Development of a Derivatization Reagent with a 2-Nitrophenylsulfonyl Moiety for UHPLC-HRMS/MS and Its Application to Detect Amino Acids Including Taurine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis and Evaluation of 2,5-Dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl(4-(((2-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)oxy)-6-(3-oxomorpholino)quinoline-2-carbonyl)pyrrolidine-3-carboxylate (Ns-MOK-β-Pro-OSu)
2.2. Derivatization of Amino Acid with Ns-MOK-(R)- or -(S)-β-Pro-OSu
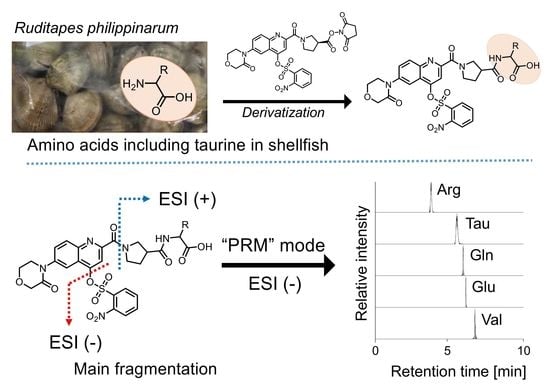
2.3. Fragmentation of Amino Acid Derivatives with Ns-MOK-(S)-β-Pro-OSu
2.4. Detection of Amino Acids
2.5. Detection of Amino Acids in Bivalve
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Preparation of 2,5-Dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl(4-(((2-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)oxy)-6-(3-oxomorpholino)quinoline-2-carbonyl)pyrrolidine-3-carboxylate (Ns-MOK-β-Pro-OSu)

4.3. Time-Course Study on Derivatization of Amino Acids with Ns-MOK-Pro-OSu and Ns-MOK-β-Pro-OSu
4.4. Pre-Treatment Procedure
4.5. Assessment of Fragmentation Patterns of Derivatives
4.6. Linearity and Limit of Quantification
4.7. Pre-Treatment of Bivalve
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Wu, J.Y.; Prentice, H. Role of taurine in the central nervous system. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ripps, H.; Shen, W. Review: Taurine: A “very essential” amino acid. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 2673–2686. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Menzie, J.; Pan, C.; Prentice, H.; Wu, J.Y. Taurine and central nervous system disorders. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uekusa, S.; Onozato, M.; Umino, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Ichiba, H.; Tsujino, N.; Funatogawa, T.; Tagata, H.; Nemoto, T.; Mizuno, M.; et al. Increased inosine levels in drug-free individuals with at-risk mental state: A serum metabolomics study. Early Interv. Psychiatry 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Aniello, A.; Nardi, G.; De Santis, A.; Vetere, A.; di Cosmo, A.; Marchelli, R.; Dossena, A.; Fisher, G. Free l-amino acids and d-aspartate content in the nervous system of cephalopoda. A comparative study. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 112, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Konosu, S. Presence of taurine in the extract of hard clam. Nippon Suisan Gakkai Shi 1972, 38, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucco, E.; Gosetti, F.; Bobba, M.; Marengo, E.; Robotti, E.; Gennaro, M.C. High-performance liquid chromatography-Ultraviolet detection method for the simultaneous determination of typical biogenic amines and precursor amino acids. Applications in Food Chemistry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuke, S.; Konosu, S. Taste-active components in some foods: A review of Japanese research. Physiol. Behavior 1991, 49, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, F.; Ibáñez, M.; Bade, R.; Bijlsma, L.; Sancho, J.V. Investigation of pharmaceuticals and illicit drugs in waters by liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 63, 140–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z.; Wu, H.; Li, N.; Cheng, Y.; Wen, H.M.; Liu, R.; Chai, C. Rapid determination of free amino acids, nucleosides, and nucleobases in commercial clam species harvested at different seasons in Jiangsu, China, using UFLC-MS/MS. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 1520–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uekusa, S.; Onozato, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Umino, M.; Ichiba, H.; Fukushima, T. Fluorimetric determination of the enantiomers of vigabatrin, an antiepileptic drug, by reversed-phase HPLC with a novel diastereomer derivatisation reagent. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2021, 35, e5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santa, T. Derivatization in liquid chromatography for mass spectrometric detection. Drug Discov. Ther. 2013, 7, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franconi, F.; Loizzo, A.; Ghirlanda, G.; Seghieri, G. Taurine supplementation and diabetes mellitus. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2006, 9, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Militante, J.D.; Lombardini, J.B. Treatment of hypertension with oral taurine: Experimental and clinical studies. Amino Acids 2002, 23, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sole, M.J.; Jeejeebhoy, K.N. Conditioned nutritional requirements and the pathogenesis and treatment of myocardial failure. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2000, 3, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, C.P.; Allott, K.A.; Murphy, B.P.; Yuen, H.P.; Proffitt, T.M.; Papas, A.; Moral, J.; Pham, T.; O’Regan, M.K.; Phassouliotis, C.; et al. Adjunctive taurine in first-episode psychosis: A phase 2, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2016, 77, e1610–e1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Kraal, A.Z.; Prawdzik, A.M.; Ringold, A.E.; Ellingrod, V. Dietary glutamic acid, obesity, and depressive symptoms in patients with schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 620097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Amino Acid Content per 1 g of the Edible Portion (mg) | Mean | ± | sd |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tau | 5.33 | ± | 1.91 |
| Val | 0.28 | ± | 0.10 |
| Glu | 1.16 | ± | 0.49 |
| Gln | 0.20 | ± | 0.12 |
| Arg | 0.66 | ± | 0.33 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uekusa, S.; Onozato, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Umino, M.; Ichiba, H.; Okoshi, K.; Fukushima, T. Development of a Derivatization Reagent with a 2-Nitrophenylsulfonyl Moiety for UHPLC-HRMS/MS and Its Application to Detect Amino Acids Including Taurine. Molecules 2021, 26, 3498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123498
Uekusa S, Onozato M, Sakamoto T, Umino M, Ichiba H, Okoshi K, Fukushima T. Development of a Derivatization Reagent with a 2-Nitrophenylsulfonyl Moiety for UHPLC-HRMS/MS and Its Application to Detect Amino Acids Including Taurine. Molecules. 2021; 26(12):3498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123498
Chicago/Turabian StyleUekusa, Shusuke, Mayu Onozato, Tatsuya Sakamoto, Maho Umino, Hideaki Ichiba, Kenji Okoshi, and Takeshi Fukushima. 2021. "Development of a Derivatization Reagent with a 2-Nitrophenylsulfonyl Moiety for UHPLC-HRMS/MS and Its Application to Detect Amino Acids Including Taurine" Molecules 26, no. 12: 3498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123498
APA StyleUekusa, S., Onozato, M., Sakamoto, T., Umino, M., Ichiba, H., Okoshi, K., & Fukushima, T. (2021). Development of a Derivatization Reagent with a 2-Nitrophenylsulfonyl Moiety for UHPLC-HRMS/MS and Its Application to Detect Amino Acids Including Taurine. Molecules, 26(12), 3498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123498