Gomisin M2 Ameliorates Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions via Inhibition of STAT1 and NF-κB Activation in 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene/Dermatophagoides farinae Extract-Induced BALB/c Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Effects of GM2 on the Phenotypic Characteristics of DNCB/DFE-Induced AD Lesions
2.2. The Effects of GM2 on the Infiltration of Inflammatory Cells in DNCB/DFE-Induced AD Lesions
2.3. The Effects of GM2 on the Inflammatory Mediators in DNCB/DFE-Induced AD Lesions
2.4. The Effects of GM2 on AD-Related Immunoglobulin and Protein Levels in DNCB/DFE-Induced AD Mice
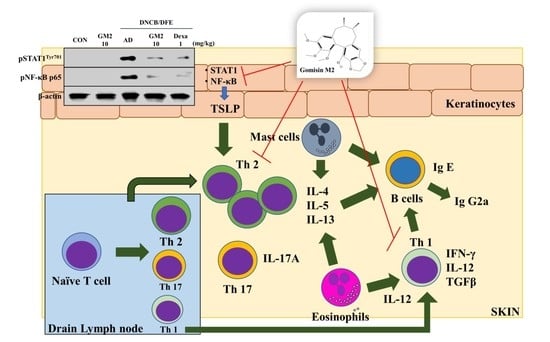
2.5. The Effects of GM2 on the Activated Keratinocytes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Extraction, Isolation, and Identification of GM2
4.2. Reagents
4.3. Ethics Statement and Cell Maintenance
4.4. Induction of AD-like Skin Inflammation in the Mouse Ears and Administration of GM2
4.5. Preparation of Animal Experimental Samples
4.6. Histological Analysis
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
4.8. Western Blot
4.9. ELISA
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Drucker, A.M.; Wang, A.R.; Li, W.Q.; Sevetson, E.; Block, J.K.; Qureshi, A.A. The Burden of Atopic Dermatitis: Summary of a Report for the National Eczema Association. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esche, C.; De Benedetto, A.; Beck, L.A. Keratinocytes in atopic dermatitis: Inflammatory signals. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2004, 4, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, T. Atopic dermatitis. Ann. Dermatol. 2010, 22, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weidinger, S.; Beck, L.A.; Bieber, T.; Kabashima, K.; Irvine, A.D. Atopic dermatitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, N.A.; Bennett, B.L.; Graham, N.M.; Pirozzi, G.; Stahl, N.; Yancopoulos, G.D. Targeting key proximal drivers of type 2 inflammation in disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellberg, B.; Edwards, J.E., Jr. Type 1/Type 2 immunity in infectious diseases. J. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 76–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.H.; Drucker, A.M.; Lebwohl, M.; Silverberg, J.I. A systematic review of the safety and efficacy of systemic corticosteroids in atopic dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 733–740.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rosso, J.; Friedlander, S.F. Corticosteroids: Options in the era of steroid-sparing therapy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 53, S50–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.Y.; Chang, H.H.; Sung, F.C.; Chen, P.C. Characteristics of Traditional Chinese Medicine Use in Pediatric Dislocations, Sprains and Strains. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Ahn, Y.T.; Kim, Y.S.; Cho, S.I.; An, W.G. Antiasthmatic effects of schizandrae fructus extract in mice with asthma. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2014, 10, S80–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, B.; Bae, E.A.; Trinh, H.T.; Shin, Y.W.; Phuong, T.T.; Bae, K.H.; Kim, D.H. Inhibitory effect of schizandrin on passive cutaneous anaphylaxis reaction and scratching behaviors in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 1153–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maeda, S.; Sudo, K.; Miyamoto, Y.; Takeda, S.; Shinbo, M.; Aburada, M.; Ikeya, Y.; Taguchi, H.; Harada, M. Pharmacological studies on schizandra fruits. II. Effects of constituents of shizandra fruits on drugs induced hepatic damage in rats. Yakugaku Zasshi 1982, 102, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szopa, A.; Ekiert, R.; Ekiert, H. Current knowledge of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. (Chinese magnolia vine) as a medicinal plant species: A review on the bioactive components, pharmacological properties, analytical and biotechnological studies. Phytochem. Rev. 2017, 16, 195–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ikeya, Y.; Taguchi, H.; Yosioka, I. The constituents of Schizandra chinensis BAILL. X. The structures of γ-schizandrin and four new lignans,(-)-gomisins L1 and L2,(±)-gomisin M1 and (+)-gomisin M2. J. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1982, 30, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, Y.-W.; Takamatsu, S.; Khan, S.I.; Srinivas, P.V.; Ferreira, D.; Zhao, J.; Khan, I.A. Schisandrene, a dibenzocyclooctadiene lignan from schisandra c hinensis: Structure− antioxidant activity relationships of dibenzocyclooctadiene lignans. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, H.; Lee, S.; Kim, E.N.; Choi, J.K.; Kim, M.J.; Kang, J.; Choi, Y.A.; Baek, M.C.; Lee, B.; Lee, H.S.; et al. Gomisin M2 Inhibits Mast Cell-Mediated Allergic Inflammation via Attenuation of FcepsilonRI-Mediated Lyn and Fyn Activation and Intracellular Calcium Levels. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, Y.H.; Shin, H.M. Inhibitory effects of Schizandra chinensis extract on atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2012, 34, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Jo, S.; Ryu, J.; Jeong, H.S.; Lee, G.; Ryu, M.H.; Jung, M.H.; Kim, H.; Kim, B.J. Effects of Schisandra chinensis Turcz. fruit on contact dermatitis induced by dinitrofluorobenzene in mice. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 2135–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatirishvili, M.; Burk, A.S.; Franz, C.M.; Pace, G.; Kastilan, T.; Breuhahn, K.; Hinterseer, E.; Dierich, A.; Bakiri, L.; Wagner, E.F.; et al. Epidermal-specific deletion of CD44 reveals a function in keratinocytes in response to mechanical stress. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugovic-Mihic, L.; Novak-Bilic, G.; Vucic, M.; Japundzic, I.; Bukvic, I. CD44 expression in human skin: High expression in irritant and allergic contact dermatitis and moderate expression in psoriasis lesions in comparison with healthy controls. Contact Dermatitis 2020, 82, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. J. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2017, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaplan, M.H. STAT signaling in inflammation. JAKSTAT 2013, 2, e24198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brunner, P.M.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Leung, D.Y. The immunology of atopic dermatitis and its reversibility with broad-spectrum and targeted therapies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, S65–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carlo, A.; Jean, -L.B.; Susan, F.-T.; Albert, F.; Ines, G.; Hannu, K.; Pagona, L.; Martinus, L.; Rosangela, M.; Ambroise, M.; et al. Protection of DNA, proteins and lipids from oxidative damage. EFSA J. 2010, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szopa, A.; Dziurka, M.; Warzecha, A.; Kubica, P.; Klimek-Szczykutowicz, M.; Ekiert, H. Targeted Lignan Profiling and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Schisandra rubriflora and Schisandra chinensis Extracts. Molecules 2018, 23, 3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Kilgore, N.; Lee, K.H.; Chen, D.F. Rubrisandrins A and B, lignans and related anti-HIV compounds from Schisandra rubriflora. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1697–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak-Bilic, G.; Vucic, M.; Japundzic, I.; Mestrovic-Stefekov, J.; Stanic-Duktaj, S.; Lugovic-Mihic, L. Irritant and Allergic Contact Dermatitis—Skin Lesion Characteristics. Acta Clin. 2018, 57, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Werfel, T.; Heratizadeh, A.; Niebuhr, M.; Kapp, A.; Roesner, L.M.; Karch, A.; Erpenbeck, V.J.; Losche, C.; Jung, T.; Krug, N.; et al. Exacerbation of atopic dermatitis on grass pollen exposure in an environmental challenge chamber. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 96–103.e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corry, D.B.; Kheradmand, F. Induction and regulation of the IgE response. Nature 1999, 402, B18–B23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, T.; Honda, T.; Kabashima, K. Multipolarity of cytokine axes in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis in terms of age, race, species, disease stage and biomarkers. Int. Immunol. 2018, 30, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brandt, E.B.; Sivaprasad, U. Th2 Cytokines and Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Cell. Immunol. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimber, I.; Cumberbatch, M.; Dearman, R.; Bhushan, M.; Griffiths, C. REVIEW: Cytokines and chemokines in the initiation and regulation of epidermal Langerhans cell mobilization. Br. J. Dermatol. 2000, 142, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raphael, I.; Nalawade, S.; Eagar, T.N.; Forsthuber, T.G. T cell subsets and their signature cytokines in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. J. Cytokine 2015, 74, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taneichi, M.; Naito, S.; Kato, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Mori, M.; Nakano, Y.; Yamamura, H.; Ishida, H.; Komuro, K.; Uchida, T. T cell-independent regulation of IgE antibody production induced by surface-linked liposomal antigen. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 4246–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albanesi, C. Keratinocytes in allergic skin diseases. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 10, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuzun, Y.; Antonov, M.; Dolar, N.; Wolf, R. Keratinocyte cytokine and chemokine receptors. Dermatol. Clin. 2007, 25, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, O.Y.E.; Elazomi, A.; Mohamed, M.S.; Abdalla, F.B. Local elevation of CCL22: A new trend in immunotherapy (skin model). J. Cell Immunother. 2016, 2, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richmond, A. NF-κB, chemokine gene transcription and tumour growth. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmann, U.; Gerhartz, C.; Heesel, B.; Sasse, J.; Kurapkat, G.; Grotzinger, J.; Wollmer, A.; Zhong, Z.; Darnell, J.E., Jr.; Graeve, L.; et al. Differential activation of acute phase response factor/Stat3 and Stat1 via the cytoplasmic domain of the interleukin 6 signal transducer gp130. II. Src homology SH2 domains define the specificity of stat factor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 12999–13007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Zhang, T.; Sun, H.; Gu, H.; Wang, H.; Su, X.; Li, C.; Li, B.; Chen, R.; Kang, J. A New Nortriterpenoid, a Sesquiterpene and Hepatoprotective Lignans Isolated from the Fruit of Schisandra chinensis. Molecules 2017, 22, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.-E.; Kim, E.-N.; Jeong, G.-S. Isolation and Quantitative Analysis of Schisandrin, Gomisin A and Gomisin M 2 from Schisandra chinensis. Kor. J. Pharmacogn. 2019, 50, 148–153. [Google Scholar]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, N.; Dhakal, H.; Kwon, T.-K.; Kim, E.-N.; Jeong, G.-S.; Kim, S.-H. Gomisin M2 Ameliorates Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions via Inhibition of STAT1 and NF-κB Activation in 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene/Dermatophagoides farinae Extract-Induced BALB/c Mice. Molecules 2021, 26, 4409. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154409
Kang J, Lee S, Kim N, Dhakal H, Kwon T-K, Kim E-N, Jeong G-S, Kim S-H. Gomisin M2 Ameliorates Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions via Inhibition of STAT1 and NF-κB Activation in 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene/Dermatophagoides farinae Extract-Induced BALB/c Mice. Molecules. 2021; 26(15):4409. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154409
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Jinjoo, Soyoung Lee, Namkyung Kim, Hima Dhakal, Taeg-Kyu Kwon, Eun-Nam Kim, Gil-Saeng Jeong, and Sang-Hyun Kim. 2021. "Gomisin M2 Ameliorates Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions via Inhibition of STAT1 and NF-κB Activation in 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene/Dermatophagoides farinae Extract-Induced BALB/c Mice" Molecules 26, no. 15: 4409. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154409
APA StyleKang, J., Lee, S., Kim, N., Dhakal, H., Kwon, T. -K., Kim, E. -N., Jeong, G. -S., & Kim, S. -H. (2021). Gomisin M2 Ameliorates Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions via Inhibition of STAT1 and NF-κB Activation in 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene/Dermatophagoides farinae Extract-Induced BALB/c Mice. Molecules, 26(15), 4409. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154409