In Silico Analysis and In Vitro Characterization of the Bioactive Profile of Three Novel Peptides Identified from 19 kDa α-Zein Sequences of Maize
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of the Synthesized Peptides and In Silico Prediction of Bioactivity
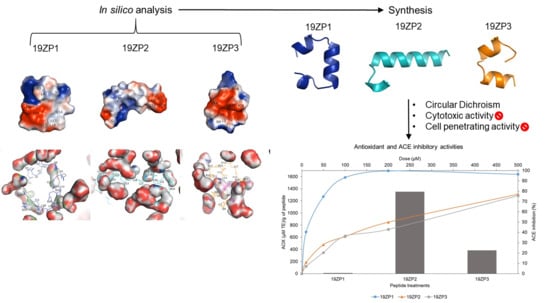
2.2. Predicted Peptide Structural Characteristics and Peptide-Solvent Interactions
2.3. Peptide Structure
2.4. Cytotoxicity
2.5. Cell Penetration of Peptides
2.6. Antioxidant Activity
2.7. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-Inhibitory Activity
3. Discussion
3.1. Peptide Properties
3.2. In Silico Analysis
3.3. Peptide Cytotoxicity and Cell-Penetrating Capacity
3.4. Peptide Antioxidant Activity
3.5. Peptide ACE Inhibitory Activity
3.6. Coherence between In Silico and Experimental Bioactivity Data
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Peptide Design
4.3. In Silico Prediction of Peptide Bioactivities: Simulation of Structural Changes and Peptide–Solvent Interactions
4.4. Peptide Synthesis and Purification
4.5. Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
4.6. Cell Culture and Cell Viability Assay
4.7. Cellular Uptake Assay
4.8. Antioxidant Activity Assay
4.9. ACE Inhibition Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sánchez, A.; Vázquez, A. Bioactive peptides: A review. Food Qual. Saf. 2017, 1, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marqus, S.; Pirogova, E.; Piva, T.J. Evaluation of the use of therapeutic peptides for cancer treatment. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Craik, D.J.; Fairlie, D.P.; Liras, S.; Price, D. The future of peptide-based drugs. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 81, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Gómez, J.L.; Castorena-Torres, F.; Preciado-Ortiz, R.E.; García-Lara, S. Anti-cancer activity of maize bioactive peptides. Front. Chem. 2017, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrelli, A.; Tornesello, A.L.; Tornesello, M.L.; Buonaguro, F.M. Cell penetrating peptides as molecular carriers for anti-cancer agents. Molecules 2018, 23, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heitz, F.; Morris, M.C.; Divita, G. Twenty years of cell-penetrating peptides: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutics. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lobo, V.; Patil, A.; Phatak, A.; Chandra, N. Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daliri, E.B.; Oh, D.H.; Lee, B.H. Bioactive peptides. Foods 2017, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagani, S.; Kapil, V.; Lobo, M.D. Hypertension. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018, 46, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; He, H.; Hou, T. A comprehensive review of corn protein-derived bioactive peptides: Production, characterization, bioactivities, and transport pathways. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mäde, V.; Els-Heindl, S.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G. Automated solid-phase peptide synthesis to obtain therapeutic peptides. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 1197–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daliri, E.B.M.; Lee, B.H.; Oh, D.H. Current trends and perspectives of bioactive peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 2273–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Guha, S.; Majumder, K. Food-derived bioactive peptides in human health: Challenges and opportunities. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ortiz-Martinez, M.; Winkler, R.; García-Lara, S. Preventive and therapeutic potential of peptides from cereals against cancer. J. Proteom. 2014, 111, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Yu, W.; Liu, Z.; Wu, M.; Wang, J. Induction of apoptosis in cervix neoplasms hela cells by a rapeseed peptide hydrolysate fraction. J. Food Biochem. 2011, 35, 1283–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Martinez, M.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E.; García-Lara, S.; Aguilar, O.; Lopez-Castillo, L.M.; Otero-Pappatheodorou, J.T. Antiproliferative effect of peptide fractions isolated from a quality protein maize, a white hybrid maize, and their derived peptides on hepatocarcinoma human HepG2 cells. