 123.3 | 7.95 (d, 7.98 Hz) | 124.5 | |
| 13 | 8.65 (s) | 122.7 | 139.6; 125.4; 123.3; 122.7 | 8.61 (s) | 121.5 | |
| 14a | - | 131.8 | - | - | 131.9 | |
| 14 | - | 139.6 | - | - | 139.6 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, S.; Badshah, G.; Da Ros Montes D’Oca, C.; Ramos Campos, F.; Nagata, N.; Khan, A.; de Fátima Costa Santos, M.; Barison, A. High-Resolution Magic Angle Spinning (HR-MAS) NMR-Based Fingerprints Determination in the Medicinal Plant Berberis laurina. Molecules 2020, 25, 3647. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163647
Ali S, Badshah G, Da Ros Montes D’Oca C, Ramos Campos F, Nagata N, Khan A, de Fátima Costa Santos M, Barison A. High-Resolution Magic Angle Spinning (HR-MAS) NMR-Based Fingerprints Determination in the Medicinal Plant Berberis laurina. Molecules. 2020; 25(16):3647. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163647
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Sher, Gul Badshah, Caroline Da Ros Montes D’Oca, Francinete Ramos Campos, Noemi Nagata, Ajmir Khan, Maria de Fátima Costa Santos, and Andersson Barison. 2020. "High-Resolution Magic Angle Spinning (HR-MAS) NMR-Based Fingerprints Determination in the Medicinal Plant Berberis laurina" Molecules 25, no. 16: 3647. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163647
APA StyleAli, S., Badshah, G., Da Ros Montes D’Oca, C., Ramos Campos, F., Nagata, N., Khan, A., de Fátima Costa Santos, M., & Barison, A. (2020). High-Resolution Magic Angle Spinning (HR-MAS) NMR-Based Fingerprints Determination in the Medicinal Plant Berberis laurina. Molecules, 25(16), 3647. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163647