Ethanolic Extract of Salvia hispanica L. Regulates Blood Pressure by Modulating the Expression of Genes Involved in BP-Regulatory Pathways
Abstract
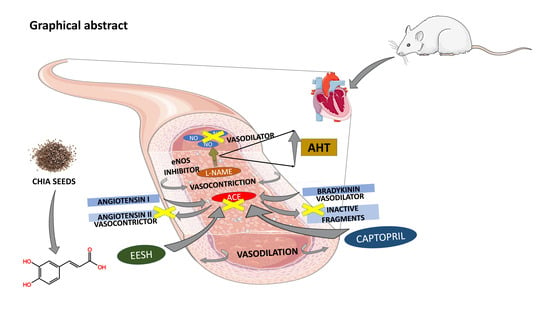
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Inhibitory Activity of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme In Vitro
2.2. Induction of Hypertension and Effect of Antihypertensive Treatments
2.3. Effect of Antihypertensive Treatments on Gene Expression
2.3.1. Ace Gene Expression
2.3.2. Agtr1a Gene Expression
2.3.3. Nos3 Gene Expression
2.3.4. Bdkrb2 Gene Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Origin and Characteristics of Chia (Salvia hispanica) Seeds
4.2. Preparation of Ethanolic Extracts of Salvia hispanica L. Seeds
4.3. Quantification of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Activity In Vitro
4.4. Hypertensive Animal Model
4.5. Identification of Sequences Encoding Ace, Agtr1a, Nos3, Bdkrb2 and Gapdh Genes
4.6. Gene Expression Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- James, P.; Oparil, S.; Carter, B.; Cushman, W.; Dennison-Himmelfarb, C.; Handler, J.; Lackland, D.; LeFevre, M.; MacKenzie, T.; Ogedegbe, O.; et al. Evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: Report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA 2014, 311, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joyner, M.; Wallin, B.; Charkoudian, N. Sex differences and blood pressure regulation in humans. Exp. Physiol. 2016, 101, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferini-Strambi, L.; Walters, A.; Sica, D. The relationship among restless legs syndrome (Willis–Ekbom Disease), hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and cerebrovascular disease. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 1051–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tetzner, A.; Gebolys, K.; Meinert, C.; Klein, S.; Uhlich, A.; Trebicka, J.; Villacañas, O.; Walther, T. G-Protein-coupled receptor MrgD is a receptor for angiotensin-(1-7) involving adenylyl cyclase, cAMP, and phosphokinase A. Hypertension 2016, 68, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soubrier, F.; Wei, L.; Hubert, C.; Clauser, E.; Alhenc-Gelas, F.; Corvol, P. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) gene structure and polymorphism: Relation to enzyme function and gene expression. In Cellular and Molecular Biology of the Renin-Angiotensin System; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 221–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, N.; Head, G.; Kaye, D. Say NO to obesity-related hypertension: Role of the l-arginine–nitric oxide pathway. Hypertension 2016, 67, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Heran, B.; Wright, J. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors versus angiotensin receptor blockers for primary hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD009096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessy, H.; Wang, K.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, M.; Hu, Z. Enrichment and biotransformation of phenolic compounds from litchi pericarps with angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition activity. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 87, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knez Hrnčič, M.; Ivanovski, M.; Cör, D.; Knez, Ž. Chia seeds (Salvia hispanica L.): An Overview-phytochemical profile, isolation methods, and application. Molecules 2020, 25, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ullah, R.; Nadeem, M.; Khalique, A.; Imran, M.; Mehmood, S.; Javid, A.; Hussain, J. Nutritional and therapeutic perspectives of Chia (Salvia hispanica L.): A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, S.; Bains, K. Chia (Salvia hispanica L.)–a rediscovered ancient grain, from Aztecs to food laboratories. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 50, 463–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan-Zapata, I.; Arana-Argáez, V.E.; Torres-Romero, J.C.; Segura-Campos, M.R. Anti-inflammatory effects of the protein hydrolysate and peptide fractions isolated from Salvia hispanica L. seeds. Food Agric. Immunol. 