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 34, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Ramírez, M.d.C.; Ramón-Gallegos, E.; Mora-Escobedo, R.; Torres-Torres, N. A peptide fraction from germinated soybean protein down-regulates PTTG1 and TOP2A mRNA expression, inducing apoptosis in cervical cancer cells. J. Exp. Ther. Oncol. 2012, 9, 255–263. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.H.; Sun, J.; He, H.; Dong, H.W.; Li, J.T. Antihypertensive effect of corn peptides, produced by a continuous production in enzymatic membrane reactor, in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, B.; Xiong, Y.L. Antioxidant activity of zein hydrolysates in a liposome system and the possible mode of action. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6059–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Chalamaiah, M.; Ren, X.; Ma, H.; Wu, J. Identification of new anti-inflammatory peptides from zein hydrolysate after simulated gastrointestinal digestion and transport in Caco-2 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Zhuang, H. Evaluation of antioxidant activities of zein protein fractions. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, C2174–C2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, W. Isolation and identification of a novel peptide from zein with antioxidant and antihypertensive activities. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3799–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.T.; Zhang, J.L.; He, H.; Ma, Z.L.; Nie, Z.K.; Wang, Z.Z.; Xu, X.G. Apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells induced by corn peptides and its anti-tumor efficacy in H22 tumor bearing mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 51, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, D.X.; Liu, X.L.; Zheng, X.Q.; Wang, X.J.; He, J.F. Preparation of antioxidative corn protein hydrolysates, purification and evaluation of three novel corn antioxidant peptides. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Xing, L. Preparation of active corn peptides from zein through double enzymes immobilized with calcium alginate-chitosan beads. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 1682–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Hu, J.; Ma, H.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Yu, X.; Owusu, J.; Ma, H.; Qin, X. Antioxidant peptides from corn gluten meal: Orthogonal design evaluation. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Tang, N.; Yuan, Y. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from corn gluten meal. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1810–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Gómez, J.L.; Ortíz-Martínez, M.; Aguilar, O.; García-Lara, S.; Castorena-Torres, F. Antioxidant activity of zein hydrolysates from Zea species and their cytotoxic effects in a hepatic cell culture. Molecules 2018, 23, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puchalska, P.; Luisa Marina, M.; Concepción García, M. Development of a high-performance liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization-quadrupole-time-of-flight-mass spectrometry methodology for the determination of three highly antihypertensive peptides in maize crops. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1285, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Ma, H.; Ding, Q.; Lin, L.; Yu, X.; Luo, L.; Dai, C.; Yagoub, A.E.-G.A. Ultrasonic pretreatment of corn gluten meal proteins and neutrase: Effect on protein conformation and preparation of ACE (angiotensin converting enzyme) inhibitory peptides. Food Bioprod. Process. 2013, 91, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innovagen AB Peptide Property Calculator. Available online: https://pepcalc.com/ (accessed on 1 September 2019).
- Cell Penetrating Peptides. Available online: http://bioware.ucd.ie/~compass/biowareweb/Server_pages/cpppred.php (accessed on 1 November 2020).
- A Sequence-Based Tool for Identifying Anticancer Peptides. Available online: http://lin-group.cn/server/iACP (accessed on 1 November 2020).
- Antioxidant and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibition. Available online: http://www.uwm.edu.pl/biochemia/index.php/en/bi (accessed on 1 November 2020).
