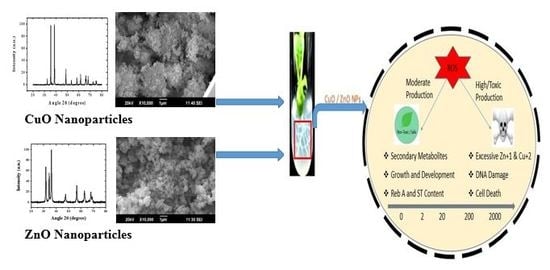
Engineered ZnO and CuO Nanoparticles Ameliorate Morphological and Biochemical Response in Tissue Culture Regenerants of Candyleaf (Stevia rebaudiana)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of ENPs
2.2. Effects of ENPs on Plant Physiology
2.3. Evaluation of Steviol Glycosides
2.4. Estimation of Antioxidant Activities
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis and Characterization of ZnO and CuO ENPs
4.2. Medium Preparation for Organogenesis
4.3. Growth Conditions of Organogenesis
4.4. Steviol Glycosides (SGs) Analysis
4.5. Antioxidant Assays
4.6. Quantification of Total Flavonoid Content (TFC)
4.7. Quantification of Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
4.8. Quantification of DPPH-FRSA
4.9. Quantification of Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC)
4.10. Quantification of the Total Reducing Power (TRP)
4.11. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Sanzari, I.; Leone, A.; Ambrosone, A. Nanotechnology in Plant Science: To Make a Long Story Short. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allhof, F.; Lin, P.; Moore, D. What Is Nanotechnology and Why Does It Matter: From Science to Ethics; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
- Aslani, F.; Bagheri, S.; Muhd Julkapli, N.; Juraimi, A.S.; Hashemi, F.S.G.; Baghdadi, A. Effects of Engineered Nanomaterials on Plants Growth: An Overview. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 641759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahan, S.; Alias, Y.B.; Bakar, A.F.B.A.; Yusoff, I.B. Toxicity evaluation of ZnO and TiO2 nanomaterials in hydroponic red bean (Vigna angularis) plant: Physiology, biochemistry and kinetic transport. J. Environ. Sci. China 2018, 72, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.-M.; Kwak, J.I.; An, Y.-J. Effect of silver nanoparticles in crop plants Phaseolus radiatus and Sorghum bicolor: Media effect on phytotoxicity. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, J.; Dou, R.; Gao, X.; Mao, C.; Wang, L. Assessment of the Phytotoxicity of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles on Two Crop Plants, Maize (Zea mays L.) and Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2015, 12, 15100–15109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuverza-Mena, N.; Armendariz, R.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Effects of Silver Nanoparticles on Radish Sprouts: Root Growth Reduction and Modifications in the Nutritional Value. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konate, A.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Adeel, M.; Zhang, P.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Kizito, S.; et al. Comparative effects of nano and bulk-Fe3O4 on the growth of cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 165, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: A green expertise. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, S.; Mehata, M.S. Medicinal Plant Leaf Extract and Pure Flavonoid Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and their Enhanced Antibacterial Property. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Malarkodi, C.; Paulkumar, K.; Vanaja, M.; Gnanajobitha, G.; Annadurai, G. Algae Mediated Green Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles and Examination of Its Antifungal Activity against Clinical Pathogens. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ijmet/2014/692643/ (accessed on 20 September 2019).
- Bondarenko, O.; Juganson, K.; Ivask, A.; Kasemets, K.; Mortimer, M.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of Ag, CuO and ZnO nanoparticles to selected environmentally relevant test organisms and mammalian cells in vitro: A critical review. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1181–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keller, A.A.; McFerran, S.; Lazareva, A.; Suh, S. Global life cycle releases of engineered nanomaterials. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, H.; Haq, I.-U.; Nasreen, S.A.; Zia, M.A. Toxicological effect of CuO nanoparticles to Brassica nigra L. seedlings: A comparative in vivo and in vitro response. Pak. J. Bot. 2019, 51, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, I. Assessment of phytotoxicity of ZnO NPs on a medicinal plant, Fagopyrum esculentum. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Chung, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, I. The Genotoxic Effect of ZnO and CuO Nanoparticles on Early Growth of Buckwheat, Fagopyrum Esculentum. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendhran, S.; Rajiv, P.; Sivaraj, R. Influence of zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth of sesamum indicum l. In zinc deficient soil. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- Samart, S.; Chutipaijit, S.; Phakamas, N. Evaluating the effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the physiological responses of nine non-photoperiod sensitive rice cultivars. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 6430–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.P.; Li, Q.Q.; Pei, Z.M.; Wang, S.C. Effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the growth, photosynthetic traits, and antioxidative enzymes in tomato plants. Biol. Plant. 2018, 62, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margenot, A.J.; Rippner, D.A.; Dumlao, M.R.; Nezami, S.; Green, P.G.; Parikh, S.J.; McElrone, A.J. Copper oxide nanoparticle effects on root growth and hydraulic conductivity of two vegetable crops. Plant Soil 2018, 431, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soejarto, D.D. Botany of Stevia and Stevia Rebaudiana; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, A.; Kundu, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Bhattacharjee, A. Efficient micropropagation and chlorocholine chloride induced stevioside production of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. C. R. Biol. 2013, 336, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwell, M. Stevia, Nature’s Zero-Calorie Sustainable Sweetener: A New Player in the Fight Against Obesity. Nutr. Today 2015, 50, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hossain, M.F.; Islam, M.T.; Islam, M.A.; Akhtar, S. Cultivation and uses of stevia (Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni): A review. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2017, 17, 12745–12757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, R.; Gürel, E. Salt stress by NaCl alters the physiology and biochemistry of tissue culture-grownStevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2019, 43, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, R.; Yücesan, B.; Gurel, E. Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Steviol Glycosides Accumulation and Enhancement of Antioxidant Activities in Leaf Tissues of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Sugar Tech 2018, 20, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, R.; Yucesan, B.; Zia, M.; Gurel, E. Differential effects of plant growth regulators on physiology, steviol glycosides content, and antioxidant capacity in micropropagated tissues of Stevia rebaudiana. Biologia 2017, 72, 1156–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, M.; Dahot, M.U.; Muhamamd, S.; Naqvi, H.A.; Qarshi, I.A. In Vitro Clonal Propagation And Biochemical Analysis Of Field Established Stevia Rebaudiana Bertoni. Pakitan J. Bot. 2007, 39, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar]
- Bayraktar, M.; Naziri, E.; Karabey, F.; Akgun, I.H.; Bedir, E.; Röck-Okuyucu, B.; Gürel, A. Enhancement of stevioside production by using biotechnological approach in in vitro culture of Stevia rebaudiana. Int. J. Second. Metab. 2018, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, A.; Khan, M.A.; Mohammad, S.; Ali, A.; Kamil, A.; Arif, M.; Ali, H. Elicitation directed growth and production of steviol glycosides in the adventitious roots of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 139, 111530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, H.; Tavakoli, N.; Moradi, F. The effect of the elicitors on the steviol glycosides biosynthesis pathway in Stevia rebaudiana. Funct. Plant Biol. FPB 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai Heta, B.; Desai Charmi, V.; Desai Charmi, P.; Singh, D.; Suthar H, G. Effect of magnesium nanoparticles on physiology and stevioside in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Eur. J. Biomed. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 4, 642–646. [Google Scholar]
- Hendawey, M.H.; Fadl, R.E.A.E. Biochemical Studies on the Production of Active Constituents in Stevia Rebaudiana. Global J. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 9, 76–93. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, R.; Usman, M.; Yücesan, B.; Zia, M.; Gürel, E. Effect of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles on physiology and steviol glycosides production in micropropagated shoots of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Plant Physiol. Biochem. PPB 2017, 110, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, R.; Mohamed, A.; Yücesan, B.; Gürel, E.; Kausar, R.; Zia, M. CuO nanoparticles significantly influence in vitro culture, steviol glycosides, and antioxidant activities of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. PCTOC 2017, 131, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, R.; Zia, M.; Yücesan, B.; Gürel, E. Abiotic stress of ZnO-PEG, ZnO-PVP, CuO-PEG and CuO-PVP nanoparticles enhance growth, sweetener compounds and antioxidant activities in shoots of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, R.; Yucesan, B.; Zia, M.; Gurel, E. Elicitation of Secondary Metabolites in Callus Cultures of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni Grown Under ZnO and CuO Nanoparticles Stress. Sugar Tech 2018, 20, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majlesi, Z.; Ramezani, M.; Gerami, M. Investigation on some main glycosides content of Stevia rebaudian B. under different concentrations of commercial and synthesized silver nanoparticles. Pharm. Biomed. Res. 2018, 4, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaizad, M.; Hashemi-Moghaddam, H.; Abbaspour, H.; Gerami, M.; Mueller, A. Photocatalytic Effect of TiO2 Nanoparticles on Morphological and Photochemical Properties of Stevia Plant (Stevia Rebaudiana Bertoni). Sugar Tech 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Zivcak, M.; Sytar, O.; Kalaji, H.M.; He, X.; Mbarki, S.; Brestic, M. Impact of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles on Plant: A Critical Review. Front. Chem. 2017, 5, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cullity, B.D. Elements of x-Ray Diffraction; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc.: Reading, MA, USA, 1978; ISBN 978-0-201-01174-6. [Google Scholar]
- Pate, K.; Safier, P. 12—Chemical metrology methods for CMP quality. In Advances in Chemical Mechanical Planarization (CMP); Babu, S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston/Cambridge, UK, 2016; pp. 299–325. ISBN 978-0-08-100165-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ain, N.U.; Haq, I.U.; Abbasi, B.H.; Javed, R.; Zia, M. Influence of PVP/PEG impregnated CuO NPs on physiological and biochemical characteristics of Trigonella foenum-graecum L. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 12, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Raja, N.I.; Mashwani, Z.-U.-R.; Iqbal, M.; Ejaz, M.; Yasmeen, F.; Sohail. In vitro germination and biochemical profiling of citrus reticulata in response to green synthesised zinc and copper nanoparticles. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 790–796. [Google Scholar]
- Jasim, B.; Thomas, R.; Mathew, J.; Radhakrishnan, E.K. Plant growth and diosgenin enhancement effect of silver nanoparticles in Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.). Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, A.; Khan, M.A.; Adil, M.; Mashwani, Z.U.R. Production of Callus Biomass and Antioxidant Secondary Metabolites in Black Cumin. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2018, 28, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Mohammad, S.; Khan, M.A.; Raja, N.I.; Arif, M.; Kamil, A.; Mashwani, Z.-U.-R. Silver nanoparticles elicited in vitro callus cultures for accumulation of biomass and secondary metabolites in Caralluma tuberculata. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mosavat, N.; Golkar, P.; Yousefifard, M.; Javed, R. Modulation of callus growth and secondary metabolites in different Thymus species and Zataria multiflora micropropagated under ZnO nanoparticles stress. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2019, 66, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, H.; Ali, A.; Ali, J.S.; Haq, I.U.; Zia, M. Effect of ZnO Nanoparticles on Brassica nigra Seedlings and Stem Explants: Growth Dynamics and Antioxidative Response. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thunugunta, T.; Channa Reddy, A.; Kodthalu Seetharamaiah, S.; Ramanna Hunashikatti, L.; Gowdra Chandrappa, S.; Cherukatu Kalathil, N.; Dhoranapalli Chinnappa Reddy, L.R. Impact of Zinc oxide nanoparticles on eggplant (S. melongena): Studies on growth and the accumulation of nanoparticles. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 12, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, O.S.; Pant, N.C.; Laishram, L.; Tewari, M.; Dhoundiyal, R.; Joshi, K.; Pandey, C. Effect of CuO nanoparticles on polyphenols content and antioxidant activity in Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera L. Dunal). J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 3433–3439. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, O.; Hu, Z. Size Dependent and Reactive Oxygen Species Related Nanosilver Toxicity to Nitrifying Bacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4583–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaper, R.; Crago, J.; Barr, J.; Arndt, D.; Setyowati, K.; Chen, J. Toxicity biomarker expression in daphnids exposed to manufactured nanoparticles: Changes in toxicity with functionalization. Environ. Pollut. Barking Essex 1987 2009, 157, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Jha, A.B.; Dubey, R.S.; Pessarakli, M. Reactive Oxygen Species, Oxidative Damage, and Antioxidative Defense Mechanism in Plants under Stressful Conditions. J. Bot. 2012, 2012, 217037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manke, A.; Wang, L.; Rojanasakul, Y. Mechanisms of Nanoparticle-Induced Oxidative Stress and Toxicity. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/bmri/2013/942916/ (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, H.; Tu, C.; Hu, X.; Li, L.; Luo, Y.; Christie, P. Phytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles and the released Zn(II) ion to corn (Zea mays L.) and cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) during germination. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 11109–11117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Xu, L.; Xu, L.; Yu, X.; Wei, Y.; Xing, B. Interaction of CuO nanoparticles with plant cells: Internalization, oxidative stress, electron transport chain disruption, and toxicogenomic responses. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 2269–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Wei, B.; Li, S.; Wang, X. Toxic effects of different types of zinc oxide nanoparticles on algae, plants, invertebrates, vertebrates and microorganisms. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-N.; Zhang, M.; Xia, L.; Zhang, J.; Xing, G. The Toxic Effects and Mechanisms of CuO and ZnO Nanoparticles. Materials 2012, 5, 2850–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Javed, R.; Usman, M.; Tabassum, S.; Zia, M. Effect of capping agents: Structural, optical and biological properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 386, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, R.; Ahmed, M.; Haq, I.U.; Nisa, S.; Zia, M. PVP and PEG doped CuO nanoparticles are more biologically active: Antibacterial, antioxidant, antidiabetic and cytotoxic perspective. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 79, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F.K. A Revised Medium for Rapid Growth and Bio Assays with Tobacco Tissue Cultures. Physiol. Plantrum 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |






| Nanofluid | Zeta Potential (mV) | Conductivity (mS/cm) |
|---|---|---|
| ZnO | −12.8 | 0.0229 |
| CuO | −11.7 | 0.0201 |
| Conc. of ZnO NPs (mg/L) | % Rooting of Shoot Explants | Mean Length of Regenerants (cm) | Mean Length of Roots (cm) | Mean no. of Roots | Mean no. of Nodes | Mean no. of Leaves | FW of Regenerants (g) | FW of Leaves (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 82.7 | 15.5 ± 0.68 c | 4.04 ± 0.68 b | 11.6 ± 0.68 b | 6.23 ± 0.02 b | 15.3 ± 0.26 c | 0.59 ± 0.03 c | 0.14 ± 0.02 c |
| 2 | 90.5 | 27.3 ± 0.66 a | 7.16 ± 0.92 a | 17.3 ± 1.76 a | 9.33 ± 0.33 a | 20.6 ± 0.66 a | 0.80 ± 0.16 a | 0.36 ± 0.06 a |
| 20 200 | 88.7 77.3 | 20.3 ± 1.52 b 12.3 ± 0.44 d | 2.83 ± 0.16 c 0.33 ± 0.16 d | 9.15 ± 2.30 c 2.33 ± 1.20 d | 5.66 ± 0.88 c 4.61 ± 0.88 d | 19.2 ± 1.76 b 10.2 ± 2.03 d | 0.72 ± 0.20 b 0.52 ± 0.07 d | 0.26 ± 0.06 b 0.09 ± 0.03 d |
| 2000 | 50.8 | 10.8 ± 0.26 e | 0.00 ± 0.11 e | 0.00 ± 0.01 e | 2.18 ± 0.01 e | 8.16 ± 0.12 e | 0.46 ± 0.05 e | 0.05 ± 0.01 d |
| Conc. of CuO NPs (mg/L) | % of Shoot Explants Rooting | Mean Length of Regenerants (cm) | Mean Length of Roots (cm) | Mean no. of Roots | Mean no. of Nodes | Mean no. of Leaves | FW of Regenerants (g) | FW of Leaves (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 76.4 | 15.8 ± 0.51 c | 5.82 ± 0.35 c | 18.8 ± 1.91 c | 7.89 ± 0.54 d | 11.1 ± 1.63 c | 0.67 ± 0.07 b | 0.25 ± 0.01 b |
| 2 | 89.4 | 19.6 ± 0.66 b | 7.33 ± 0.60 b | 23.6 ± 1.45 b | 10.4 ± 0.33 b | 17.8 ± 0.02 b | 0.74 ± 0.17 a | 0.34 ± 0.02 a |
| 20 200 | 94.2 60.8 | 21.1 ± 1.16 a 12.6 ± 0.44 d | 8.54 ± 0.51 a 4.41 ± 0.08 d | 26.3 ± 0.88 a 6.02 ± 1.15 d | 11.0 ± 1.15 a 8.33 ± 0.88 c | 19.3 ± 1.76 a 7.12 ± 2.09 d | 0.76 ± 0.13 a 0.62 ± 0.04 c | 0.36 ± 0.03 a 0.13 ± 0.02 c |
| 2000 | 48.5 | 10.4 ± 0.21 e | 0.00 ± 0.02 e | 0.00 ± 0.08 e | 3.02 ± 0.21 e | 5.16 ± 0.37 e | 0.55 ± 0.02 d | 0.08 ± 0.01 d |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, M.A.; Javed, R.; Adeel, M.; Rizwan, M.; Ao, Q.; Yang, Y. Engineered ZnO and CuO Nanoparticles Ameliorate Morphological and Biochemical Response in Tissue Culture Regenerants of Candyleaf (Stevia rebaudiana). Molecules 2020, 25, 1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061356
Ahmad MA, Javed R, Adeel M, Rizwan M, Ao Q, Yang Y. Engineered ZnO and CuO Nanoparticles Ameliorate Morphological and Biochemical Response in Tissue Culture Regenerants of Candyleaf (Stevia rebaudiana). Molecules. 2020; 25(6):1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061356
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Muhammad Arslan, Rabia Javed, Muhammad Adeel, Muhammad Rizwan, Qiang Ao, and Yuesuo Yang. 2020. "Engineered ZnO and CuO Nanoparticles Ameliorate Morphological and Biochemical Response in Tissue Culture Regenerants of Candyleaf (Stevia rebaudiana)" Molecules 25, no. 6: 1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061356
APA StyleAhmad, M. A., Javed, R., Adeel, M., Rizwan, M., Ao, Q., & Yang, Y. (2020). Engineered ZnO and CuO Nanoparticles Ameliorate Morphological and Biochemical Response in Tissue Culture Regenerants of Candyleaf (Stevia rebaudiana). Molecules, 25(6), 1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061356