2019, 30, 786–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Güzel, S.; Ülger, M.; Yusuf, Ö.Z.A.Y. Antimicrobial and antiproliferative activities of Chia (Salvia hispanica L.) seeds. Int. J. Second. Metab. 2020, 7, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, B.; Amato, M.; Lanzotti, V. Chia seeds products: An overview. Phytochem. Rev. 2017, 16, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinek, K.; Krejpcio, Z. Chia seeds (Salvia hispanica): Health promoting properties and therapeutic applications-a review. Rocz. Panstw. Zakł. Hig. 2017, 68, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Peiretti, P.; Gai, F. Fatty acid and nutritive quality of chia (Salvia hispanica L.) seeds and plant during growth. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2009, 148, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Caudillo, E.; Tecante, A.; Valdivia-López, M. Dietary fibre content and antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds present in Mexican chia (Salvia hispanica L.) seeds. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, A. Identificación de la actividad inhibitoria presente en extractos de semilla de chía (Salvia hispanica L.) sobre la enzima convertidora de angiotensina. Master’s Thesis, Autonomous University of Nuevo Leon, Nuevo León, Mexico, September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Eriz, G.; Sanhueza, V.; Roeckel, M.; Fernández, K. Inhibition of the angiotensin-converting enzyme by grape seed and skin proanthocyanidins extracted from Vitis vinifera L. cv. País. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, V. Efecto hipotensor e inhibición de la actividad de la enzima convertidora de angiotensina I de extractos de semillas de Salvia hispanica L. in vitro e in vivo. Master’s Thesis, Autonomous University of Nuevo Leon, Nuevo León, Mexico, December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Steinkamp-Fenske, K.; Bollinger, L.; Völler, N.; Xu, H.; Yao, Y.; Bauer, R.; Förstermann, U.; Li, H. Ursolic acid from the chinese herb danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza L.) upregulates eNOS and downregulates Nox4 expression in human endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2007, 195, e104–e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Campos, M.R.; Chel-Guerrero, L.A.; Rosado-Rubio, J.G.; Betancur-Ancona, D.A. Biofunctionality of Chia (Salvia hispanica L.) Protein Hydrolysates. In Functional Properties of Traditional Foods; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 12, pp. 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, M.; Lucas-Gonzalez, R.; Sayas-Barberá, E.; Fernández-López, J.; Pérez-Álvarez, J.; Viuda-Martos, M. Bioaccessibility of Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity of Chia (Salvia hispanica L.) Seeds. Plant. Foods Hum. Nutr. 2016, 73, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulios, E.; Giaginis, C.; Vasios, G.K. Current State of the Art on the Antioxidant Activity of Sage (Salvia spp.) and Its Bioactive Components. Planta Med. 2020, 86, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, B.F.; Walchc, S.G.; Tinzoh, L.N.; Stühlinger, W.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Rapid UHPLC determination of polyphenols in aqueous infusions of Salvia officinalis L. (sage tea). J. Chromatogr. B. Biomed. Appl. 2011, 879, 2459–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Ferrer, E.; Hernández Badillo, F.; González-Cortazar, M.; Tortoriello, J.; Herrera-Ruiz, M. Antihypertensive activity of Salvia elegans Vahl. (Lamiaceae): ACE inhibition and angiotensin II antagonism. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 130, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, M.; Gardouh, A.; Abogresha, N.; Gad, S. Factorial design, formulation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of rapid orally disintegrating tablets prepared by sublimation technique using captopril as a model drug. J. Drug. Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Vital, D.; González, E.; Mendoza, S.; Loarca-Piña, G. Peptides present in the non-digestible fraction of common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) inhibit the angiotensin-I converting enzyme by interacting with its catalytic cavity independent of their antioxidant capacity. Food Funct. 