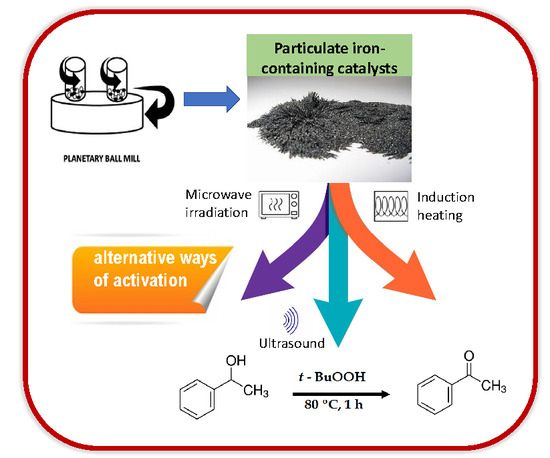
Ultrasound and Radiation-Induced Catalytic Oxidation of 1-Phenylethanol to Acetophenone with Iron-Containing Particulate Catalysts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the Dispersed Materials
2.2. Catalytic Studies
2.2.1. Catalysts Screening
2.2.2. Optimization of Parameters
2.2.3. Effect of the Energy Input
2.2.4. Catalyst Recycling Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Instrumentation
3.2. Catalyst Preparation
3.3. Catalytic Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tojo, G.; Fernandez, M. Oxidation of Alcohols to Aldehydes and Ketones; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 1–253. ISBN 978-0-387-25725-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kopylovich, M.N.; Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Martins, N.M.R.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Catalytic oxidation of alcohols: Recent advances. In Advances in Organometallic Chemistry, ADOMC Volume 63; Pérez, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 91–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, S. (Ed.) Alcohol Oxidation: Reaction, Effects and Applications; Nova: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–238. ISBN 978-1-53614-604-2. [Google Scholar]
- Faísca Phillips, A.M.; Pombeiro, A.J.L.; Kopylovich, M.N. Recent advances in cascade reactions initiated by alcohol oxidation. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 217–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Moteki, T.; Gokhale, A.A.; Flaherty, D.W.; Toste, F.D. Production of fuels and chemicals from biomass: Condensation reactions and beyond. Chem 2016, 1, 32–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grand View Research. Market Research Report ID: GVR-2-68038-236-5. 2017. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/industrial-alcohol-market (accessed on 1 July 2018).
- Parmeggian, C.; Cardona, F. Transition metal based catalysts in the aerobic oxidation of alcohols. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.E.; Ide, M.S.; Davis, R.J. Selective oxidation of alcohols and aldehydes over supported metal nanoparticles. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 17–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontolan, E.; Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Kopylovich, M.N.; Bertani, R.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Ball milling as an effective method to prepare magnetically recoverable heterometallic catalysts for alcohol oxidation. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2017, 455, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Fontolan, E.; Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Kopylovich, M.N.; Domingos, C.; Ferraria, A.M.; Bertani, R.; Botelho do Rego, A.M.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Simple solvent-free preparation of dispersed composites and their application as catalysts in oxidation and hydrocarboxylation of cyclohexane. Mater. Today Chem. 2017, 5, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, M.L.; Dessolin, S.; Serres, F.; Bruyas, L.; Chatel, G. Effect of ultrasound on the green selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol to benzaldehyde. Molecules 2019, 24, 4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Fontolan, E.; Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Kopylovich, M.N.; Bertani, R.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. The influence of multiwalled carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide additives on the catalytic activity of 3d metal catalysts towards 1-phenylethanol oxidation. J. Mol. Catal. A. Chem. 2017, 426, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, F.; Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Ferraria, A.M.; Kopylovich, M.N.; Guedes da Silva, M.F.C.; Marchetti, F.