Identification of Anti-Inflammatory Compounds from Hawaiian Noni (Morinda citrifolia L.) Fruit Juice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
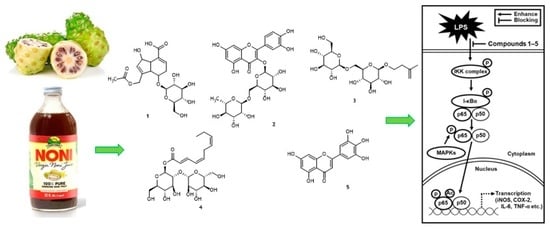
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Bioactive Compounds from Noni Fruit Juice
2.2. NF-κB Inhibitory Activity of Compounds 1–5
2.3. Effects of Compounds 1–5 on Nitric Oxide Production
2.4. Effects of Compounds 1–5 on the LPS-Induced Expression of IKKα/β, I-κBα, and NF-κB p65 in RAW 264.7 Mouse Macrophages
2.5. Effects of Compounds 1–5 on the LPS-Induced Expression of iNOS and COX-2 in RAW 264.7 Mouse Macrophages
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Noni Juices
3.3. HP20 Open Column, Preparative, and Semi-Preparative HPLC Purification of Noni Fruit Juice Extract
3.4. NF-κB Assay
3.5. Cell Culture
3.6. Measurement of Cell Viability
3.7. Measurement of NO Production
3.8. Western Blot Analysis
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pandy, V.; Narasingam, M.; Mohamed, Z. Antipsychotic-like activity of Noni (Morinda citrifolia Linn.) in mice. BMC Complement. Altern Med. 2012, 12, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McClatchey, W. From Polynesian healers to health food stores: Changing ethnopharmacology of Morinda citrifolia. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potterat, O.; Hamburger, M. Morinda citrifolia (Noni) fruit-phytochemistry, pharmacology, safety. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samoylenko, V.; Zhao, J.; Dunbar, D.C.; Khan, I.A.; Rushing, J.W.; Muhammad, I. New constituents from noni (Morinda citrifolia) fruit juice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6398–6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.-Y.; West, B.J.; Jensen, C.J.; Nowicki, D.; Su, C.; Palu, A.K.; Anderson, G. Morinda citrifolia (Noni): A literature review and recent advances in Noni research. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2002, 23, 1127–1141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nelson, S.C.; Elevitch, C.R. Noni: The Complete Guide for Consumers and Growers; Permanent Agriculture Resources: Holualoa, HI, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Albensi, B.C. What is nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) doing in and to the mitochondrion? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.H.; Hong, J.T. Roles of NF-κB in cancer and inflammatory diseases and their therapeutic approaches. Cells 2016, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escarcega, R.; Fuentes-Alexandro, S.; Garcia-Carrasco, M.; Gatica, A.; Zamora, A. The transcription factor nuclear factor-kappa B and cancer. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 19, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.K. Are immune responses pivotal to cancer patient‘s long term survival? Two clinical case-study reports on the effects of Morinda citrifolia (Noni). Hawaii Med. J. 2004, 63, 182–184. [Google Scholar]
- Olaku, O.; White, J.D. Herbal therapy use by cancer patients: A literature review on case reports. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Senger, D.R.; Li, D.; Jaminet, S.-C.; Cao, S. Activation of the Nrf2 cell defense pathway by ancient foods: Disease prevention by important molecules and microbes lost from the modern western diet. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manavalan, A.; Qader, M.; Wu, X.; Cao, S. Nrf2 activation by Morinda citrifolia L. (Noni) fruit juices. World J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.-S.; Xu, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Manavalan, A.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Cao, S. Compound Analysis of Jing Liqueur and nrf2 Activation by Jing Liqueur—One of the Most Popular Beverages in China. Beverages 2019, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.S.; Roh, H.S.; Baek, K.H.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; So, H.M.; Moon, E.; Pang, C.; Jang, T.S.; Kim, K.H. Bioactivity-guided isolation of ginsenosides from Korean Red Ginseng with cytotoxic activity against human lung adenocarcinoma cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Lee, D.S.; Jung, K.; Hwang, G.S.; Lee, H.L.; Yamabe, N.; Lee, H.J.; Eom, D.W.; Kim, K.H.; Kang, K.S. Protective effect of ginsenoside Rb1 against tacrolimus-induced apoptosis in renal proximal tubular LLC-PK1 cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzakou, O.; Mylonas, P.; Vagias, C.; Petrakis, P.V. Iridoid glucosides with insecticidal activity from Galium melanantherum. Z. Naturforsch. Sect. C J. Biosci. 2007, 62, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, J.G.; Lankin, D.C.; Chen, S.N.; Pauli, G.F. Complete 1H NMR spectral analysis of ten chemical markers of Ginkgo biloba. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2012, 50, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Kikuzaki, H.; Jin, Y.; Nakatani, N.; Zhu, N.; Csiszar, K.; Boyd, C.; Rosen, R.T.; Ghai, G.; Ho, C.-T. Novel glycosides from noni (Morinda citrifolia). J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1182–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.-X.; Zhang, H.-C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.-M.; Liu, L. Two new glycosides from the fruits of Morinda citrifolia L. Molecules 2012, 17, 12651–12656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lal, C.; Sharma, M.C.; Shakyawar, D.B.; Raja, A.; Sharma, K.K.; Pareek, P.K. Natural Dye constituents from rind of Punica granatum and its application on Pashmina fabrics. Arch. Appl. Sci. Res 2011, 3, 350–357. [Google Scholar]