2012, 6, 1470–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puga, A.; López-Oliva, S.; Trives, C.; Partearroyo, T.; Varela-Moreiras, G. Effects of Drugs and Excipients on Hydration Status. Nutrients 2019, 11, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arenas-Carvajal, R.; Pachón-Gómez, E.; Méndez-Callejas, G.; Guzmán-Avendaño, A. Estudio del efecto inhibitorio de extractos de Salvia scutellarioides sobre la actividad de la enzima convertidora de angiotensina. Univ. Sci. 2009, 14, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ryu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, P.; Li, C.; Zhou, C.; Yang, P.; Hong, P.; Qian, Z. Comparison of an angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) with captopril: Inhibition kinetics, in vivo effect, simulated gastrointestinal digestion and a molecular docking study. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 2019, 100, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Miao, A. Cryptotanshinone inhibits endothelin-1 expression and stimulates nitric oxide production in human vascular endothelial cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1760, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Hara, K.; Watanabe, S.; Higashi, T.; Matsuoka, H. Effect of imidapril on myocardial remodeling in L-NAME-induced hypertensive rats is associated with gene expression of NOS and ACE mRNA. Am. J. Hypertens. 2000, 13, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Gennaro, V.; Rigamonti, A.; Fioretti, S.; Bonomo, S.; Manfredi, B.; Ferrario, P.; Bianchi, M.; Berti, F.; Muller, E.; Rossoni, G. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin AT1-receptor antagonism equally improve endothelial vasodilator function in L-NAME-induced hypertensive rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 516, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.; Dirsch, V. Modulation of endothelial nitric oxide by plant-derived products. Nitric Oxide 2009, 21, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallerath, T.; Li, H.; Gödtel-Ambrust, U.; Schwarz, P.; Förstermann, U. A blend of polyphenolic compounds explains the stimulatory effect of red wine on human endothelial NO synthase. Nitric Oxide 2005, 12, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, R.; Siragy, H. Newly recognized components of the renin-angiotensin system: Potential roles in cardiovascular and renal regulation. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hara, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Watanabe, S.; Tsubokou, Y.; Matsuoka, H. Effects of quinapril on expression of eNOS, ACE, and AT1 receptor in deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertensive rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 2001, 14, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marketou, M.; Kontaraki, J.; Zacharis, E.; Parthenakis, F.; Maragkoudakis, S.; Gavras, I.; Gavras, H.; Vardas, P. Differential gene expression of bradykinin receptors 1 and 2 in peripheral monocytes from patients with essential hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2014, 28, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, A.; Wotherspoon, G.; McNair, K.; Hudson, L.; Patel, S.; Gentry, C.; Winter, J. Regulation and function of spinal and peripheral neuronal B1 bradykinin receptor in inflammatory mechanical hyperalgesia. Pain 2003, 104, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, R.; Cabrini, D.; Ferreira, J.; Fernandes, E.; Mori, M.; Pesquero, B.; Bader, M.; Avellar, M.; Campos, M.; Calixto, B. Bradykinin B1 receptor expression induced by tissue damage in the rat portal vein a critical role for mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López, A.; Ortega, A. Caracterización de semilla de chía (Salvia hispanica L.): Cuantificación parcial de compuestos fenólicos y capacidad de inhibición de la enzima convertidora de angiotensina I in vitro. (Tesis de licenciatura) Master’s Thesis, Facultad de Salud Pública y Nutrición, Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León, Nuevo León, México, October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Turck, D.