- Neundorf, I.; Rennert, R.; Hoyer, J.; Schramm, F.; Löbner, K.; Kitanovic, I.; Wölfl, S. Fusion of a short HA2-derived peptide sequence to cell-penetrating peptides improves cytosolic uptake, but enhances cytotoxic activity. Pharmaceuticals 2009, 2, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klimpel, A.; Neundorf, I. Bifunctional peptide hybrids targeting the matrix of mitochondria. J. Control. Release 2018, 291, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avci, F.G.; Akbulut, B.S.; Ozkirimli, E. Membrane active peptides and their biophysical characterization. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fanghänel, S.; Wadhwani, P.; Strandberg, E.; Verdurmen, W.P.R.; Bürck, J.; Ehni, S.; Mykhailiuk, P.K.; Afonin, S.; Gerthsen, D.; Komarov, I.V.; et al. Structure analysis and conformational transitions of the cell penetrating peptide transportan 10 in the membrane-bound state. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Momany, F.A.; Sessa, D.J.; Lawton, J.W.; Selling, G.W.; Hamaker, S.A.; Willett, J.L. Structural characterization of α-zein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argos, P.; Pedersen, K.; Marks, M.D.; Larkins, B. A structural model for maize zein proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 9984–9990. [Google Scholar]
- Cabra, V.; Arreguin, R.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R.; Farres, A. Effect of temperature and pH on the secondary structure and processes of oligomerization of 19 kDa alpha-zein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1764, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronewold, A.; Horn, M.; Neundorf, I. Design and biological characterization of novel cell-penetrating peptides preferentially targeting cell nuclei and subnuclear regions. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 1378–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wender, P.A.; Mitchell, D.J.; Pattabiraman, K.; Pelkey, E.T.; Steinman, L.; Rothbard, J.B. The design, synthesis, and evaluation of molecules that enable or enhance cellular uptake: Peptoid molecular transporters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13003–13008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolhassani, A. Potential efficacy of cell-penetrating peptides for nucleic acid and drug delivery in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Rev. Cancer 2011, 1816, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, A.; Thomas, I.; Schmauck, J.; Giernoth, R.; Schulze, A.; Neundorf, I. Electron beam immobilization of novel antimicrobial, short peptide motifs leads to membrane surfaces with promising antibacterial properties. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gronewold, A.; Horn, M.; Ranđelović, I.; Tóvári, J.; Muñoz Vázquez, S.; Schomäcker, K.; Neundorf, I. Characterization of a cell-penetrating peptide with potential anticancer activity. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidi, S.; Deratani, A.; Belleville, M.-P.; Ben Amar, R. Antioxidant properties of peptide fractions from tuna dark muscle protein by-product hydrolysate produced by membrane fractionation process. Food Res. Int. 2014, 65, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfranceschi, G.L.; Gianfranceschi, G.; Quassinti, L.; Bramucci, M. Biochemical requirements of bioactive peptides for nutraceutical efficacy. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 47, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Cheryan, M. Zein: The industrial protein from corn. Ind. Crops Prod. 2001, 13, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canabady-Rochelle, L.L.S.; Harscoat-Schiavo, C.; Kessler, V.; Aymes, A.; Fournier, F.; Girardet, J.M. Determination of reducing power and metal chelating ability of antioxidant peptides: Revisited methods. Food Chem. 2015, 183, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgih, A.T.; He, R.; Malomo, S.; Offengenden, M.; Wu, J.; Aluko, R.E. Structural and functional characterization of hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) protein-derived antioxidant and antihypertensive peptides. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 6, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milletti, F. Cell-penetrating peptides: Classes, origin, and current landscape. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derakhshankhah, H.; Jafari, S. Cell penetrating peptides: A concise review with emphasis on biomedical applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, G.M. Endocytosis. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK9831/ (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- Zhou, K.; Sun, S.; Canning, C. Production and functional characterisation of antioxidative hydrolysates from corn protein via enzymatic hydrolysis and ultrafiltration. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Martinez, M.; Otero-Pappatheodorou, J.T.; Serna-Saldívar, S.O.; García-Lara, S. Antioxidant activity and characterization of protein fractions and hydrolysates from normal and quality protein maize kernels. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 76, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Rodríguez, A.; Osuna-Gallardo, E.I.; Cabrera-Chávez, F.; Milán-Carrillo, J.; Reyes-Moreno, C.; Milán-Noris, E.M.; Cuevas-Rodríguez, E.O.; Mora-Rochín, S. Evaluation of the in vitro and in vivo antihypertensive effect and antioxidant activity of blue corn hydrolysates derived from wet-milling. Biotecnia 2020, 22, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Dai, C.; Li, Z.; Ma, H. Antioxidative activities and peptide compositions of corn protein hydrolysates pretreated by different ultrasonic methods. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2015, 3, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ding, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Ma, S.; Liu, J. Intracellular ROS scavenging and antioxidant enzyme regulating capacities of corn gluten meal-derived antioxidant peptides in HepG2 cells. Food Res. Int. 2016, 90, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tao, G.; Liu, P.; Liu, J. Peptide with angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity from hydrolyzed corn gluten meal. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 7891–7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Chen, L.; Liang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Cai, M.; Li, Y. Pilot-scale production of low molecular weight peptides from corn wet milling byproducts and the antihypertensive effects in vivo and in vitro. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parris, N.; Moreau, R.A.; Johnston, D.B.; Dickey, L.C.; Aluko, R.E. Angiotensin I converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides from commercial wet- and dry-milled corn germ. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 2620–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, S.; Suzuki, K.; Funatsu, G. Isolation from α-zein of thermolysin peptides with angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1996, 60, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, K.; Wu, B.; Wu, P.; Duan, Y.; Ma, H. Production of ACE inhibitory peptides from corn germ meal by an enzymatic membrane reactor with a novel gradient diafiltration feeding working-mode and in vivo evaluation of antihypertensive effect. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, S.; Miyoshi, S.; Tanaka, H. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors derived from Ficus carica. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1989, 53, 2763–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyoshi, S.; Ishikawa, H.; Kaneko, T.; Fukui, F.; Tanaka, H.; Maruyama, S. Structures and activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in an α-zein hydrolysate. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1991, 55, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suetsuna, K.; Chen, J.R. Identification of antihypertensive peptides from peptic digest of two microalgae, Chlorella vulgaris and Spirulina platensis. Mar. Biotechnol. 2001, 3, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Platerink, C.J.; Janssen, H.G.; Haverkamp, J. Application of at-line two-dimensional liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry for identification of small hydrophilic angiotensin I-inhibiting peptides in milk hydrolysates. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Feng, F.; Shan, W. A novel angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from the milk casein: Virtual screening and docking studies. Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Han, L.; Chen, L. In vitro antioxidant activity of protein hydrolysates prepared from corn gluten meal. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2008, 88, 1660–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.C.; Li, J.T.; He, H.; Huang, W.H.; Zhang, W.J. Ultrafiltration preparation of potent bioactive corn peptide as alcohol metabolism stimulator in vivo and study on its mechanism of action. J. Food Biochem. 2013, 37, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Aluko, R.E.; Nakai, S. Structural requirements of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides: Quantitative structure-activity relationship modeling of peptides containing 4-10 amino acid residues. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2006, 25, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, V.T.T.; Ito, K.; Ohno, M.; Motoyama, T.; Ito, S.; Kawarasaki, Y. Analyzing a dipeptide library to identify human dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Buso, N.; Gur, T.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Basutkar, P.