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Synergistic catalytic action of vanadia-titania composites towards the microwave-assisted benzoin oxidation. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 3198–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabach, Y.Y.; Kopylovich, M.N.; Mahmudov, K.T.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Microwave-assisted catalytic oxidation of alcohols to carbonyl compounds. In Advances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis’ (The Silver/Gold Jubilee ICOMC Celebratory Book); Pombeiro, A.J.L., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; Chapter 18; pp. 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopylovich, M.N.; Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Alegria, E.C.B.A. Mechanochemical activation and catalysis. In Noncovalent Interactions in Catalysis; Mahmudov, K.T., Kopylovich, M.N., Guedes da Silva, M.F.C., Pombeiro, A.J.L., Eds.; RCS Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Chapter 25; pp. 548–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, K. Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds, 5th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, D.; Singh, H.; Jouen, S.; Hannoyer, B.; Banerjee, S. Effect of precursor on the formation of different phases of iron oxide nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 7138–7150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaterian, H.R.; Ghashang, M. Ferric hydrogensulfate catalyzed synthesis of aryl 14H-dibenzoxanthene derivatives under thermal and solvent-free conditions. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2008, 19, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inam, M.A.; Khan, R.; Park, D.R.; Lee, Y.-W.; Yeom, I.T. Removal of Sb(III) and Sb(V) by ferric chloride coagulation: Implications of Fe solubility. Water 2018, 10, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kortuem, G. Reflectance Spectroscopy: Principles, Methods and Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Naumkin, A.; Kraut-Vass, V.A.; Gaarenstroom, S.W.; Powell, C.J. (Eds.) NIST X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Database; Standard Reference Database 20, Measurement Services Division of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST); Material Measurement Laboratory (MML): Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.H.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, B.J.; Huh, S.H. Magnetic properties of needle-like α-FeOOH and γ-FeOOH nanoparticles. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2004, 45, 1019. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Matias, I.A.S.; Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Ferraria, A.M.; Botelho do Rego, A.M.; Pombeiro, A.J.L.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S. New trendy magnetic C-scorpionate iron catalyst and its performance towards cyclohexane oxidation. Catalysts 2018, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutradhar, M.; Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Barman, T.R.; Scorcelletti, F.; Guedes da Silva, M.F.C.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Microwave-assisted peroxidative oxidation of toluene and 1-phenylethanol with monomeric keto and polymeric enol aroylhydrazone Cu(II) complexes. Mol. Catal. 2017, 439, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutradhar, M.; Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Mahmudov, K.T.; Guedes da Silva, M.F.C.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Iron(III) and cobalt(III) complexes with both tautomeric (keto and enol) forms of aroylhydrazone ligands: Catalysts for the microwave assisted oxidation of alcohols. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 8079–8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizarova, G.L.; Matvienko, L.G.; Kuzmin, A.O.; Savinova, E.R.; Parmon, V.N. Copper and iron hydroxides as new catalysts for redox reactions in aqueous solutions. Mendeleev Commun. 