- Carrillo, J.L.M.; García, F.P.C.; Coronado, O.G.; García, M.A.M.; Cordero, J.F.C. Physiology and pathology of innate immune response against pathogens. In Physiology and Pathology of Immunology; InTech: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ruttimann, J. Macrophages and nitric oxide: A deadly combination. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Al-Omran, A.; Parvathy, S. Role of nitric oxide in inflammatory diseases. Inflammopharmacology 2007, 15, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, G.; Pagano, F.; Adesso, S.; Sommella, E.; Ostacolo, C.; Manfra, M.; Chieppa, M.; Sala, M.; Russo, M.; Marzocco, S. Bioavailable Citrus sinensis extract: Polyphenolic composition and biological activity. Molecules 2017, 22, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, S.Y.; Woo, Y.; Hyun, J.; Yong, Y.; Koh, D.; Lee, Y.H.; Lim, Y. Relationship between the structures of flavonoids and their NF-κB-dependent transcriptional activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 6036–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, É.S.; de Oliveira, D.; Hotza, D. Properties and applications of Morinda citrifolia (noni): A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 883–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dussossoy, E.; Bichon, F.; Bony, E.; Portet, K.; Brat, P.; Vaillant, F.; Michel, A.; Poucheret, P. Pulmonary anti-inflammatory effects and spasmolytic properties of Costa Rican noni juice (Morinda citrifolia L.). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 192, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussossoy, E.; Bony, E.; Michel, A.; Boudard, F.; Giaimis, J.; Brat, P.; Vaillant, F. Anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects of the Morinda citrifolia fruit (Noni). Acta Hortic. 2014, 1040, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Lu, X.; Wei, T.; Dong, Y.; Cai, Z.; Tang, L.; Liu, M. Asperuloside and asperulosidic acid exert an anti-inflammatory effect via suppression of the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.-J.; Lee, S.Y.; Ha, H.J.; Cha, S.H.; Lee, S.K.; Hur, S.J. Rutin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in macrophage cells. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2015, 3, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geraets, L.; Haegens, A.; Brauers, K.; Haydock, J.A.; Vernooy, J.H.; Wouters, E.F.; Bast, A.; Hageman, G.J. Inhibition of LPS-induced pulmonary inflammation by specific flavonoids. Biochem. Biophys Res. Commun. 2009, 382, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi, E.; Rothwarf, D.M.; Delhase, M.; Hayakawa, M.; Karin, M. The IκB kinase complex (IKK) contains two kinase subunits, IKKα and IKKβ, necessary for IκB phosphorylation and NF-κB activation. Cell 1997, 91, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lousse, J.-C.; Van Langendonckt, A.; González-Ramos, R.; Defrère, S.; Renkin, E.; Donnez, J. Increased activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) in isolated peritoneal macrophages of patients with endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2008, 90, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Proinflammatory cytokines. Chest 2000, 118, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.M.; Lee, E.K.; Gong, S.Y.; Sohng, J.K.; Kang, Y.J.; Jung, H.J. Sparassis crispa exerts anti-inflammatory activity via suppression of TLR-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in LPS-induced RAW264. 7 macrophage cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 231, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Palu, A.K.; West, B.J.; Su, C.X.; Zhou, B.-N.; Jensen, J.C. Lipoxygenase inhibitory constituents of the fruits of noni (Morinda citrifolia) collected in Tahiti. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.-F.; Hu, P.-F.; Xiong, Y.; Bao, J.-P.; Qian, J.; Wu, L.-D. Tricetin protects rat chondrocytes against IL-1β-induced inflammation and apoptosis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kondratyuk, T.P.; Park, E.-J.; Yu, R.; Van Breemen, R.B.; Asolkar, R.N.; Murphy, B.T.; Fenical, W.; Pezzuto, J.M. Novel marine phenazines as potential cancer chemopreventive and anti-inflammatory agents. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kee, J.-Y.; Hong, S.-H. Ginsenoside Rg3 suppresses mast cell–mediated allergic inflammation via mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.; Yu, J.S.; Huang, P.; Qader, M.; Manavalan, A.; Wu, X.; Kim, J.-C.; Pang, C.; Cao, S.; Kang, K.S.; et al. Identification of Anti-Inflammatory Compounds from Hawaiian Noni (Morinda citrifolia L.) Fruit Juice. Molecules 2020, 25, 4968. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25214968
Lee D, Yu JS, Huang P, Qader M, Manavalan A, Wu X, Kim J-C, Pang C, Cao S, Kang KS, et al. Identification of Anti-Inflammatory Compounds from Hawaiian Noni (Morinda citrifolia L.) Fruit Juice. Molecules. 2020; 25(21):4968. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25214968
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Dahae, Jae Sik Yu, Peng Huang, Mallique Qader, Arulmani Manavalan, Xiaohua Wu, Jin-Chul Kim, Changhyun Pang, Shugeng Cao, Ki Sung Kang, and et al. 2020. "Identification of Anti-Inflammatory Compounds from Hawaiian Noni (Morinda citrifolia L.) Fruit Juice" Molecules 25, no. 21: 4968. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25214968
APA StyleLee, D., Yu, J. S., Huang, P., Qader, M., Manavalan, A., Wu, X., Kim, J. -C., Pang, C., Cao, S., Kang, K. S., & Kim, K. H. (2020). Identification of Anti-Inflammatory Compounds from Hawaiian Noni (Morinda citrifolia L.) Fruit Juice. Molecules, 25(21), 4968. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25214968