Practical Synthesis of Quinoline-Protected Morpholino Oligomers for Light-Triggered Regulation of Gene Function
Abstract
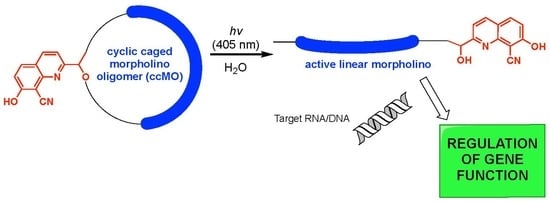
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Design and Synthesis of the Linker Moiety
2.2. MO Coupling and Final Cyclization
2.3. In-vitro DNA Hybridization
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Information
4.2. Preparation of Linker 4
4.3. Preparation of ccMOs 7a–b
4.4. DNA Hybridization Experiment
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Summerton, J.; Weller, D. Morpholino Antisense Oligomers: Design, Preparation, and Properties. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 1997, 7, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karkare, S.; Bhatnagar, D. Promising nucleic acid analogs and mimics: Characteristic features and applications of PNA, LNA, and morpholino. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 71, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudziak, R.M.; Barofsky, E.; Barofsky, D.F.; Weller, D.L.; Huang, S.-B.; Weller, D.D. Resistance of Morpholino Phosphorodiamidate Oligomers to Enzymatic Degradation. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 1996, 6, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Caruthers, M.H. Synthesis of Phosphorodiamidate Morpholino Oligonucleotides and Their Chimeras Using Phosphoramidite Chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 15663–15672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summerton, J. Morpholino antisense oligomers: The case for an RNase H-independent structural type. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1489, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heasman, J.; Kofron, M.; Wylie, C. βCatenin Signaling Activity Dissected in the Early Xenopus Embryo: A Novel Antisense Approach. Dev. Biol. 2000, 222, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasevicius, A.; Ekker, S.C. Effective targeted gene ‘knockdown’ in zebrafish. Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung-Htut, M.T.; McIntosh, C.S.; West, K.A.; Fletcher, S.; Wilton, S.D. In Vitro Validation of Phosphorodiamidate Morpholino Oligomers. Molecules 2019, 24, 2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shestopalov, I.A.; Sinha, S.; Chen, J.K. Light-controlled gene silencing in zebrafish embryos. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 650–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Shestopalov, I.A.; Sinha, S.; Zheng, G.; Pitt, C.L.W.; Li, W.-H.; Olson, A.J.; Chen, J.K. Versatile Synthesis and Rational Design of Caged Morpholinos. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 13255–13269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tallafuss, A.; Gibson, D.; Morcos, P.; Li, Y.; Seredick, S.; Eisen, J.; Washbourne, P. Turning gene function ON and OFF using sense and antisense photo-morpholinos in zebrafish. Development 2012, 139, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomasini, A.J.; Schuler, A.D.; Zebala, J.A.; Mayer, A.N. PhotoMorphs: A novel light-activated reagent for controlling gene expression in zebrafish. Genesis 2009, 47, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deiters, A.; Garner, R.A.; Lusic, H.; Govan, J.M.; Dush, M.; Nascone-Yoder, N.M.; Yoder, J.A. Photocaged Morpholino Oligomers for the Light-Regulation of Gene Function in Zebrafish and Xenopus Embryos. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15644–15650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamazoe, S.; Shestopalov, I.A.; Provost, E.; Leach, S.D.; Chen, J.K. Cyclic Caged Morpholinos: Conformationally Gated Probes of Embryonic Gene Function. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6908–6911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, P.; Lv, C.; Yang, Z.; Tang, X. Manipulation of gene expression in zebrafish using caged circular morpholino oligomers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 11155–11162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamazoe, S.; Liu, Q.; McQuade, L.E.; Deiters, A.; Chen, J.K. Sequential gene silencing using wavelength-selective caged morpholino oligonucleotides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 10114–10118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamazoe, S.; McQuade, L.E.; Chen, J.K. Nitroreductase-activatable morpholino oligonucleotides for in vivo gene silencing. Acs Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 1985–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griepenburg, J.C.; Rapp, T.L.; Carroll, P.J.; Eberwine, J.; Dmochowski, I.J. Ruthenium-Caged Antisense Morpholinos for Regulating Gene Expression in Zebrafish Embryos. Chem Sci 2015, 6, 2342–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Connor, M.J.; Beebe, L.L.; Deodato, D.; Ball, R.E.; Page, A.T.; VanLeuven, A.J.; Harris, K.T.; Park, S.; Hariharan, V.; Lauderdale, J.D.; et al. Bypassing Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase 1 (Gad1) Induced Craniofacial Defects with a Photoactivatable Translation Blocker Morpholino. Acs Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kool, E.T. Circular Oligonucleotides: New Concepts in Oligonucleotide Design. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1996, 25, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfried, P.; Eiden, L.; Grebenovsky, N.; Mayer, G.; Heckel, A. Photo-Tethers for the (Multi-)Cyclic, Conformational Caging of Long Oligonucleotides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, J.L.; Seward, G.K.; Wang, Y.-H.; Dmochowski, I.J. Turning the 10–23 DNAzyme On and Off with Light. ChemBioChem 2010, 11, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griepenburg, J.C.; Ruble, B.K.; Dmochowski, I.J. Caged oligonucleotides for bidirectional photomodulation of let-7 miRNA in zebrafish embryos. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 6198–6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Liang, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Feng, M.; Yi, F.; Xu, L.; Lei, L.; et al. Caged circular siRNAs for photomodulation of gene expression in cells and mice. Chem Sci 2018, 9, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, M.J.; Kragor, C.H.; Reddie, K.G.; Wilson, H.C.; Zhu, Y.; Dore, T.M. Substituent effects on the sensitivity of a quinoline photoremovable protecting group to one- and two-photon excitation. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 1721–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostovtsev, V.V.; Green, L.G.; Fokin, V.V.; Sharpless, K.B. A Stepwise Huisgen Cycloaddition Process: Copper(I)-Catalyzed Regioselective “Ligation” of Azides and Terminal Alkynes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 2596–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, N.; Deodato, D.; Lan, X.; Widegren, M.B.; Phillips, D.L.; Du, L.; Dore, T.M. Photochemical Activation of Tertiary Amines for Applications in Studying Cell Physiology. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 12591–12600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Rea, A.C.; An, H.; Ma, C.; Guan, X.; Li, M.D.; Su, T.; Yeung, C.S.; Harris, K.T.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Unraveling the mechanism of the photodeprotection reaction of 8-bromo- and 8-chloro-7-hydroxyquinoline caged acetates. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 6854–6865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klan, P.; Solomek, T.; Bochet, C.G.; Blanc, A.; Givens, R.; Rubina, M.; Popik, V.; Kostikov, A.; Wirz, J. Photoremovable protecting groups in chemistry and biology: Reaction mechanisms and efficacy. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 119–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Irving, D.; Qiao, W.; Ge, D.; Levicky, R. Kinetic Mechanisms in Morpholino–DNA Surface Hybridization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 11588–11596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, P.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Shepard, K.; Levicky, R. Molecular Mechanisms in Morpholino−DNA Surface Hybridization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 9663–9671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y. Spatiotemporal control of gene expression by a light-switchable transgene system. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu-Sato, S.; Huq, E.; Tepperman, J.M.; Quail, P.H. A light-switchable gene promoter system. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 1041–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Baba, M.D.-E.; Peng, R.-W.; Fussenegger, M. A Synthetic Optogenetic Transcription Device Enhances Blood-Glucose Homeostasis in Mice. Science 2011, 332, 1565–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedoryak, O.D.; Dore, T.M. Brominated hydroxyquinoline as a photolabile protecting group with sensitivity to multiphoton excitation. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 3419–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deodato, D.; Dore, T.M. Practical Synthesis of Quinoline-Protected Morpholino Oligomers for Light-Triggered Regulation of Gene Function. Molecules 2020, 25, 2078. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092078
Deodato D, Dore TM. Practical Synthesis of Quinoline-Protected Morpholino Oligomers for Light-Triggered Regulation of Gene Function. Molecules. 2020; 25(9):2078. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092078
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeodato, Davide, and Timothy M. Dore. 2020. "Practical Synthesis of Quinoline-Protected Morpholino Oligomers for Light-Triggered Regulation of Gene Function" Molecules 25, no. 9: 2078. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092078
APA StyleDeodato, D., & Dore, T. M. (2020). Practical Synthesis of Quinoline-Protected Morpholino Oligomers for Light-Triggered Regulation of Gene Function. Molecules, 25(9), 2078. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092078