2001, 11, 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopylovich, M.N.; Karabach, Y.Y.; Mahmudov, K.T.; Haukka, M.; Kirillov, A.M.; Figiel, P.J.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Heterometallic copper(II)-potassium 3D coordination polymers driven by multi-functionalized azoderivatives of β-diketones. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 4247–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Mai, F.; Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Guedes da Silva, M.F.C.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Synthesis and characterization of copper(II) 4′-phenyl-terpyridine compounds and catalytic application for aerobic oxidation of benzylic alcohols. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 4048–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutradhar, M.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Guedes da Silva, M.F.C.; Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Liu, C.-M.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Dinuclear Mn(II,II) complexes: Magnetic properties and microwave assisted oxidation of alcohols. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 3966–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Ferraria, A.M.; Botelho do Rego, A.M.; Kopylovich, M.N.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Comparison of microwave and mechanochemical energy inputs in the catalytic oxidation of cyclohexane. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 8193–8198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, B.; Baruah, M.J.; Sharma, M.; Sarma, B.; Karunakar, G.V.; Satyanarayana, L.; Roy, S.; Bhattacharyya, P.K.; Borah, K.K.; Bania, K.K. Self pH regulated iron(II) catalyst for radical free oxidation of benzyl alcohols. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 589, 117292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A.; Arends, I.W.C.E. Organocatalytic oxidations mediated by nitroxyl radicals. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2004, 346, 1051–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finger, L.W.; Hazen, R.M.; Hofmeister, A.M. High-Pressure crystal chemistry of spinel (MgAl2O4) and magnetite (Fe3O4): Comparisons with silicate spinels. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1986, 13, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.J.; Putnis, A. Magnetic properties of the magnetite-spinel solid solution: Curie temperatures, magnetic susceptibilities, and cation ordering. Am. Mineral. 1996, 81, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |











| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic concentrations (%) | ||||||
| C | 11.4 | 19.5 | 45.7 | 52.2 | ||
| O | 43.8 | 59.3 | 18.5 | 21.2 | ||
| Cl | 2.4 | 0.8 | 20.6 | 11.6 | ||
| N | 0.0 | 1.3 | 6.7 | 6.4 | ||
| S | 0.0 | 0.0* | 1.2 | 1.6 | * traces | |
| Fe | 26.3 | 19.3** | 7.4 | 6.8 | ** underestimated (see text) | |
| Na | 16.1 | 0.0 | — | 0.0 | ||
| Atomic ratios in precursors or oxides | ||||||
| Experimental atomic ratios | (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2·6H2O | FeCl3 (6H2O) | ||||
| N/Fe | 0.06 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 2.0 | ||
| S/Fe | 0.2 | 0.2 | 2.0 | |||
| Cl/Fe | 0.09 | 0.04 | 2.8 | 1.7 | 3.0 | |
| Fe3O4 | ||||||
| O530 eV/Fe | 1.3 | 1.7 | *** | *** | 1.3 | *** O530 eV in the tail of O 1s |
| Entry | Catalyst | Catalyst Amount (mmol) | Yield (%) b | TOF c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | <1 | - |
| 2 | FeCl3·6H2O | 1 | 28 | 1 |
| 3 | FeCl3 anhydrous | 1 | 11 | <1 |
| 4 | FeSO4·(NH4)2·6H2O | 1 | 2.5 | <1 |
| 5 | 1 | 0.05 | 2.3 | 2 |
| 6 | 0.1 | 2.2 | 1 | |
| 7 | 0.33 | 2.7 | <1 | |
| 8 | 0.5 | 3.3 | <1 | |
| 9 | 2 | 0.05 | 3.8 | 4 |