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Potter, S.C.; Finn, R.D.; et al. The EMBL-EBI search and sequence analysis tools APIs in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W636–W641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.A.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2—A multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bateman, A. UniProt: A worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holton, T.A.; Pollastri, G.; Shields, D.C.; Mooney, C. CPPpred: Prediction of cell penetrating peptides. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 3094–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Ding, H.; Feng, P.; Lin, H.; Chou, K.-C. iACP: A sequence-based tool for identifying anticancer peptides. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 16895–16909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minkiewicz, P.; Iwaniak, A.; Darewicz, M. BIOPEP-UWM database of bioactive peptides: Current opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, Y. Ab initio protein structure assembly using continuous structure fragments and optimized knowledge-based force field. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2012, 80, 1715–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, Y. Toward optimal fragment generations for ab initio protein structure assembly. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2013, 81, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLano, W.L. PhysiologyMOL Molecular Graphics System, version 1.8; Schödinger LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jurrus, E.; Engel, D.; Star, K.; Monson, K.; Brandi, J.; Felberg, L.E.; Brookes, D.H.; Wilson, L.; Chen, J.; Liles, K.; et al. Improvements to the APBS biomolecular solvation software suite. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horn, M.; Neundorf, I. Design of a novel cell-permeable chimeric peptide to promote wound healing. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freshney, R.I. Culture of Animal Cells, 6th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; ISBN 9780470649367. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarenga, E.C.; Fonseca, M.C.; Carvalho, C.C.; Florentino, R.M.; França, A.; Matias, E.; Guimarães, P.B.; Batista, C.; Freire, V.; Carmona, A.K.; et al. Angiotensin converting enzyme regulates cell proliferation and migration. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |







| Name | Peptide Sequence | MWcalc [Da] 1 | Mwexp [Da] | Net Charge | Purity 2 | CPP 3 | ACP 4 | AOP 5 | ACEIP 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19ZP1 | FNQLAALNSAAYLQQQQLLPFSQLA | 2777.14 | 2777.88 | ≥95% | 0.098 | 0.000009 | 0.08 | 0.48 | |
| 19ZP2 | QLADVSPAAFLTQQQLLPFYLHAM | 2702.13 | 2702.54 | −1 | ≥70% | 0.11 | 0.000004 | 0.125 | 0.375 |
| 19ZP3 | AYLQAQQLLPFNQLVRSPAA | 2227.56 | 2228.11 | +1 | ≥95% | 0.33 | 0.005109 | 0.1 | 0.45 |
| CF19ZP1 | CF-FNQLAALNSAAYLQQQQLLPFSQLA | 3135.44 | 3136.07 | >90% | nd | nd | nd | nd | |
| CF19ZP2 | CF-QLADVSPAAFLTQQQLLPFYLHAM | 3060.43 | 3060.19 | −1 | >70% | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| CF19ZP3 | CF-AYLQAQQLLPFNQLVRSPAA | 2585.86 | 2586.32 | +1 | >90% | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Sample | IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|
| Captopril | 0.29 ± 0.02 b |
| 19ZP1 | 14.19 ± 0.12 b |
| 19ZP2 | 174.43 ± 49.6 a |
| 19ZP3 | 202.04 ± 0.63 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz-Gómez, J.L.; Neundorf, I.; López-Castillo, L.-M.; Castorena-Torres, F.; Serna-Saldívar, S.O.; García-Lara, S. In Silico Analysis and In Vitro Characterization of the Bioactive Profile of Three Novel Peptides Identified from 19 kDa α-Zein Sequences of Maize. Molecules 2020, 25, 5405. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225405
Díaz-Gómez JL, Neundorf I, López-Castillo L-M, Castorena-Torres F, Serna-Saldívar SO, García-Lara S. In Silico Analysis and In Vitro Characterization of the Bioactive Profile of Three Novel Peptides Identified from 19 kDa α-Zein Sequences of Maize. Molecules. 2020; 25(22):5405. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225405
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz-Gómez, Jorge L., Ines Neundorf, Laura-Margarita López-Castillo, Fabiola Castorena-Torres, Sergio O. Serna-Saldívar, and Silverio García-Lara. 2020. "In Silico Analysis and In Vitro Characterization of the Bioactive Profile of Three Novel Peptides Identified from 19 kDa α-Zein Sequences of Maize" Molecules 25, no. 22: 5405. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225405
APA StyleDíaz-Gómez, J. L., Neundorf, I., López-Castillo, L. -M., Castorena-Torres, F., Serna-Saldívar, S. O., & García-Lara, S. (2020). In Silico Analysis and In Vitro Characterization of the Bioactive Profile of Three Novel Peptides Identified from 19 kDa α-Zein Sequences of Maize. Molecules, 25(22), 5405. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225405