Design and Development of Spray-Dried Microsystems to Improve Technological and Functional Properties of Bioactive Compounds from Hazelnut Shells
Abstract
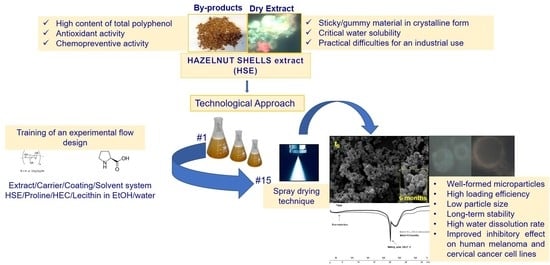
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Microencapsulation Process, Morphological, and Dimensional Characterization
2.2. Thermal Analyses
2.3. In Vitro Dissolution/Release Tests
2.4. Stability Studies of Batch-15
2.5. Functional Activity of Batch-15
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Liquid Feeds Preparation and Spray Drying Conditions
- -
- Hot-Cold-Hot method (H-C-H): The liquid feed was produced using 0.2% w/v HEC, 5% w/v P and 0.2% L at 85.0:3.4:8.2:3.4 P:HEC:PEC:L ratio (total amount 6.15 g). PEC was added in 80 mL of water at 75 °C; at room temperature P was included, and finally, at 50 °C, HEC was dissolved, leaving under stirring overnight. Separately, 0.25% or 0.50% w/v of HSE was dissolved adding 20 mL of ethanol and 20 mL of a 1% w/v L solution by homogenization with an Ultra-Turrax T-25 (IKA ULTRA-TURRAX T25 digital) at 10,000 RPM for 5 min. The suspension containing the extract (HSE) was slowly poured into the feed under continuous magnetic stirring.
3.3. Powders Characterization
3.3.1. Yield and Loading Efficiency
3.3.2. Quantitative Analysis by HPLC Method
3.3.3. Particle-Size Analyses
3.3.4. Morphological Analyses
3.3.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.3.6. Dissolution/Release Tests
3.4. Stability Studies
Hygroscopicity
3.5. Cell Viability Assay
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kammerer, D.R.; Kammerer, J.; Valet, R.; Carle, R. Recovery of polyphenols from the by-products of plant food processing and application as valuable food ingredients. Food Res. Int. 2014, 65, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, T.; Celano, R.; Pane, C.; Piccinelli, A.L.; Sansone, F.; Picerno, P.; Zaccardelli, M.; Aquino, R.P.; Mencherini, T. Chestnut (castanea sativa miller.) burs extracts and functional compounds: Uhplc-uv-hrms profiling, antioxidant activity, and inhibitory effects on phytopathogenic fungi. Molecules 2019, 24, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sansone, F.; Mencherini, T.; Picerno, P.; Lauro, M.R.; Cerrato, M.; Aquino, R.P. Development of Health Products from Natural Sources. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 4606–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlotogorski, A.; Dayan, A.; Dayan, D.; Chaushu, G.; Salo, T.; Vered, M. Nutraceuticals as new treatment approaches for oral cancer: II. Green tea extracts and resveratrol. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio-Fernández, X.; García-Gasca, T.; Yousef, G.G.; Lila, M.A.; De Mejia, E.G.; Loarca-Pina, G. Chemopreventive activity of polyphenolics from black Jamapa bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) on HeLa and HaCaT cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2116–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.G.; Murillo, G.; Naithani, R.; Peng, X. Cancer chemoprevention by natural products: How far have we come? Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinelli, A.L.; Pagano, I.; Esposito, T.; Mencherini, T.; Porta, A.; Petrone, A.M.; Gazzerro, P.; Picerno, P.; Sansone, F.; Rastrelli, L.; et al. HRMS Profile of a Hazelnut Skin Proanthocyanidin-rich Fraction with Antioxidant and Anti-Candida albicans Activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, T.; Sansone, F.; Franceschelli, S.; Del Gaudio, P.; Picerno, P.; Aquino, R.P.; Mencherini, T. Hazelnut (Corylus avellana l.) shells extract: Phenolic composition, antioxidant effect and cytotoxic activity on human cancer cell lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, T.; Sansone, F.; Russo, P.; Picerno, P.; Aquino, R.P.; Gasparri, F.; Mencherini, T. A water-soluble microencapsulated milk thistle extract as active ingredient for dermal formulations. Molecules 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pudziuvelyte, L.; Marksa, M.; Jakstas, V.; Ivanauskas, L.; Kopustinskiene, D.M.; Bernatoniene, J. Microencapsulation of Elsholtzia ciliata Herb Ethanolic Extract by Spray-Drying: Impact of resistant-maltodextrin complemented with sodium caseinate, skim milk, and beta-cyclodextrin on the quality of spray-dried powders. Molecules 2019, 24, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munin, A.; Edwards-Lévy, F. Encapsulation of natural polyphenolic compounds; a review. Pharmaceutics 2011, 3, 793–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corrêa-Filho, L.C.; Lourenço, S.C.; Duarte, D.F.; Moldão-Martins, M.; Alves, V.D. Microencapsulation of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) pomace ethanolic extract by spray drying: Optimization of process conditions. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sansone, F.; Esposito, T.; Lauro, M.R.; Picerno, P.; Mencherini, T.; Gasparri, F.; De Santis, S.; Chieppa, M.; Cirillo, C.; Aquino, R.P. Application of spray drying particle engineering to a high-functionality/low-solubility milk thistle extract: Powders production and characterization. Molecules 2018, 23, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shishir, M.R.I.; Chen, W. Trends of spray drying: A critical review on drying of fruit and vegetable juices. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 65, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizzon, G.P.; Bueno, F.G.; Ueda-Nakamura, T.; Nakamura, C.V.; Filho, B.P.D. Preparation of spray-dried soy isoflavone-loaded gelatin microspheres for enhancement of dissolution: Formulation, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2014, 6, 599–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sosnik, A.; Seremeta, K.P. Advantages and challenges of the spray-drying technology for the production of pure drug particles and drug-loaded polymeric carriers. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 223, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, F.; Mencherini, T.; Picerno, P.; Esposito, T.; Del Gaudio, P.; Russo, P.; Pepe, G.; Lauro, M.R.; Aquino, R.P. Microencapsulation by spray drying of Lannea microcarpa extract: Technological characteristics and antioxidant activity. J. Pharm. Pharmacogn. Res. 2014, 2, 100–109. [Google Scholar]
- Sansone, F.; Picerno, P.; Mencherini, T.; Porta, A.; Lauro, M.R.; Russo, P.; Aquino, R.P. Technological properties and enhancement of antifungal activity of a Paeonia rockii extract encapsulated in a chitosan-based matrix. J. Food Eng. 2014, 120, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, C.; Zamora, O.; Parada, J.; Ricardo, P.; Uribe, M.; Kalazich, J. Microencapsulation of Anthocyanin Extracted from Purple Flesh Cultivated Potatoes by Spray Drying and Its E ff ects on In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion. Molecules 2020, 25, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sansone, F.; Esposito, T.; Mencherini, T.; Lauro, M.R.; Del Gaudio, P.; Picerno, P.; Pepe, G.; Aquino, R.P. Particle technology applied to a lactose/NaCMC blend: Production and characterization of a novel and stable spray-dried ingredient. Powder Technol. 2018, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iurckevicz, G.; Dahmer, D.; Santos, V.A.Q.; Vetvicka, V.; Barbosa-Dekker, A.M.; Dekker, R.F.H.; Malfatti, C.R.M.; da Cunha, M.A.A. Encapsulated Microparticles of (1→6)-β-d-Glucan Containing Extract of Baccharis dracunculifolia: Production and characterization. Molecules 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.X.; Yang, J.J.; Pan, R.L.; Chang, Q.; Liao, Y.H. Anti-hygroscopic effect of leucine on spray-dried herbal extract powders. Powder Technol. 2014, 266, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, G.; Cai, S.; Jing, H.; Huang, Y.; Pan, X.; et al. Moisture-resistant co-spray-dried netilmicin with l-leucine as dry powder inhalation for the treatment of respiratory infections. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kasten, G.; Duarte, Í.; Paisana, M.; Löbmann, K.; Rades, T.; Grohganz, H. Process optimization and upscaling of spray-dried drug-amino acid co-amorphous formulations. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hyung, W.; Kim, Y.; Chung, C.H.; Haam, S. Drowning-out crystallization of l-proline: Effect of anti-solvent composition and processing parameters on crystal size and shape. Powder Technol. 2008, 186, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.K.; Zhu, W.; Liang, X.; Zhang, L.; Demers, A.J.; Zimmerman, M.C.; Simpson, M.A.; Becker, D.F. Proline dehydrogenase is essential for proline protection against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.Z.; Cao, Z.Y.; Li, J.N.; Hu, H.X.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Huang, Y.M.; Liu, Z.Z.; Hu, D.; Liao, L.M.; Du, J. Ethyl acetate extract from Jiedu Xiaozheng Yin inhibits the proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by suppressing polycomb gene product Bmi1 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncology reports 2014, 32, 2710–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.K.; Becker, D.F. Role of apoptosis-inducing factor, proline dehydrogenase, and NADPH oxidase in apoptosis and oxidative stress. Cell Health Cytoskelet. 2012, 4, 11–27. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, N.; Dickman, M.B.; Becker, D.F. Proline modulates the intracellular redox environment and protects mammalian cells against oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leal, J.; Teixeira-Santos, L.; Pinho, D.; Afonso, J.; Carvalho, J.; de Lourdes Bastos, M.; Albino-Teixeira, A.; Fraga, S.; Sousa, T. L-proline supplementation improves nitric oxide bioavailability and counteracts the blood pressure rise induced by angiotensin II in rats. Nitric Oxide - Biol. Chem. 2019, 82, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehring, R. Pharmaceutical particle engineering via spray drying. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 999–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murtaza, G. Ethylcellulose microparticles: A review. Acta Pol. Pharm. - Drug Res. 2012, 69, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Chen, T.; Liu, L.; Li, G. Electrochemical characteristics of heme proteins in hydroxyethylcellulose film. Sensors Actuators, B Chem. 2006, 113, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Skinner, G.W.; Harcum, W.W.; Barnum, P.E. Pharmaceutical applications of naturally occurring water-soluble polymers. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 1998, 1, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, F.; Mencherini, T.; Picerno, P.; D’Amore, M.; Aquino, R.P.; Lauro, M.R. Maltodextrin/pectin microparticles by spray drying as carrier for nutraceutical extracts. J. Food Eng. 2011, 105, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Ahmad, T.; Aadil, R.M.; Spotti, M.J.; Bakry, A.M.; Khan, I.M.; Zhao, L.; Riaz, T.; Tong, Q. Pectin polymers as wall materials for the nano-encapsulation of bioactive compounds. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 90, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivorotova, T.; Cirkovas, A.; Maciulyte, S.; Staneviciene, R.; Budriene, S.; Serviene, E.; Sereikaite, J. Nisin-loaded pectin nanoparticles for food preservation. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 54, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainudin, B.H.; Wong, T.W.; Hamdan, H. Design of low molecular weight pectin and its nanoparticles through combination treatment of pectin by microwave and inorganic salts. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 147, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngouémazong, E.D.; Christiaens, S.; Shpigelman, A.; Van Loey, A.; Hendrickx, M. The Emulsifying and Emulsion-Stabilizing Properties of Pectin: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.J.; Erk, K.A. Stability and interfacial viscoelasticity of oil-water nanoemulsions stabilized by soy lecithin and Tween 20 for the encapsulation of bioactive carvacrol. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 517, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, J.J.; Norwood, E.A.; O’Mahony, J.A.; Kelly, A.L. Atomisation technologies used in spray drying in the dairy industry: A review. J. Food Eng. 2019, 243, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francia, V.; Martín, L.; Bayly, A.E.; Simmons, M.J.H. Agglomeration during spray drying: Airborne clusters or breakage at the walls? Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 162, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzidaki, M.D.; Mitsou, E.; Yaghmur, A.; Xenakis, A.; Papadimitriou, V. Formulation and characterization of food-grade microemulsions as carriers of natural phenolic antioxidants. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 483, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boopathi, K.; Ramasamy, P. Synthesis, growth and characterization of a new metal-organic NLO material: Dibromo bis (L-proline) Cd (II). J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1080, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szcześniak, L.; Rachocki, A.; Tritt-Goc, J. Glass transition temperature and thermal decomposition of cellulose powder. Cellulose 2008, 15, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohuriaan, M.J.; Shokrolahi, F. Thermal studies on natural and modified gums. Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einfal, T.; Planinšek, O.; Hrovat, K. Methods of amorphization and investigation of the amorphous state. Acta Pharm. 2013, 63, 305–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagliarulo, C.; Sansone, F.; Moccia, S.; Russo, G.L.; Aquino, R.P.; Salvatore, P.; Di Stasio, M.; Volpe, M.G. Preservation of Strawberries with an Antifungal Edible Coating Using Peony Extracts in Chitosan. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2016, 9, 1951–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, P.G.; Bao, Y.; Prorock, A.; Zigrino, P.; Nischt, R.; Politi, V.; Mauch, C.; Dragulev, B.; Fox, J.W. Gene expression profiling reveals cross-talk between melanoma and fibroblasts: Implications for host-tumor interactions in metastasis. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4134–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Borchert, G.L.; Surazynski, A.; Hu, C.A.; Phang, J.M. Proline oxidase activates both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways for apoptosis: The role of ROS/superoxides, NFAT and MEK/ERK signaling. Oncogene 2006, 25, 5640–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kardos, G.R.; Wastyk, H.C.; Robertson, G.P. Disruption of proline synthesis in melanoma inhibits protein production mediated by the GCN2 pathway. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 1408–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prasad, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Tyagi, A.K. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and cancer: Role of antioxidative nutraceuticals. Cancer Lett. 2017, 387, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansone, F.; Picerno, P.; Mencherini, T.; Russo, P.; Gasparri, F.; Giannini, V.; Lauro, M.R.; Puglisi, G.; Aquino, R.P. Enhanced technological and permeation properties of a microencapsulated soy isoflavones extract. J. Food Eng. 2013, 115, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, F.; Picerno, P.; Mencherini, T.; Villecco, F.; D’Ursi, A.M.; Aquino, R.P.; Lauro, M.R. Flavonoid microparticles by spray-drying: Influence of enhancers of the dissolution rate on properties and stability. J. Food Eng. 2011, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerbab, K.; Mekhelfi, T.; Zaiter, L.; Benayache, S.; Benayache, F.; Picerno, P.; Mencherini, T.; Sansone, F.; Aquino, R.P.; Rastrelli, L. Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of a polar extract of Thymelaea microphylla Coss. et Dur. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencherini, T.; Picerno, P.; Festa, M.; Russo, P.; Capasso, A.; Aquino, R. Triterpenoid constituents from the roots of Paeonia rockii ssp. rockii. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the raw extract (HSE) and Spray-dried powder are available from the authors. |








| Sample | P g/100mL | HEC g/100mL | PEC g/100mL | LEtOH g/100mL | HSE g/100mL | Yield % | AEC a % | AAC b % | EE c % | d50 µm (span) e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSE raw | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3.16 ± 1.5d | - | - |
| HEC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 277.22 (1.60) |
| P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 250.10 (1.71) |
| PEC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 50.53 (1.32) |
| Batch-3 | 5.00 | 0.20 | - | - | 39.8 ± 4.2 d | - | - | - | - | |
| Batch-9 | 5.00 | 0.20 | 0.50 | - | - | 45.0 ± 3.1 d | - | - | - | - |
| Batch-12 | 5.00 | 0.20 | 0.50 | 0.20 | - | 50.0 ± 2.0 d | - | - | - | - |
| Batch-13 | 5.00 | 0.20 | - | - | 0.25 | 39.8 ± 9.42 d | 4.30 | 3.11 ± 0.90 d | 92.10 | 18.41 (1.63) |
| Batch-15 | 5.00 | 0.20 | 0.50 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 43.00 ± 3.54 d | 3.90 | 2.10 ± 0.93 d | 95.12 | 3.02 (1.21) |
| 0 | 6 Months | 0 | 6 Months | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | AAC% a,b | DPPH test EC50 a,c,d | ||
| HSE Unprocessed extract | 3.16 ± 0.80 | 1.15 ± 0.40 * | 33.42 ± 1.40 | 40.04 ± 2.11 * |
| Batch-15 | 2.10 ± 0.40 | 2.00 ± 0.60 | 33.20 ± 0.61 | 32.80 ±1.01 |
| α-tocopherol e | 10.1 ± 1.32 | 10.12 ± 1.20 | ||
| Cell Line a | IC50 HSE Raw mg/mLb | IC50 Batch-15 mg/mL c |
|---|---|---|
| HaCaT | 0.500 ± 0.731 d | >15 d |
| SK-Mel-28 | 0.459 ± 0.831 d | 10.550 ± 3.010 |
| A375 | 0.584 ± 0.900 d | 4.550 ± 1.240 d |
| HeLa | 0.526 ± 0.890 d | 8.070 ± 2.150 d |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Esposito, T.; Mencherini, T.; Del Gaudio, P.; Auriemma, G.; Franceschelli, S.; Picerno, P.; Aquino, R.P.; Sansone, F. Design and Development of Spray-Dried Microsystems to Improve Technological and Functional Properties of Bioactive Compounds from Hazelnut Shells. Molecules 2020, 25, 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061273
Esposito T, Mencherini T, Del Gaudio P, Auriemma G, Franceschelli S, Picerno P, Aquino RP, Sansone F. Design and Development of Spray-Dried Microsystems to Improve Technological and Functional Properties of Bioactive Compounds from Hazelnut Shells. Molecules. 2020; 25(6):1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061273
Chicago/Turabian StyleEsposito, Tiziana, Teresa Mencherini, Pasquale Del Gaudio, Giulia Auriemma, Silvia Franceschelli, Patrizia Picerno, Rita P. Aquino, and Francesca Sansone. 2020. "Design and Development of Spray-Dried Microsystems to Improve Technological and Functional Properties of Bioactive Compounds from Hazelnut Shells" Molecules 25, no. 6: 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061273
APA StyleEsposito, T., Mencherini, T., Del Gaudio, P., Auriemma, G., Franceschelli, S., Picerno, P., Aquino, R. P., & Sansone, F. (2020). Design and Development of Spray-Dried Microsystems to Improve Technological and Functional Properties of Bioactive Compounds from Hazelnut Shells. Molecules, 25(6), 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061273