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.; Kearney, J.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.; Naska, A.; Pelaez, C.; et al. Safety of chia seeds (Salvia hispanica L.) as a novel food for extended uses pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Aluko, R.; Muir, A. Improved method for direct high-performance liquid chromatography assay of angiotensin-converting enzyme-catalyzed reactions. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 950, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, V.; Mohan, V.; Bodhankar, S. Antihypertensive and cardioprotective effects of the Lagenaria siceraria fruit in NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) induced hypertensive rats. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 50, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, M.; Contreras, M.; Recio, I.; Aleixandre, A. ACE-inhibitory and antihypertensive properties of a bovine casein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Singh, A.K.; Pandey, P.; Chandra, S.; Singh, K.A.; Gambhir, I.S. Molecular genetics of essential hypertension. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2016, 38, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botzer, A.; Grossman, E.; Moult, J.; Unger, R. A system view and analysis of essential hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, F.; Hu, J.; Wang, H.; Tan, N.; Li, S.; Wang, X. Pathway-based gene-gene interaction network modelling to predict potential biomarkers of essential hypertension. BioSystems 2018, 172, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |

| Groups | Pre-Treatment SBP (mmHg) | Post-Treatment SBP (mmHg) |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy | 100.0 ± 5.4 ab | 86.7 ± 9.6 be |
| L-NAME | 310.7 ± 27.3 cd | 414.1 ± 7.1 f |
| Captopril | 328.2 ± 26.2 cd | 327.8 ± 8.7 dh |
| EESH | 318.3 ± 22.1 cd | 317.7 ± 8.1 dh |
| Gene | NCBI-RS | Primer Sequence (5′→3′) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Amplicon Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ace | NM_012544.1 | Fw: CAGGAGTTTGCAGAGGTCTGGGGC Rv: CCAGCAGATGAGCGGGAATAGGACC | 62 | 577 |
| Agtr1a | NM_030985.4 | Fw: CACCTATGTAAGATCGCTTCGGCC Rv: GGGTATAGCTGGTGAGAATGATAAGG | 60 | 355 |
| Nos3 | NM_021838.2 | Fw: GACCCTCCGCCATCCACAGAGCCTG Rv: GCACCGGGTCTCCTGCCTTGAGTTGG | 64 | 514 |
| Bdkrb2 | NM_001270713.2 | Fw: GCTCATAACGGGACCTTTTCAGAGG Rv: CAGTGGCCTTCTTCTCCGTCTGG | 63 | 700 |
| Gapdh | NM_017008.4 | Fw: CCCACGGCAAGTTCAACGGC Rv: CCATGTAGGCCATGAGGTCCACC | 64 | 840 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arredondo-Mendoza, G.I.; Jiménez-Salas, Z.; Garza, F.J.G.-d.l.; Solís-Pérez, E.; López-Cabanillas-Lomelí, M.; González-Martínez, B.E.; Campos-Góngora, E. Ethanolic Extract of Salvia hispanica L. Regulates Blood Pressure by Modulating the Expression of Genes Involved in BP-Regulatory Pathways. Molecules 2020, 25, 3875. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173875
Arredondo-Mendoza GI, Jiménez-Salas Z, Garza FJG-dl, Solís-Pérez E, López-Cabanillas-Lomelí M, González-Martínez BE, Campos-Góngora E. Ethanolic Extract of Salvia hispanica L. Regulates Blood Pressure by Modulating the Expression of Genes Involved in BP-Regulatory Pathways. Molecules. 2020; 25(17):3875. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173875
Chicago/Turabian StyleArredondo-Mendoza, Gerardo I., Zacarías Jiménez-Salas, Francisco Javier Guzmán-de la Garza, Elizabeth Solís-Pérez, Manuel López-Cabanillas-Lomelí, Blanca Edelia González-Martínez, and Eduardo Campos-Góngora. 2020. "Ethanolic Extract of Salvia hispanica L. Regulates Blood Pressure by Modulating the Expression of Genes Involved in BP-Regulatory Pathways" Molecules 25, no. 17: 3875. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173875
APA StyleArredondo-Mendoza, G. I., Jiménez-Salas, Z., Garza, F. J. G. -d. l., Solís-Pérez, E., López-Cabanillas-Lomelí, M., González-Martínez, B. E., & Campos-Góngora, E. (2020). Ethanolic Extract of Salvia hispanica L. Regulates Blood Pressure by Modulating the Expression of Genes Involved in BP-Regulatory Pathways. Molecules, 25(17), 3875. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173875