| 10 | 0.1 | 5 | 3 | |
| 11 | 0.33 | 7.6 | 1 | |
| 12 | 0.5 | 11 | 1 | |
| 13 | 3 | 0.05 | 25 | 25 |
| 14 | 0.1 | 52 | 26 | |
| 15 | 0.33 | 58 | 9 | |
| 16 | 0.5 | 61 | 6 | |
| 17 | 4 | 0.05 | 19 | 19 |
| 18 | 0.1 | 39 | 20 | |
| 19 | 0.33 | 65 | 10 | |
| 20 | 0.5 | 65 | 7 |
| Entry | Catalyst | Reaction Time (h) | Temperature (°C) | Additive (mmol) | Yield (%) b | TOF c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 0.5 | 80 | - | 52 | 16 |
| 2 | 1 | 80 | - | 58 | 9 | |
| 3 | 1.5 | 80 | - | 72 | 7 | |
| 4 | 3 | 80 | - | 69 | 3 | |
| 5 | 1 | 80 | HNO3 (0.125) | 67 | 10 | |
| 6 | 1 | 80 | K2CO3 (0.125) | 55 | 8 | |
| 7 | 1 | 80 | HPCA (0.125) | 50 | 8 | |
| 8 | 1 | 80 | TEMPO (0.125) | 70 | 11 | |
| 9 | 1 | 60 | - | 36 | 5 | |
| 10 | 1 | 80 | - | 58 | 9 | |
| 11 | 1 | 100 | - | 70 | 11 | |
| 12 | 1 | 120 | - | 61 | 9 | |
| 13 | 4 | 0.5 | 80 | - | 55 | 17 |
| 14 | 1 | 80 | - | 65 | 10 | |
| 15 | 1.5 | 80 | - | 73 | 11 | |
| 16 | 3 | 80 | - | 82 | 12 | |
| 17 | 1 | 80 | HNO3 (0.125) | 68 | 10 | |
| 18 | 1 | 80 | K2CO3 (0.125) | 50 | 8 | |
| 19 d | 1 | 80 | K2CO3 (0.125) | 19 | 3 | |
| 20 | 1 | 80 | HPCA (0.125) | 62 | 9 | |
| 21 | 1 | 80 | TEMPO (0.125) | 67 | 10 | |
| 22 | 1 | 60 | - | 18 | 3 | |
| 23 | 1 | 80 | - | 65 | 10 | |
| 24 | 1 | 100 | - | 68 | 10 | |
| 25 | 1 | 120 | - | 67 | 10 | |
| 26 e | 1 | 80 | - | 72 | 11 | |
| 27 f | 1 | 80 | - | 2.5 | <1 | |
| 28 g | 1 | 80 | - | 6.7 | 1 | |
| 29 h | 1 | 80 | - | 2.9 | <1 |
| Entry | Catalyst | Method b | Temperature (°C) | Yield (%) c | TOF d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | CONV | 80 | 5 | 1 |
| 2 | MW | 80 | 3 | <1 | |
| 3 | US | 80 | 6 | 1 | |
| 4 | IND | 70 | 11 | 2 | |
| 5 | BM | r.t. | 5 | 1 | |
| 6 | 2 | CONV | 80 | 9 | 1 |
| 7 | MW | 80 | 11 | 2 | |
| 8 | US | 80 | 10 | 2 | |
| 9 | IND | 70 | 41 | 6 | |
| 10 | BM | r.t. | 7 | 1 | |
| 11 | 3 | CONV | 80 | 61 | 9 |
| 12 | MW | 80 | 58 | 9 | |
| 13 | US | 80 | 70 | 11 | |
| 14 | IND | 70 | 65 | 10 | |
| 15 | BM | r.t. | 2 | <1 | |
| 16 | 4 | CONV | 80 | 37 | 6 |
| 17 | MW | 80 | 65 | 10 | |
| 18 | US | 80 | 66 | 10 | |
| 19 | IND | 70 | 66 | 10 | |
| 20 | BM | r.t. | 17 | 4 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soliman, M.M.A.; Kopylovich, M.N.; Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Ribeiro, A.P.C.; M. Ferraria, A.; M. Botelho do Rego, A.; Correia, L.M.M.; Saraiva, M.S.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Ultrasound and Radiation-Induced Catalytic Oxidation of 1-Phenylethanol to Acetophenone with Iron-Containing Particulate Catalysts. Molecules 2020, 25, 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030740
Soliman MMA, Kopylovich MN, Alegria ECBA, Ribeiro APC, M. Ferraria A, M. Botelho do Rego A, Correia LMM, Saraiva MS, Pombeiro AJL. Ultrasound and Radiation-Induced Catalytic Oxidation of 1-Phenylethanol to Acetophenone with Iron-Containing Particulate Catalysts. Molecules. 2020; 25(3):740. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030740
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoliman, Mohamed M. A., Maximilian N. Kopylovich, Elisabete C. B. A. Alegria, Ana P. C. Ribeiro, Ana M. Ferraria, Ana M. Botelho do Rego, Luís M. M. Correia, Marta S. Saraiva, and Armando J. L. Pombeiro. 2020. "Ultrasound and Radiation-Induced Catalytic Oxidation of 1-Phenylethanol to Acetophenone with Iron-Containing Particulate Catalysts" Molecules 25, no. 3: 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030740
APA StyleSoliman, M. M. A., Kopylovich, M. N., Alegria, E. C. B. A., Ribeiro, A. P. C., M. Ferraria, A., M. Botelho do Rego, A., Correia, L. M. M., Saraiva, M. S., & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2020). Ultrasound and Radiation-Induced Catalytic Oxidation of 1-Phenylethanol to Acetophenone with Iron-Containing Particulate Catalysts. Molecules, 25(3), 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030740